Deck 1: Charting the Heavens: the Foundations of Astronomy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Charting the Heavens: the Foundations of Astronomy
1
At the equinoxes, the declination of the Sun must be zero degrees.
True
2
The celestial sphere is divided into 88 modern constellations.
True
3
The vernal equinox marks the beginning of spring in the northern hemisphere.
True
4
The sidereal day is determined by the Earth's rotation with respect to the stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
From Earth, the Sun and Moon have about the same angular diameter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Constellations are close clusters of stars, all at about the same distance from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A tropical year is the same as a sidereal year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In general, the brightest star in a given constellation is designated as alpha.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An hour of right ascension corresponds to 60 degrees in the sky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
From full moon to third quarter moon takes about a week.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Latitude and right ascension are coordinate systems used to find objects on the celestial sphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Over 20,000 stars are visible to the naked eye on the darkest, clearest nights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As it orbits the Earth, the Moon appears to move its own diameter (0.5 degrees) eastward every hour against the background stars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
At the solstices, the Sun's declination will be 23.5 degrees from the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A star with a right ascension of 2.6 hrs will rise 2.6 hours after the vernal equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The closest terrestrial analog to hours of right ascension is angle of longitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Right ascension in the sky is very similar to latitude on the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the sky, declination is measured in degrees north or south of the celestial equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The south celestial pole is located at a declination of - 90 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
There are 3,600 arc seconds in a degree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Drawing on Eratosthenes' method, if two observers are due north and south of each other and are separated by 400 km, what is the circumference of their spherical world if they see the same star on their meridian at altitudes of 23 degrees and 47 degrees respectively, and at the exact same time?
A) 2,000 km
B) 4,000 km
C) 6,000 km
D) 8,000 km
E) 12,000 km
A) 2,000 km
B) 4,000 km
C) 6,000 km
D) 8,000 km
E) 12,000 km

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The greatest distance above or below the ecliptic the Moon can move is
A) 5.2 degrees.
B) 23.5 degrees.
C) 27.3 degrees.
D) 29.5 degrees.
E) 30 degrees.
A) 5.2 degrees.
B) 23.5 degrees.
C) 27.3 degrees.
D) 29.5 degrees.
E) 30 degrees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A total solar eclipse will only occur when the new moon is both on the ecliptic and at its greatest distance from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If you are in the Earth's umbra on the Earth's surface, then
A) it is night time.
B) the Moon is always visible.
C) it must be a total solar eclipse.
D) it must be a lunar eclipse of some type.
E) the Sun is always visible.
A) it is night time.
B) the Moon is always visible.
C) it must be a total solar eclipse.
D) it must be a lunar eclipse of some type.
E) the Sun is always visible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the scientific method, it is not necessary to test your theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The synodic month is
A) about two days shorter than the sidereal month.
B) based on the Moon's position relative to the stars.
C) caused by both the Earth's and Moon's rotations.
D) 29.5 days.
E) the basis of the year we use in our modern calendar.
A) about two days shorter than the sidereal month.
B) based on the Moon's position relative to the stars.
C) caused by both the Earth's and Moon's rotations.
D) 29.5 days.
E) the basis of the year we use in our modern calendar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the Moon appears half lit, and is almost overhead about 6:00 AM, its phase is
A) first quarter.
B) waxing crescent.
C) waning crescent.
D) full.
E) third quarter.
A) first quarter.
B) waxing crescent.
C) waning crescent.
D) full.
E) third quarter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The star Wolf 1061 has a parallax of 2.34 arc seconds, while the star Ross 652 has a parallax of 1.70 arc seconds. What can you correctly conclude?
A) Ross 652 must have a larger proper motion than Wolf 1061.
B) Wolf 1061 must have a larger proper motion than Ross 652.
C) Both stars are outside the Milky Way galaxy.
D) Wolf 1061 is closer to Earth than Ross 652.
E) Ross 652 is closer to Earth than Wolf 1061.
A) Ross 652 must have a larger proper motion than Wolf 1061.
B) Wolf 1061 must have a larger proper motion than Ross 652.
C) Both stars are outside the Milky Way galaxy.
D) Wolf 1061 is closer to Earth than Ross 652.
E) Ross 652 is closer to Earth than Wolf 1061.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If you are in the Moon's umbral shadow, then you are witnessing
A) a total solar eclipse.
B) nighttime.
C) some kind of lunar eclipse.
D) a partial solar eclipse.
E) a total lunar eclipse.
A) a total solar eclipse.
B) nighttime.
C) some kind of lunar eclipse.
D) a partial solar eclipse.
E) a total lunar eclipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A solar eclipse can only happen during a
A) full moon.
B) new moon.
C) solstice.
D) first quarter moon.
E) perihelion passage of the Sun.
A) full moon.
B) new moon.
C) solstice.
D) first quarter moon.
E) perihelion passage of the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
There is a solar eclipse of some kind every new moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The larger the parallax shift, the closer an object is to us.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What will occur when the full moon is on the ecliptic?
A) an annular lunar eclipse
B) a total solar eclipse
C) a partial lunar eclipse if the Moon is at perigee
D) a partial solar eclipse
E) a total lunar eclipse
A) an annular lunar eclipse
B) a total solar eclipse
C) a partial lunar eclipse if the Moon is at perigee
D) a partial solar eclipse
E) a total lunar eclipse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If new moon fell on March 2nd, what is the Moon's phase on March 14th?
A) waning crescent
B) waxing gibbous
C) first quarter
D) full
E) waxing crescent
A) waning crescent
B) waxing gibbous
C) first quarter
D) full
E) waxing crescent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If we are the Moon's penumbra, then we will see a partial lunar eclipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Increasing the baseline will increase the parallax angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Eighteen days past new moon, the Moon's phase is waning gibbous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In an annular eclipse,
A) the Sun appears as a thin, bright ring.
B) the Moon appears as a thin, bright ring.
C) the Sun is totally blocked by the Moon.
D) the Sun is partially blocked by the Earth.
E) the Moon is totally blocked by the Earth.
A) the Sun appears as a thin, bright ring.
B) the Moon appears as a thin, bright ring.
C) the Sun is totally blocked by the Moon.
D) the Sun is partially blocked by the Earth.
E) the Moon is totally blocked by the Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The parallax shift for all stars is very small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Only people in the Moon's umbral shadow can see a total solar eclipse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A star with a declination of +60.0 degrees will be
A) south of the celestial equator.
B) east of the vernal equinox.
C) west of the vernal equinox.
D) north of the celestial equator.
E) None of these answers is correct.
A) south of the celestial equator.
B) east of the vernal equinox.
C) west of the vernal equinox.
D) north of the celestial equator.
E) None of these answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The fact that the Earth has moved along its orbit in the time it took to rotate once is the reason for
A) Earth's 23.5- degree tilt.
B) the position of the Celestial Equator.
C) the difference between solar and sidereal time.
D) seasons.
E) precession.
A) Earth's 23.5- degree tilt.
B) the position of the Celestial Equator.
C) the difference between solar and sidereal time.
D) seasons.
E) precession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
You note that a particular star is directly overhead. It will be directly overhead again in
A) 1 hour.
B) 12 hours.
C) 23 hours 56 minutes.
D) 24 hours.
E) 24 hours 4 minutes.
A) 1 hour.
B) 12 hours.
C) 23 hours 56 minutes.
D) 24 hours.
E) 24 hours 4 minutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
From the horizon to the observer's zenith is an angle of
A) 90 degrees for everyone on the Earth.
B) 23.5 degrees for observers at the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
C) 0.0 degrees for an observer at the Earth's north pole.
D) 66.5 degrees for everyone on the Earth.
E) 30 degrees for observers at a latitude of 30 degrees north.
A) 90 degrees for everyone on the Earth.
B) 23.5 degrees for observers at the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
C) 0.0 degrees for an observer at the Earth's north pole.
D) 66.5 degrees for everyone on the Earth.
E) 30 degrees for observers at a latitude of 30 degrees north.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
If Taurus is now rising at sunset, which constellation will rise at sunset next month?
A) Gemini
B) Aries
C) Scorpius
D) Pisces
E) Aquarius
A) Gemini
B) Aries
C) Scorpius
D) Pisces
E) Aquarius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
This diagram explains 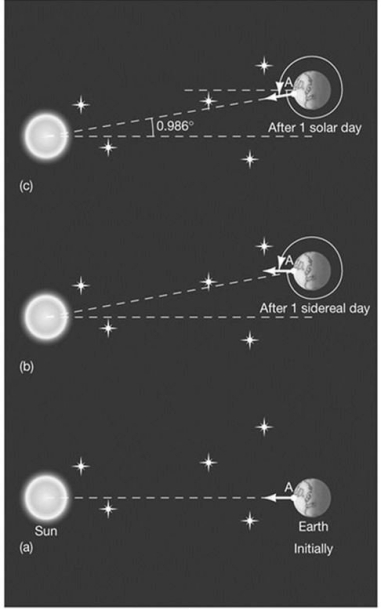
A) precession.
B) the reason for the solstices.
C) the difference between solar time and sidereal time.
D) the sidereal day's relation to the seasons.
E) the solar day's relation to the Moon.

A) precession.
B) the reason for the solstices.
C) the difference between solar time and sidereal time.
D) the sidereal day's relation to the seasons.
E) the solar day's relation to the Moon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The twelve constellations the solar system bodies move through are the
A) equatorial constellations.
B) stages of heaven.
C) signs of the zodiac.
D) galactic equator.
E) nodes of the ecliptic.
A) equatorial constellations.
B) stages of heaven.
C) signs of the zodiac.
D) galactic equator.
E) nodes of the ecliptic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the Moon rises at sunset, then its phase must be
A) full.
B) new.
C) waning gibbous.
D) third quarter.
E) waxing crescent.
A) full.
B) new.
C) waning gibbous.
D) third quarter.
E) waxing crescent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A star with a right ascension of 1.0 hours will rise
A) 1.0 hours after the vernal equinox.
B) 13.0 hours before the vernal equinox.
C) 11.0 hours after the vernal equinox.
D) at the same time as the vernal equinox.
E) 1.0 hours before the vernal equinox.
A) 1.0 hours after the vernal equinox.
B) 13.0 hours before the vernal equinox.
C) 11.0 hours after the vernal equinox.
D) at the same time as the vernal equinox.
E) 1.0 hours before the vernal equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The star Thuban in Draco
A) lies halfway between the bowls of the Big and Little Dippers.
B) was an excellent north pole star in 3,000 BC.
C) is brighter than Polaris.
D) is used to locate the vernal equinox.
E) lies as the center of the precession cycle.
A) lies halfway between the bowls of the Big and Little Dippers.
B) was an excellent north pole star in 3,000 BC.
C) is brighter than Polaris.
D) is used to locate the vernal equinox.
E) lies as the center of the precession cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
That Polaris will not always be the pole star is due to
A) the Moon following the ecliptic, instead of the equator.
B) the Earth's revolution being slightly less than exactly 365.25 days.
C) the sidereal day being shorter than the solar day.
D) the Solar winds blowing the Earth farther away from the Sun.
E) precession shifting the celestial pole.
A) the Moon following the ecliptic, instead of the equator.
B) the Earth's revolution being slightly less than exactly 365.25 days.
C) the sidereal day being shorter than the solar day.
D) the Solar winds blowing the Earth farther away from the Sun.
E) precession shifting the celestial pole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Into how many constellations is the celestial sphere divided?
A) 12
B) 44
C) 57
D) 88
E) 110
A) 12
B) 44
C) 57
D) 88
E) 110

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What are constellations?
A) ancient story boards, useless to modern astronomers
B) apparent groupings of stars and planets visible on a given evening
C) groups of stars making an apparent pattern in the celestial sphere
D) groups of stars gravitationally bound and appearing close together in the sky
E) groups of galaxies gravitationally bound and close together in the sky
A) ancient story boards, useless to modern astronomers
B) apparent groupings of stars and planets visible on a given evening
C) groups of stars making an apparent pattern in the celestial sphere
D) groups of stars gravitationally bound and appearing close together in the sky
E) groups of galaxies gravitationally bound and close together in the sky

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the Moon is directly opposite the Sun in the sky, its phase is
A) full.
B) new.
C) first or third quarter.
D) waxing or waning crescent.
E) waxing or waning gibbous.
A) full.
B) new.
C) first or third quarter.
D) waxing or waning crescent.
E) waxing or waning gibbous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The 26,000 year cycle that changes the poles and equinoxes is called
A) the Earth's rotation.
B) precession.
C) regression.
D) a retrograde loop.
E) revolution.
A) the Earth's rotation.
B) precession.
C) regression.
D) a retrograde loop.
E) revolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The time for the Moon to orbit Earth, relative to the stars is
A) 23 hours, 56 minutes.
B) about 7 days.
C) 27.3 days.
D) 29.5 days.
E) 18 years, 11.3 days.
A) 23 hours, 56 minutes.
B) about 7 days.
C) 27.3 days.
D) 29.5 days.
E) 18 years, 11.3 days.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If Scorpius is now prominent in the summer sky, in 13,000 years it will be best seen
A) at the same season; the heavens do not change.
B) in the winter sky.
C) in the spring sky.
D) in the autumn.
E) It will not be visible then at all. All of its stars will have vanished by then.
A) at the same season; the heavens do not change.
B) in the winter sky.
C) in the spring sky.
D) in the autumn.
E) It will not be visible then at all. All of its stars will have vanished by then.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The interval from new Moon to first quarter is about a(n)
A) hour.
B) day.
C) week.
D) month.
E) year.
A) hour.
B) day.
C) week.
D) month.
E) year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In general, what is true of the alpha star in a constellation?
A) It is the reddest star in the constellation.
B) It is the westernmost star in the constellation.
C) It is the star that is closest to Earth.
D) It is the brightest star in the constellation.
E) It is the easternmost star in the constellation.
A) It is the reddest star in the constellation.
B) It is the westernmost star in the constellation.
C) It is the star that is closest to Earth.
D) It is the brightest star in the constellation.
E) It is the easternmost star in the constellation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
As you watch a star, you see it move 15 degrees across the sky. How long have you been watching it?
A) 1 hour
B) 1 minute
C) 15 minutes
D) 15 seconds
E) 3 hours
A) 1 hour
B) 1 minute
C) 15 minutes
D) 15 seconds
E) 3 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How is right ascension similar to longitude on Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What are the minimum and maximum values for right ascension in the sky?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The time for the Moon to orbit the Earth, relative to the distant stars is the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If the Moon is on the ecliptic, new, and at its farthest distance from Earth, we will get a(n) eclipse.
A) total solar
B) annual lunar
C) total lunar
D) partial solar
E) annular solar
A) total solar
B) annual lunar
C) total lunar
D) partial solar
E) annular solar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The apparent angular shift of any object across a distant background, when viewed from two different places, is called shift.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The time interval of 365.242 days is defined as the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How are right ascension in the sky and longitude on Earth different?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The twelve constellations through which the Sun passes are signs of the _ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Like latitude on Earth, in the sky is measured in degrees north and south of the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Define the celestial sphere.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Our seasons are a consequence of the Earth's 23.5 degree .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If one star has a parallax ten times larger than another's, the first star is _ than the second.
A) five times further
B) five times closer
C) ten times further
D) ten times closer
A) five times further
B) five times closer
C) ten times further
D) ten times closer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Over the course of the year, the Sun's noon altitude varies by degrees.
A) 180
B) 90
C) 23.5
D) 47
E) 45
A) 180
B) 90
C) 23.5
D) 47
E) 45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What are the minimum and maximum values for declination in the sky for both north and south?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
That we do not get eclipses every new and full Moon is due to the _ degree tilt of the Moon's orbit, relative to the ecliptic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Sirius has a parallax of 0.38", while Alpha Centauri's is 0.77." Alpha Centauri is about
as Sirius.
as Sirius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The apparent annual path the Sun takes through the sky is called the _ _.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
One of the requirements of the Scientific Method is that an experiment must be .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What do both latitude on Earth and declination in the sky measure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
If two observatories on opposite sides of the Earth were to measure the position of a star to calculate its parallax, then the diameter of the Earth would be the _ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



