Deck 24: Economic Growth, Business Cycles, and Unemployment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/96
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: Economic Growth, Business Cycles, and Unemployment
1
If the economy is in a structural stagnation, it can be expected to return to its historical trend soon.
False
2
Active demand management policies are based on the work of John Maynard Keynes.
True
3
The four phases of the business cycle are, in order, upturn, peak, recession, and trough.
True
4
"Classical economist" is often used interchangeably with which term?
A)Laissez-faire economist
B)Keynesian economist
C)Activist economist
D)Marxian economist
A)Laissez-faire economist
B)Keynesian economist
C)Activist economist
D)Marxian economist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Before the Great Depression the popular view of government was:
A)laissez-faire; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was activist.
B)activist; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was laissez-faire.
C)activist; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was still activist.
D)laissez-faire; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was still laissez-faire.
A)laissez-faire; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was activist.
B)activist; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was laissez-faire.
C)activist; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was still activist.
D)laissez-faire; and after the Great Depression, the popular view of government was still laissez-faire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Laissez-faire economists favor government intervention in the market process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the post-war era, the average business expansion has lasted about 59 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Keynesian economists believe:
A)government policies do not affect economic activity.
B)government can implement policy proposals that can positively impact the economy.
C)most government policies would probably make things worse.
D)the economy ought to be left to market forces.
A)government policies do not affect economic activity.
B)government can implement policy proposals that can positively impact the economy.
C)most government policies would probably make things worse.
D)the economy ought to be left to market forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the economy were producing at its potential output, then the unemployment rate would be less than the target rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Laissez-faire economists believe:
A)government policies mostly do not affect economic activity.
B)government can implement policy proposals that have mostly positively impacts on the economy.
C)most government policies would probably make things worse.
D)government intervention in the market is necessary for a smoothly operating economy.
A)government policies mostly do not affect economic activity.
B)government can implement policy proposals that have mostly positively impacts on the economy.
C)most government policies would probably make things worse.
D)government intervention in the market is necessary for a smoothly operating economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The unemployment rate is the percentage of people in the labor force who are both able to and looking for work but who cannot find jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Cyclical unemployment is caused by fluctuations in economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The terms business cycle and structural stagnation can be used interchangeably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Between 2007 and 2009, the U.S.unemployment rate rose from under 5 percent to over 8 percent.A Keynesian economist would most likely blame this increase in unemployment on:
A)an increase in the minimum wage.
B)an increase in the bargaining power of labor unions.
C)a decline in the level of aggregate demand.
D)a decline in aggregate supply.
A)an increase in the minimum wage.
B)an increase in the bargaining power of labor unions.
C)a decline in the level of aggregate demand.
D)a decline in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The difference between the long-run and short-run frameworks is that the long-run framework focuses on demand while the short-run framework focuses on supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following explains why Keynesian economics lost influence in the 1970s?
A)A change in the how the Federal Reserve was constructed
B)A crash in the stock market
C)The damaging effects of inflation
D)An increase in the marginal tax rate
A)A change in the how the Federal Reserve was constructed
B)A crash in the stock market
C)The damaging effects of inflation
D)An increase in the marginal tax rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Policy issues of business cycles are considered in a long-run framework

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Keynesian economists tend to focus their analysis on:
A)the long run.
B)the short run.
C)aggregate supply.
D)economic growth.
A)the long run.
B)the short run.
C)aggregate supply.
D)economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements would a Classical economist of the 1930s most likely disagree with?
A)The market, left to its own devices, is self-adjusting.
B)Wages and prices will adjust to eliminate unemployment.
C)In the short-run the economy might experience some problems.
D)Unions do not impede wage and price adjustment.
A)The market, left to its own devices, is self-adjusting.
B)Wages and prices will adjust to eliminate unemployment.
C)In the short-run the economy might experience some problems.
D)Unions do not impede wage and price adjustment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The sum of the number of employed persons and the number of unemployed persons equals the civilian non-institutional population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following was not a solution to the Great Depression favored by Classical economists?
A)Break up labor unions
B)Hire unemployed workers for public works programs
C)Let market forces operate
D)Stop government measures that held up wages and prices
A)Break up labor unions
B)Hire unemployed workers for public works programs
C)Let market forces operate
D)Stop government measures that held up wages and prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements best depicts laypeople's explanation of the Great Depression at that time?
A)Government policies kept prices too high.
B)An oversupply of goods had glutted the market.
C)Unions were keeping the good jobs for themselves.
D)An oversupply of goods is impossible.
A)Government policies kept prices too high.
B)An oversupply of goods had glutted the market.
C)Unions were keeping the good jobs for themselves.
D)An oversupply of goods is impossible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The short-run business cycle framework focuses primarily on factors:
A)affecting demand.
B)affecting supply.
C)affecting both supply and demand.
D)other than supply and demand.
A)affecting demand.
B)affecting supply.
C)affecting both supply and demand.
D)other than supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The highest amount of output an economy can sustainably produce and sell using existing production processes and resources is called:
A)nominal output.
B)actual output.
C)potential output.
D)utilized output.
A)nominal output.
B)actual output.
C)potential output.
D)utilized output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A period of protracted slow growth and high unemployment is called:
A)deflation.
B)cyclical stagnation.
C)structural stagnation.
D)stagflation.
A)deflation.
B)cyclical stagnation.
C)structural stagnation.
D)stagflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a country of 300 million people has a total income of $12 trillion, its per capita income is:
A)$36,000.
B)$40,000.
C)$360,000.
D)$400,000.
A)$36,000.
B)$40,000.
C)$360,000.
D)$400,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Issues of growth are generally considered in:
A)the short-run framework.
B)the long-run framework.
C)both the short-run and the long-run frameworks.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run frameworks.
A)the short-run framework.
B)the long-run framework.
C)both the short-run and the long-run frameworks.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run frameworks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When Classical economists of the 1930s looked at the Great Depression, they:
A)lacked a good explanation of why it was happening.
B)suggested wages were too flexible.
C)blamed it on activist fiscal and monetary policies.
D)thought it was a result of prices adjusting too quickly.
A)lacked a good explanation of why it was happening.
B)suggested wages were too flexible.
C)blamed it on activist fiscal and monetary policies.
D)thought it was a result of prices adjusting too quickly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Classical economists argued that:
A)a market economy will not experience unemployment in the short run.
B)if unemployment occurs, it will cure itself because wages will fall.
C)aggregate expenditures may be too low.
D)if inflation occurs it will cure itself because prices, wages, and interest rates will rise.
A)a market economy will not experience unemployment in the short run.
B)if unemployment occurs, it will cure itself because wages will fall.
C)aggregate expenditures may be too low.
D)if inflation occurs it will cure itself because prices, wages, and interest rates will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to Classical economists in the 1930s, a recession will end when:
A)government creates enough jobs for all of the unemployed.
B)wages rise enough to eliminate unemployment.
C)wages fall enough to eliminate unemployment.
D)taxes are cut enough to stimulate private spending.
A)government creates enough jobs for all of the unemployed.
B)wages rise enough to eliminate unemployment.
C)wages fall enough to eliminate unemployment.
D)taxes are cut enough to stimulate private spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Potential output:
A)is purely a physical phenomenon.
B)is related to the long-term growth trend.
C)requires government expenditures.
D)requires the purchase of new equipment.
A)is purely a physical phenomenon.
B)is related to the long-term growth trend.
C)requires government expenditures.
D)requires the purchase of new equipment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Keynesians:
A)generally favor activist government policies.
B)generally favor laissez-faire policies.
C)believe that frictional unemployment does not exist.
D)believe that all unemployment is cyclical unemployment.
A)generally favor activist government policies.
B)generally favor laissez-faire policies.
C)believe that frictional unemployment does not exist.
D)believe that all unemployment is cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Classical economists believe that in the short-run, in the real world:
A)prices and wages are flexible.
B)prices and wages aren't flexible enough to bring about equilibrium.
C)prices are flexible but wages were not flexible.
D)wages are flexible but prices were not flexible.
A)prices and wages are flexible.
B)prices and wages aren't flexible enough to bring about equilibrium.
C)prices are flexible but wages were not flexible.
D)wages are flexible but prices were not flexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Classicals:
A)generally favor activist government policies.
B)generally favor laissez-faire policies.
C)believe that frictional unemployment does not exist.
D)believe that all unemployment is cyclical unemployment.
A)generally favor activist government policies.
B)generally favor laissez-faire policies.
C)believe that frictional unemployment does not exist.
D)believe that all unemployment is cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The two frameworks conventional economists generally use to analyze macroeconomic issues are:
A)the inflation and the unemployment frameworks.
B)the short-run and the long-run frameworks.
C)the business cycle and the growth cycle frameworks.
D)the stagnationist and the Post-Keynesian frameworks.
A)the inflation and the unemployment frameworks.
B)the short-run and the long-run frameworks.
C)the business cycle and the growth cycle frameworks.
D)the stagnationist and the Post-Keynesian frameworks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The long-run growth framework focuses on factors affecting:
A)incentives to spend.
B)incentives to produce.
C)both supply and demand.
D)the business cycle.
A)incentives to spend.
B)incentives to produce.
C)both supply and demand.
D)the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Great Depression occurred in the early:
A)1900s.
B)1930s.
C)1950s.
D)1960s.
A)1900s.
B)1930s.
C)1950s.
D)1960s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Keynesian economics focuses on:
A)the long run.
B)the short run.
C)both the long run and the short run.
D)neither the long run nor the short run.
A)the long run.
B)the short run.
C)both the long run and the short run.
D)neither the long run nor the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Classical economists are generally associated with:
A)laissez-faire.
B)their support of inflation.
C)an activist policy.
D)price controls.
A)laissez-faire.
B)their support of inflation.
C)an activist policy.
D)price controls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The laissez-faire policy prescription to eliminate unemployment was to:
A)eliminate labor unions and government policies that hold real wages too high.
B)strengthen unions and government regulations protecting unions and workers.
C)increase real wages so that people are encouraged to work.
D)have government guarantee jobs for everyone.
A)eliminate labor unions and government policies that hold real wages too high.
B)strengthen unions and government regulations protecting unions and workers.
C)increase real wages so that people are encouraged to work.
D)have government guarantee jobs for everyone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If U.S.real GDP increases by 3.3 percent, we can infer that the United States experiences:
A)a recession.
B)an upturn.
C)a depression.
D)a trough.
A)a recession.
B)an upturn.
C)a depression.
D)a trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During the business cycle, an economic upturn occurs:
A)at the peak of the business cycle.
B)at the trough of the business cycle.
C)in between the peak and trough of the business cycle
D)in between the trough and peak of the business cycle
A)at the peak of the business cycle.
B)at the trough of the business cycle.
C)in between the peak and trough of the business cycle
D)in between the trough and peak of the business cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following countries, or groups of countries, has grown at the fastest rate in the last ten years?
A)Western Europe
B)China
C)The United States
D)Eastern Europe
A)Western Europe
B)China
C)The United States
D)Eastern Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What turns a business cycle into a structural stagnation?
A)A trough that is lower than the peak.
B)Multiple business cycles in a short period of time.
C)A slow upturn that keeps the economy below trend.
D)An upturn that exceeds potential.
A)A trough that is lower than the peak.
B)Multiple business cycles in a short period of time.
C)A slow upturn that keeps the economy below trend.
D)An upturn that exceeds potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Per capita output would be certain to increase if:
A)both real output and population increase.
B)both real output and population decrease.
C)real output increases and population decreases.
D)real output decreases and population increases.
A)both real output and population increase.
B)both real output and population decrease.
C)real output increases and population decreases.
D)real output decreases and population increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Policies that affect aggregate expenditures are primarily relevant to the:
A)short-run business cycle framework.
B)long-run growth framework.
C)short-run growth framework.
D)long-run business cycle framework.
A)short-run business cycle framework.
B)long-run growth framework.
C)short-run growth framework.
D)long-run business cycle framework.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The business cycle is:
A)the term used to describe fluctuations in output around its long-term trend.
B)the length of time required by a firm to buy inputs and produce and sell output.
C)the pattern of increases and decreases in the money supply.
D)regular and predictable.
A)the term used to describe fluctuations in output around its long-term trend.
B)the length of time required by a firm to buy inputs and produce and sell output.
C)the pattern of increases and decreases in the money supply.
D)regular and predictable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The secular trend growth rate is the:
A)rate of growth in any one year.
B)rate of growth in per capita output in any one year.
C)rate of growth of potential output.
D)difference between actual output and the average growth in the economy.
A)rate of growth in any one year.
B)rate of growth in per capita output in any one year.
C)rate of growth of potential output.
D)difference between actual output and the average growth in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The top of the business cycle is called:
A)a growth trend.
B)a recession.
C)an upturn.
D)a peak.
A)a growth trend.
B)a recession.
C)an upturn.
D)a peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The business cycle consists of several stages or phases.Which is the accurate sequence?
A)Recession, peak, upturn, trough
B)Recession, peak, trough, upturn
C)Recession, upturn, peak, trough
D)Recession, trough, upturn, peak
A)Recession, peak, upturn, trough
B)Recession, peak, trough, upturn
C)Recession, upturn, peak, trough
D)Recession, trough, upturn, peak

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The secular trend growth rate in the United States is approximately:
A)1 to 1.5 percent per year.
B)2.5 to 3.5 percent per year.
C)5 to 5.5 percent per year.
D)7 to 7.5 percent per year.
A)1 to 1.5 percent per year.
B)2.5 to 3.5 percent per year.
C)5 to 5.5 percent per year.
D)7 to 7.5 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose a country's output is $440 billion and its population is 110 million.Now suppose that both its output and its population increase by 24 percent.As a result of these changes, its new level of per capita output will be:
A)00.
B)40.
C)$4,000.
D)$4,400.
A)00.
B)40.
C)$4,000.
D)$4,400.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Fluctuations around the long-term growth rate are called:
A)recessions.
B)depressions.
C)expansions.
D)business cycles.
A)recessions.
B)depressions.
C)expansions.
D)business cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The growth trend in the graph shown is depicted by: 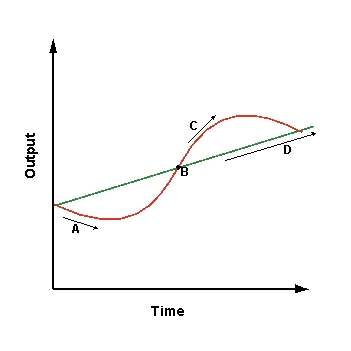
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following statements best characterizes the Keynesian view of business cycles?
A)Fluctuations in business activity occur in regular and predictable patterns that cannot be altered.
B)Fluctuations in business activity are to be expected and should be accepted just as changes in the seasons are accepted.
C)Business cycles of the business cycle are symptoms of underlying problems and should be dealt with through activist government policies.
D)The appropriate macroeconomic policy can easily eliminate all fluctuations in business activity.
A)Fluctuations in business activity occur in regular and predictable patterns that cannot be altered.
B)Fluctuations in business activity are to be expected and should be accepted just as changes in the seasons are accepted.
C)Business cycles of the business cycle are symptoms of underlying problems and should be dealt with through activist government policies.
D)The appropriate macroeconomic policy can easily eliminate all fluctuations in business activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements best characterizes the Classical view of business cycles?
A)Fluctuations in business activity occur in regular and predictable patterns.
B)Fluctuations in business activity are to be expected and should be accepted
C)Business cycles are symptoms of underlying problems and should be addressed by macroeconomic policy.
D)The appropriate macroeconomic policy can eliminate fluctuations in business activity.
A)Fluctuations in business activity occur in regular and predictable patterns.
B)Fluctuations in business activity are to be expected and should be accepted
C)Business cycles are symptoms of underlying problems and should be addressed by macroeconomic policy.
D)The appropriate macroeconomic policy can eliminate fluctuations in business activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Business cycles are generally considered in:
A)the short-run framework.
B)the long-run framework.
C)both the short-run and long-run frameworks.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run frameworks.
A)the short-run framework.
B)the long-run framework.
C)both the short-run and long-run frameworks.
D)neither the short-run nor the long-run frameworks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In order of their occurrence, the phases of the business cycle are:
A)peak, downturn, upturn, trough.
B)peak, upturn, downturn, trough.
C)peak, downturn, trough, upturn.
D)peak, upturn, trough, downturn.
A)peak, downturn, upturn, trough.
B)peak, upturn, downturn, trough.
C)peak, downturn, trough, upturn.
D)peak, upturn, trough, downturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a country's output and population are, respectively, $500 billion and 200 million, then its per capita output is:
A)50.
B)$1,000.
C)$2,500.
D)$24,000.
A)50.
B)$1,000.
C)$2,500.
D)$24,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Over the last ten years which geographic area or country had the highest per capita growth rate?
A)China
B)Western Europe
C)North America
D)Latin America
A)China
B)Western Europe
C)North America
D)Latin America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In contrast to a recession in industrialized nations, a recession in pre-industrial nations:
A)is more visible in its effects on the unemployment rate but it has a smaller effect on wage rates.
B)is less visible in its effects on the unemployment rate but it has a larger effect on wage rates.
C)has larger effects on both unemployment and wage rates.
D)has smaller effects on both unemployment and wage rates.
A)is more visible in its effects on the unemployment rate but it has a smaller effect on wage rates.
B)is less visible in its effects on the unemployment rate but it has a larger effect on wage rates.
C)has larger effects on both unemployment and wage rates.
D)has smaller effects on both unemployment and wage rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Unemployment caused by people entering the job market and people quitting a job just long enough to look for and find another one is called:
A)structural unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)are not counted in the unemployment rate.
A)structural unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)are not counted in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Prior to the Industrial Revolution, unemployment was not generally considered a social problem because:
A)there were no fluctuations in how much people spent so there was nothing similar to recessions.
B)a reduction in spending would cause wages and income to fall rather than unemployment to rise.
C)governments, influenced by religious values, provided jobs to anyone unfortunate to be unemployed.
D)employers before the Industrial Revolution generally offered workers lifetime contracts and rarely dismissed them.
A)there were no fluctuations in how much people spent so there was nothing similar to recessions.
B)a reduction in spending would cause wages and income to fall rather than unemployment to rise.
C)governments, influenced by religious values, provided jobs to anyone unfortunate to be unemployed.
D)employers before the Industrial Revolution generally offered workers lifetime contracts and rarely dismissed them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Technological change is most likely to affect:
A)structural unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)seasonal unemployment.
A)structural unemployment.
B)frictional unemployment.
C)cyclical unemployment.
D)seasonal unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Unemployment caused by a recession, assuming the time it takes to find a job constant, is called:
A)frictional unemployment.
B)cyclical unemployment.
C)natural unemployment.
D)structural unemployment.
A)frictional unemployment.
B)cyclical unemployment.
C)natural unemployment.
D)structural unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the graph shown. 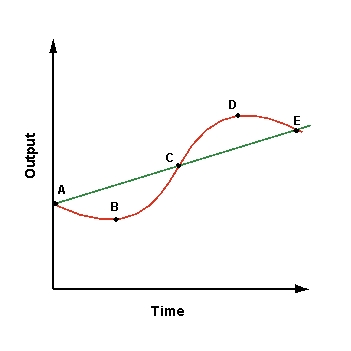 A movement from points A to B represents a(n):
A movement from points A to B represents a(n):
A)trough.
B)peak.
C)upturn.
 A movement from points A to B represents a(n):
A movement from points A to B represents a(n):A)trough.
B)peak.
C)upturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The unemployment rate is the number of people without a job:
A)divided by the population.
B)and looking divided by the population.
C)divided by the labor force.
D)and looking for work divided by the labor force.
A)divided by the population.
B)and looking divided by the population.
C)divided by the labor force.
D)and looking for work divided by the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Some economists talk about a non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment (NAIRU).The term the text uses for this concept is:
A)the natural rate of unemployment.
B)cyclical unemployment.
C)structural unemployment.
D)the target rate of unemployment.
A)the natural rate of unemployment.
B)cyclical unemployment.
C)structural unemployment.
D)the target rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the standard unemployment rate, discouraged workers are counted as:
A)part of the population over16.
B)employed.
C)unemployed.
D)part of the labor force.
A)part of the population over16.
B)employed.
C)unemployed.
D)part of the labor force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Refer to the graph shown. 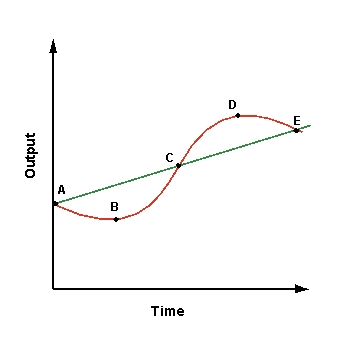 A movement from points B to C represents a(n):
A movement from points B to C represents a(n):
A)trough.
B)peak.
C)recession.
D)upturn.
 A movement from points B to C represents a(n):
A movement from points B to C represents a(n):A)trough.
B)peak.
C)recession.
D)upturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Another term for what the text calls the "target rate of unemployment" is:
A)Keynesian unemployment.
B)nominal unemployment.
C)real unemployment.
D)the natural rate of unemployment.
A)Keynesian unemployment.
B)nominal unemployment.
C)real unemployment.
D)the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
After the Great Depression, until 2008, economic downturns:
A)disappeared.
B)became longer.
C)became shorter.
D)continued more or less as they had prior to the Depression.
A)disappeared.
B)became longer.
C)became shorter.
D)continued more or less as they had prior to the Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A structural stagnation is:
A)a business cycle with greater fluctuations around the trend.
B)a slow expansion that involves slower growth than the previous long run trend.
C)a business cycle in which unemployment rises during the downturn and rises during the expansion.
D)a business cycle with smaller fluctuations around the trend.
A)a business cycle with greater fluctuations around the trend.
B)a slow expansion that involves slower growth than the previous long run trend.
C)a business cycle in which unemployment rises during the downturn and rises during the expansion.
D)a business cycle with smaller fluctuations around the trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The longest business-cycle expansion in U.S.history occurred during the ten years from:
A)1919 until1929.
B)1938 until1948.
C)1959 until1969.
D)1991 until2001.
A)1919 until1929.
B)1938 until1948.
C)1959 until1969.
D)1991 until2001.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Keynesians tend to agree that during a depression:
A)decreasing government spending is likely to improve economic conditions.
B)increasing taxes is likely to improve economic conditions
C)increasing government spending is likely to improve economic conditions
D)governments should not do anything because anything they do will likely make the situation worse.
A)decreasing government spending is likely to improve economic conditions.
B)increasing taxes is likely to improve economic conditions
C)increasing government spending is likely to improve economic conditions
D)governments should not do anything because anything they do will likely make the situation worse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is one reason the government collects data about discouraged workers?
A)Some people argue that the unemployment rate underestimates true unemployment because it does not include discouraged workers.
B)Some people argue that the unemployment rate overestimates true unemployment because it includes discouraged workers.
C)The number of discouraged workers is a better indicator of unemployment.
D)To include them in the standard measure of unemployment because they can't find jobs.
A)Some people argue that the unemployment rate underestimates true unemployment because it does not include discouraged workers.
B)Some people argue that the unemployment rate overestimates true unemployment because it includes discouraged workers.
C)The number of discouraged workers is a better indicator of unemployment.
D)To include them in the standard measure of unemployment because they can't find jobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cyclical unemployment is defined as unemployment that results from:
A)fluctuations in economic activity.
B)structural changes in the economy.
C)changes in technology.
D)the aging of the population.
A)fluctuations in economic activity.
B)structural changes in the economy.
C)changes in technology.
D)the aging of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The lowest sustainable rate of unemployment that policy makers believe is achievable under existing conditions is:
A)zero.
B)called the target rate of unemployment.
C)called the optimal rate of unemployment.
D)called cyclical unemployment.
A)zero.
B)called the target rate of unemployment.
C)called the optimal rate of unemployment.
D)called cyclical unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following contributes to structural unemployment?
A)A general short-run downturn in the economy.
B)People quitting a job just long enough to look for and find another one.
C)People over 65 who don't really want to work.
D)People losing a job when their skills become obsolete due to technological innovations.
A)A general short-run downturn in the economy.
B)People quitting a job just long enough to look for and find another one.
C)People over 65 who don't really want to work.
D)People losing a job when their skills become obsolete due to technological innovations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A recession is often considered to be:
A)an economic downturn that persists for more than two consecutive quarters of the year.
B)an economic downturn that persists for more than four consecutive quarters of the year.
C)any period of more than six months in which unemployment is rising.
D)any period when the unemployment rate exceeds 6 percent.
A)an economic downturn that persists for more than two consecutive quarters of the year.
B)an economic downturn that persists for more than four consecutive quarters of the year.
C)any period of more than six months in which unemployment is rising.
D)any period when the unemployment rate exceeds 6 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 96 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



