Deck 35: International Financial Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/164
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 35: International Financial Policy
1
The balance of payments is made up of three accounts: the merchandise trade account, the service account, and the investment income account.
False
2
If a European billionaire buys stock in General Motors, then the purchase will be recorded in the:
A)U.S.current account.
B)European current account.
C)European financial and capital account.
D)U.S.government financial account.
A)U.S.current account.
B)European current account.
C)European financial and capital account.
D)U.S.government financial account.
European financial and capital account.
3
Fixed exchange rates restrict macroeconomic policy more than flexible exchange rates.
True
4
Some economists believe that if Greece had its own currency, it would not have been as vulnerable to a financial crisis, as was the case with being in the Eurozone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Joining the Eurozone meant that countries could have unlimited budget deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the U.S.current account, most of the trade deficit results from an excess of imported:
A)merchandise and services.
B)merchandise.
C)services.
D)transfers.
A)merchandise and services.
B)merchandise.
C)services.
D)transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The euro was adopted solely for economic reasons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Because an expansionary monetary policy decreases domestic interest rates, it can be used to fix the value of the domestic currency below the market equilibrium rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
It is impossible for a country to have a current account surplus and a balance of payments deficit at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Official reserves are essential for countries that fix the value of their currencies beneath the market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the U.S.price level rises relative to the Japanese price level, purchasing power parity predicts a long run increase in the value of the dollar relative to the yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The part of the balance of payments account that lists all long-term flows of payments is called the:
A)current account.
B)financial and capital account.
C)government financial account.
D)balance of trade.
A)current account.
B)financial and capital account.
C)government financial account.
D)balance of trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If General Motors buys steel from Russia, then the purchase will be recorded in the:
A)U.S.current account.
B)U.S.financial and capital account.
C)U.S.government financial account.
D)Russian government financial account.
A)U.S.current account.
B)U.S.financial and capital account.
C)U.S.government financial account.
D)Russian government financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A country with limited official reserves is better off pursuing fixed exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The balance of payment account is made up of:
A)a current account and a financial and capital account.
B)an import account and an export account.
C)an investment account and a consumption account.
D)a monetary account and a fiscal account.
A)a current account and a financial and capital account.
B)an import account and an export account.
C)an investment account and a consumption account.
D)a monetary account and a fiscal account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Expansionary monetary policy definitely lowers the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Eurozone would be well equipped to deal with their member countries defaulting on their debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Because a contractionary fiscal policy raises domestic interest rates, it can be used to fix the value of the domestic currency above the market equilibrium rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The difference between the value of goods exported and imported is the:
A)current account balance.
B)financial and capital account balance.
C)government financial balance.
D)balance of merchandise trade.
A)current account balance.
B)financial and capital account balance.
C)government financial balance.
D)balance of merchandise trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Expansionary fiscal policy definitely raises the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
U.S.imports involve an:
A)outflow of dollars from the United States to foreigners.
B)inflow of dollars from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
C)outflow of foreign currency from the United States to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currency from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
A)outflow of dollars from the United States to foreigners.
B)inflow of dollars from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
C)outflow of foreign currency from the United States to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currency from foreigners to the U.S.economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
General Electric, a U.S.company, buys $50 million of Japanese securities.This transaction causes the U.S.:
A)current account balance to increase.
B)current account balance to decrease.
C)financial and capital account balance to increase.
D)financial and capital account balance to decrease.
A)current account balance to increase.
B)current account balance to decrease.
C)financial and capital account balance to increase.
D)financial and capital account balance to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The 2004 South Asian tsunami killed more than 150,000 people in countries around the Indian Ocean.Many Americans donated to help the victims of this natural disaster.These donations:
A)would not be included in the balance of payments account because there was no purchase or sale.
B)are part of the export of services in the balance of payments account.
C)are part of the import of services in the balance of payments account.
D)are part of net transfers in the balance of payments account.
A)would not be included in the balance of payments account because there was no purchase or sale.
B)are part of the export of services in the balance of payments account.
C)are part of the import of services in the balance of payments account.
D)are part of net transfers in the balance of payments account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is the difference between the balance of trade and the balance of payments?
A)The balance of trade is only part of the balance of payments.
B)The balance of payments is only part of the balance of trade.
C)The two are different parts of the balance of merchandise accounts.
D)The two are different parts of the balance of financial and capital accounts.
A)The balance of trade is only part of the balance of payments.
B)The balance of payments is only part of the balance of trade.
C)The two are different parts of the balance of merchandise accounts.
D)The two are different parts of the balance of financial and capital accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
During the last decade, the United States ran the largest trade deficits in its history.These trade deficits imply:
A)a U.S.balance of payments deficit.
B)a U.S.private balance of payments surplus.
C)a U.S.balance of payments equilibrium.
D)nothing about the overall U.S.balance of payments.
A)a U.S.balance of payments deficit.
B)a U.S.private balance of payments surplus.
C)a U.S.balance of payments equilibrium.
D)nothing about the overall U.S.balance of payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the balance of payments accounts, imports and exports are listed as part of:
A)the current account.
B)the financial and capital account.
C)the statistical discrepancy.
D)net transfers.
A)the current account.
B)the financial and capital account.
C)the statistical discrepancy.
D)net transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Refer to the graph shown.An increase in the U.S.price level would shift: 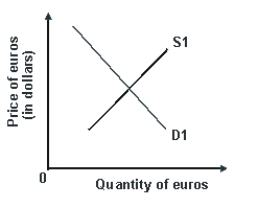
A)D1 right and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
B)D1 left and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
C)D1 right and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
D)D1 left and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.

A)D1 right and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
B)D1 left and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
C)D1 right and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
D)D1 left and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the financial and capital account has a deficit, the:
A)balance of payments must have a deficit.
B)balance of payments must have a surplus.
C)balance on the current account must have a deficit.
D)balance on the current account must have a surplus.
A)balance of payments must have a deficit.
B)balance of payments must have a surplus.
C)balance on the current account must have a deficit.
D)balance on the current account must have a surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Canadian imports involve an:
A)outflow of Canadian dollars from Canada to foreigners.
B)inflow of Canadian dollars from foreigners to Canada.
C)outflow of foreign currencies from Canada to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currencies from foreigners to Canada.
A)outflow of Canadian dollars from Canada to foreigners.
B)inflow of Canadian dollars from foreigners to Canada.
C)outflow of foreign currencies from Canada to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currencies from foreigners to Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
U.S.exports involve an:
A)outflow of dollars from the United States to foreigners.
B)inflow of dollars from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
C)outflow of foreign currency from the United States to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currency from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
A)outflow of dollars from the United States to foreigners.
B)inflow of dollars from foreigners to the U.S.economy.
C)outflow of foreign currency from the United States to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currency from foreigners to the U.S.economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Canadian exports involve an:
A)outflow of Canadian dollars from Canada to foreigners.
B)inflow of Canadian dollars from foreigners to Canada.
C)outflow of foreign currencies from Canada to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currencies from foreigners to Canada.
A)outflow of Canadian dollars from Canada to foreigners.
B)inflow of Canadian dollars from foreigners to Canada.
C)outflow of foreign currencies from Canada to foreigners.
D)inflow of foreign currencies from foreigners to Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When a worker in the United States sends money to his family in Mexico, this transaction is recorded in the U.S.balance of payment as an:
A)outflow in the merchandise account.
B)outflow in the net transfer account.
C)inflow in the service account.
D)inflow in the investment income account.
A)outflow in the merchandise account.
B)outflow in the net transfer account.
C)inflow in the service account.
D)inflow in the investment income account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A Chinese purchase of Boeing aircraft is recorded in the American balance of payments as a:
A)positive entry in the current account.
B)positive entry in the financial and capital account.
C)negative entry in the current account.
D)negative entry in the financial and capital account.
A)positive entry in the current account.
B)positive entry in the financial and capital account.
C)negative entry in the current account.
D)negative entry in the financial and capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In your last vacation trip to Cancún, Mexico, you spent $1 ,000.This amount is recorded in the:
A)balance of merchandise trade as an export.
B)balance of merchandise trade as an import.
C)balance of trade as an export.
D)balance of trade as an import.
A)balance of merchandise trade as an export.
B)balance of merchandise trade as an import.
C)balance of trade as an export.
D)balance of trade as an import.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Other things equal, a reduction in American income should:
A)increase the U.S.current account but lower the dollar.
B)increase the U.S.current account and raise the dollar.
C)decrease the U.S.current account and lower the dollar.
D)decrease the U.S.current account but raise the dollar.
A)increase the U.S.current account but lower the dollar.
B)increase the U.S.current account and raise the dollar.
C)decrease the U.S.current account and lower the dollar.
D)decrease the U.S.current account but raise the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When a U.S.company purchases a foreign company, the transaction is recorded in the balance of payments as part of:
A)the current account.
B)the financial and capital account.
C)the statistical discrepancy.
D)net transfers.
A)the current account.
B)the financial and capital account.
C)the statistical discrepancy.
D)net transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Refer to the graph shown.An increase in U.S.income would shift: 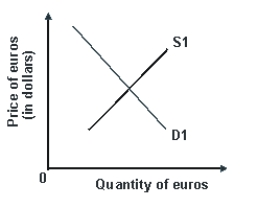
A)S1 left and cause the euro to gain value.
B)S1 right and cause the euro to lose value.
C)D1 right and cause the euro to gain value.
D)D1 left and cause the euro to lose value.

A)S1 left and cause the euro to gain value.
B)S1 right and cause the euro to lose value.
C)D1 right and cause the euro to gain value.
D)D1 left and cause the euro to lose value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The purchase of a meal by an American tourist at La Tour d'Argen (a restaurant in Paris) would find its way into the American balance of payments as a:
A)positive entry in the current account.
B)positive entry in the financial and capital account.
C)negative entry in the current account.
D)negative entry in the financial and capital account.
A)positive entry in the current account.
B)positive entry in the financial and capital account.
C)negative entry in the current account.
D)negative entry in the financial and capital account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Refer to the graph shown.An increase in American interest rates would shift: 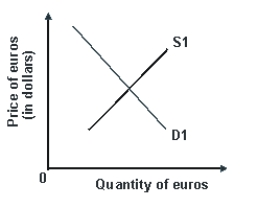
A)D1 right and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
B)D1 right and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
C)D1 left and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
D)D1 left and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.

A)D1 right and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
B)D1 right and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.
C)D1 left and S1 left, causing an appreciation of the euro.
D)D1 left and S1 right, causing a depreciation of the euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Since the mid-1980s, the dollar's value has fallen from over 300 yen per dollar to about 136 yen per dollar.This trend might be explained by:
A)higher economic growth in Japan.
B)lower interest rates in Japan.
C)lower inflation in Japan.
D)Japanese purchases of U.S.dollars.
A)higher economic growth in Japan.
B)lower interest rates in Japan.
C)lower inflation in Japan.
D)Japanese purchases of U.S.dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Other things being equal, an increase in trade restrictions on imports will:
A)reduce the demand for foreign currency, causing it to appreciate.
B)reduce the demand for foreign currency, causing it to depreciate.
C)increase the demand for foreign currency, causing it to appreciate.
D)increase the demand for foreign currency, causing it to depreciate.
A)reduce the demand for foreign currency, causing it to appreciate.
B)reduce the demand for foreign currency, causing it to depreciate.
C)increase the demand for foreign currency, causing it to appreciate.
D)increase the demand for foreign currency, causing it to depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In 1923 Germany experienced a very severe inflation.As prices in Germany rose, the demand in the foreign exchange market for Reichsmarks, the German currency of the time,:
A)rose and the supply of them fell, decreasing their value.
B)rose and the supply of them also rose, decreasing their value.
C)fell and the supply of them also fell, increasing their value.
D)fell and the supply of them rose, decreasing their value.
A)rose and the supply of them fell, decreasing their value.
B)rose and the supply of them also rose, decreasing their value.
C)fell and the supply of them also fell, increasing their value.
D)fell and the supply of them rose, decreasing their value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A country that fixes a price for its currency that is above the market price will:
A)accumulate official reserves.
B)increase its money supply.
C)lose official reserves.
D)eventually increase the value of its currency.
A)accumulate official reserves.
B)increase its money supply.
C)lose official reserves.
D)eventually increase the value of its currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A country that fixes a price for its currency that is below the market price must:
A)accumulate official reserves.
B)decrease its money supply.
C)lose official reserves.
D)eventually increase the value of its currency.
A)accumulate official reserves.
B)decrease its money supply.
C)lose official reserves.
D)eventually increase the value of its currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exchange rate fundamentals, such as the income level, interest rates, and the price levels:
A)do not affect exchange rates in the short run or the long run.
B)affect exchange rates but are not as important as expectations in the long run.
C)affect exchange rates and are more important than expectations in the long run.
D)affect exchange rates, but only in the short run.
A)do not affect exchange rates in the short run or the long run.
B)affect exchange rates but are not as important as expectations in the long run.
C)affect exchange rates and are more important than expectations in the long run.
D)affect exchange rates, but only in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Refer to the graph shown.An exchange rate of $2.40 per dinar creates excess: 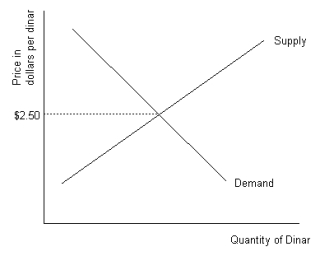
A)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are sold by the government.
B)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are bought by the government.
C)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are sold by the government.
D)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are bought by the government.

A)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are sold by the government.
B)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are bought by the government.
C)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are sold by the government.
D)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are bought by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the price level in the United States falls relative to the price level in foreign nations, U.S.exports:
A)increase and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to rise and the supply of dollars to fall.
B)decrease and U.S.imports increase, causing the demand for dollars to fall and the supply of dollars to rise.
C)decrease and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to rise and the supply of dollars to rise.
D)increase and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to fall and the supply of dollars to rise.
A)increase and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to rise and the supply of dollars to fall.
B)decrease and U.S.imports increase, causing the demand for dollars to fall and the supply of dollars to rise.
C)decrease and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to rise and the supply of dollars to rise.
D)increase and U.S.imports decrease, causing the demand for dollars to fall and the supply of dollars to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In 1923, Germany experienced a very severe inflation.As prices in Germany rose, the demand in the foreign exchange market for U.S.dollars:
A)rose and the supply of them fell, increasing their value.
B)rose and the supply of them also rose, decreasing their value.
C)fell and the supply of them also fell, increasing their value.
D)fell and the supply of them rose, decreasing their value.
A)rose and the supply of them fell, increasing their value.
B)rose and the supply of them also rose, decreasing their value.
C)fell and the supply of them also fell, increasing their value.
D)fell and the supply of them rose, decreasing their value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Refer to the graph shown.An exchange rate of $2.95 per dinar creates excess: 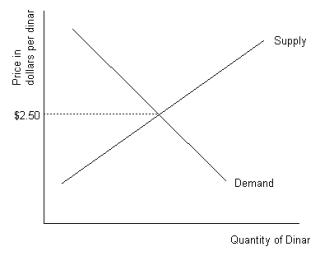
A)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are sold by the government.
B)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are bought by the government.
C)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are sold by the government.
D)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are bought by the government.

A)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are sold by the government.
B)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to lose value unless dinar are bought by the government.
C)demand for dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are sold by the government.
D)supply of dinar that will cause the dinar to gain value unless dinar are bought by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Refer to the graph shown.A shift in the supply of dollars from S1 to S2 is most likely the result of: 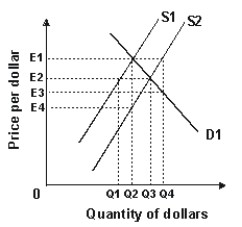
A)a decrease in the U.S.price level relative to foreign prices.
B)an increase in U.S.interest rates relative to foreign interest rates.
C)an increase in U.S.incomes relative to foreign incomes.
D)the U.S.government's attempt to support its own currency.

A)a decrease in the U.S.price level relative to foreign prices.
B)an increase in U.S.interest rates relative to foreign interest rates.
C)an increase in U.S.incomes relative to foreign incomes.
D)the U.S.government's attempt to support its own currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Refer to the graph shown.To maintain the price of euros at $1.00 the government must: 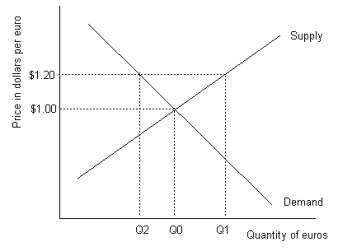
A)buy Q1-Q0 euros.
B)buy Q1-Q2 euros.
C)sell Q2-Q0 euros.
D)do nothing.

A)buy Q1-Q0 euros.
B)buy Q1-Q2 euros.
C)sell Q2-Q0 euros.
D)do nothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Foreign governments are holding fewer dollars as reserves.As a result, the value of the dollar is declining.If foreign governments want to keep the U.S.dollar from declining, they could:
A)implement domestic contractionary monetary policies.
B)implement domestic export subsidies to accumulate dollars.
C)buy more U.S.dollars.
D)reduce their U.S.dollar holdings even more.
A)implement domestic contractionary monetary policies.
B)implement domestic export subsidies to accumulate dollars.
C)buy more U.S.dollars.
D)reduce their U.S.dollar holdings even more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A country with a balance of payments deficit that wants to maintain the current exchange rate:
A)gains official reserves.
B)loses official reserves.
C)gains foreign liabilities.
D)loses foreign assets.
A)gains official reserves.
B)loses official reserves.
C)gains foreign liabilities.
D)loses foreign assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The buying of a currency by a government to maintain its value above its long-run equilibrium value is called currency:
A)ceiling.
B)management.
C)stabilization.
D)support.
A)ceiling.
B)management.
C)stabilization.
D)support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Refer to the graph shown.A purchase of shekels by the Israeli government would shift the: 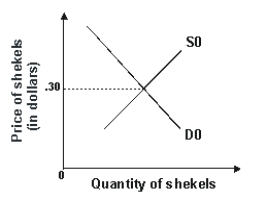
A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Refer to the graph shown.To maintain the price of euros at $1.20, the European Central Bank must buy: 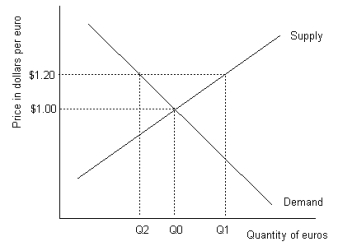
A)Q1-Q0 euros.
B)Q1-Q2 euros.
C)Q0-Q2 euros.
D)Q2 euros.

A)Q1-Q0 euros.
B)Q1-Q2 euros.
C)Q0-Q2 euros.
D)Q2 euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Exchange rate expectations:
A)do not affect exchange rates in the short run or the long run.
B)affect exchange rates but are not as important as fundamentals in the short run.
C)affect exchanges rates and are more important than fundamentals in the short run.
D)affect exchange rates, but only in the long run.
A)do not affect exchange rates in the short run or the long run.
B)affect exchange rates but are not as important as fundamentals in the short run.
C)affect exchanges rates and are more important than fundamentals in the short run.
D)affect exchange rates, but only in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Refer to the graph shown.The least likely cause of the shift from D1 to D2 is: 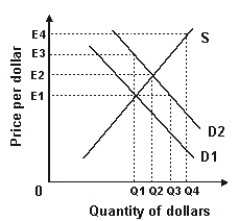
A)an increase in the U.S.inflation rate.
B)an increase in U.S.interest rates.
C)expansionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.

A)an increase in the U.S.inflation rate.
B)an increase in U.S.interest rates.
C)expansionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the 1990s, inflation in many Latin American countries fell to about 10 to 15 percent per year from annual rates of up to 1,000 percent a year in the 1980s.You would expect that as this occurred, the value of many Latin American currencies would:
A)have fallen more rapidly.
B)have fallen less rapidly.
C)not be affected.
D)move unpredictably.
A)have fallen more rapidly.
B)have fallen less rapidly.
C)not be affected.
D)move unpredictably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Refer to the graph shown.As a result of the shift from D1 to D2, the value of the dollar will: 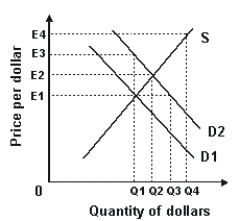
A)increase in response to excess demand equal to Q4 -Q2.
B)increase in response to excess demand equal to Q3 -Q1.
C)decrease in response to excess supply equal to Q4 -Q2.
D)decrease in response to excess supply equal to Q3 -Q1.

A)increase in response to excess demand equal to Q4 -Q2.
B)increase in response to excess demand equal to Q3 -Q1.
C)decrease in response to excess supply equal to Q4 -Q2.
D)decrease in response to excess supply equal to Q3 -Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A country that wants to increase its exchange rate to a higher level than the market exchange rate would most likely adopt:
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the late 1990s Argentina suffered a serious recession but was able, unlike Brazil, to prevent a sharp devaluation of its currency.This is most likely because:
A)Argentina pursued a contractionary monetary policy but Brazil did not.
B)Argentina pursued an expansionary monetary policy but Brazil did not.
C)Brazil pursued a more contractionary monetary policy than Argentina.
D)Brazil pursued a more expansionary monetary policy than Argentina.
A)Argentina pursued a contractionary monetary policy but Brazil did not.
B)Argentina pursued an expansionary monetary policy but Brazil did not.
C)Brazil pursued a more contractionary monetary policy than Argentina.
D)Brazil pursued a more expansionary monetary policy than Argentina.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When Turkey tried to preserve its fixed exchange rate in the early 2000s, it was unable to to do so and its currency depreciated.Which policy would have been most likely to help Turkey preserve the value of its exchange rate?
A)Tax cut
B)Spending hike
C)Drop in the money supply
D)Drop in central bank lending rates
A)Tax cut
B)Spending hike
C)Drop in the money supply
D)Drop in central bank lending rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Expansionary monetary policy tends to:
A)lower the U.S.interest rate and increase the U.S.exchange rate.
B)lower the U.S.interest rate and decrease the U.S.exchange rate.
C)increase the U.S.interest rate and decrease the U.S.exchange rate.
D)increase the U.S.interest rate and increase the U.S.exchange rate.
A)lower the U.S.interest rate and increase the U.S.exchange rate.
B)lower the U.S.interest rate and decrease the U.S.exchange rate.
C)increase the U.S.interest rate and decrease the U.S.exchange rate.
D)increase the U.S.interest rate and increase the U.S.exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the graph shown.A purchase of shekels by the Israeli government would shift the: 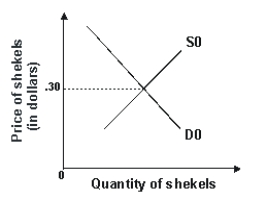
A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Refer to the graph shown.A sale of shekels by the Israeli government would shift the: 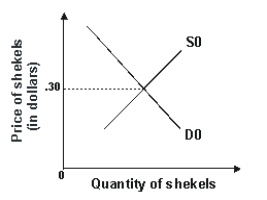
A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

A)demand curve to the left and reduce the price of shekels.
B)demand curve to the right and raise the price of shekels.
C)supply curve to the right and reduce the price of shekels.
D)supply curve to the left and raise the price of shekels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Contractionary monetary policy generally:
A)lowers U.S.interest rates.
B)decreases the inflow of financial capital.
C)increases the inflow of financial capital.
D)decreases the U.S.exchange rate.
A)lowers U.S.interest rates.
B)decreases the inflow of financial capital.
C)increases the inflow of financial capital.
D)decreases the U.S.exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Monetary policy affects exchange rates in all the following ways except through its effects on:
A)the interest rate.
B)taxes.
C)price level and inflation.
D)income.
A)the interest rate.
B)taxes.
C)price level and inflation.
D)income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Higher U.S.interest rates usually cause:
A)foreign capital to leave the United States.
B)no change in foreign investment in the United States.
C)a drop in the U.S.dollar exchange rate.
D)foreign capital to enter the United States.
A)foreign capital to leave the United States.
B)no change in foreign investment in the United States.
C)a drop in the U.S.dollar exchange rate.
D)foreign capital to enter the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Exchange rate fluctuations:
A)do not have economic consequences.
B)have minor economic consequences.
C)have important economic consequences.
D)have as yet undetermined economic consequences.
A)do not have economic consequences.
B)have minor economic consequences.
C)have important economic consequences.
D)have as yet undetermined economic consequences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The direct effect of expansionary monetary policy is to:
A)increase both U.S.imports and the value of the dollar.
B)increase U.S.imports but reduce the value of the dollar.
C)reduce both U.S.imports and the value of the dollar.
D)reduce U.S.imports but increase the value of the dollar.
A)increase both U.S.imports and the value of the dollar.
B)increase U.S.imports but reduce the value of the dollar.
C)reduce both U.S.imports and the value of the dollar.
D)reduce U.S.imports but increase the value of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Expansionary monetary policy:
A)reduces the demand for the domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and increases the supply.
B)reduces only the demand for the domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
C)reduces only the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
D)increases the demand for domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and reduces the supply.
A)reduces the demand for the domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and increases the supply.
B)reduces only the demand for the domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
C)reduces only the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market.
D)increases the demand for domestic currency in the foreign exchange market and reduces the supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
From the late 1990s into the early 2000s, Hong Kong suffered from deflation.Most economists believed that the period of deflation ended and that inflation would begin to pick up slowly.Prices, however, were believed to be held in check because the Hong Kong dollar is pegged to the U.S.dollar.What does the monetary authority in Hong Kong have to do to peg its dollar to the U.S.dollar?
A)It does not allow free trade in U.S.dollars; the foreign exchange market is illegal.
B)It will sell Hong Kong dollars when the price of the Hong Kong dollar drops and buy them when the price of the Hong Kong dollar rises.
C)It will sell Hong Kong dollars when the price of the Hong Kong dollar rises and buy them when the price of the Hong Kong dollar drops.
D)It will raise tariffs when the value of the Hong Kong dollar falls and lower them when the value of the Hong Kong dollar rises.
A)It does not allow free trade in U.S.dollars; the foreign exchange market is illegal.
B)It will sell Hong Kong dollars when the price of the Hong Kong dollar drops and buy them when the price of the Hong Kong dollar rises.
C)It will sell Hong Kong dollars when the price of the Hong Kong dollar rises and buy them when the price of the Hong Kong dollar drops.
D)It will raise tariffs when the value of the Hong Kong dollar falls and lower them when the value of the Hong Kong dollar rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A country that wants to fix its exchange rate at a higher level than the market exchange rate would most likely:
A)raise income taxes.
B)raise government spending.
C)reduce the money supply.
D)increase the money supply.
A)raise income taxes.
B)raise government spending.
C)reduce the money supply.
D)increase the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Contractionary monetary policy tends to:
A)reduce the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar.
B)reduce the interest rate, increase capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar.
C)raise the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar.
D)raise the interest rate, raise capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar.
A)reduce the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar.
B)reduce the interest rate, increase capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar.
C)raise the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar.
D)raise the interest rate, raise capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Expansionary monetary policy tends to:
A)reduce both the interest rate and capital inflows.
B)reduce the interest rate and increase capital inflows.
C)increase the interest rate and reduce capital inflows.
D)increase both the interest rate and capital inflows.
A)reduce both the interest rate and capital inflows.
B)reduce the interest rate and increase capital inflows.
C)increase the interest rate and reduce capital inflows.
D)increase both the interest rate and capital inflows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The government of Crossland wants to influence its exchange rate.It will do so by buying and selling:
A)currencies in its official reserves.
B)commodities.
C)goods and services from the current account.
D)transfers.
A)currencies in its official reserves.
B)commodities.
C)goods and services from the current account.
D)transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Fiscal policy affects:
A)both the supply and demand for a currency.
B)the demand for a currency but not the supply.
C)the supply of a currency but not the demand.
D)neither the supply of a currency nor the demand.
A)both the supply and demand for a currency.
B)the demand for a currency but not the supply.
C)the supply of a currency but not the demand.
D)neither the supply of a currency nor the demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When the euro appreciated significantly against the U.S.dollar, European policymakers were concerned.To stop the appreciation of the euro, the European Central Bank could have adopted a macroeconomic policy that:
A)reduced both the supply and demand for euros.
B)reduced the supply of euros but increased the demand.
C)increased both the supply and the demand for euros.
D)reduced the demand for euros but increased the supply.
A)reduced both the supply and demand for euros.
B)reduced the supply of euros but increased the demand.
C)increased both the supply and the demand for euros.
D)reduced the demand for euros but increased the supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Expansionary monetary policy generally:
A)raises U.S.interest rates.
B)increases the inflow of financial capital.
C)increases the U.S.exchange rate.
D)pushes down the value of the U.S.dollar.
A)raises U.S.interest rates.
B)increases the inflow of financial capital.
C)increases the U.S.exchange rate.
D)pushes down the value of the U.S.dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 164 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



