Deck 37: Structural Stagnation and Globalization
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/97
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 37: Structural Stagnation and Globalization
1
To remain on its growth trend, an economy must grow more in an expansion then it fell during the recession.
True
2
Structural stagnation requires difficult supply-side structural changes to accompany any demand-side stimulus if it is to be successful in reducing unemployment significantly.
True
3
The United States has done very poorly at the high end of the value-added chain.
False
4
A trade surplus results when the world supply curve is below the domestic economy's price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The higher the reservation wage the more likely one is to be unemployed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The economy recovered quickly from the 2007 recession to return to its trend growth path..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to structural stagnationists, expansionary monetary and fiscal policy has allowed the economy to address its structural problems and allow the economy to adjust in an expedient manner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the structural stagnation hypothesis, expansionary macro policy tends to lead to:
A)goods inflation.
B)goods deflation
C)asset price inflation.
D)low exchange rates.
A)goods inflation.
B)goods deflation
C)asset price inflation.
D)low exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Structural problems associated with globalization are no longer a concern for policy makers or economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The housing market boom raised people's perceived wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The U.S.economy is currently experiencing a standard business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to the structural stagnation hypothesis, what is the long-run cause of the recent problems facing the United States?
A)Globalization.
B)Too low investment.
C)Inflation.
D)Unemployment.
A)Globalization.
B)Too low investment.
C)Inflation.
D)Unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Compared to earlier recessions, in the 2008 downturn employment:
A)took longer to return to its pre-recession peak.
B)returned to its pre-recession peak in less time.
C)took about the same amount of time to return to its pre-recession peak.
D)Changes in employment cannot be compared across recessions because every recession is different.
A)took longer to return to its pre-recession peak.
B)returned to its pre-recession peak in less time.
C)took about the same amount of time to return to its pre-recession peak.
D)Changes in employment cannot be compared across recessions because every recession is different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Suppose an economy's trend growth rate is 3% and current output is $10 trillion.If the economy enters a recession where output declines by 5% in one year, by how much does output have to rise to return the economy back to its trend? Assume it takes two years for the economy to return to its trend.
A)$0.5 trillion.
B)$0.6 trillion.
C)$1.4 trillion.
D)$1.7 trillion.
A)$0.5 trillion.
B)$0.6 trillion.
C)$1.4 trillion.
D)$1.7 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If an economy has a trade deficit, shifting the domestic SAS curve down will shift the globally constrained potential output to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the difference between the structural stagnation hypothesis and secular stagnation theory?
A)Structural stagnation sees globalization as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees too little investment as the cause.
B)Structural stagnation sees too little investment as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees globalization as the cause.
C)Structural stagnation sees foreign countries moving down the value added chain as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees foreign countries moving up the value added chain as the cause of a stagnation.
D)There is no difference, they both attribute stagnation to too little investment.
A)Structural stagnation sees globalization as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees too little investment as the cause.
B)Structural stagnation sees too little investment as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees globalization as the cause.
C)Structural stagnation sees foreign countries moving down the value added chain as the cause of a stagnation, while secular stagnation sees foreign countries moving up the value added chain as the cause of a stagnation.
D)There is no difference, they both attribute stagnation to too little investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The government can deal with the effects of the decline in wealth without causing new problems down the road.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When the financial crisis occurred policy makers were more concerned about the deficit than they were about addressing the financial crisis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the structural stagnation hypothesis, structural stagnation has only short-run causes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The globalized AS/AD model takes trade into account while the standard AD/AS model does not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What does the structural stagnation hypothesis say about how soon the economy will return to its trend growth?
A)The economy has already returned to its previous trend growth rate.
B)The economy will return to its previous trend growth rate soon.
C)It will be long time before the economy returns to its previous trend growth rate.
D)The economy will never return to its previous trend growth rate.
A)The economy has already returned to its previous trend growth rate.
B)The economy will return to its previous trend growth rate soon.
C)It will be long time before the economy returns to its previous trend growth rate.
D)The economy will never return to its previous trend growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Structural stagnation focuses on _______ in terms of understanding why the economy experiences slow growth.
A)low investment
B)low consumption
C)low government spending
D)globalization
A)low investment
B)low consumption
C)low government spending
D)globalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A theory in which advanced countries stop growing because investment opportunities would be eliminated is referred to as:
A)structural stagnation.
B)frictional stagnation.
C)reservation stagnation
D)secular stagnation.
A)structural stagnation.
B)frictional stagnation.
C)reservation stagnation
D)secular stagnation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to the structural stagnation theory,
A)U.S.economic growth will return to the world average growth rate, but by that time the U.S.share of world output will have declined.
B)U.S.economic growth will return to the world average growth rate and its current share of world output.
C)U.S.economic growth will never return to the world average growth rate because foreign economies have so far to catch up.
D)After a period of slower growth U.S.economic growth will exceed world growth.
A)U.S.economic growth will return to the world average growth rate, but by that time the U.S.share of world output will have declined.
B)U.S.economic growth will return to the world average growth rate and its current share of world output.
C)U.S.economic growth will never return to the world average growth rate because foreign economies have so far to catch up.
D)After a period of slower growth U.S.economic growth will exceed world growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The time it has taken for employment to return to its pre-recession level has:
A)stayed about the same.
B)fallen over time.
C)risen over time.
D)shown no trend.
A)stayed about the same.
B)fallen over time.
C)risen over time.
D)shown no trend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
An explanation after the Great Depression for why output growth would stop is called:
A)the structural stagnation hypothesis.
B)secular stagnation theory.
C)the frictional stagnation hypothesis.
D)the slow growth model.
A)the structural stagnation hypothesis.
B)secular stagnation theory.
C)the frictional stagnation hypothesis.
D)the slow growth model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following statements is correct with regards to the business cycle?
A)Up to the 1980s the economy slowly got back to its previous level of employment.
B)After the 1980s economic recoveries took increasingly longer.
C)After the 1980s economic recoveries took a short period of time.
D)The 1990 recovery was slower than the 2001 recovery.
A)Up to the 1980s the economy slowly got back to its previous level of employment.
B)After the 1980s economic recoveries took increasingly longer.
C)After the 1980s economic recoveries took a short period of time.
D)The 1990 recovery was slower than the 2001 recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If an economy declined by 3 percent in one year in order for the economy to return to trend growth within two years, it would have to increase at an annual rate that is
A)less than three percent.
B)equal to three percent.
C)greater than three percent.
D)unknown.
A)less than three percent.
B)equal to three percent.
C)greater than three percent.
D)unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The structural stagnation hypothesis provides a general explanation for why:
A)the economy is experiencing a weak recovery.
B)a bubble occurred in the housing market.
C)demand-side policies have been successful in the economic recovery in 2010-12.
D)the economy is experiencing such a strong recovery.
A)the economy is experiencing a weak recovery.
B)a bubble occurred in the housing market.
C)demand-side policies have been successful in the economic recovery in 2010-12.
D)the economy is experiencing such a strong recovery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In order for the economy to return to its growth rate, the rate at which the economy expands must be:
A)equal to the trend rate.
B)less than the trend rate.
C)greater than the trend rate.
D)equal to the rate of inflation.
A)equal to the trend rate.
B)less than the trend rate.
C)greater than the trend rate.
D)equal to the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The central difference between the standard theory and the structural stagnation hypothesis when it comes to growth is:
A)the level of inflation.
B)the trend growth rate.
C)the federal funds rate.
D)the natural rate of unemployment.
A)the level of inflation.
B)the trend growth rate.
C)the federal funds rate.
D)the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Structural stagnation is used to describe a:
A)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major structural changes in the economy.
B)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major political changes in the economy.
C)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major legal changes in the economy.
D)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major cyclical changes in the economy.
A)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major structural changes in the economy.
B)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major political changes in the economy.
C)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major legal changes in the economy.
D)downturn followed by a period of slow growth that is not expected to speed up anytime soon without major cyclical changes in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the lines represents the structural stagnation's assumption about trend growth? 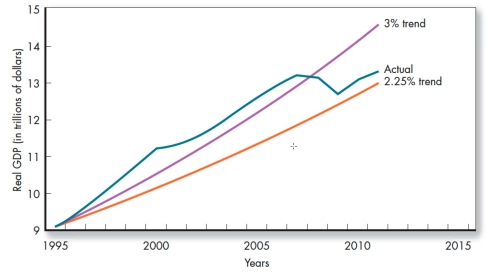
A)3% trend.
B)Actual.
C)2.25% trend.
D)It is not represented.

A)3% trend.
B)Actual.
C)2.25% trend.
D)It is not represented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The short-run cause of structural stagnation is tied to:
A)globalization.
B)the financial crisis aftermath.
C)the trade deficit.
D)exchange rates.
A)globalization.
B)the financial crisis aftermath.
C)the trade deficit.
D)exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the structural stagnation hypothesis is correct, demand-side government policy has been far too expansionary since the mid:
A)2000s.
B)1980s.
C)1990s.
D)1970s.
A)2000s.
B)1980s.
C)1990s.
D)1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The central difference between the structural stagnation hypothesis and the secular stagnation theory is that:
A)structural stagnation applied in the 1940s and secular stagnation applies today.
B)structural stagnation focuses on declining investment while secular stagnation focuses on globalization.
C)structural stagnation focuses on globalization while secular stagnation focuses on declining investment.
D)structural stagnation is a hypothesis while secular stagnation is theory.
A)structural stagnation applied in the 1940s and secular stagnation applies today.
B)structural stagnation focuses on declining investment while secular stagnation focuses on globalization.
C)structural stagnation focuses on globalization while secular stagnation focuses on declining investment.
D)structural stagnation is a hypothesis while secular stagnation is theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the structural stagnation hypothesis is true, what happened to the economy in the early 2000s that made it prone to a financial crisis?
A)Too expansionary demand-side policies.
B)Too expansionary supply-side policies.
C)Increased trade restrictions.
D)Slowing technological advance.
A)Too expansionary demand-side policies.
B)Too expansionary supply-side policies.
C)Increased trade restrictions.
D)Slowing technological advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Refer to the graph. 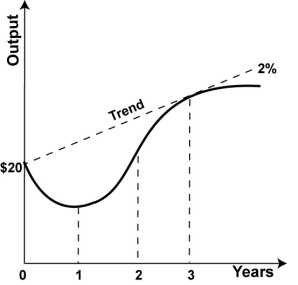 The economy begins at a level of output of $20 billion and experiences a one-year recession in which output declines by 4 percent.What is output in year 1?
The economy begins at a level of output of $20 billion and experiences a one-year recession in which output declines by 4 percent.What is output in year 1?
A)$800 million.
B)$800 billion
C)$19.2 million.
D)$19.2 billion.
 The economy begins at a level of output of $20 billion and experiences a one-year recession in which output declines by 4 percent.What is output in year 1?
The economy begins at a level of output of $20 billion and experiences a one-year recession in which output declines by 4 percent.What is output in year 1?A)$800 million.
B)$800 billion
C)$19.2 million.
D)$19.2 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The hypothesis about the macro economy that sees the recent problems of the U.S.economy directly related to the structural problems caused by globalization is referred to as the ________ hypothesis.
A)low investment
B)secular stagnation
C)structural stagnation
D)comparative stagnation
A)low investment
B)secular stagnation
C)structural stagnation
D)comparative stagnation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The standard macro policy is the assumption that the long-run trend growth rate is:
A)1 to 2 percent.
B)5 to 6 percent.
C)3 to 3.5 percent.
D)0 to 1 percent.
A)1 to 2 percent.
B)5 to 6 percent.
C)3 to 3.5 percent.
D)0 to 1 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following statements best describes the figure shown? 
A)The world price level equals the domestic price level.
B)The economy is operating below potential because of globalization.
C)Domestic aggregate supply is less than domestic aggregate demand.
D)Potential output is constrained by globalization.

A)The world price level equals the domestic price level.
B)The economy is operating below potential because of globalization.
C)Domestic aggregate supply is less than domestic aggregate demand.
D)Potential output is constrained by globalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the graph shown, the country has: 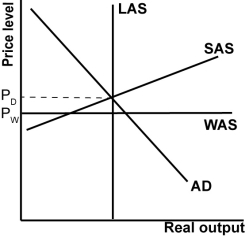
A)a trade surplus.
B)a budget deficit.
C)a trade deficit.
D)neither a trade deficit nor trade surplus; exports are equal to imports.

A)a trade surplus.
B)a budget deficit.
C)a trade deficit.
D)neither a trade deficit nor trade surplus; exports are equal to imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the globalized model, the eventual equivalency of domestic and world prices follows from the:
A)law of demand.
B)law of supply.
C)law of comparative advantage.
D)law of one price.
A)law of demand.
B)law of supply.
C)law of comparative advantage.
D)law of one price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the graph shown, which of the world supply curves creates a trade surplus? 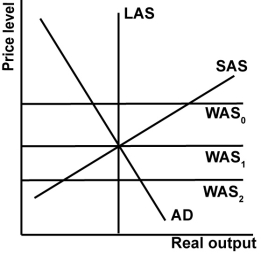
A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create surpluses.

A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How is the globalized AS/AD model different from the standard AS/AD model?
A)It has an added world demand curve.
B)The AD curve is upward sloping.
C)It has an added world supply curve.
D)The AS curve is downward sloping.
A)It has an added world demand curve.
B)The AD curve is upward sloping.
C)It has an added world supply curve.
D)The AS curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
When did structural stagnation begin according to the hypothesis?
A)The mid-1960s
B)The mid-1970s
C)The mid-1980s
D)Tmid-1990s
A)The mid-1960s
B)The mid-1970s
C)The mid-1980s
D)Tmid-1990s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the graph shown, the globally constrained potential output is: 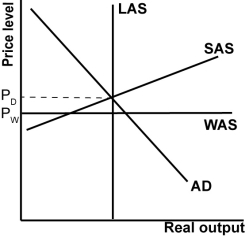
A)to the right of the LAS curve shown.
B)to the left of the LAS curve shown.
C)the same as the LAS curve shown.
D)the LAS curve shown, but horizontal.

A)to the right of the LAS curve shown.
B)to the left of the LAS curve shown.
C)the same as the LAS curve shown.
D)the LAS curve shown, but horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The globalized AS/AD model relates:
A)to tradable goods only.
B)directly to both tradable and non-tradable goods.
C)to tradable services only.
D)directly to tradable and indirectly to non-tradable goods.
A)to tradable goods only.
B)directly to both tradable and non-tradable goods.
C)to tradable services only.
D)directly to tradable and indirectly to non-tradable goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the graph shown, what could balance the trade deficit by reducing domestic consumption? 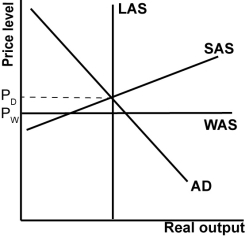
A)Contractionary monetary policy.
B)Lower domestic wages.
C)A hurricane that damages domestic manufacturing plants.
D)Expansionary fiscal policy.

A)Contractionary monetary policy.
B)Lower domestic wages.
C)A hurricane that damages domestic manufacturing plants.
D)Expansionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the globalized AS/AD model, the world supply curve is:
A)horizontal.
B)downward-sloping.
C)vertical.
D)upward-sloping.
A)horizontal.
B)downward-sloping.
C)vertical.
D)upward-sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the figure shown, 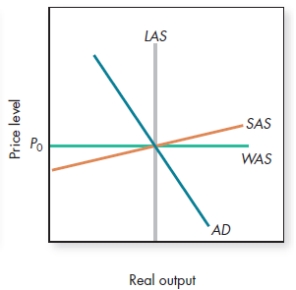
A)there is a trade deficit because of globalization.
B)there is a trade surplus because actual output equals potential output.
C)there is a trade balance because the world price level equals the domestic price level.
D)the country isn't exporting or importing because world and domestic prices are equal.

A)there is a trade deficit because of globalization.
B)there is a trade surplus because actual output equals potential output.
C)there is a trade balance because the world price level equals the domestic price level.
D)the country isn't exporting or importing because world and domestic prices are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Looking at the globalized AS/AD model, the economy can exceed potential output without generating accelerating goods inflation because:
A)the world price level puts a cap on the domestic price level.
B)the domestic price level always exceeds the world price level.
C)the world price level always exceeds the domestic price level.
D)the LRAS curve is no longer vertical.
A)the world price level puts a cap on the domestic price level.
B)the domestic price level always exceeds the world price level.
C)the world price level always exceeds the domestic price level.
D)the LRAS curve is no longer vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
According to the globalized AS/AD model, expansionary monetary policy shifts the AD curve to the right and:
A)increases goods inflation.
B)has no effect on goods inflation.
C)shifts potential output to the right.
D)shifts potential output to the left.
A)increases goods inflation.
B)has no effect on goods inflation.
C)shifts potential output to the right.
D)shifts potential output to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The globalized AS/AD curve is the standard AS/AD model with an added:
A)world demand curve.
B)domestic supply curve.
C)world supply curve.
D)long-run aggregate supply curve.
A)world demand curve.
B)domestic supply curve.
C)world supply curve.
D)long-run aggregate supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the figure shown, domestic production 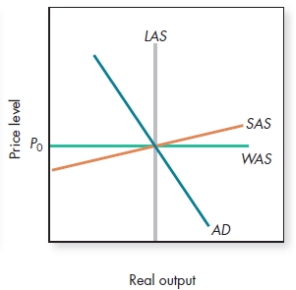
A)exceeds global constrained potential output.
B)is less than exports less imports.
C)exceeds global constrained prices.
D)equals domestic consumption.

A)exceeds global constrained potential output.
B)is less than exports less imports.
C)exceeds global constrained prices.
D)equals domestic consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Adding globalization with large trade deficits to the standard AS/AD model shows:
A)reduced domestic production and consumption.
B)increased domestic production and consumption.
C)increased domestic production and reduced consumption.
D)decreased domestic production and increased consumption.
A)reduced domestic production and consumption.
B)increased domestic production and consumption.
C)increased domestic production and reduced consumption.
D)decreased domestic production and increased consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Refer to the graph shown.According to the globalized AS/AD model, which best represents to the world aggregate supply and trade in the 2000s? 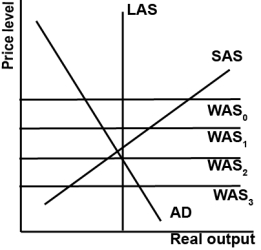
A)WAS0 and the United States had a large trade surplus.
B)WAS1 and the United States had a small trade deficit.
C)WAS2 and the United States had a small trade surplus.
D)WAS3 and the United States had a large trade deficit.

A)WAS0 and the United States had a large trade surplus.
B)WAS1 and the United States had a small trade deficit.
C)WAS2 and the United States had a small trade surplus.
D)WAS3 and the United States had a large trade deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the graph shown, which of the world supply curves is associated with a trade balance? 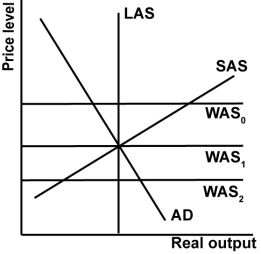
A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create surpluses.

A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the graph shown, which of the world supply curves creates a trade deficit? 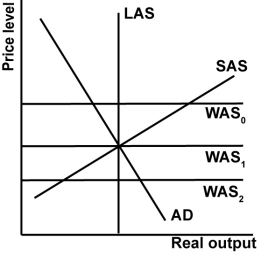
A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create deficits.

A)WAS0.
B)WAS1.
C)WAS2.
D)None create deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Based on what we know about the globalized AS/AD model, the standard model does not include an analysis of:
A)investment.
B)government spending in the United States.
C)net exports.
D)consumption.
A)investment.
B)government spending in the United States.
C)net exports.
D)consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the graph shown, what would eliminate a trade deficit if there were one? 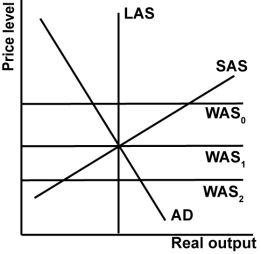
A)The exchange rate appreciates.
B)Domestic reservation wages rise.
C)Foreign wages rise relative to domestic wages.
D)Government runs expansionary policy.

A)The exchange rate appreciates.
B)Domestic reservation wages rise.
C)Foreign wages rise relative to domestic wages.
D)Government runs expansionary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
In the globalized AS/AD model, what curve tells the amount of tradable goods that other countries in the world will supply to the country at a given price level and exchange rate:
A)world demand curve
B)domestic supply curve
C)world supply curve
D)domestic demand curve
A)world demand curve
B)domestic supply curve
C)world supply curve
D)domestic demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
According to the structural stagnation model, an increasing trade deficit translates into___ unemployment and ___ globally constrained potential output.
A)lower; higher
B)lower; lower
C)higher; higher
D)higher; lower
A)lower; higher
B)lower; lower
C)higher; higher
D)higher; lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which group most benefited from globalization?
A)International traders and those associated with them.
B)Workers in the "commodities" sector.
C)Workers in the non-tradable goods sector.
D)No one benefitted.
A)International traders and those associated with them.
B)Workers in the "commodities" sector.
C)Workers in the non-tradable goods sector.
D)No one benefitted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Refer to the graph shown.What will reduce the trade deficit? 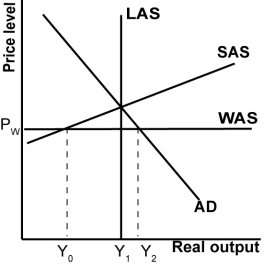
A)The AD curve shifts to the left.
B)The SAS curve shifts down.
C)The WAS curve shifts up.
D)All the answers are correct.

A)The AD curve shifts to the left.
B)The SAS curve shifts down.
C)The WAS curve shifts up.
D)All the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Looking at the graph shown, the structural adjustments necessary to bring the economy back to domestic and international equilibrium include: 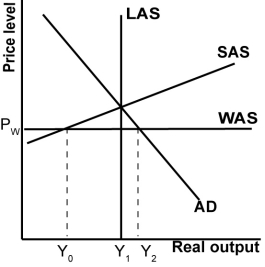
A)an increase in the U.S.exchange rate.
B)an increase in the U.S.wages and costs of production.
C)an increase in aggregate demand.
D)a fall in the U.S.exchange rate.

A)an increase in the U.S.exchange rate.
B)an increase in the U.S.wages and costs of production.
C)an increase in aggregate demand.
D)a fall in the U.S.exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the graph shown, what would shift the WAS curve from WAS0 to WAS1? 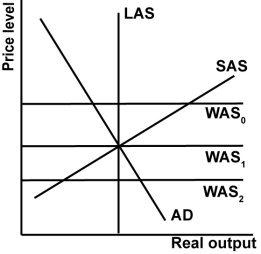
A)The country's exchange rate appreciates.
B)Domestic reservation wages fall.
C)Input prices fall.
D)Government runs contractionary policy.

A)The country's exchange rate appreciates.
B)Domestic reservation wages fall.
C)Input prices fall.
D)Government runs contractionary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the graph shown, what is globally constrained potential output? 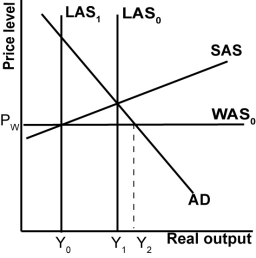
A)Y2 -Y1.
B)Y2 -Y0.
C)Y0.
D)Y1.

A)Y2 -Y1.
B)Y2 -Y0.
C)Y0.
D)Y1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The primary signal to policy makers that the economy has exceeded potential output is typically:
A)deflation.
B)stagflation.
C)inflation.
D)unemployment.
A)deflation.
B)stagflation.
C)inflation.
D)unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the graph shown, what represents the trade deficit? 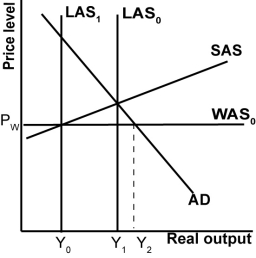
A)Y2 -Y1.
B)Y2 -Y0.
C)Y0.
D)Y1.

A)Y2 -Y1.
B)Y2 -Y0.
C)Y0.
D)Y1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The most likely explanation for why the U.S.government was not worried about the growth in deficits caused by its expansionary policy was:
A)they wanted inflation to occur in order to wipe out the value of government debt.
B)they knew they could pass significant tax increases to manage the deficit.
C)they expected that the economy would grow out of the deficit.
D)they wanted to make the dollar exchange rate favorable compared to the Yuan.
A)they wanted inflation to occur in order to wipe out the value of government debt.
B)they knew they could pass significant tax increases to manage the deficit.
C)they expected that the economy would grow out of the deficit.
D)they wanted to make the dollar exchange rate favorable compared to the Yuan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The gap between a country's potential output and its consumption is most directly related to its:
A)budget deficit.
B)trade deficit.
C)exchange rate.
D)comparative advantage.
A)budget deficit.
B)trade deficit.
C)exchange rate.
D)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the graph shown, a shift in the AD curve to the right: 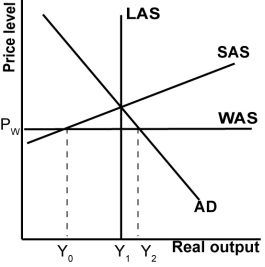
A)Raises domestic consumption.
B)Lowers domestic consumption.
C)Lowers globally constrained potential output.
D)Causes goods inflation.

A)Raises domestic consumption.
B)Lowers domestic consumption.
C)Lowers globally constrained potential output.
D)Causes goods inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
In the graph shown, a downward shift in the SAS curve: 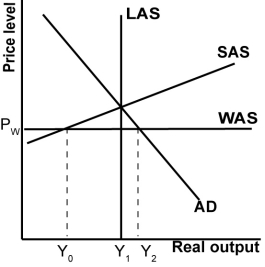
A)Raises domestic consumption because domestic producers produce more.
B)Raises the trade deficit because domestic producers are more competitive.
C)Raises domestic production because input prices have fallen.
D)Lowers globalized potential output because domestic producers are more competitive.

A)Raises domestic consumption because domestic producers produce more.
B)Raises the trade deficit because domestic producers are more competitive.
C)Raises domestic production because input prices have fallen.
D)Lowers globalized potential output because domestic producers are more competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose a young person asked you for job advice in a globalized economy.Which of the following sectors would you try to dissuade them most from entering?
A)Finance sector
B)Skilled profession in tradable sectors
C)Manufacturing sector
D)Commodities
A)Finance sector
B)Skilled profession in tradable sectors
C)Manufacturing sector
D)Commodities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In the graph shown, an upward shift in the WAS curve: 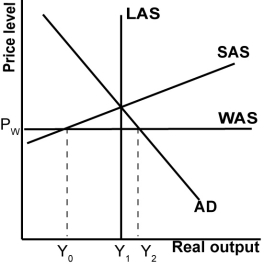
A)Raises domestic consumption because domestic producers produce more.
B)Lowers the trade deficit because domestic producers are more competitive.
C)Lowers domestic production because domestic consumption has fallen.
D)Raises globalized potential output because U.S.producers are less competitive.

A)Raises domestic consumption because domestic producers produce more.
B)Lowers the trade deficit because domestic producers are more competitive.
C)Lowers domestic production because domestic consumption has fallen.
D)Raises globalized potential output because U.S.producers are less competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to the structural stagnation hypothesis, the expansionary policy carried out by the government led to the illusion that the policies were:
A)leading to long-term economic health.
B)effective in reducing the trade deficit.
C)improving U.S comparative advantages.
D)causing goods inflation.
A)leading to long-term economic health.
B)effective in reducing the trade deficit.
C)improving U.S comparative advantages.
D)causing goods inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the early 2000s, policy makers were able to:
A)run contractionary policy without causing deflation.
B)run expansionary policy without causing inflation.
C)run contractionary policy without causing a rise in unemployment.
D)impose tariffs on foreign goods without causing retaliation by foreign countries.
A)run contractionary policy without causing deflation.
B)run expansionary policy without causing inflation.
C)run contractionary policy without causing a rise in unemployment.
D)impose tariffs on foreign goods without causing retaliation by foreign countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which group has fared the worst in the globalization process?
A)International traders
B)Skilled workers in the nontradable sector
C)Workers involved in the manufacture of commodities
D)Government workers
A)International traders
B)Skilled workers in the nontradable sector
C)Workers involved in the manufacture of commodities
D)Government workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which would help resolve structural stagnation?
A)Domestic exchange rates rise.
B)Domestic wages rise.
C)Productivity rises.
D)Productivity falls.
A)Domestic exchange rates rise.
B)Domestic wages rise.
C)Productivity rises.
D)Productivity falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 97 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



