Deck 9: Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/215
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
1
Thermochemistry is the study of how is produced and consumed during chemical reactions.
A)carbon dioxide
B)temperature
C)energy
D)work
E)matter
A)carbon dioxide
B)temperature
C)energy
D)work
E)matter
energy
2
Internal energy is defined as
A)the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
B)the total potential energy of all the system components.
C)the total of the potential and kinetic energies of all the system components.
D)the total potential energy minus the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
E)the total kinetic energy minus the total potential energy of all the system components.
A)the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
B)the total potential energy of all the system components.
C)the total of the potential and kinetic energies of all the system components.
D)the total potential energy minus the total kinetic energy of all the system components.
E)the total kinetic energy minus the total potential energy of all the system components.
the total of the potential and kinetic energies of all the system components.
3
What is the change in internal energy ( E) of the system when it loses 76.0 J of heat while the surroundings perform 29.0 J of work?
A)-76.0 J
B)+105.0 J
C)-105.0 J
D)+47.0 J
E)-47.0 J
A)-76.0 J
B)+105.0 J
C)-105.0 J
D)+47.0 J
E)-47.0 J
-47.0 J
4
A sample of helium gas is contained in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston.Calculate the change in the internal energy of the helium if it absorbs 85 J of heat while it performs 33 J of work through expansion.
A)-52 J
B)+52 J
C)-118 J
D)+118 J
E)+85 J
A)-52 J
B)+52 J
C)-118 J
D)+118 J
E)+85 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the change in internal energy E of a system when 4.50 *103J of work is done on the system while it releases 12.0 kJ of energy to the surroundings?
A)(-7.5 kJ)
B)(-16.5 kJ)
C)(+16.5 kJ)
D)(+7.5 kJ)
E)(-12.0 kJ)
A)(-7.5 kJ)
B)(-16.5 kJ)
C)(+16.5 kJ)
D)(+7.5 kJ)
E)(-12.0 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the change in internal energy ( E) of a system when it does 25.0 J of work while absorbing 35.0 J of heat?
A)+60.0 J
B)-60.0 J
C)-10.0 J
D)+10.0 J
E)+35.0 J
A)+60.0 J
B)-60.0 J
C)-10.0 J
D)+10.0 J
E)+35.0 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the first law of thermodynamics, which of the following will always increase the internal energy of a system? q = energy transferred, w = work done)
A)q > 0, w < 0
B)q > 0, w > 0
C)q < 0, w < 0
D)q < 0, w > 0
E)None will always increase the internal energy of a system.
A)q > 0, w < 0
B)q > 0, w > 0
C)q < 0, w < 0
D)q < 0, w > 0
E)None will always increase the internal energy of a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the change in the energy of surroundings when the system absorbs 17.5 kJ of energy and performs 5.00 *3 J of work on the surroundings?
A)(+22.5 kJ)
B)+17.5 kJ
C)-22.5 kJ
D)+12.5 kJ
E)-12.5 kJ
A)(+22.5 kJ)
B)+17.5 kJ
C)-22.5 kJ
D)+12.5 kJ
E)-12.5 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The first law of thermodynamics states that
A)energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system during a combustion reaction.
B)if a system loses energy to the surroundings, then the surroundings must do an equal amount of work on the system.
C)if the surroundings gain energy from the system, then the system must lose an equal amount of energy.
D)energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings during a combustion reaction.
E)if a system does work on the surroundings, then the surroundings must transfer an equal amount of energy to the system.
A)energy is transferred from the surroundings to the system during a combustion reaction.
B)if a system loses energy to the surroundings, then the surroundings must do an equal amount of work on the system.
C)if the surroundings gain energy from the system, then the system must lose an equal amount of energy.
D)energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings during a combustion reaction.
E)if a system does work on the surroundings, then the surroundings must transfer an equal amount of energy to the system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Heat is best defined as
A)massless substance emitted when something burns.
B)a form of potential energy.
C)a form of work.
D)the total energy that a substance has.
E)energy transferred as the result of a temperature difference.
A)massless substance emitted when something burns.
B)a form of potential energy.
C)a form of work.
D)the total energy that a substance has.
E)energy transferred as the result of a temperature difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about energy, systems, and surroundings is NOT true?
A)The system can be a chemical reaction that occurs in a sample of matter.
B)The surroundings experience the same energy change as the system in order to keep the total energy in the universe constant.
C)The system is the part of the universe that is the focus of thermochemical study.
D)The surroundings can provide thermal energy to the system.
E)The system can do work on the surroundings.
A)The system can be a chemical reaction that occurs in a sample of matter.
B)The surroundings experience the same energy change as the system in order to keep the total energy in the universe constant.
C)The system is the part of the universe that is the focus of thermochemical study.
D)The surroundings can provide thermal energy to the system.
E)The system can do work on the surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The energy stored in chemical bonds is a form of
A)kinetic energy.
B)thermal energy.
C)potential energy.
D)heat.
E)mechanical energy.
A)kinetic energy.
B)thermal energy.
C)potential energy.
D)heat.
E)mechanical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Energy that an object has by virtue of its motion is called
A)kinetic energy.
B)thermal energy.
C)potential energy.
D)orbital energy.
E)mechanical energy.
A)kinetic energy.
B)thermal energy.
C)potential energy.
D)orbital energy.
E)mechanical energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The surroundings perform work on a system while the system releases heat to the surroundings.Which of the following is true from the system's perspective? (q =heat, w = work, E = internal energy change)
A)q 0, w 0, E 0
B)q 0, w 0, E 0
C)q =-w, E = 0
D)q = 0, w 0, more information is needed to determine E
E)q 0, w 0, more information is needed to determine E
A)q 0, w 0, E 0
B)q 0, w 0, E 0
C)q =-w, E = 0
D)q = 0, w 0, more information is needed to determine E
E)q 0, w 0, more information is needed to determine E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Work requires
A)a use of potential energy.
B)a release of kinetic energy.
C)a change in temperature.
D)that a force moves an object.
E)the application of a force.
A)a use of potential energy.
B)a release of kinetic energy.
C)a change in temperature.
D)that a force moves an object.
E)the application of a force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The capacity to do work is a definition of
A)heat.
B)thermochemistry.
C)work.
D)energy.
E)force.
A)heat.
B)thermochemistry.
C)work.
D)energy.
E)force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following will always increase the internal energy of a system?
A)The system gains energy and performs work.
B)The system gains energy and work is performed on it.
C)The system loses energy and performs work.
D)The system loses energy and work is performed on it.
E)None of the changes A-D will always increase the internal energy of a system.
A)The system gains energy and performs work.
B)The system gains energy and work is performed on it.
C)The system loses energy and performs work.
D)The system loses energy and work is performed on it.
E)None of the changes A-D will always increase the internal energy of a system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A system performs work on the surroundings, but no thermal energy is transferred.Which of the following is true from the system's perspective? (q= heat, w = work, E = internal energy change)
A)q = 0, w > 0, E > 0
B)q = 0, w > 0, E < 0
C)q = 0, w < 0, E < 0
D)q < 0, w > 0, E = 0
E)q = - w, E = 0
A)q = 0, w > 0, E > 0
B)q = 0, w > 0, E < 0
C)q = 0, w < 0, E < 0
D)q < 0, w > 0, E = 0
E)q = - w, E = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A)In any physical change, such as dew forming on grass or carbon dioxide subliming, the internal energy of the system does not change.
B)When dry ice sublimes to form CO2g), the internal energy of the surroundings decreases.
C)When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the water molecules decreases.
D)When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the surroundings grass, air, etc.) increases.
E)When dry ice sublimes to form CO2g), the energy of the carbon dioxide increases.
A)In any physical change, such as dew forming on grass or carbon dioxide subliming, the internal energy of the system does not change.
B)When dry ice sublimes to form CO2g), the internal energy of the surroundings decreases.
C)When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the water molecules decreases.
D)When dew forms on grass overnight, the energy of the surroundings grass, air, etc.) increases.
E)When dry ice sublimes to form CO2g), the energy of the carbon dioxide increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The kinetic energy associated with the random motion of molecules is called
A)motional energy.
B)work.
C)heat.
D)microscopic energy.
E)thermal energy.
A)motional energy.
B)work.
C)heat.
D)microscopic energy.
E)thermal energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose a system returns to its original internal energy after the following changes.In step 1, 25 J of work is done on the system as it releases 37 J of heat energy.If, in step 2, the system performs 12 J of work, what is the value of q?
A)0 J
B)(-24 J)
C)(+24 J)
D)(-49 J)
E)(+49 J)
A)0 J
B)(-24 J)
C)(+24 J)
D)(-49 J)
E)(+49 J)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The inside of a perfectly insulated capped thermos bottle is an example of
A)an open system.
B)a closed system.
C)an isolated system.
D)an undefined system.
E)a system plus surroundings.
A)an open system.
B)a closed system.
C)an isolated system.
D)an undefined system.
E)a system plus surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The combustion reaction of methane burning in a gas stove is an example of
A)an open system.
B)a closed system.
C)an isolated system.
D)an undefined system.
E)surroundings.
A)an open system.
B)a closed system.
C)an isolated system.
D)an undefined system.
E)surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a mass of 150.0 g moves through a distance of 20.0 m with an acceleration of 15.0 ms-2, how much work was necessary to move the mass? F = ma , where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration.(1 J = 1 kgm2s - 2 )
A)45.0 kJ
B)4.50 kJ
C)450.0 J
D)45.0 J
E)4.50 J
A)45.0 kJ
B)4.50 kJ
C)450.0 J
D)45.0 J
E)4.50 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a chemical reaction causes the temperature of the reaction vessel to increase, it is an) reaction.
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)spontaneous
D)fast
E)slow
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)spontaneous
D)fast
E)slow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following regarding the energy of particles in a sample of matter is false?
A)The average kinetic energy of gas-phase particles is directly proportional to their absolute temperature.
B)Gas-phase molecules have multiple forms of kinetic and potential energy.
C)The atomic or molecular composition of a material affects the amount of energy required to change the kinetic energy of its constituent particles.
D)The speed at which particles move is directly proportional to their molar mass.
E)Molecular vibrations contribute both kinetic and potential energy to gas-phase molecules.
A)The average kinetic energy of gas-phase particles is directly proportional to their absolute temperature.
B)Gas-phase molecules have multiple forms of kinetic and potential energy.
C)The atomic or molecular composition of a material affects the amount of energy required to change the kinetic energy of its constituent particles.
D)The speed at which particles move is directly proportional to their molar mass.
E)Molecular vibrations contribute both kinetic and potential energy to gas-phase molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a chemical reaction causes the temperature of the reaction vessel to decrease, it is an) reaction.
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)spontaneous
D)fast
E)slow
A)endothermic
B)exothermic
C)spontaneous
D)fast
E)slow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following regarding state and path functions is FALSE?
A)The value of a path function depends on how change occurs.
B)The value of a state function does not depend on the history of the system.
C)Heat and work describe the manner in which a system attains its current energy.
D)The internal energy of a system can be the result of many combinations of work and heat.
E)The value of a state function depends on the nature in which it was attained.
A)The value of a path function depends on how change occurs.
B)The value of a state function does not depend on the history of the system.
C)Heat and work describe the manner in which a system attains its current energy.
D)The internal energy of a system can be the result of many combinations of work and heat.
E)The value of a state function depends on the nature in which it was attained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
During an) process, energy is transferred from the system to the surroundings.
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)thermodynamic
D)thermochemical
E)physical
A)exothermic
B)endothermic
C)thermodynamic
D)thermochemical
E)physical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When solid NH4NO3 is dissolved in water, the temperature of the water and beaker gets noticeably colder.The formation of an aqueous solution of ammonium nitrate is
A)an exothermic process.
B)an endothermic process.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a thermodynamic cycle.
E)a redox reaction.
A)an exothermic process.
B)an endothermic process.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a thermodynamic cycle.
E)a redox reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Calculate the work performed on/by a gas when it is compressed under a constant pressure of 8.00 atm from 95.0 L to 9.5 L.(101.3 J = 1 L.atm)
A)+77.0 kJ
B)+69.3 kJ
C)-69.3 kJ
D)+85.5 J
E)-85.5 J
A)+77.0 kJ
B)+69.3 kJ
C)-69.3 kJ
D)+85.5 J
E)-85.5 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a not state function?
A)volume
B)work
C)internal energy
D)temperature
E)position
A)volume
B)work
C)internal energy
D)temperature
E)position

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The initial internal energy of a system is 43.5 kJ.It absorbs 8.3 kJ of heat while performing 3.5 kJ of work on the surroundings.What is its final internal energy?
A)48.3 kJ
B)55.3 kJ
C)38.7 kJ
D)31.7 kJ
E)4.8 kJ
A)48.3 kJ
B)55.3 kJ
C)38.7 kJ
D)31.7 kJ
E)4.8 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An endothermic process is best described as an energy transfer to the from the .
A)surroundings; system
B)system; surroundings
C)system; universe
D)surroundings; universe
E)universe; surroundings
A)surroundings; system
B)system; surroundings
C)system; universe
D)surroundings; universe
E)universe; surroundings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How much work does a gas do when it expands against a constant pressure of 0.750 atm from a volume of 40.00 mL to a volume of 275.00 mL? (101.3 J = 1 L.atm)
A)+17.9 J
B)+17.9 kJ
C)-1.74 J
D)- 17.9 J
E)- 17.9 kJ
A)+17.9 J
B)+17.9 kJ
C)-1.74 J
D)- 17.9 J
E)- 17.9 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is an endothermic process the system is in italics)?
A)dry ice subliming
B)iodine vapor depositing on a cool surface
C)water condensing on a cold glass
D)propane burning
E)water freezing
A)dry ice subliming
B)iodine vapor depositing on a cool surface
C)water condensing on a cold glass
D)propane burning
E)water freezing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the kinetic energy of 25,000 L of water (18.02 g/mol) traveling at 5.8 mph? Assume that the density of water is 1.0 g/mL.(1 mi= 1.609 km,1 J =1 kg m2s - 2 )
A)170 kJ
B)84 kJ
C)1.8 kJ
D)64 kJ
E)4.7 kJ
A)170 kJ
B)84 kJ
C)1.8 kJ
D)64 kJ
E)4.7 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A sample of neon gas is contained in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston that has a mass of 0.580 kg.If the gas expands and pushes the piston out through a distance of 5.00 m with an acceleration of 11.5 ms-2, calculate w for the gas.F = ma, where F is force, m is mass, and a is acceleration.(1J =1 kg m2s - 2 )
A)+50.0 J
B)+11.6 J
C)-11.6 J
D)-33.4 J
E)+33.4 J
A)+50.0 J
B)+11.6 J
C)-11.6 J
D)-33.4 J
E)+33.4 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When solid sodium hydroxide NaOH) pellets are dissolved in water, the temperature of the water and beaker rises.The formation of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is
A)an exothermic process.
B)an endothermic process.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a thermodynamic cycle.
E)an acid-base reaction.
A)an exothermic process.
B)an endothermic process.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a thermodynamic cycle.
E)an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is an example of an open system?
A)ice in an ice chest
B)antifreeze in a car coolant system
C)mercury in a thermometer
D)compressed gas in a cylinder
E)acetone in an uncovered beaker
A)ice in an ice chest
B)antifreeze in a car coolant system
C)mercury in a thermometer
D)compressed gas in a cylinder
E)acetone in an uncovered beaker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A container of water is heated with 10 J of energy at constant pressure.What is the enthalpy change H ) for this process?
A)(-10 J)
B)>10 J
C)+10 J
D)<10 J
E)0
A)(-10 J)
B)>10 J
C)+10 J
D)<10 J
E)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A heating curve for some substance is shown below.Which of the line segments I-V) represents heating of the liquid? 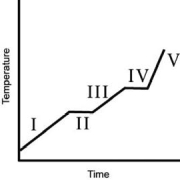
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
During an exothermic process, _______ for the system.
A)q 0
B)w 0
C)( H 0)
D)( H 0)
E)q + w = 0
A)q 0
B)w 0
C)( H 0)
D)( H 0)
E)q + w = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When one mole of zinc and two moles of hydrochloric acid undergo the reaction Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) ZnCL2 (aq) + H2(g), 150.0 kJ of thermal energy are released at 25.00 C and 1.000 atm.The H2 gas generated does approximately 2.500 kJ of work on the surroundings as it expands.Calculate E for the reaction (assume only P - V work is done).
A)+103.3 kJ
B)(-145.5 kJ)
C)(-147.5 kJ)
D)+152.5 kJ
E)(-152.5 kJ)
A)+103.3 kJ
B)(-145.5 kJ)
C)(-147.5 kJ)
D)+152.5 kJ
E)(-152.5 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How much energy is needed to change the temperature of 25.00 mL of water from 10.0 C to 95.0 C? [cp= 4.18 J/(g . C), d =1.00 g/mL]
A)1.60 * 102 kJ
B)28.2 kJ
C)8.89 kJ
D)6.41 kJ
E)105 kJ
A)1.60 * 102 kJ
B)28.2 kJ
C)8.89 kJ
D)6.41 kJ
E)105 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which statement below regarding heat capacity is FALSE?
A)Specific heat capacity refers to the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1 C at constant pressure.
B)Different substances have different heat capacities.
C)The amount of energy required to change the temperature of a substance depends on whether the process occurs at constant pressure or at constant volume.
D)Heat capacity is an extensive property.
E)The molar heat capacity of a substance is an extensive property.
A)Specific heat capacity refers to the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1 C at constant pressure.
B)Different substances have different heat capacities.
C)The amount of energy required to change the temperature of a substance depends on whether the process occurs at constant pressure or at constant volume.
D)Heat capacity is an extensive property.
E)The molar heat capacity of a substance is an extensive property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which statement below regarding heating curves is FALSE?
A)A heating curve tracks the temperature of a system as it is heated at a constant rate.
B)Different substances will have different heating curves.
C)A heating curve will reflect the amount of material present.
D)When a substance undergoes a phase change, there is no energy change because the temperature is constant.
E)If a cooling curve were to be made, the amounts of energy would be equal to those in a heating curve but opposite in sign.
A)A heating curve tracks the temperature of a system as it is heated at a constant rate.
B)Different substances will have different heating curves.
C)A heating curve will reflect the amount of material present.
D)When a substance undergoes a phase change, there is no energy change because the temperature is constant.
E)If a cooling curve were to be made, the amounts of energy would be equal to those in a heating curve but opposite in sign.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When trinitrotoluene TNT) detonates according to the reaction
2 C7H5N3O6 (s) 3 N2(g) +5 H2(g) + 12 CO(g) + 2 C(s), the enthalpy change at 25 C and 1 atm is -1475 kJ while the volume increases by about 489 L.What is the internal energy change (assume only P-V work is done)?
C and 1 atm is -1475 kJ while the volume increases by about 489 L.What is the internal energy change (assume only P-V work is done)?
A)+986 kJ
B)(-1525 kJ)
C)(-1425 kJ)
D)+1425 kJ
E)(-1964 kJ)
2 C7H5N3O6 (s) 3 N2(g) +5 H2(g) + 12 CO(g) + 2 C(s), the enthalpy change at 25
 C and 1 atm is -1475 kJ while the volume increases by about 489 L.What is the internal energy change (assume only P-V work is done)?
C and 1 atm is -1475 kJ while the volume increases by about 489 L.What is the internal energy change (assume only P-V work is done)?A)+986 kJ
B)(-1525 kJ)
C)(-1425 kJ)
D)+1425 kJ
E)(-1964 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The heating curve for a substance is shown below.The substance initially is a solid.It then becomes a liquid and a gas.Which of the line segments I-V) represents the solid-to-liquid phase transition? 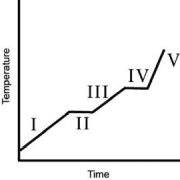
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV
E)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Sodium azide (NaN3) decomposes to form sodium metal and nitrogen gas, and it is used to rapidly generate gas to fill automobile airbags during a crash.In a particular test of an airbag, the N2 gas generated does 6.25 kJ of expansion work under a constant pressure of 1.015 atm.What is the volume change experienced by the gas? (101.3 J= 1 L. atm)
A)-6.16 L
B)+60.8 L
C)+61.7 L
D)+62.6 L
E)+6,160 L
A)-6.16 L
B)+60.8 L
C)+61.7 L
D)+62.6 L
E)+6,160 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Enthalpy change is defined as
A)the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and only P-V work is done.
B)the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant.
C)the change in internal energy of a system when the volume is constant.
D)the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
E)the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
A)the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and only P-V work is done.
B)the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant.
C)the change in internal energy of a system when the volume is constant.
D)the energy that is transferred into or out of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.
E)the change in internal energy of a system when the pressure is constant and no work is done.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The reaction of nitrogen with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide gas at 25  C and 1 atm requires approximately 66.4 kJ of thermal energy.The change in internal energy is about 68.9 kJ.Which statement below is true?
C and 1 atm requires approximately 66.4 kJ of thermal energy.The change in internal energy is about 68.9 kJ.Which statement below is true?
2N2 (g) +O2 (g) 2 NO2 (g)
A)The reaction is exothermic and work is done on the system by the surroundings.
B)The reaction is exothermic and work is done by the system on the surroundings.
C)The reaction is endothermic and work is done on the system by the surroundings.
D)The reaction is endothermic and work is done by the system on the surroundings.
E)The heat and work associated with the reaction cannot be determined without more information.
 C and 1 atm requires approximately 66.4 kJ of thermal energy.The change in internal energy is about 68.9 kJ.Which statement below is true?
C and 1 atm requires approximately 66.4 kJ of thermal energy.The change in internal energy is about 68.9 kJ.Which statement below is true? 2N2 (g) +O2 (g) 2 NO2 (g)
A)The reaction is exothermic and work is done on the system by the surroundings.
B)The reaction is exothermic and work is done by the system on the surroundings.
C)The reaction is endothermic and work is done on the system by the surroundings.
D)The reaction is endothermic and work is done by the system on the surroundings.
E)The heat and work associated with the reaction cannot be determined without more information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a steam engine, steam in a cylinder expands against a piston exerting 10.00 atm of external pressure.The volume of the cylinder increases by 10.00 L and simultaneously the steam cools, losing 3.000 * 103 kJ of energy to the surroundings.What is the change in energy of the steam? (101.3 J =1 L. atm)
A)(-3.010 *103 kJ)
B)(-3.001 *103 kJ)
C)(-3.100 * 103 kJ)
D)(-1.313 * 104 kJ)
E)(-2.990 *103 kJ)
A)(-3.010 *103 kJ)
B)(-3.001 *103 kJ)
C)(-3.100 * 103 kJ)
D)(-1.313 * 104 kJ)
E)(-2.990 *103 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a steam engine, steam in a cylinder is compressed by a piston exerting 16.5 atm of external pressure.The volume of the cylinder decreases by 22.4 L, and simultaneously the steam heats up.If the total energy change of the steam is 42.6 kJ, calculate the heat flow into/out of the steam. (101.3 J =1 L.atm)
A)+80.0 kJ
B)+37.4 kJ
C)-37.4 kJ
D)+5.2 kJ
E)-5.2 kJ
A)+80.0 kJ
B)+37.4 kJ
C)-37.4 kJ
D)+5.2 kJ
E)-5.2 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The reaction of sulfur dioxide gas with oxygen to form sulfur trioxide gas at 25  C and 1 atm releases approximately 198.5 kJ of heat while absorbing approximately 2.5 kJ of work.Which of the following is true?
C and 1 atm releases approximately 198.5 kJ of heat while absorbing approximately 2.5 kJ of work.Which of the following is true?
2SO2 (g) + O2(g) 2 SO3(g)
A)The reaction enthalpy cannot be determined without more information.
B)The reaction is endothermic and E is less positive than H.
C)The reaction is endothermic and E is more positive than H .
D)The reaction is exothermic and E is more negative than H .
E)The reaction is exothermic and E is less negative than H .
 C and 1 atm releases approximately 198.5 kJ of heat while absorbing approximately 2.5 kJ of work.Which of the following is true?
C and 1 atm releases approximately 198.5 kJ of heat while absorbing approximately 2.5 kJ of work.Which of the following is true? 2SO2 (g) + O2(g) 2 SO3(g)
A)The reaction enthalpy cannot be determined without more information.
B)The reaction is endothermic and E is less positive than H.
C)The reaction is endothermic and E is more positive than H .
D)The reaction is exothermic and E is more negative than H .
E)The reaction is exothermic and E is less negative than H .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The volume change associated with a chemical reaction is often approximated as being directly proportional to the change in the number of moles of gas moles of gaseous products - moles of gaseous reactants).The combustion of methanol at 25 C and 1 atm releases about 1453 kJ of heat.Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between E and H ? 2 CH3 OH(l) + 3 O2(g) 2 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l)
A)( H -1453 kJ, E =-1453 kJ)
B)( H -1453 kJ, E = -1453 kJ)
C)( H = -1453 kJ, E -1453 kJ)
D)( H =-1453 kJ, E -1453 kJ)
E)( H= -1453 kJ, E = -1453 kJ)
A)( H -1453 kJ, E =-1453 kJ)
B)( H -1453 kJ, E = -1453 kJ)
C)( H = -1453 kJ, E -1453 kJ)
D)( H =-1453 kJ, E -1453 kJ)
E)( H= -1453 kJ, E = -1453 kJ)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following reactions would you predict is endothermic?
A)2 H2 (g) + O2g) 2 H2 O(l)
B)Na(s)+ 1/2 CL2(g) NaCl (s)
C)2 Cl(g) CL2(g)
D)3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g)
E)H2O2 (aq) H2O(l)+ 1/2 O2 (s)
A)2 H2 (g) + O2g) 2 H2 O(l)
B)Na(s)+ 1/2 CL2(g) NaCl (s)
C)2 Cl(g) CL2(g)
D)3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g)
E)H2O2 (aq) H2O(l)+ 1/2 O2 (s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a steam engine, steam in a cylinder returns to its original state after an expansion/compression cycle.In the expansion step, the volume of the steam increases by exactly 15 L at a constant pressure of exactly 10 atm while 7325 J of heat flows in.In the compression step, the volume of the gas decreases by exactly 15 L at a constant pressure of exactly 15 atm.Calculate the heat flow into/out of the steam in the second step.(101.3 J =1 L.atm)
A)(-270 J)
B)(-7598 J)
C)(-14,920 J)
D)(-30,660 J)
E)(-45,310 J)
A)(-270 J)
B)(-7598 J)
C)(-14,920 J)
D)(-30,660 J)
E)(-45,310 J)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A cup of coffee is heated in a microwave oven.It absorbs 40 kJ of energy from the microwave, and the volume slightly increases.Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship between the change in enthalpy H and the change in internal energy E of the coffee?
A)( H = 40 kJ, E 40 kJ)
B)( H = 40 kJ, E 40 kJ)
C)( H =40 kJ, E =40 kJ)
D)( H = 40 kJ, E = 40 kJ)
E)( H = 40 kJ, E = 40 kJ).
A)( H = 40 kJ, E 40 kJ)
B)( H = 40 kJ, E 40 kJ)
C)( H =40 kJ, E =40 kJ)
D)( H = 40 kJ, E = 40 kJ)
E)( H = 40 kJ, E = 40 kJ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Water has a molar heat capacity of 75.38 J/(mol . C) and its vaporization enthalpy at 100 C is 40.7 kJ/mol.How much energy is needed to boil 54.0 grams of water at 100 C?
A)22.6 kJ
B)145 kJ
C)179 kJ
D)122 kJ
E)2.20 * 103 kJ
A)22.6 kJ
B)145 kJ
C)179 kJ
D)122 kJ
E)2.20 * 103 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In an experiment, 2.00 *102 g of silicon dioxide is heated to 96.7 C and then quickly transferred to 1.25 *102 g of water at 15.2 C.The final temperature comes to 32.5 C.What is the approximate specific heat capacity of SiO2? [cpwater) = 4.18 J/(g . C)]
A)10.1 J/(g . C)
B)0.153 J/(g . C)
C)0.313 J/(g . C)
D)0.878 J/(g . C)
E)0.704 J/(g . C)
A)10.1 J/(g . C)
B)0.153 J/(g . C)
C)0.313 J/(g . C)
D)0.878 J/(g . C)
E)0.704 J/(g . C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A 19.5 g piece of titanium [cp =0.523 J/(g . C)] is heated and then submerged in 1.50 *102 grams of water [cp = 4.18 J/(g . C)] initially at 22.7 C.The final temperature comes to 23.7 C.What was the initial temperature of the Ti metal?
A)24.7 C
B)32.2 C
C)46.4 C
D)61.5 C
E)85.2 C
A)24.7 C
B)32.2 C
C)46.4 C
D)61.5 C
E)85.2 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The typical energy content of a pealed banana is 89 Cal per 100 grams.What volume of water can be heated from 25 C to 95 C by the energy content in 118 g of pealed banana? [d(water) = 1.00 g/mL, cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C), 1 Cal = 4.184 kJ]
A)1.5 mL
B)86 mL
C)0.15 L
D)0.36 L
E)1.5 L
A)1.5 mL
B)86 mL
C)0.15 L
D)0.36 L
E)1.5 L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Given 150 grams each of water and of gold, which requires more energy to raise its temperature by 80.0 C and by what factor? [Au: cp = 0.129 J/(g . C); H2O: cp = 4.18 J/(g. C)]
A)gold; 10 times more
B)gold; 19 times more
C)water; 3.1 times more
D)water; 32 times more
E)water; 330 times more
A)gold; 10 times more
B)gold; 19 times more
C)water; 3.1 times more
D)water; 32 times more
E)water; 330 times more

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
At a certain elevation, the boiling point of water is 98.5 C.How much energy is needed to heat 35.0 mL of water from 23.4 C to the boiling point at this elevation? [cp =4.18 J/(g . C), D = 1.00 g/mL]
A)8.50 kJ
B)11.0 kJ
C)198 kJ
D)1.00 kJ
E)25.6 kJ
A)8.50 kJ
B)11.0 kJ
C)198 kJ
D)1.00 kJ
E)25.6 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How much energy is required to convert 2.785 moles of liquid ammonia at -50.00 C to gas at 25.00 C? [cp(liquid) = 80.80 J/(mol . C); cp(gas) = 35.06 J/(mol . C); Hvap =23.35 kJ/mol at the normal boiling point of -33.34 C]
A)74.48 kJ
B)38.11 kJ
C)14.76 kJ
D)24.20 kJ
E)69.84 kJ
A)74.48 kJ
B)38.11 kJ
C)14.76 kJ
D)24.20 kJ
E)69.84 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A 1.20 kg piece of granite [cp= 0.790 J/(g . C)] at 60.0 C must be cooled to 24.0 C by submersion in water.How much water [cp = 4.18 J/(g . C)], initially at 18 C, would be required?
A)0.302 kg
B)0.907 kg
C)1.36 kg
D)1.72 kg
E)8.16 kg
A)0.302 kg
B)0.907 kg
C)1.36 kg
D)1.72 kg
E)8.16 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Find the minimum amount of energy it takes to raise 1.00 pound of lead (454 g) from room temperature (25 C) to its melting point (327 C) and then melt it.The specific heat capacity of lead is 0.129 J/(g . C), the enthalpy of fusion is 24.7 J/g, and the molar mass is 207 g/mol.
A)11.2 kJ
B)17.7kJ
C)28.9 kJ
D)3390 kJ
E)2.89 * 104 kJ
A)11.2 kJ
B)17.7kJ
C)28.9 kJ
D)3390 kJ
E)2.89 * 104 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In an experiment, 0.250 kg water at 95.0 C is quickly transferred to a 0.500 kg alumina crucible at 25 C.The final temperature comes to 61.8 C.What is the approximate specific heat capacity of alumina? [cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C)]
A)7.94 J/(g . C)
B)5.17 J/(g . C)
C)1.89 J/(g. C)
D)0.664 J/(g . C)
E)2.32 J/(g . C)
A)7.94 J/(g . C)
B)5.17 J/(g . C)
C)1.89 J/(g. C)
D)0.664 J/(g . C)
E)2.32 J/(g . C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at 20.0![<strong>In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at 20.0 C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.0 C.How much energy is required for this process? \Delta H<sub>vap</sub>= 2260J/(g; \Delta H<sub>fus</sub> = 334 J/g; c<sub>p</sub> (ice) = 2.06 J/(g . C); c<sub>p</sub> (water) = 4.18 J/g = C); C<sub>p</sub>(steam) = 1.99 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)30.7 kJ B)26.8 kJ C)34.9 kJ D)30.3 kJ E)38.7 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11.jpg) C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.011eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11C.How much energy is required for this process?
C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.011eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11C.How much energy is required for this process?
Hvap= 2260J/(g; Hfus = 334 J/g; cp (ice) = 2.06 J/(g .![<strong>In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at 20.0 C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.0 C.How much energy is required for this process? \Delta H<sub>vap</sub>= 2260J/(g; \Delta H<sub>fus</sub> = 334 J/g; c<sub>p</sub> (ice) = 2.06 J/(g . C); c<sub>p</sub> (water) = 4.18 J/g = C); C<sub>p</sub>(steam) = 1.99 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)30.7 kJ B)26.8 kJ C)34.9 kJ D)30.3 kJ E)38.7 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11.jpg) C); cp (water) = 4.18 J/g =11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C); Cp(steam) = 1.99 J/(g .11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C)]
C); cp (water) = 4.18 J/g =11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C); Cp(steam) = 1.99 J/(g .11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C)]
A)30.7 kJ
B)26.8 kJ
C)34.9 kJ
D)30.3 kJ
E)38.7 kJ
![<strong>In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at 20.0 C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.0 C.How much energy is required for this process? \Delta H<sub>vap</sub>= 2260J/(g; \Delta H<sub>fus</sub> = 334 J/g; c<sub>p</sub> (ice) = 2.06 J/(g . C); c<sub>p</sub> (water) = 4.18 J/g = C); C<sub>p</sub>(steam) = 1.99 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)30.7 kJ B)26.8 kJ C)34.9 kJ D)30.3 kJ E)38.7 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11.jpg) C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.011eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11C.How much energy is required for this process?
C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.011eed8b0_f471_8cdf_a0ba_73e821850ec7_TB6562_11C.How much energy is required for this process? Hvap= 2260J/(g; Hfus = 334 J/g; cp (ice) = 2.06 J/(g .
![<strong>In an experiment, 10.0 g of ice at 20.0 C is converted into steam with a temperature of 110.0 C.How much energy is required for this process? \Delta H<sub>vap</sub>= 2260J/(g; \Delta H<sub>fus</sub> = 334 J/g; c<sub>p</sub> (ice) = 2.06 J/(g . C); c<sub>p</sub> (water) = 4.18 J/g = C); C<sub>p</sub>(steam) = 1.99 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)30.7 kJ B)26.8 kJ C)34.9 kJ D)30.3 kJ E)38.7 kJ](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11.jpg) C); cp (water) = 4.18 J/g =11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C); Cp(steam) = 1.99 J/(g .11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C)]
C); cp (water) = 4.18 J/g =11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C); Cp(steam) = 1.99 J/(g .11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C)]A)30.7 kJ
B)26.8 kJ
C)34.9 kJ
D)30.3 kJ
E)38.7 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In an experiment, 1.50 kg of concrete at 52.0 C is quickly transferred to 805 g of water at 19.0 C.The final temperature comes to 28.3 C.What is the approximate specific heat capacity of concrete? [cp(water) =4.18 J/(g . C)]
A)1.23 J/(g. C)
B)0.880 J/(g . C)
C)0.313 J/(g . C)
D)0.533 J/(g . C)
E)23.3 J/(g . C)
A)1.23 J/(g. C)
B)0.880 J/(g . C)
C)0.313 J/(g . C)
D)0.533 J/(g . C)
E)23.3 J/(g . C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A 15 g piece of iron [cp = 25.09 J/(mol . C)] is heated to a temperature of 95 C and placed into a bucket containing 4.5 gal of water [cp =75.38 J/(mol . C)], initially at 25 C.Eventually,
A)the water will be warmer than the iron.
B)the iron will be warmer than the water.
C)the iron will be colder than the water.
D)the iron and the water will be at the same temperature.
E)the temperature will be the average of 98 C and 25 C.
A)the water will be warmer than the iron.
B)the iron will be warmer than the water.
C)the iron will be colder than the water.
D)the iron and the water will be at the same temperature.
E)the temperature will be the average of 98 C and 25 C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
You hold a 50 g sphere of copper [cp= 0.4 J/(g . C)] in one hand and a 25 g sphere of aluminum [cp= 0.9 J/(g . C)] in the other hand.If both absorb energy at the same rate, which will come to your body temperature first and why?
A)copper, because the mass is larger
B)aluminum, because the specific heat is larger
C)aluminum, because the mass is smaller
D)copper, because the heat capacity is smaller
E)Both reach body temperature at the same time because they absorb energy at the same rate.
A)copper, because the mass is larger
B)aluminum, because the specific heat is larger
C)aluminum, because the mass is smaller
D)copper, because the heat capacity is smaller
E)Both reach body temperature at the same time because they absorb energy at the same rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Given equal masses of the following, which will cool the fastest from the same initial temperature?
A)an aluminum pan [cp =0.90 J/(g . C)]
B)a copper pot [cp = 0.39 J/(g . C)]
C)an iron skillet [cp = 0.45 J/(g . C)]
D)a container of water [cp =4.2 J/(g . C)]
E)a container of ethanol [cp =2.5 J/(g . C)]
A)an aluminum pan [cp =0.90 J/(g . C)]
B)a copper pot [cp = 0.39 J/(g . C)]
C)an iron skillet [cp = 0.45 J/(g . C)]
D)a container of water [cp =4.2 J/(g . C)]
E)a container of ethanol [cp =2.5 J/(g . C)]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
You devise an experiment to use the condensation of acetone vapor 58.1 g/mol, boiling point (56![<strong>You devise an experiment to use the condensation of acetone vapor 58.1 g/mol, boiling point (56 C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.0 C to steam at 100.0 C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.0 C would be required? [acetone \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 31.3 kJ/mol; water \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 40.7 kJ/mol; c<sub>p</sub>(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C); C<sub>p</sub>(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)440 g B)581 g C)817 g D)75.5 g E)61.4 g](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11.jpg) C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C to steam at 100.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C would be required? [acetone Hvap = 31.3 kJ/mol; water Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol; cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g .
C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C to steam at 100.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C would be required? [acetone Hvap = 31.3 kJ/mol; water Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol; cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g .![<strong>You devise an experiment to use the condensation of acetone vapor 58.1 g/mol, boiling point (56 C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.0 C to steam at 100.0 C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.0 C would be required? [acetone \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 31.3 kJ/mol; water \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 40.7 kJ/mol; c<sub>p</sub>(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C); C<sub>p</sub>(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)440 g B)581 g C)817 g D)75.5 g E)61.4 g](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11.jpg) C); Cp(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g .11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11C)]
C); Cp(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g .11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11C)]
A)440 g
B)581 g
C)817 g
D)75.5 g
E)61.4 g
![<strong>You devise an experiment to use the condensation of acetone vapor 58.1 g/mol, boiling point (56 C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.0 C to steam at 100.0 C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.0 C would be required? [acetone \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 31.3 kJ/mol; water \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 40.7 kJ/mol; c<sub>p</sub>(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C); C<sub>p</sub>(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)440 g B)581 g C)817 g D)75.5 g E)61.4 g](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11.jpg) C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C to steam at 100.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C would be required? [acetone Hvap = 31.3 kJ/mol; water Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol; cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g .
C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C to steam at 100.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.011eed8b1_56ca_8d60_a0ba_cbf98f76ff34_TB6562_11C would be required? [acetone Hvap = 31.3 kJ/mol; water Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol; cp(water) = 4.18 J/(g .![<strong>You devise an experiment to use the condensation of acetone vapor 58.1 g/mol, boiling point (56 C) to provide enough thermal energy to heat 0.180 kilograms of water at 56.0 C to steam at 100.0 C.About how many grams of acetone vapor at 56.0 C would be required? [acetone \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 31.3 kJ/mol; water \Delta H<sub>vap</sub> = 40.7 kJ/mol; c<sub>p</sub>(water) = 4.18 J/(g . C); C<sub>p</sub>(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g . C)]</strong> A)440 g B)581 g C)817 g D)75.5 g E)61.4 g](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6562/11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11.jpg) C); Cp(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g .11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11C)]
C); Cp(acetone vapor) . 1.29 J/(g .11eed8b2_2d82_a951_a0ba_55ddc23a4114_TB6562_11C)]A)440 g
B)581 g
C)817 g
D)75.5 g
E)61.4 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Water has a molar heat capacity of 75.38 J/(mol . C) and its enthalpy of vaporization is 40.7 kJ/mol at 100 C.How much energy is needed to convert 186 g liquid H2O at 20.0 C to steam at 100 C?
A)62.2 kJ
B)482 kJ
C)1120 kJ
D)1540 kJ
E)8690 kJ
A)62.2 kJ
B)482 kJ
C)1120 kJ
D)1540 kJ
E)8690 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What will be the final temperature of a 10.0 g piece of iron [cp = 0.45 J/(g . C)], initially at 25 C, if it is supplied with 9.5 J from a stove?
A)25 C
B)27 C
C)23 C
D)1356 C
E)20 C
A)25 C
B)27 C
C)23 C
D)1356 C
E)20 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
How much energy is needed to change the temperature of 275 grams of lead from 10.0 C to 95.0 C? [cp= 0.129 J/(g . C)]
A)35.5 J
B)113 J
C)302 J
D)7340 J
E)23,400 J
A)35.5 J
B)113 J
C)302 J
D)7340 J
E)23,400 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The cooling system in an automobile holds 10.0 L of ethylene glycol antifreeze.How much energy is absorbed from the engine when the temperature of the ethylene glycol goes from 20.0 C to 100.0 C? The density and specific heat capacity of ethylene glycol are 1.11 g/mL and 2.42 J/(g . C), respectively.
A)2150 J
B)2150 kJ
C)1940 kJ
D)1940 J
E)215 J
A)2150 J
B)2150 kJ
C)1940 kJ
D)1940 J
E)215 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which statement below regarding water and its heat capacity is true?
A)Water has an unusually high heat capacity because it has many ways to disperse heat flowing into it.
B)Ice has more ways to disperse heat energy than liquid water.
C)Hydrogen bonding in water does not affect its heat capacity to any appreciable extent.
D)Steam has a higher heat capacity than liquid water because there are very few interactions between molecules.
E)Water has an unusually high heat capacity because all heat added goes toward increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules.
A)Water has an unusually high heat capacity because it has many ways to disperse heat flowing into it.
B)Ice has more ways to disperse heat energy than liquid water.
C)Hydrogen bonding in water does not affect its heat capacity to any appreciable extent.
D)Steam has a higher heat capacity than liquid water because there are very few interactions between molecules.
E)Water has an unusually high heat capacity because all heat added goes toward increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 215 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



