Deck 19: Accounting for Post-Retirement Benefits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Accounting for Post-Retirement Benefits
1
The projected benefit obligation PBO) is equal to the
A) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using current salary levels in the pension plan formula.
B) difference between the annual pension expense and the amount actually funded during the year.
C) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using anticipated future salary levels in the pension plan formula.
D) actuarial present value of benefits attributed by the pension plan formula to services rendered by employees during the current year.
A) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using current salary levels in the pension plan formula.
B) difference between the annual pension expense and the amount actually funded during the year.
C) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using anticipated future salary levels in the pension plan formula.
D) actuarial present value of benefits attributed by the pension plan formula to services rendered by employees during the current year.
C
2
The corridor is defined as 10% of the greater of the beginning of the year projected benefit obligation or the end of the year fair value of the plan.
False
3
GAAP requires that a company accrue the cost of other post-retirement benefits OPRBs) during the periods in which its employees earn the benefits.
True
4
Which of the following statements is true concerning prior service cost?
A) Prior service costs are the costs of retroactive benefits.
B) Prior service cost is reported as a liability at the date of the plan amendment.
C) Prior service cost is reported as a negative element of other comprehensive income at the date of the plan amendment.
D) All of these answer choices are correct.
A) Prior service costs are the costs of retroactive benefits.
B) Prior service cost is reported as a liability at the date of the plan amendment.
C) Prior service cost is reported as a negative element of other comprehensive income at the date of the plan amendment.
D) All of these answer choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In June of 2011, IASB amended IAS 19, Employee Benefits, changing its method of accounting for pensions in order to make the accounting for pensions similar under U.S. GAAP and IFRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not one of the pension expense components that a company recognizes?
A) expected return on plan assets
B) service cost
C) amortization of prior service cost
D) administrative cost
A) expected return on plan assets
B) service cost
C) amortization of prior service cost
D) administrative cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To improve usefulness of defined pension plans, GAAP requires disclosure of reconciliations of the beginning and ending amounts of the projected benefit obligation, including the amounts of the service cost, interest cost, actuarial gains and losses, benefits paid, and plan amendments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A pension plan provides for future retirement income based on the employee's earnings and length of service with the company. This type of pension plan is termed a
A) contributory plan.
B) defined contribution plan.
C) noncontributory plan.
D) defined benefit plan.
A) contributory plan.
B) defined contribution plan.
C) noncontributory plan.
D) defined benefit plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Other postretirement benefits are provided to former employees after employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The vested benefit obligation is the present value of the benefits the employee is entitled to receive even if the employee is no longer employed by the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
GAAP for pension plans requires companies with defined benefit pension plans to
A) recognize pension expense based on accrual-basis concepts.
B) recognize pension expense as an amount equal to the actual cash paid to retired employees for the current year.
C) recognize a pension liability based on the projected benefit obligation concept.
D) disclose annual pension cost in a footnote only; pension cost was not required to be reported on the income statement.
A) recognize pension expense based on accrual-basis concepts.
B) recognize pension expense as an amount equal to the actual cash paid to retired employees for the current year.
C) recognize a pension liability based on the projected benefit obligation concept.
D) disclose annual pension cost in a footnote only; pension cost was not required to be reported on the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The defined benefit plan is a type of plan in which the employer's contribution into the pension fund is based on a formula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The accumulated benefit obligation ABO) is equal to the
A) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using current salary levels in the pension plan formula.
B) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using anticipated future salary levels in the pension plan formula.
C) difference between the annual pension expense and the amount actually funded during the year.
D) actuarial present value of benefits attributed by the pension plan formula to services rendered by employees during the current year.
A) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using current salary levels in the pension plan formula.
B) actuarial present value of all benefits earned as of a specified date, both vested and nonvested, by employees using anticipated future salary levels in the pension plan formula.
C) difference between the annual pension expense and the amount actually funded during the year.
D) actuarial present value of benefits attributed by the pension plan formula to services rendered by employees during the current year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Under contributory plans the employees bear the majority of the risks of the plan and contribute towards the plan with deductions from their salaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following statements is true regarding a defined benefit pension plan?
A) Defined benefit plans are relatively easy to handle from an accounting perspective.
B) Employers that use defined benefit plans are assuming more risks than employers that use defined contribution plans.
C) Defined benefit plans require an employer to contribute a defined sum each period to a pension fund.
D) A defined benefit plan requires the employer to fund the plan each year for an amount equal to the pension expense.
A) Defined benefit plans are relatively easy to handle from an accounting perspective.
B) Employers that use defined benefit plans are assuming more risks than employers that use defined contribution plans.
C) Defined benefit plans require an employer to contribute a defined sum each period to a pension fund.
D) A defined benefit plan requires the employer to fund the plan each year for an amount equal to the pension expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An Internal Revenue Code rule that impacts the design of pension plans is that:
A) employee contributions to the pension fund are not taxable to the employee until pension benefits are actually received.
B) pension fund earnings are taxable.
C) employer contributions to the pension fund are not taxable to the employee at the time pension benefits are actually received.
D) all employer pension expenses are deductible for income tax purposes.
A) employee contributions to the pension fund are not taxable to the employee until pension benefits are actually received.
B) pension fund earnings are taxable.
C) employer contributions to the pension fund are not taxable to the employee at the time pension benefits are actually received.
D) all employer pension expenses are deductible for income tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Vested benefits are
A) estimated benefits.
B) benefits to be received as a lump-sum payment.
C) benefits that will be lost when employment is terminated.
D) benefits the employee has the right to receive even if the employment is terminated.
A) estimated benefits.
B) benefits to be received as a lump-sum payment.
C) benefits that will be lost when employment is terminated.
D) benefits the employee has the right to receive even if the employment is terminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In deciding how to recognize prior period cost, accounting regulators opted to recognize the liability and reduce other comprehensive income, then amortize the prior service cost as a component of pension expense. The liability is reduced and other comprehensive income is increased as the prior service amount is amortized. This method was chosen in response to constituent arguments even though it violates the matching concept .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Accounting for prior service cost prospectively would violate the matching concept because all the services performed by the employees were completed in previous periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is true regarding a defined contribution pension plan?
A) The pension benefits to be received by the employee during retirement are defined in the plan.
B) Defined contribution plans have the more complex accounting issues than defined benefit plans.
C) Defined contribution plans do not define the benefits that the pension plan must pay to retired employees.
D) Employers that use defined contribution plans are assuming more risks than employers that use defined benefit plans.
A) The pension benefits to be received by the employee during retirement are defined in the plan.
B) Defined contribution plans have the more complex accounting issues than defined benefit plans.
C) Defined contribution plans do not define the benefits that the pension plan must pay to retired employees.
D) Employers that use defined contribution plans are assuming more risks than employers that use defined benefit plans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The cost of retroactive benefits granted in a plan amendment or at the initial adoption of a pension plan is called
A) accumulated benefit cost.
B) service cost benefits.
C) prior service cost.
D) vested benefits.
A) accumulated benefit cost.
B) service cost benefits.
C) prior service cost.
D) vested benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Disclosures for a defined benefit pension plan should include which of the following? I. number of beneficiaries
II) reconciliation of the ending value of the projected benefit obligation
III) reconciliation of the ending fair value of the plan assets
IV) the composition of plan assets
V) the discount rate used
VI) expected long-term rate of return on plan assets
A) I, II, III, IV
B) I, III, V, VI
C) II, III, V, VI
D) III, IV, V, VI
II) reconciliation of the ending value of the projected benefit obligation
III) reconciliation of the ending fair value of the plan assets
IV) the composition of plan assets
V) the discount rate used
VI) expected long-term rate of return on plan assets
A) I, II, III, IV
B) I, III, V, VI
C) II, III, V, VI
D) III, IV, V, VI

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The corridor is defined as
A) 1% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
B) 5% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
C) 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
D) 15% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
A) 1% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
B) 5% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
C) 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
D) 15% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The Maggie Company has a defined benefit pension plan for its employees. The following information pertains to the pension plan as of December 31, 2015: 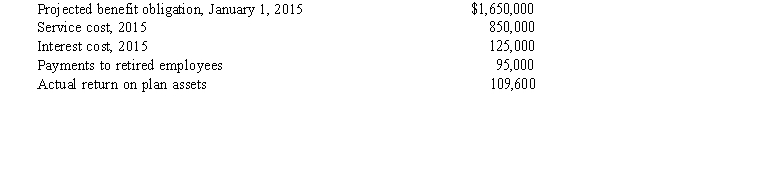 The amount of the December 31, 2015, projected benefit obligation is
The amount of the December 31, 2015, projected benefit obligation is
A) $2,515,400.
B) $2,270,400.
C) $2,530,000.
D) $2,420,400.
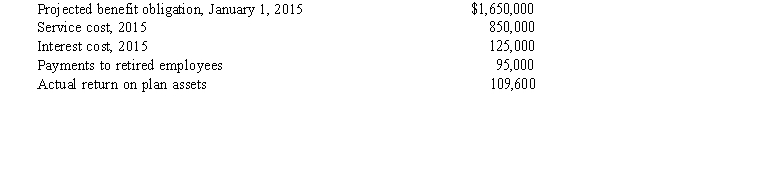 The amount of the December 31, 2015, projected benefit obligation is
The amount of the December 31, 2015, projected benefit obligation isA) $2,515,400.
B) $2,270,400.
C) $2,530,000.
D) $2,420,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following pension-related definitions is not correct?
A) Vested benefits are payments that are not contingent on the employee's continuing in the service of the employer.
B) Present value is the current worth of an amount or amounts payable or receivable in the future.
C) Actuarial assumptions are those made by actuaries concerning future events affecting pension costs.
D) Service cost is the amount paid annually to a funding agency under an unfunded pension plan.
A) Vested benefits are payments that are not contingent on the employee's continuing in the service of the employer.
B) Present value is the current worth of an amount or amounts payable or receivable in the future.
C) Actuarial assumptions are those made by actuaries concerning future events affecting pension costs.
D) Service cost is the amount paid annually to a funding agency under an unfunded pension plan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Amortization of any net gain or loss is included in pension expense of a given year if at the
A) end of the year, the cumulative net gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
B) beginning of the year, the cumulative net gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual accumulated benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
C) end of the year, the cumulative gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual accumulated benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
D) beginning of the year, the cumulative gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
A) end of the year, the cumulative net gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
B) beginning of the year, the cumulative net gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual accumulated benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
C) end of the year, the cumulative gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual accumulated benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.
D) beginning of the year, the cumulative gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the actual projected benefit obligation or the fair value of the plan assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following would not be a component of pension expense?
A) prior service cost amortization
B) interest cost
C) deferred compensation
D) return on assets
A) prior service cost amortization
B) interest cost
C) deferred compensation
D) return on assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which statement is false?
A) In the computation of pension expense, a negative return on plan assets can be added.
B) The amount of prior service cost is not included as an asset or a liability.
C) Interest cost is equal to the projected benefit obligation at the end of the period multiplied by the discount rate used by the company.
D) A lower-than-expected mortality rate creates a pension loss to a company.
A) In the computation of pension expense, a negative return on plan assets can be added.
B) The amount of prior service cost is not included as an asset or a liability.
C) Interest cost is equal to the projected benefit obligation at the end of the period multiplied by the discount rate used by the company.
D) A lower-than-expected mortality rate creates a pension loss to a company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Current GAAP regarding employers' accounting for defined benefit pension plans defines a pension plan as being underfunded at the end of the period when the
A) fair value of plan assets exceeds the projected benefit obligation.
B) projected benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets.
C) accumulated benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of the plan assets.
D) fair value of the plan assets exceed the accumulated benefit obligation.
A) fair value of plan assets exceeds the projected benefit obligation.
B) projected benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets.
C) accumulated benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of the plan assets.
D) fair value of the plan assets exceed the accumulated benefit obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Gage began a defined benefit pension plan on January 1, 2015. During 2015, the service cost was $450,000. Gage contributed $450,000 to the pension plan for 2015. The actuary said the projected benefit obligation at December 31, 2015 was $450,000. As of December 31, 2015, what statements can Gage make about the pension plan? I. The pension plan is fully funded.
II) Gage does not need to report a liability regarding the pension plan at December 31, 2015.
A) I
B) II
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
II) Gage does not need to report a liability regarding the pension plan at December 31, 2015.
A) I
B) II
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the computation of pension expense, interest cost is the
A) expected increase in the plan assets due to investing activities.
B) increase in the projected benefit obligation due to the passage of time.
C) actuarial present value of benefits.
D) expected return on plan assets.
A) expected increase in the plan assets due to investing activities.
B) increase in the projected benefit obligation due to the passage of time.
C) actuarial present value of benefits.
D) expected return on plan assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a pension plan amendment is adopted and retroactive benefits are granted to employees, the amount of the prior service cost at the date of grant is accounted for
A) as an intangible asset and liability that are recognized on the plan amendment date.
B) as a prior period adjustment for the total amount of the prior service cost that is reported on the statement of retained earnings.
C) as the total amount of the prior service cost that is recognized as an expense on the current period's income statement.
D) initially as an unamortized amount to be included in the computation of pension expense over future periods.
A) as an intangible asset and liability that are recognized on the plan amendment date.
B) as a prior period adjustment for the total amount of the prior service cost that is reported on the statement of retained earnings.
C) as the total amount of the prior service cost that is recognized as an expense on the current period's income statement.
D) initially as an unamortized amount to be included in the computation of pension expense over future periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Benefits for which the employee's right to receive a present or future pension benefit is no longer contingent on remaining in the service of the employer are called
A) vested benefits.
B) accumulated benefits.
C) periodic benefits.
D) prior service benefits.
A) vested benefits.
B) accumulated benefits.
C) periodic benefits.
D) prior service benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If an employer were to account for a defined benefit pension plan on the cash basis, it would be a violation of the
A) going-concern assumption.
B) accrual concept.
C) separate entity concept.
D) historical accounting.
A) going-concern assumption.
B) accrual concept.
C) separate entity concept.
D) historical accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Lucas Company offers employees a defined contribution pension plan. In 2015, Lucas contributed $175,000 to the plan, which paid $195,000 to retired employees. Which of the following statements is true?
A) Lucas will record an accrued liability of $20,000.
B) Lucas will report pension expense of $175,000.
C) Lucas will recognize prior service cost of $20,000.
D) Lucas will recognize actuarial gains and losses on the plan over current and future periods.
A) Lucas will record an accrued liability of $20,000.
B) Lucas will report pension expense of $175,000.
C) Lucas will recognize prior service cost of $20,000.
D) Lucas will recognize actuarial gains and losses on the plan over current and future periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In June 2011, the IASB amended IAS 19, Employee Benefits, and significantly changed the method of accounting for defined benefit plan pensions. Regarding these changes, which of the following statements is false?
A) Prior to this amendment, the basic principles of accounting for defined benefit plans under IFRS were the same as U.S. GAAP.
B) Under IAS 19, prior service cost is immediately recognized on the income statement as an expense, while under U.S. GAAP prior service cost is recognized in other comprehensive income and reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income on the balance sheet.
C) The changes in the amendment to IAS 19 make it less likely that GAAP will change to converge with IFRS for pension accounting.
D) The major result of the IASB amendments was to remove many of the smoothing devices in pension accounting.
A) Prior to this amendment, the basic principles of accounting for defined benefit plans under IFRS were the same as U.S. GAAP.
B) Under IAS 19, prior service cost is immediately recognized on the income statement as an expense, while under U.S. GAAP prior service cost is recognized in other comprehensive income and reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income on the balance sheet.
C) The changes in the amendment to IAS 19 make it less likely that GAAP will change to converge with IFRS for pension accounting.
D) The major result of the IASB amendments was to remove many of the smoothing devices in pension accounting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In 2015, the Rachel Company initiated a defined benefit pension plan. It recorded $240,000 as pension expense and paid $280,000 to a funding agency. As a result, Rachel will report
A) pension assets of $280,000 and pension liabilities of $240,000.
B) an accrued liability of $50,000.
C) service cost of $280,000 and unfunded prior service cost of $40,000.
D) prepaid pension cost of $40,000.
A) pension assets of $280,000 and pension liabilities of $240,000.
B) an accrued liability of $50,000.
C) service cost of $280,000 and unfunded prior service cost of $40,000.
D) prepaid pension cost of $40,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not a component of pension expense to be reported on a company's income statement?
A) interest cost
B) unrecognized past service cost
C) service cost
D) expected return on plan assets
A) interest cost
B) unrecognized past service cost
C) service cost
D) expected return on plan assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Code: A = amortization of unrecognized prior service cost
B = interest cost
C = gain or loss to the extent recognized) D = service cost
E = expected return on plan assets
F = pension expense
Which equation would be correct for the calculation of pension expense?
A) F = D + B − E + A ± C
B) F = B + D ± A ± C + E
C) F = D − B ± C − E ± A
D) F = B ± C − E − D ± A
B = interest cost
C = gain or loss to the extent recognized) D = service cost
E = expected return on plan assets
F = pension expense
Which equation would be correct for the calculation of pension expense?
A) F = D + B − E + A ± C
B) F = B + D ± A ± C + E
C) F = D − B ± C − E ± A
D) F = B ± C − E − D ± A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A company's pension expense includes all of the following items except
A) service cost.
B) employer's contribution to the pension fund.
C) amortization of unrecognized prior service cost.
D) interest cost on the projected benefit obligation.
A) service cost.
B) employer's contribution to the pension fund.
C) amortization of unrecognized prior service cost.
D) interest cost on the projected benefit obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Given the following information  What is pension expense for 2016?
What is pension expense for 2016?
A) $17,950
B) $30,050
C) $16,850
D) $24,000
 What is pension expense for 2016?
What is pension expense for 2016?A) $17,950
B) $30,050
C) $16,850
D) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Disclosures for vested benefits
A) are not required.
B) are related to the projected benefit obligation.
C) are related to the accumulated benefit obligation.
D) are related to the plan assets.
A) are not required.
B) are related to the projected benefit obligation.
C) are related to the accumulated benefit obligation.
D) are related to the plan assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Vested benefits are
A) estimated benefits.
B) not contingent on future service to a company.
C) to be received as a lump sum payment.
D) lost when employment is terminated.
A) estimated benefits.
B) not contingent on future service to a company.
C) to be received as a lump sum payment.
D) lost when employment is terminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation's purpose is to
A) allow companies to exit bankruptcy.
B) insure defined contribution pension plans.
C) insure defined benefit pension plans.
D) guarantee taxpayers that the federal government will pay pension benefits.
A) allow companies to exit bankruptcy.
B) insure defined contribution pension plans.
C) insure defined benefit pension plans.
D) guarantee taxpayers that the federal government will pay pension benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
John Company adopted a defined benefit pension plan on January 1, 2015, and prior service credit was granted to employees. The present value of that prior service obligation as of January 1, 2015 was $1,400,000 and is being amortized by the straight-line method over the remaining 20-year service life of the company's active employees. Additional information relating to the company's pension plan for 2015 is presented below:  What amount should be recorded in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost when recording the 2015 pension expense and funding at December 31, 2015?
What amount should be recorded in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost when recording the 2015 pension expense and funding at December 31, 2015?
A) $1,200
B) $48,000
C) $87,000
D) $94,800
 What amount should be recorded in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost when recording the 2015 pension expense and funding at December 31, 2015?
What amount should be recorded in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost when recording the 2015 pension expense and funding at December 31, 2015?A) $1,200
B) $48,000
C) $87,000
D) $94,800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a company uses the indirect method to report cash flows, it
A) subtracts any increase in its accrued pension cost from net income.
B) subtracts any increase in accrued pension cost as an investing activity.
C) adds any increase in its accrued pension cost to net income.
D) adds any increase in accrued pension cost as a financing activity.
A) subtracts any increase in its accrued pension cost from net income.
B) subtracts any increase in accrued pension cost as an investing activity.
C) adds any increase in its accrued pension cost to net income.
D) adds any increase in accrued pension cost as a financing activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Exhibit 19-02
The Sophia Company adopted a defined benefit pension plan on January 1, 2015, and prior service credit was granted to employees. The present value of those benefits was calculated to be $1,245,300 at that date. The service cost is funded in full at the end of each year, plus an additional amount of $225,000 is funded each year-end. The unrecognized prior service cost is being amortized by the straight-line method over the remaining 10-year service life of the company's active employees. Additional information relating to the company's pension plan is presented below: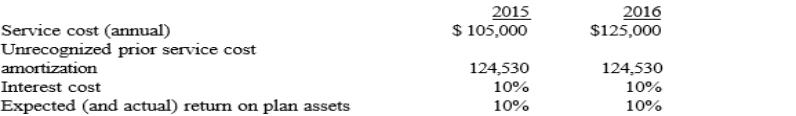
Refer to Exhibit 19-02. What is the pension expense for 2015?
A) $105,000
B) $229,530
C) $315,000
D) $354,060
The Sophia Company adopted a defined benefit pension plan on January 1, 2015, and prior service credit was granted to employees. The present value of those benefits was calculated to be $1,245,300 at that date. The service cost is funded in full at the end of each year, plus an additional amount of $225,000 is funded each year-end. The unrecognized prior service cost is being amortized by the straight-line method over the remaining 10-year service life of the company's active employees. Additional information relating to the company's pension plan is presented below:
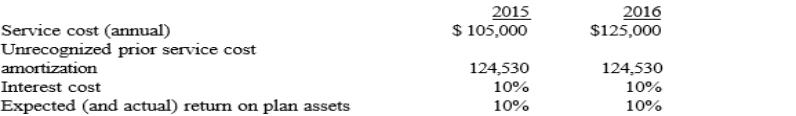
Refer to Exhibit 19-02. What is the pension expense for 2015?
A) $105,000
B) $229,530
C) $315,000
D) $354,060

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The Peanut Company has a defined benefit pension plan for its employees. The following information pertains to the pension plan: 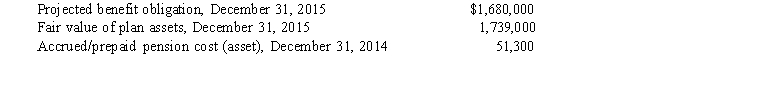 The December 31, 2015 adjusting journal entries include a
The December 31, 2015 adjusting journal entries include a
A) debit to Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost for $7,700.
B) debit to Other Comprehensive Income for $7,700.
C) credit to Other Comprehensive Income for $110,300.
D) credit to Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost for $110,300.
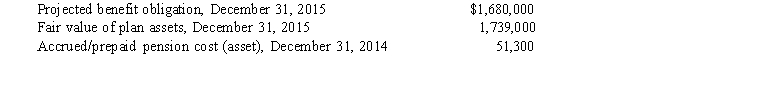 The December 31, 2015 adjusting journal entries include a
The December 31, 2015 adjusting journal entries include aA) debit to Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost for $7,700.
B) debit to Other Comprehensive Income for $7,700.
C) credit to Other Comprehensive Income for $110,300.
D) credit to Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost for $110,300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Current GAAP requires that the net gain or loss from a settlement or curtailment be included in the
A) statement of retained earnings.
B) income statement.
C) balance sheet.
D) statement of cash flows.
A) statement of retained earnings.
B) income statement.
C) balance sheet.
D) statement of cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A company must fund its pension plan each year at an amount that at least equals service cost for the year plus the amount needed to amortize any underfunding over a
A) maximum of three years.
B) maximum of five years.
C) minimum of three years but not more than six years.
D) maximum of seven years.
A) maximum of three years.
B) maximum of five years.
C) minimum of three years but not more than six years.
D) maximum of seven years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
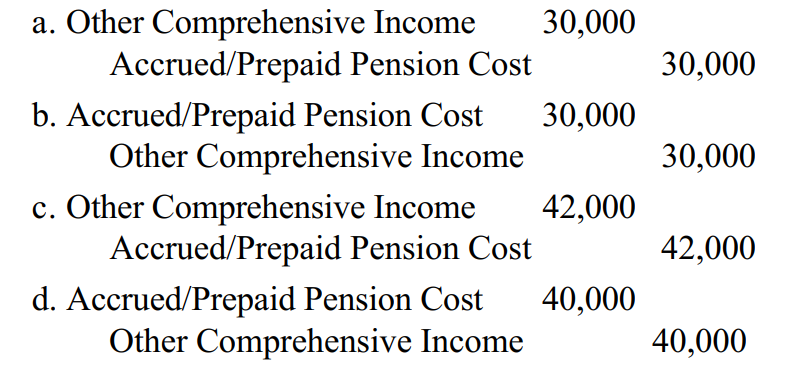
Exhibit 19-01
Marley Co. has an underfunded prepaid/accrued pension cost of $2,000 debit balance) at December 31, 2015. The following information pertains to 2016:
-Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The December 31, 2016, adjusting entry should be
Marley Co. has an underfunded prepaid/accrued pension cost of $2,000 debit balance) at December 31, 2015. The following information pertains to 2016:

-Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The December 31, 2016, adjusting entry should be


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Exhibit 19-01
Marley Co. has an underfunded prepaid/accrued pension cost of $2,000 debit balance) at December 31, 2015. The following information pertains to 2016:
Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The balance in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost at December 31, 2016, should be
A) $30,000 debit.
B) $30,000 credit.
C) $8,000 credit.
D) $10,000 credit.
Marley Co. has an underfunded prepaid/accrued pension cost of $2,000 debit balance) at December 31, 2015. The following information pertains to 2016:

Refer to Exhibit 19-1. The balance in Prepaid/Accrued Pension Cost at December 31, 2016, should be
A) $30,000 debit.
B) $30,000 credit.
C) $8,000 credit.
D) $10,000 credit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is legally required, and contributions are tax deductible.
B) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is legally required, but contributions are not tax deductible.
C) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is not legally required, and contributions are not tax deductible.
D) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is not legally required, but contributions are tax deductible.
A) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is legally required, and contributions are tax deductible.
B) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is legally required, but contributions are not tax deductible.
C) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is not legally required, and contributions are not tax deductible.
D) Funding for postretirement health care benefits is not legally required, but contributions are tax deductible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
ERISA Pension Reform Act of 1974) provides guidance for
A) accumulated benefit obligation.
B) actual return on plan assets.
C) minimum funding during the year.
D) projected benefit obligations.
A) accumulated benefit obligation.
B) actual return on plan assets.
C) minimum funding during the year.
D) projected benefit obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
On January 1, 2015, a company had $84,000 of unrecognized prior service cost. The years-of-future-service method of amortization is used. The company has seven employees, as indicated below:  What amount of prior service cost should be included in pension expense for 2015?
What amount of prior service cost should be included in pension expense for 2015?
A) $2,000
B) $9,333
C) $12,000
D) $14,000
 What amount of prior service cost should be included in pension expense for 2015?
What amount of prior service cost should be included in pension expense for 2015?A) $2,000
B) $9,333
C) $12,000
D) $14,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
GAAP requires that a company record a loss and liability for termination benefits when
A) the amount can be reasonably estimated.
B)
B) the employee accepts the offer.
C) the corporation extends the offer.
D) both a and
A) the amount can be reasonably estimated.
B)
B) the employee accepts the offer.
C) the corporation extends the offer.
D) both a and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The expense for other postretirement benefits, such as health care benefits, dental benefits, and eye care benefits, currently is accounted for
A) on an accrual basis.
B) on a cash basis.
C) on either a cash basis or an accrual basis; both methods are acceptable.
D) by footnote disclosure only.
A) on an accrual basis.
B) on a cash basis.
C) on either a cash basis or an accrual basis; both methods are acceptable.
D) by footnote disclosure only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements regarding postretirement benefits other than pensions is true?
A) A liability for postretirement benefits other than pensions is not required to be reported on the balance sheet.
B) The interest component of the net postretirement benefit expense is based on the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation APBO).
C) The interest component of the net postretirement benefit expense is based on the expected postretirement benefit obligation EPBO).
D) An intangible asset for other postemployment benefits OPEB) is required to be reported on a company's balance sheet.
A) A liability for postretirement benefits other than pensions is not required to be reported on the balance sheet.
B) The interest component of the net postretirement benefit expense is based on the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation APBO).
C) The interest component of the net postretirement benefit expense is based on the expected postretirement benefit obligation EPBO).
D) An intangible asset for other postemployment benefits OPEB) is required to be reported on a company's balance sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
ACE has a defined benefit pension plan. ACE is preparing the December 31, 2015 financial statement disclosures related to the plan assets. It should disclose which of the following? I. Expected Return on Plan Assets
II) Actual Return on Plan Assets
A) I
B) II
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II
II) Actual Return on Plan Assets
A) I
B) II
C) both I and II
D) neither I nor II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following items attributable to a defined benefit pension plan would be recognized on a company's balance sheet? 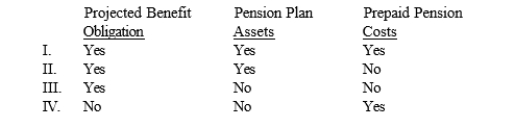
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is typically the most significant OPEB other postemployment benefits)?
A) life insurance
B) health care
C) legal service
D) tuition assistance
A) life insurance
B) health care
C) legal service
D) tuition assistance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
With respect to the process of assigning the cost of postretirement benefits to periods of employee service, the attribution period starts on the
A) hiring date.
B) vesting date.
C) termination date.
D) retirement date.
A) hiring date.
B) vesting date.
C) termination date.
D) retirement date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What are the advantages of qualified pension plans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In 2016, the Ballaster Company decided to amend its defined benefit pension plan. The amendment gave 7 employees the right to receive future benefits based upon their prior service. Ballaster's actuary determined that the prior service cost for this amendment amounts to $550,000. One employee will retire in 1 year, 2 expect to retire in 2 years,1 in three years, 1 in 4 years, and 2 in five years.
Required:
Using the straight line method
1)compute the remaining service life round to 5 decimals)
2) prepare an amortization schedule to amortize the prior service cost
Required:
Using the straight line method
1)compute the remaining service life round to 5 decimals)
2) prepare an amortization schedule to amortize the prior service cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
During 2015, the Electric Company experienced a difference between its expected and actual projected benefit obligation. At the beginning of 2016, Electric's actuary notified them of the following accumulated information related to their plan:  On December 31, 2016, Electric is in the process of calculating the net gain or loss to include in its pension expense for 2016. The average remaining service life of its employees is 10 years and there are no differences between the company's expected and annual rate of return on plan assets in 2016.
On December 31, 2016, Electric is in the process of calculating the net gain or loss to include in its pension expense for 2016. The average remaining service life of its employees is 10 years and there are no differences between the company's expected and annual rate of return on plan assets in 2016.
Required:
Compute the amount of the net gain or loss to include in the pension expense for 2016. Note whether it is an addition or subtraction to the pension expense.
 On December 31, 2016, Electric is in the process of calculating the net gain or loss to include in its pension expense for 2016. The average remaining service life of its employees is 10 years and there are no differences between the company's expected and annual rate of return on plan assets in 2016.
On December 31, 2016, Electric is in the process of calculating the net gain or loss to include in its pension expense for 2016. The average remaining service life of its employees is 10 years and there are no differences between the company's expected and annual rate of return on plan assets in 2016.Required:
Compute the amount of the net gain or loss to include in the pension expense for 2016. Note whether it is an addition or subtraction to the pension expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Martha Co. has a defined benefit pension plan for its employees. The plan was amended at the beginning of 2016 which increased benefits based on services rendered by certain employees in prior periods. The actuary has reported that unrecognized prior service cost resulting from the amendment is $385,000. Five employees expect to receive the increased benefits. Shown below is a schedule of the employees and their expected years of future service: 
Required:
Using the straight-line method:
a. Compute the average remaining service life.
b. Determine the amount of unrecognized prior service cost to be included in the 2016 pension expense calculation.

Required:
Using the straight-line method:
a. Compute the average remaining service life.
b. Determine the amount of unrecognized prior service cost to be included in the 2016 pension expense calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
On December 31, 2015, Clemson Company determined that the 2015 service cost on its defined benefit pension plan was $245,000. At the beginning of 2015, Clemson had pension plan assets totaling $990,000 and a projected benefit obligation of $750,000. Its discount rate and expected long-term rate of return on plan assets for 2015 were both 12%.
Required:
1) Compute the amount of Clemson's pension expense for 2015.
2) Record the journal entries for Clemson's 2015 pension expense if it funds the pension plan in the amount of a)
$225,000 and b) $210,000.
Required:
1) Compute the amount of Clemson's pension expense for 2015.
2) Record the journal entries for Clemson's 2015 pension expense if it funds the pension plan in the amount of a)
$225,000 and b) $210,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The following information is related to a company's pension plan: 
Required:
a. Prepare the adjusting journal entry to update the pension liability.
b. Assume that instead of Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost having a credit balance of $800, it had a $600 debit balance. Prepare the adjusting journal entry to record the pension liability.

Required:
a. Prepare the adjusting journal entry to update the pension liability.
b. Assume that instead of Accrued/Prepaid Pension Cost having a credit balance of $800, it had a $600 debit balance. Prepare the adjusting journal entry to record the pension liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
With respect to the process of assigning the cost of postretirement benefits to periods of employee service, attribution period ends at
A) the expected retirement date.
B)
B) the actual retirement date.
C) the full eligibility date.
D) either a or
A) the expected retirement date.
B)
B) the actual retirement date.
C) the full eligibility date.
D) either a or

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In 2016, the Electrician Company decided to amend its defined benefit pension plan. The amendment gave 7 employees the right to receive future benefits based upon their prior service. Electrician's actuary determined that the prior service cost for this amendment amounts to $550,000. Employee A will retire in 1 year, employee's B & C expect to retire in 2 years, employee D in three years, employee E in 4 years, and employee's F & G in five years.
Required:
Using the years-of-future service method, prepare the schedules to determine:
1) the amortization fraction for each year
2) the amortization of the prior service cost
Required:
Using the years-of-future service method, prepare the schedules to determine:
1) the amortization fraction for each year
2) the amortization of the prior service cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Teresa Company had the following information related to its pension plan: 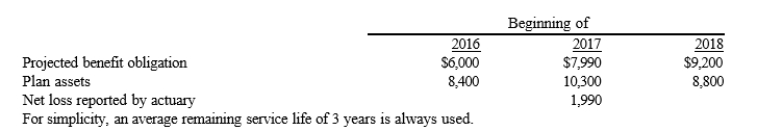 An additional net loss of $1,990 was reported as of January 1, 2017 see table). This amount has been included in the
An additional net loss of $1,990 was reported as of January 1, 2017 see table). This amount has been included in the
January 1, 2017, projected benefit obligation balance.
Required:
Compute the amount of loss that should be included in pension expense in:
a. 2017
b. 2018
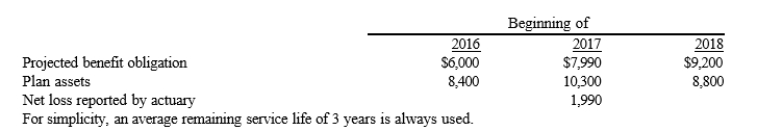 An additional net loss of $1,990 was reported as of January 1, 2017 see table). This amount has been included in the
An additional net loss of $1,990 was reported as of January 1, 2017 see table). This amount has been included in theJanuary 1, 2017, projected benefit obligation balance.
Required:
Compute the amount of loss that should be included in pension expense in:
a. 2017
b. 2018

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Postemployment benefits are provided to former employees
A) after employment.
B) after retirement.
C) before retirement.
D) after employment but before retirement.
A) after employment.
B) after retirement.
C) before retirement.
D) after employment but before retirement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following disclosures are required by GAAP for OPEBs?
A) the assumed healthcare cost trend rates
B) the amounts of securities included in the plan assets
C) the types of securities included in the plan assets
D) All of these answer choices are required
A) the assumed healthcare cost trend rates
B) the amounts of securities included in the plan assets
C) the types of securities included in the plan assets
D) All of these answer choices are required

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
On January 1, 2016, Jackson Hole Company decided to provide a healthcare plan for retired employees. In order for benefits to be determined for each employee, the company gives credit to the date of hire for each employee. This is a retroactive benefit. The following information regarding the plan is as follows:
Accumulated postretirement benefit obligation for employees fully
Required:
1) Compute the OPRB expense for 2016 using the average remaining service life to amortize the prior service cost.
2) Prepare all the required journal entries for 2016 if the plan is not funded.
3) Compute the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation.
Accumulated postretirement benefit obligation for employees fully

Required:
1) Compute the OPRB expense for 2016 using the average remaining service life to amortize the prior service cost.
2) Prepare all the required journal entries for 2016 if the plan is not funded.
3) Compute the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Robin Co. has a defined benefit pension plan that has experienced differences between its expected and actual projected benefit obligation. Data on the plan as of January 1, 2016, follow:  There was no difference between the company's expected and actual return on plan assets during 2016. The average remaining service life of the company's employees is 12 years.
There was no difference between the company's expected and actual return on plan assets during 2016. The average remaining service life of the company's employees is 12 years.
Required:
Determine the amount of the net gain or loss to be included in pension expense for 2016 and indicate whether it is an increase or decrease in the pension expense calculation.
 There was no difference between the company's expected and actual return on plan assets during 2016. The average remaining service life of the company's employees is 12 years.
There was no difference between the company's expected and actual return on plan assets during 2016. The average remaining service life of the company's employees is 12 years.Required:
Determine the amount of the net gain or loss to be included in pension expense for 2016 and indicate whether it is an increase or decrease in the pension expense calculation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Two were expected to retire at the end of 2020, two more at the end of 2022, and four at the end of 2024.
Required:
Using the years-of-future-service method, compute the amount of prior service cost to be amortized in the first year.
Required:
Using the years-of-future-service method, compute the amount of prior service cost to be amortized in the first year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Karen Company began a defined benefit pension plan on January 1, 2016. No prior service credit was granted to employees. Service costs amounted to $34,000 in 2016 and $37,000 in 2017. All contributions to the fund were made at the end of the year. A 10% discount rate was used. The expected and actual) rate of return of plan assets was
12%.
Required:
Prepare journal entries for December 31, 2016 and 2017, assuming:
a. Funding equaled expense.
b. $31,000 was funded each year.
c. $38,000 was funded each year.
12%.
Required:
Prepare journal entries for December 31, 2016 and 2017, assuming:
a. Funding equaled expense.
b. $31,000 was funded each year.
c. $38,000 was funded each year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Joan, Inc. started a pension plan on January 1, 2016. At that date, prior service cost of $1,100,000 was recognized as a result of prior service credit granted to existing employees. At December 31, 2016, the following information was available:  Required:
Required:
a. Compute the pension expense for 2016.
b. Prepare appropriate journal entries for 2016.
 Required:
Required: a. Compute the pension expense for 2016.
b. Prepare appropriate journal entries for 2016.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The following information is provided regarding a company's pension plan: 
Required:
a. Prepare the December 31 journal entry to record pension expense.
b. Explain the difference between "interest cost" and the "expected return on plan assets."

Required:
a. Prepare the December 31 journal entry to record pension expense.
b. Explain the difference between "interest cost" and the "expected return on plan assets."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Marjorie, Inc.'s records contained the following data as of December 31, 2016, on its OPEB plan:  Required:
Required:
a. Compute the OPEB expense for 2016.
b. Prepare the journal entry to record the 2016 OPEB expense.
 Required:
Required: a. Compute the OPEB expense for 2016.
b. Prepare the journal entry to record the 2016 OPEB expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



