Deck 15: Antimicrobial Drugs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Antimicrobial Drugs
1
Which of the following antimicrobials does not match its potential shortcomings?
A) Phenicols: Has a narrow therapeutic index and is associated with bone marrow toxicity that results in aplastic anemia.
B) Macrolides: This narrow- spectrum drug must be administered parenterally.
C) Aminoglycosides: Are known to cause irreversible hearing loss when administered other than topically.
D) Lincosoamides: One common lincosoamide is associated with pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile.
E) Tetracyclines: Induce photosensitivity, causes detrimental effects on bones and teeth in children younger than 8 years old, and are associated with an increased risk of Clostridium difficile infection
A) Phenicols: Has a narrow therapeutic index and is associated with bone marrow toxicity that results in aplastic anemia.
B) Macrolides: This narrow- spectrum drug must be administered parenterally.
C) Aminoglycosides: Are known to cause irreversible hearing loss when administered other than topically.
D) Lincosoamides: One common lincosoamide is associated with pseudomembranous colitis caused by Clostridium difficile.
E) Tetracyclines: Induce photosensitivity, causes detrimental effects on bones and teeth in children younger than 8 years old, and are associated with an increased risk of Clostridium difficile infection
Macrolides: This narrow- spectrum drug must be administered parenterally.
2
An antibiotic is
A) a naturally occurring compound that kills microbes or inhibits their growth.
B) a drug which is wholly manufactured by chemical processes.
C) medicine that removes pathogenic organisms from the body.
D) a chemical that kills or removes bacteria, viruses, protozoa, helminths, or fungi.
E) a preparation used to sterilize a person or object.
A) a naturally occurring compound that kills microbes or inhibits their growth.
B) a drug which is wholly manufactured by chemical processes.
C) medicine that removes pathogenic organisms from the body.
D) a chemical that kills or removes bacteria, viruses, protozoa, helminths, or fungi.
E) a preparation used to sterilize a person or object.
a naturally occurring compound that kills microbes or inhibits their growth.
3
Which of the following is not a beta- lactam drug?
A) carbapenem
B) monobactam
C) cephalosporin
D) quinolone
E) penicillin
A) carbapenem
B) monobactam
C) cephalosporin
D) quinolone
E) penicillin
quinolone
4
Which organs are particularly susceptible to damage by certain antimicrobial drugs?
A) heart and lungs
B) stomach and intestines
C) brain and spleen
D) kidneys and liver
E) pancreas and gallbladder
A) heart and lungs
B) stomach and intestines
C) brain and spleen
D) kidneys and liver
E) pancreas and gallbladder

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why is it difficult to develop drugs that specifically target viruses and eukaryotic pathogens?
A) The drugs often inflict collateral damage on our own cells.
B) The ethical concerns with testing these drugs are too great.
C) Viruses and eukaryotes evolve too rapidly for drugs to be effective.
D) Security enzymes break down these foreign drugs before they can exert their effects.
E) There are often duplicate metabolic pathways that pick up the slack from any disturbance caused by these drugs.
A) The drugs often inflict collateral damage on our own cells.
B) The ethical concerns with testing these drugs are too great.
C) Viruses and eukaryotes evolve too rapidly for drugs to be effective.
D) Security enzymes break down these foreign drugs before they can exert their effects.
E) There are often duplicate metabolic pathways that pick up the slack from any disturbance caused by these drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following would pertain to a bad antibiotic?
A) low toxicity
B) narrow therapeutic index
C) no contraindications
D) no drug interactions
E) long half- life
A) low toxicity
B) narrow therapeutic index
C) no contraindications
D) no drug interactions
E) long half- life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following drugs are not matched correctly with their uses?
A) allyamines: systemic fungal infections like in coccidioidomycosis caused by Coccidioides immitis
B) azoles: athlete's foot, ringworm, and yeast infections
C) Flucytosine: administered in combination with amphotericin B for severe fungal infections such as Cryptococcus meningitis and systemic Candidiasis infections
D) polyenes: cutaneous candidiasis caused by Candida albicans or treating life- threatening systemic fungal infections
E) echinocandin drugs: systemic fungal infections in immune- compromised patients
A) allyamines: systemic fungal infections like in coccidioidomycosis caused by Coccidioides immitis
B) azoles: athlete's foot, ringworm, and yeast infections
C) Flucytosine: administered in combination with amphotericin B for severe fungal infections such as Cryptococcus meningitis and systemic Candidiasis infections
D) polyenes: cutaneous candidiasis caused by Candida albicans or treating life- threatening systemic fungal infections
E) echinocandin drugs: systemic fungal infections in immune- compromised patients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Why don't sulfa drugs target mammalian cells?
A) Mammalian cells do not use folic acid and therefore do not have the enzyme that these drugs target.
B) Mammals make their own folic acid but use a completely different substrate to start the process and therefore sulfa drugs are unable to disrupt the process.
C) Mammals do not make their own folic acid and therefore do not have the enzyme that these drugs target.
D) Sulfa drugs do target mammalian cells but the bacteria die so quickly that the patient experiences mild symptoms but can then stop taking the medication before experiencing any serious symptoms.
E) Mammalian cells produce inhibitors to the sulfa drugs.
A) Mammalian cells do not use folic acid and therefore do not have the enzyme that these drugs target.
B) Mammals make their own folic acid but use a completely different substrate to start the process and therefore sulfa drugs are unable to disrupt the process.
C) Mammals do not make their own folic acid and therefore do not have the enzyme that these drugs target.
D) Sulfa drugs do target mammalian cells but the bacteria die so quickly that the patient experiences mild symptoms but can then stop taking the medication before experiencing any serious symptoms.
E) Mammalian cells produce inhibitors to the sulfa drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How do polypeptide drugs work?
A) They target the 50S subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes to block protein synthesis.
B) They work by inhibiting transpeptidase enzymes that are central to building peptidoglycan by forming the protein crosslinks that bind peptidoglycan's carbohydrate chains together in a chain link fence- like structure.
C) They interact with lipopolysaccharide and destabilize the outer membrane of the Gram- negative cell wall where they can then further destabilize the plasma membrane to cause cytoplasmic leakage and cell lysis.
D) They target the DNA replication enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerases.
E) They act as competitive inhibitors of folic acid production.
A) They target the 50S subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes to block protein synthesis.
B) They work by inhibiting transpeptidase enzymes that are central to building peptidoglycan by forming the protein crosslinks that bind peptidoglycan's carbohydrate chains together in a chain link fence- like structure.
C) They interact with lipopolysaccharide and destabilize the outer membrane of the Gram- negative cell wall where they can then further destabilize the plasma membrane to cause cytoplasmic leakage and cell lysis.
D) They target the DNA replication enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerases.
E) They act as competitive inhibitors of folic acid production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How do glycopeptide drugs differ from beta- lactam drugs?
A) Glycopeptide drugs are easily absorbed across the intestines and therefore commonly used as oral preparations against systemic infections.
B) Glycopeptide drugs are often found to be ineffective due to antibiotic- resistance.
C) Glycopeptide drugs are broad- spectrum drugs, unlike beta- lactamases which are narrow- spectrum drugs.
D) Glycopeptide drugs do not have a beta- lactam ring, so they are not susceptible to beta- lactamases.
E) Glycopeptide drugs specifically target Gram- negative bacteria.
A) Glycopeptide drugs are easily absorbed across the intestines and therefore commonly used as oral preparations against systemic infections.
B) Glycopeptide drugs are often found to be ineffective due to antibiotic- resistance.
C) Glycopeptide drugs are broad- spectrum drugs, unlike beta- lactamases which are narrow- spectrum drugs.
D) Glycopeptide drugs do not have a beta- lactam ring, so they are not susceptible to beta- lactamases.
E) Glycopeptide drugs specifically target Gram- negative bacteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is false about rifamycins?
A) They were originally isolated from bacteria.
B) They are broad- spectrum antimicrobials that are effective against most Gram- positive bacteria and some Gram- negative bacteria too.
C) The drugs are useful to combat mycobacterial species that can be especially tough to treat due to the challenges of getting drugs across their waxy mycolic acid- enriched cell wall.
D) Because the chemical structure is such a good fit with RNA polymerase, it is unlikely to cause interactions with any other medications currently known.
E) They inhibit transcription by binding to RNA polymerase.
A) They were originally isolated from bacteria.
B) They are broad- spectrum antimicrobials that are effective against most Gram- positive bacteria and some Gram- negative bacteria too.
C) The drugs are useful to combat mycobacterial species that can be especially tough to treat due to the challenges of getting drugs across their waxy mycolic acid- enriched cell wall.
D) Because the chemical structure is such a good fit with RNA polymerase, it is unlikely to cause interactions with any other medications currently known.
E) They inhibit transcription by binding to RNA polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is an example of a hepatotoxic drug?
A) aspirin
B) vancomycin
C) amoxicillin- clavulanate
D) streptomycin
E) gentamicin
A) aspirin
B) vancomycin
C) amoxicillin- clavulanate
D) streptomycin
E) gentamicin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is false about quinolones?
A) The more modern and most commonly prescribed group of quinolones contain a fluorine atom.
B) They are synthetic antimicrobials that target cell- wall synthesis.
C) They are excellent in situations where there isn't time to identify the responsible pathogen.
D) In rare instances, these drugs have been associated with more serious side effects such as nerve damage, tendonitis, and possible tendon rupture.
E) They have a broad spectrum of action, can be taken orally, and have a relatively long half- life.
A) The more modern and most commonly prescribed group of quinolones contain a fluorine atom.
B) They are synthetic antimicrobials that target cell- wall synthesis.
C) They are excellent in situations where there isn't time to identify the responsible pathogen.
D) In rare instances, these drugs have been associated with more serious side effects such as nerve damage, tendonitis, and possible tendon rupture.
E) They have a broad spectrum of action, can be taken orally, and have a relatively long half- life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Why might broad spectrum antimicrobials be initially used when treating a patient?
A) They are cheaper to use.
B) They may initially be used to protect the patient since it can take several days to make a definitive bacterial identification.
C) The physician has never encountered that pathogen before.
D) An initial round of broad spectrum antimicrobials increases the efficiency of narrow spectrum antimicrobials.
E) It's best to start with broad spectrum antimicrobials until patient records are available that show if the patient has any antimicrobial allergies.
A) They are cheaper to use.
B) They may initially be used to protect the patient since it can take several days to make a definitive bacterial identification.
C) The physician has never encountered that pathogen before.
D) An initial round of broad spectrum antimicrobials increases the efficiency of narrow spectrum antimicrobials.
E) It's best to start with broad spectrum antimicrobials until patient records are available that show if the patient has any antimicrobial allergies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A therapeutic index is a ratio between
A) maximum safe dose versus minimum effective dose.
B) patient survivability versus patient allergies.
C) toxicity versus half- life.
D) patients that benefited from drug versus patients that experienced side effects.
E) potential patients not ruled out due to drug interactions or contraindications versus patients that experienced side effects.
A) maximum safe dose versus minimum effective dose.
B) patient survivability versus patient allergies.
C) toxicity versus half- life.
D) patients that benefited from drug versus patients that experienced side effects.
E) potential patients not ruled out due to drug interactions or contraindications versus patients that experienced side effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following antimicrobials does not match its target?
A) lincosoamides: 50S subunit
B) tetracyclines: 50S subunit
C) aminoglycosides: 30S subunit
D) macrolides: 50S subunit
E) phenicols: 50S subunit
A) lincosoamides: 50S subunit
B) tetracyclines: 50S subunit
C) aminoglycosides: 30S subunit
D) macrolides: 50S subunit
E) phenicols: 50S subunit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following does not make a good target for antiviral drugs?
A) viral release
B) viral integration
C) viral replication and assembly
D) viral penetration
E) viral attachment
A) viral release
B) viral integration
C) viral replication and assembly
D) viral penetration
E) viral attachment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Why did Alexander Fleming suspect he could get penicillin from a species of mold?
A) Soldiers drinking fermented alcohol were less likely to have bacterial infections.
B) Bacteria on culture plates were unable to grow near mold contamination.
C) Wounds with superficial mold on the bandages were not becoming septic.
D) Soldiers eating moldy bread were not suffering from wound infections.
E) Patients infected with a fungus like, athlete's foot, were less likely to have bacterial infections.
A) Soldiers drinking fermented alcohol were less likely to have bacterial infections.
B) Bacteria on culture plates were unable to grow near mold contamination.
C) Wounds with superficial mold on the bandages were not becoming septic.
D) Soldiers eating moldy bread were not suffering from wound infections.
E) Patients infected with a fungus like, athlete's foot, were less likely to have bacterial infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Bactericidal drugs tend to target bacterial
A) protein synthesis and nucleic acids.
B) cell walls, cell membranes, and nucleic acids.
C) cell walls and enzyme activation.
D) nucleic acids.
E) cell walls and cell membranes.
A) protein synthesis and nucleic acids.
B) cell walls, cell membranes, and nucleic acids.
C) cell walls and enzyme activation.
D) nucleic acids.
E) cell walls and cell membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the major challenge with developing new synthetic antimicrobials?
A) finding the right dose
B) the need to screen thousands of potential candidates
C) deciding what bacteria to test it on
D) figuring out if the drug is bacteriostatic or bactericidal
E) choosing which bacterial structure to target
A) finding the right dose
B) the need to screen thousands of potential candidates
C) deciding what bacteria to test it on
D) figuring out if the drug is bacteriostatic or bactericidal
E) choosing which bacterial structure to target

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In order to identify the minimum bactericidal concentration in broth dilution tests, what must be determined first?
A) how successfully the bacteria grow in broth cultures
B) drug concentration and bacterial concentration
C) minimal bacteriostatic concentration
D) how many bacteria grow on a plate from each of the broth dilution tests
E) minimal inhibitory concentration
A) how successfully the bacteria grow in broth cultures
B) drug concentration and bacterial concentration
C) minimal bacteriostatic concentration
D) how many bacteria grow on a plate from each of the broth dilution tests
E) minimal inhibitory concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following reasons to not take unnecessary antibiotics is false?
A) Antibiotics can cause severe side effects like red man syndrome.
B) Taking unnecessary antibiotics can put you at risk for developing an antibiotic resistant bacterial infection that could be life threatening.
C) Antibiotics cost money and are time consuming to take.
D) Antibiotics can cause mild side effects like diarrhea, nausea, sunburn, headache, vomiting, and a rash.
E) Antibiotics are not safe to take during pregnancy.
A) Antibiotics can cause severe side effects like red man syndrome.
B) Taking unnecessary antibiotics can put you at risk for developing an antibiotic resistant bacterial infection that could be life threatening.
C) Antibiotics cost money and are time consuming to take.
D) Antibiotics can cause mild side effects like diarrhea, nausea, sunburn, headache, vomiting, and a rash.
E) Antibiotics are not safe to take during pregnancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most notoriously resistant pathogens. Which of the following mechanisms does this bacteria use to evade antimicrobials?
A) target alterations
B) reduced permeability
C) drug inactivation
D) efflux pumps
E) This bacteria uses all of the possible ways to evade antimicrobials, which is why it is so good at it.
A) target alterations
B) reduced permeability
C) drug inactivation
D) efflux pumps
E) This bacteria uses all of the possible ways to evade antimicrobials, which is why it is so good at it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If a superbug is resistant to an antibiotic due to horizontal gene transfer, the microbe is said to have
A) natural resistance.
B) evolutionary resistance.
C) intrinsic resistance.
D) acquired resistance.
E) mutational resistance.
A) natural resistance.
B) evolutionary resistance.
C) intrinsic resistance.
D) acquired resistance.
E) mutational resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is not an approach to combat drug- resistant bacteria?
A) find multidrug approaches
B) use lytic bacteriophages to specifically target pathogens
C) identify new antimicrobials
D) pair a redesigned antimicrobial with inhibitors that block bacterial- resistance mechanisms
E) flood a patient's system with healthy bacteria to quickly remove access to nutrients and starve the pathogen
A) find multidrug approaches
B) use lytic bacteriophages to specifically target pathogens
C) identify new antimicrobials
D) pair a redesigned antimicrobial with inhibitors that block bacterial- resistance mechanisms
E) flood a patient's system with healthy bacteria to quickly remove access to nutrients and starve the pathogen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An E- test can reveal
A) the mechanism of action for a particular drug.
B) the minimum bacteriostatic concentration.
C) the minimum bactericidal concentration.
D) the minimal inhibitory concentration of a drug.
E) if a drug is bacteriostatic or bactericidal.
A) the mechanism of action for a particular drug.
B) the minimum bacteriostatic concentration.
C) the minimum bactericidal concentration.
D) the minimal inhibitory concentration of a drug.
E) if a drug is bacteriostatic or bactericidal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Combination therapy uses two or more drugs in combination to decrease the likelihood that a pathogen will survive the therapy due to drug resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In terms of personal health, why should vegetarians still care about the misuse of antibiotics in livestock?
A) Manure- contaminated runoff is destroying aquatic life when this runoff gets into local waterways.
B) Recreational water activities become a source of infection when manure- contaminated runoff finds its way into these areas.
C) Food is often cross contaminated but it's better to have an easily treatable GI infection compared to an antibiotic resistant GI infection.
D) Manure- contaminated water and manure- based fertilizers introduce resistant bacteria into the food chain.
E) Livestock live happier lives without constantly eating antibiotics.
A) Manure- contaminated runoff is destroying aquatic life when this runoff gets into local waterways.
B) Recreational water activities become a source of infection when manure- contaminated runoff finds its way into these areas.
C) Food is often cross contaminated but it's better to have an easily treatable GI infection compared to an antibiotic resistant GI infection.
D) Manure- contaminated water and manure- based fertilizers introduce resistant bacteria into the food chain.
E) Livestock live happier lives without constantly eating antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The collected data of a Kirby- Bauer test is often presented in
A) a minimal inhibitory concentration report.
B) a pie chart.
C) an antibiogram.
D) a graph.
E) a bacteriostatic or bactericidal report.
A) a minimal inhibitory concentration report.
B) a pie chart.
C) an antibiogram.
D) a graph.
E) a bacteriostatic or bactericidal report.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following drugs are not matched correctly with their mode of action?
A) azoles: inhibits ribosome function by entering ribosome as a tRNA, covalently binding to mRNA, and forcing the destruction of the complex
B) echinocandin drugs: inhibits fungal cell wall synthesis by targeting an enzyme that makes a component of the fungal cell wall
C) allyamines: inhibits enzymes that build ergosterol which leads to improperly built plasma membranes and fungal cell lysis
D) Flucytosine: targets fungal DNA replication by blocking transcription when it is converted to a nucleic acid analog that blocks DNA and RNA synthesis
E) polyenes: directly interacts with ergosterols which causes targeted plasma membranes to become leaky and leads to cell lysis
A) azoles: inhibits ribosome function by entering ribosome as a tRNA, covalently binding to mRNA, and forcing the destruction of the complex
B) echinocandin drugs: inhibits fungal cell wall synthesis by targeting an enzyme that makes a component of the fungal cell wall
C) allyamines: inhibits enzymes that build ergosterol which leads to improperly built plasma membranes and fungal cell lysis
D) Flucytosine: targets fungal DNA replication by blocking transcription when it is converted to a nucleic acid analog that blocks DNA and RNA synthesis
E) polyenes: directly interacts with ergosterols which causes targeted plasma membranes to become leaky and leads to cell lysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Although all of the following microbes are of serious concern, which one is ranked as urgent on the CDC's list of top drug- resistant pathogens?
A) Clostridium
B) Campylobacter
C) Mycobacterium
D) Pseudomonas
E) Candida
A) Clostridium
B) Campylobacter
C) Mycobacterium
D) Pseudomonas
E) Candida

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A patient with bacterial meningitis will be given a bacteriostatic antibiotic, as well as an anti- inflammatory steroid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If two drugs target different steps of the same biochemical pathway, when used together, these two drugs tend to exhibit synergism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the mechanism of action for the antihelminthic drug praziquantel?
A) interferes with glucose uptake by targeting microtubules
B) the mechanisms of action are unclear
C) blocks anaerobic energy metabolism in protozoa
D) paralyzes the parasites
E) targets nucleic acids
A) interferes with glucose uptake by targeting microtubules
B) the mechanisms of action are unclear
C) blocks anaerobic energy metabolism in protozoa
D) paralyzes the parasites
E) targets nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why is it entirely possible for a pathogen to appear susceptible in susceptibility testing and resistant in a real- life context?
A) The ability of the pathogen to live as part of a biofilm and benefit from the protection of other bacteria does not exist in susceptibility tests.
B) Bacterial levels and active drug concentrations vary from one tissue to another in an active infection.
C) A real- life infection allows for the possibility of genetic crossover with different bacteria, whereas tests in the lab are focused on studying a single strain of bacteria.
D) A person's liver may break down the drug before it even begins to benefit the patient.
E) An active infection is more likely to mutate due to the larger population.
A) The ability of the pathogen to live as part of a biofilm and benefit from the protection of other bacteria does not exist in susceptibility tests.
B) Bacterial levels and active drug concentrations vary from one tissue to another in an active infection.
C) A real- life infection allows for the possibility of genetic crossover with different bacteria, whereas tests in the lab are focused on studying a single strain of bacteria.
D) A person's liver may break down the drug before it even begins to benefit the patient.
E) An active infection is more likely to mutate due to the larger population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following drugs demonstrates the most effective minimal inhibitory concentration? 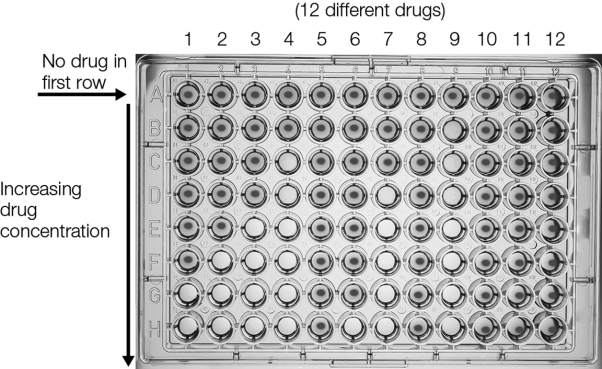
A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 9

A) 2
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When combating methicillin- and oxacillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains, it is effective to administer alternative beta- lactam drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Nephrotoxic antimicrobial drugs can induce liver damage and are leading agents of drug- induced liver injury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Artemisinin- based combination therapies are used to treat
A) mild to moderate C. difficile infections that don't have complications.
B) severe fungal infections such as Cryptococcus meningitis and systemic Candidiasis infections.
C) chronic Toxoplasma gondii infections.
D) life- threatening multidrug resistant infections, especially those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, or Klebsiella pneumoniae.
E) uncomplicated and severe cases of malaria.
A) mild to moderate C. difficile infections that don't have complications.
B) severe fungal infections such as Cryptococcus meningitis and systemic Candidiasis infections.
C) chronic Toxoplasma gondii infections.
D) life- threatening multidrug resistant infections, especially those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, or Klebsiella pneumoniae.
E) uncomplicated and severe cases of malaria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What does nitrazoxanide do in order to treat infections with Giardia and Cryptosporidium as well as against certain parasitic worms?
A) the mechanisms of action are unclear
B) interferes with glucose uptake by targeting microtubules
C) blocks anaerobic energy metabolism in protozoa
D) paralyzes the protozoans
E) targets nucleic acids
A) the mechanisms of action are unclear
B) interferes with glucose uptake by targeting microtubules
C) blocks anaerobic energy metabolism in protozoa
D) paralyzes the protozoans
E) targets nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why is there not a clinical distinction between bacteriostatic and bactericidal antibiotics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Explain what ECE stands for and how it can help you to say no to a patient requesting a prescription for antibiotics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Although protozoan parasites develop drug resistance, it's difficult and time consuming to test them for their drug response, which means the prescribed therapy tends to use a trial- and error approach.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In what ways are humans affected by agricultural practices that promote bacterial resistance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole is an antifolate drug combination that works by blocking folate production in certain bacteria as well as in certain protozoans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Clostridium difficile naturally form endospores that inherently resist most antibiotics due to their dormant nature and their tough spore coat that blocks drug entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



