Deck 9: Accounting Changes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Accounting Changes
1
For a company using the straight-line method of depreciation that changes the estimated useful life from 20 years to 15 years remaining as at the beginning of the year, the accountant should do the following:
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 15 years.
B)Adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)X 15/20.
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 15 years.
B)Adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)X 15/20.
A
2
What is the essential characteristic that distinguishes an error correction from a change in estimate?
We can distinguish an error correction from a change in accounting estimate based on whether the relevant information triggering the change was known or should have been known previously. If so, then there exists an error requiring correction. If not, then the information merely updates the accounting estimates going forward.
3
For a company using the straight-line method of depreciation that changes the estimated useful life from 20 years to 15 years as at the beginning of the year, the accountant should do (or not do)the following:
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 20 years.
B)Do not adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)× 15/20.
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 20 years.
B)Do not adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)× 15/20.
B
4
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The last-in, first-out (LIFO)cost flow assumption is an acceptable method for costing inventories in Canada.
B)Over time, the number of areas where management has a free choice over accounting policies has increased.
C)A change in accounting policy is an accounting change made at the discretion of management.
D)Changes in accounting policy occur more frequently than changes in estimates.
A)The last-in, first-out (LIFO)cost flow assumption is an acceptable method for costing inventories in Canada.
B)Over time, the number of areas where management has a free choice over accounting policies has increased.
C)A change in accounting policy is an accounting change made at the discretion of management.
D)Changes in accounting policy occur more frequently than changes in estimates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A company changes the depreciation for a piece of equipment from 20% declining- balance to units-of-production. Describe a plausible circumstance that would support this change as one of the following: (i)an error, (ii)a change in estimate, or (iii)a change in accounting policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the essential characteristic that distinguishes a change in accounting policy from either an error correction or a change in estimate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement is correct about a correction of an error from prior periods?
A)The correct information was available at the time the error was made.
B)The correct information was not available at the time the error was made.
C)One should use hindsight to judge whether there is an accounting error that requires correction.
D)An example of a correction of an error is the difference between the allowance for doubtful accounts and the actual outcome of bad debts.
A)The correct information was available at the time the error was made.
B)The correct information was not available at the time the error was made.
C)One should use hindsight to judge whether there is an accounting error that requires correction.
D)An example of a correction of an error is the difference between the allowance for doubtful accounts and the actual outcome of bad debts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Over time, has management's free will over accounting changes increased or decreased? Explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a change in policy?
A)Inventory was sold below carrying amount even though the inventory had been previously written down to lower of cost and net realizable value.
B)A company changes from the cost model to the revaluation model of measuring the value of land.
C)Development costs were capitalized when only five of six criteria for capitalization had been satisfied.
D)The company miscalculated the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding because it used the wrong date for a share issuance.
A)Inventory was sold below carrying amount even though the inventory had been previously written down to lower of cost and net realizable value.
B)A company changes from the cost model to the revaluation model of measuring the value of land.
C)Development costs were capitalized when only five of six criteria for capitalization had been satisfied.
D)The company miscalculated the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding because it used the wrong date for a share issuance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is an accounting error?
A)Inventory was sold below carrying amount even though the inventory had been previously written down to the lower of cost and net realizable value.
B)Convertible securities that were identified as dilutive for computing diluted EPS were not converted by the expiration date.
C)A change in economic conditions resulted in the fair value of goodwill declining from $15 million to $10 million.
D)Development costs of an intangible asset were capitalized when only five of six criteria for capitalization had been satisfied.
A)Inventory was sold below carrying amount even though the inventory had been previously written down to the lower of cost and net realizable value.
B)Convertible securities that were identified as dilutive for computing diluted EPS were not converted by the expiration date.
C)A change in economic conditions resulted in the fair value of goodwill declining from $15 million to $10 million.
D)Development costs of an intangible asset were capitalized when only five of six criteria for capitalization had been satisfied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a change in an estimate?
A)A company changes the presentation of operating expenses from "by function" to "by nature."
B)An enterprise switches from the gross method to the net method of presenting government grants.
C)A temporary difference was treated as a permanent difference.
D)The useful life on a building was originally estimated to be 20 years but the estimated useful life of the building is changed to only 15 years as at the beginning of the year.
A)A company changes the presentation of operating expenses from "by function" to "by nature."
B)An enterprise switches from the gross method to the net method of presenting government grants.
C)A temporary difference was treated as a permanent difference.
D)The useful life on a building was originally estimated to be 20 years but the estimated useful life of the building is changed to only 15 years as at the beginning of the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is a change in policy?
A)A company changes from the gross method to the net method of recording cash discounts.
B)A change in the terms of a loan from repayment on demand to a fixed repayment date two years after the fiscal year-end.
C)A contingency for a lawsuit that was evaluated to be likely to lead to an outflow of resources was ultimately resolved against the reporting entity.
D)A temporary tax difference was treated as permanent tax difference.
A)A company changes from the gross method to the net method of recording cash discounts.
B)A change in the terms of a loan from repayment on demand to a fixed repayment date two years after the fiscal year-end.
C)A contingency for a lawsuit that was evaluated to be likely to lead to an outflow of resources was ultimately resolved against the reporting entity.
D)A temporary tax difference was treated as permanent tax difference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Complete the table giving an example of a change in estimate from each of the given areas.
Financial Statement Items
Changes in Accounting Estimates
Employee future benefits
Deferred income taxes
Property, plant and equipment
Current liabilities and long-term debt
Goodwill
Receivables
Revenue
Financial Statement Items
Changes in Accounting Estimates
Employee future benefits
Deferred income taxes
Property, plant and equipment
Current liabilities and long-term debt
Goodwill
Receivables
Revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the following types of accounting changes, identify the relevant criteria for each accounting change by selecting "yes," "no," or "n/a" (not applicable). 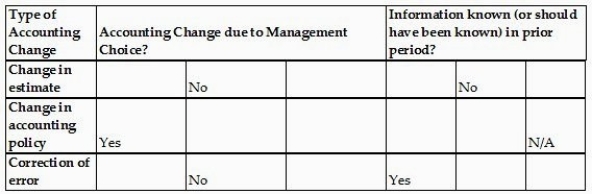


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an accounting error?
A)A company changes from the gross method to the net method of recording cash discounts.
B)A private corporation previously using ASPE chooses to adopt IFRS.
C)Costs not related to the construction of a building were included in the building cost.
D)A patent was expected to provide protection of intellectual property for the full legal life of 20 years, but technological advances made the patent obsolete after only 12 years.
A)A company changes from the gross method to the net method of recording cash discounts.
B)A private corporation previously using ASPE chooses to adopt IFRS.
C)Costs not related to the construction of a building were included in the building cost.
D)A patent was expected to provide protection of intellectual property for the full legal life of 20 years, but technological advances made the patent obsolete after only 12 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Complete the following table by giving one example of a change in accounting policy for each financial statement item.
Financial Statement Item
Changes in Accounting Policy
Revenue
Operating expenses
Receivables
Property, plant and equipment (PPE)
Government assistance
Accounting standards
Financial Statement Item
Changes in Accounting Policy
Revenue
Operating expenses
Receivables
Property, plant and equipment (PPE)
Government assistance
Accounting standards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The discussion in IAS 16 paragraphs 60-62 indicates that a change in depreciation method is usually a change in accounting estimate. Explain the logic behind why a change in depreciation method is normally considered a change in estimate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is true?
A)A correction of an error is the result of information that was unknown at the time of the error.
B)A change is accounting policy is the result of new information.
C)A change in estimate is not due to management choice and not due to information known in a prior period.
D)A correction of an error is due to management choice.
A)A correction of an error is the result of information that was unknown at the time of the error.
B)A change is accounting policy is the result of new information.
C)A change in estimate is not due to management choice and not due to information known in a prior period.
D)A correction of an error is due to management choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
For the following financial statement accounts, provide a description of a change in accounting estimates.
Financial Statement Items
Changes in Accounting Estimates
Revenue
Receivables
Property, Plant and Equipment
Goodwill
Current liabilities
Deferred income taxes
Employee future benefits
Financial Statement Items
Changes in Accounting Estimates
Revenue
Receivables
Property, Plant and Equipment
Goodwill
Current liabilities
Deferred income taxes
Employee future benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a company using the straight-line method of depreciation that changes the estimated useful life from 20 years to 15 years as at the beginning of the year, the accountant should do (or not do)the following:
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 20 years.
B)Adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Do not adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)× 15/20.
A)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount - residual value)divided by 20 years.
B)Adjust prior year's depreciation.
C)Do not adjust the amount of accumulated depreciation as at the beginning of the year.
D)Compute current year depreciation as (carrying amount)× 15/20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement is true regarding accounting accruals?
A)Errors or changes in accounting policy that affect non-current items like equipment will result in follow-through changes over a relatively short period.
B)The purchase of equipment involves an initial accrual to record the asset followed by accrual reversals in the form of depreciation expense and derecognition of the asset upon disposal.
C)Operating activities generally have relatively long cash cycles.
D)Financing and investing activities generally have relatively short cash cycles.
A)Errors or changes in accounting policy that affect non-current items like equipment will result in follow-through changes over a relatively short period.
B)The purchase of equipment involves an initial accrual to record the asset followed by accrual reversals in the form of depreciation expense and derecognition of the asset upon disposal.
C)Operating activities generally have relatively long cash cycles.
D)Financing and investing activities generally have relatively short cash cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Sawatsky & Company Ltd is involved in the construction of top class luxury condos in Vancouver, Canada. Until the end of 2022, the company used the cost ratio method to estimate the percentage complete. After that point, the company switched to using estimates from architectural engineers to estimate the degree of completion. To prepare the financial report for the 2023 fiscal year, you have gathered the following data on projects that were in progress at the end of fiscal years 2021, 2022, and 2023:
2021
2022
2023
Project Silver Sea (started 2021)
Contract price
$20,000,000
$20,000,000
-
Estimated total cost
$15,000,000
$15,400,000
-
% complete at year-end (cost ratio)
42%
100%
-
% complete at year-end (engineering estimate)
37%
100%
-
Project The Callisto (started 2021)
Contract price
$25,000,000
$25,000,000
$25,000,000
Estimated total cost
$20,000,000
$20,800,000
$20,600,000
% complete using cost ratio
16%
60%
100%
% complete using engineering estimate
12%
50%
100%
Project King's Landing (started 2022)
Contract price
-
$12,000,000
$12,000,000
Estimated total cost
-
$ 8,000,000
8,100,000
% complete using cost ratio
-
22%
70%
% complete using engineering estimate
-
25%
75%
Required:
a. Compute the amount of revenue and cost of sales that was recognized in 2021 and 2022 using the old accounting policy.
b. Compute the amount of revenue and cost of sales that should be recognized in each year using the new accounting policy.
c. Record the adjusting journal entries to adjust revenue to reflect the change in accounting policy from using the cost ratio to using engineering estimates. The general ledger accounts for 2023 have not yet been closed. Ignore income tax effects.
2021
2022
2023
Project Silver Sea (started 2021)
Contract price
$20,000,000
$20,000,000
-
Estimated total cost
$15,000,000
$15,400,000
-
% complete at year-end (cost ratio)
42%
100%
-
% complete at year-end (engineering estimate)
37%
100%
-
Project The Callisto (started 2021)
Contract price
$25,000,000
$25,000,000
$25,000,000
Estimated total cost
$20,000,000
$20,800,000
$20,600,000
% complete using cost ratio
16%
60%
100%
% complete using engineering estimate
12%
50%
100%
Project King's Landing (started 2022)
Contract price
-
$12,000,000
$12,000,000
Estimated total cost
-
$ 8,000,000
8,100,000
% complete using cost ratio
-
22%
70%
% complete using engineering estimate
-
25%
75%
Required:
a. Compute the amount of revenue and cost of sales that was recognized in 2021 and 2022 using the old accounting policy.
b. Compute the amount of revenue and cost of sales that should be recognized in each year using the new accounting policy.
c. Record the adjusting journal entries to adjust revenue to reflect the change in accounting policy from using the cost ratio to using engineering estimates. The general ledger accounts for 2023 have not yet been closed. Ignore income tax effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For the following accounting changes, identify the appropriate treatment under IFRS.
Type of Accounting Change
Accounting Treatment
Change in estimate
Change in accounting policy
Correction of an error
Type of Accounting Change
Accounting Treatment
Change in estimate
Change in accounting policy
Correction of an error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why is the retrospective approach conceptually appropriate for changes in accounting policy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement is true regarding accounting accruals?
A)The nature of accrual accounting is that accruals will reverse when cash cycles are complete.
B)Operating activities generally have relatively long cash cycles.
C)Financing and investing activities generally have relatively short cash cycles.
D)Errors or changes in accounting policy that affect non-current items like equipment will result in follow-through changes over a relatively short period.
A)The nature of accrual accounting is that accruals will reverse when cash cycles are complete.
B)Operating activities generally have relatively long cash cycles.
C)Financing and investing activities generally have relatively short cash cycles.
D)Errors or changes in accounting policy that affect non-current items like equipment will result in follow-through changes over a relatively short period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Give an example of a change in accounting policy which does not require retrospective treatment and explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Define "a retrospective adjustment."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Why are retrospective adjustments to past years' income and expenses recorded directly in retained earnings?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Define the term "prospective adjustment." Which type of accounting changes is it applied to?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
How should enterprises reflect changes in accounting standards?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How many balance sheets are required by IAS 1 when there is a change in accounting policy and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Why is the prospective treatment conceptually appropriate for changes in estimates?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A retailer increases bad debts expense from 2.5% to 3% of credit sales. Given this information, which of the following statements is correct?
A)The net income of prior years is overstated and a retrospective correction should be made.
B)This is a change in estimate and should be treated prospectively.
C)This is a change in accounting policy and treatment is retrospective.
D)This is a correction of an error and a retrospective correction should be made.
A)The net income of prior years is overstated and a retrospective correction should be made.
B)This is a change in estimate and should be treated prospectively.
C)This is a change in accounting policy and treatment is retrospective.
D)This is a correction of an error and a retrospective correction should be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
During the audit of Keats Island Brewery for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2022, the auditors identified the following issues:
For each of the three issues described below, using the following table, identify both the direction (increase or decrease)and the amount of the effect relative to the amount without the accounting change.
a. The company sells beer for $1 each plus $0.10 deposit on each bottle. The deposit collected is payable to the provincial recycling agency. During 2021, the company had recorded $12,000 of deposits as revenue. The auditors believe this amount should have been recorded as a liability.
b. The company had been using the first-in, first-out cost flow assumption for its inventories. In fiscal 2022, management decided to switch to the weighted-average method. This change reduced inventory by $25,000 at June 30, 2021, and $40,000 at June 30, 2022.
c. The company has equipment costing $6,000,000 that it has been depreciating over 10 years on a straight-line basis. The depreciation for fiscal 2021 was $600,000 and accumulated depreciation on June 30, 2021, was $1,200,000. During 2022, management revises the estimate of useful life to 12 years, reducing the amount of depreciation to $480,000 per year.
Type of Accounting Change
Treatment
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Income
a.
b.
c.
For each of the three issues described below, using the following table, identify both the direction (increase or decrease)and the amount of the effect relative to the amount without the accounting change.
a. The company sells beer for $1 each plus $0.10 deposit on each bottle. The deposit collected is payable to the provincial recycling agency. During 2021, the company had recorded $12,000 of deposits as revenue. The auditors believe this amount should have been recorded as a liability.
b. The company had been using the first-in, first-out cost flow assumption for its inventories. In fiscal 2022, management decided to switch to the weighted-average method. This change reduced inventory by $25,000 at June 30, 2021, and $40,000 at June 30, 2022.
c. The company has equipment costing $6,000,000 that it has been depreciating over 10 years on a straight-line basis. The depreciation for fiscal 2021 was $600,000 and accumulated depreciation on June 30, 2021, was $1,200,000. During 2022, management revises the estimate of useful life to 12 years, reducing the amount of depreciation to $480,000 per year.
Type of Accounting Change
Treatment
Assets
Liabilities
Equity
Income
a.
b.
c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What types of accounting changes are treated retrospectively and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Albacore Sailboats manufactures small sailing dinghies. In 2022, the company's accountant recorded the following costs into the inventory account:
Variable costs (raw materials, labour, variable overhead)
11,098,000
Fixed manufacturing overhead
3,000,000
Salary of factory manager
100,000
Shipping to customer
350,000
Commission on sales
550,000
Total
15,098,000
The company had no work in process at the end of both 2021 and 2022. Finished goods at the end of 2021 amounted to 6,000 sailboats at $300/boat. Production was 50,000 sailboats and 4,000 boats remained in inventory at December 31, 2022. The company uses a periodic inventory system and the FIFO cost flow assumption.
Required:
a. Of the $15,098,000, how much should have been capitalized into inventories?
b. Compute the ending value of inventory and the cost of goods sold for 2022.
c. If the error in inventory costing had not been corrected as per part (a), by how much would inventory be overstated at the end of 2022?
d. Record the journal entry to correct the error in inventory costing.
Variable costs (raw materials, labour, variable overhead)
11,098,000
Fixed manufacturing overhead
3,000,000
Salary of factory manager
100,000
Shipping to customer
350,000
Commission on sales
550,000
Total
15,098,000
The company had no work in process at the end of both 2021 and 2022. Finished goods at the end of 2021 amounted to 6,000 sailboats at $300/boat. Production was 50,000 sailboats and 4,000 boats remained in inventory at December 31, 2022. The company uses a periodic inventory system and the FIFO cost flow assumption.
Required:
a. Of the $15,098,000, how much should have been capitalized into inventories?
b. Compute the ending value of inventory and the cost of goods sold for 2022.
c. If the error in inventory costing had not been corrected as per part (a), by how much would inventory be overstated at the end of 2022?
d. Record the journal entry to correct the error in inventory costing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What are two reasons why an accounting change may be permitted to give modified retrospective or prospective treatment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An analysis of a company's inventory indicates that inventory at the end of 2020 was understated by $30,000 due to an inventory count error. Inventory at the end of 2021 was correctly stated. The company uses the periodic system of inventory and its fiscal year-end is December 31. Given this information, which of the following statements is correct?
A)The net income of 2020 is overstated and a retrospective correction should be made.
B)The net income of 2021 is overstated and should be corrected.
C)The 2021 year-end retained earnings are overstated and a prospective correction should be made.
D)The net income of 2021 is understated and should be corrected.
A)The net income of 2020 is overstated and a retrospective correction should be made.
B)The net income of 2021 is overstated and should be corrected.
C)The 2021 year-end retained earnings are overstated and a prospective correction should be made.
D)The net income of 2021 is understated and should be corrected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For a construction contract where the company uses the percentage of completion method and there is a change in the estimated total cost of the contract from 12 million to 13 million, the accountant should do the following:
A)Use the average cost of 12.5 million.
B)Compute the percentage completed using the new cost total if the company uses the cost ratio to estimate percentage completed.
C)Use estimated costs determined at the beginning of the contract, not actual costs to date.
D)Use retrospective treatment.
A)Use the average cost of 12.5 million.
B)Compute the percentage completed using the new cost total if the company uses the cost ratio to estimate percentage completed.
C)Use estimated costs determined at the beginning of the contract, not actual costs to date.
D)Use retrospective treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



