Deck 8: Experimental Research Design
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/62
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Experimental Research Design
1
Evelyn has a new speed reading program she wants to test. She trains 6 people on her program, then measures their reading speed. This is an example of which experimental design?
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design
A
2
Dr. Sheffield wants to investigate the causal relationship between frustration and memory. She divides participants into two groups using random assignment. One group is given a problem to solve that has no solution, inducing frustration, while the other group is given a problem to solve that has a solution. Then both groups have their memory tested. The group that is in the frustration condition can also be called the
A) comparison group
B) control group
C) experimental group
D) posttest group
A) comparison group
B) control group
C) experimental group
D) posttest group
C
3
The major fault in the non-equivalent posttest only design is that
A) it involves random assignment to groups, therefore the groups are not equivalent at the start of the study.
B) the two groups are may not be equivalent at the beginning.
C) there is no way to tell the direction of effect that the independent variable may have.
D) the two groups do not experience the same level of the independent variable.
A) it involves random assignment to groups, therefore the groups are not equivalent at the start of the study.
B) the two groups are may not be equivalent at the beginning.
C) there is no way to tell the direction of effect that the independent variable may have.
D) the two groups do not experience the same level of the independent variable.
B
4
The major fault in the one-group pretest-posttest design is that
A) there is no way to test whether participants' performance changed over time.
B) there are no statistics available to test the data this design yields.
C) there is no way to control for demand characteristics.
D) there is no way to examine the effects of history and maturation on the results.
A) there is no way to test whether participants' performance changed over time.
B) there are no statistics available to test the data this design yields.
C) there is no way to control for demand characteristics.
D) there is no way to examine the effects of history and maturation on the results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of incorporating a pretest into your experimental design?
A) it allows the experimenter to match participants on critical variables
B) it can determine if there is a potential ceiling effect in the dependent measure
C) it can sensitize the participants to the experimental treatment
D) it allows for assessment of each group's initial position on the dependent measure
A) it allows the experimenter to match participants on critical variables
B) it can determine if there is a potential ceiling effect in the dependent measure
C) it can sensitize the participants to the experimental treatment
D) it allows for assessment of each group's initial position on the dependent measure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why does a good experiment include a control group?
A) it increases the number of people in the study, and hence, the generalizability of the results
B) it gives us information about how participants would perform without experiencing the experimental treatment
C) it eliminates the effects of external validity
D) control groups have been an established part of scientific tradition for many decades
A) it increases the number of people in the study, and hence, the generalizability of the results
B) it gives us information about how participants would perform without experiencing the experimental treatment
C) it eliminates the effects of external validity
D) control groups have been an established part of scientific tradition for many decades

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the LEAST important characteristic of a good control group?
A) its members experience everything the experimental group experiences except the treatment
B) it has the same number of participants as the experimental group
C) it is equivalent to the experimental group in all important characteristics
D) it is measured on the same dependent variable as the experimental group
A) its members experience everything the experimental group experiences except the treatment
B) it has the same number of participants as the experimental group
C) it is equivalent to the experimental group in all important characteristics
D) it is measured on the same dependent variable as the experimental group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The nonequivalent posttest-only design differs from the one-group posttest-only design and the one-group pretest-posttest design in that
A) it includes randomization procedures.
B) it has a comparison group.
C) it has high externalvalidity.
D) the results can be generalized to the population.
A) it includes randomization procedures.
B) it has a comparison group.
C) it has high externalvalidity.
D) the results can be generalized to the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The one-group posttest-only design includes all the following faults EXCEPT
A) the treatment condition is given to all research participants.
B) the participants' motive of positive self-presentation affects the independent variable.
C) there are no controls for extraneous variables.
D) there is no control group for a comparison.
A) the treatment condition is given to all research participants.
B) the participants' motive of positive self-presentation affects the independent variable.
C) there are no controls for extraneous variables.
D) there is no control group for a comparison.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A group of physicians tests a new analgesic on their patients with chronic pain problems. They obtain patient ratings of pain, administer the new drug for a week, and then obtain pain ratings again. They find that pain ratings are down 10 points at their second observation. This is an example of which experimental design.
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The two most important techniques for eliminating potential rival hypotheses are
A) random assignment of participants and use of control groups.
B) random assignment of participants and use of pretests.
C) use of pretests and control groups.
D) random selection of participants and random assignment of participants.
A) random assignment of participants and use of control groups.
B) random assignment of participants and use of pretests.
C) use of pretests and control groups.
D) random selection of participants and random assignment of participants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The most important difference between weak and strong research designs is that strong designs
A) include both a pre-test and a post-test.
B) have greater internal validity.
C) have greater external validity.
D) include more than one independent variable.
A) include both a pre-test and a post-test.
B) have greater internal validity.
C) have greater external validity.
D) include more than one independent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Hannah wants to see if her new technique of ping-pong playing can decrease the time it takes to finish a ping-pong game. She asks the U.S. Olympic ping-pong team to work with her. Half of the U.S Olympic team is randomly assigned to be taught by the new style, the experimental group, and the other randomly assigned half are not, the control group. Her technique does not significantly decrease the time it takes the experimental group to finish a ping-pong game compared to the control group, perhaps because they are already so good at the sport. This could be an example of
A) the need for matching groups.
B) a floor effect.
C) the need for determining initial comparability.
D) an internally invalid study.
A) the need for matching groups.
B) a floor effect.
C) the need for determining initial comparability.
D) an internally invalid study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Hannah wants to see if her new technique of ping-pong playing can increase one's ping-pong performance. She asks the U.S. Olympic ping-pong team to work with her. Half of the U.S Olympic team is randomly assigned to be taught by the new style, the experimental group, and the other randomly assigned half are not, the control group. Her technique does not significantly increase the performance of the experimental group compared to the control group, perhaps because they are already so good at the sport. This could be an example of
A) the need for matching groups.
B) a ceiling effect.
C) the need for determining initial comparability.
D) an internally valid study.
A) the need for matching groups.
B) a ceiling effect.
C) the need for determining initial comparability.
D) an internally valid study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Two teachers who are friends teach math at different high schools. At a conference, they learn about a new program for teaching trigonometry. They decide to test it by having one teacher use it in her class and the other use the traditional program, then compare their students' scores on the AP trigonometry test. This is an example of which experimental design?
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design
A) one-group posttest-only design
B) one-group pretest-posttest design
C) non-equivalent posttest-only design
D) non-equivalent before-after pretest-posttest) design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is NOT the purpose of creating the research design for a research problem?
A) to control for unwanted variation
B) to analyze the data collected
C) to create an outline or plan for data collection
D) to suggest how the data will be collected
A) to control for unwanted variation
B) to analyze the data collected
C) to create an outline or plan for data collection
D) to suggest how the data will be collected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following factors should you consider when deciding on what research design to use?
A) number of groups
B) use of a control group
C) use of a pretest
D) all of the above
A) number of groups
B) use of a control group
C) use of a pretest
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the one-group pretest-posttest design which of the following threats to internal validity is NOT controlled?
A) history
B) maturation
C) testing
D) none are controlled
A) history
B) maturation
C) testing
D) none are controlled

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Even though the one-group pretest-posttest design is inadequate, it has one methodological advantage over the one-group posttest-only design, and that is
A) the use of randomization.
B) external validity.
C) pretest scores can be compared to posttest scores.
D) statistical tests are available to use with that design.
A) the use of randomization.
B) external validity.
C) pretest scores can be compared to posttest scores.
D) statistical tests are available to use with that design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two classes of students at different schools are closely matched on IQ scores. One class is being taught with the standard method and the other class is being taught with a new technique. The two classes are then to be compared on scores from a standardized test at the end of the year.
A) since the classes are matched, any difference at year's end is due to the teaching technique
B) even though matched on IQ scores, the classes may not be equivalent on many other variables
C) because there was no pretest, no valid comparisons can be made
D) maturation is a major confounding variable in this study
A) since the classes are matched, any difference at year's end is due to the teaching technique
B) even though matched on IQ scores, the classes may not be equivalent on many other variables
C) because there was no pretest, no valid comparisons can be made
D) maturation is a major confounding variable in this study

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is NOT an advantage of a within-participants design?
A) it tends to require fewer participants that a between-participants design
B) it usually yields a more sensitive assessment of the effects of the independent variables)
C) it is relatively immune to carryover effects
D) it allows for many assessments of the dependent measure over time
A) it tends to require fewer participants that a between-participants design
B) it usually yields a more sensitive assessment of the effects of the independent variables)
C) it is relatively immune to carryover effects
D) it allows for many assessments of the dependent measure over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the following table to answer questions
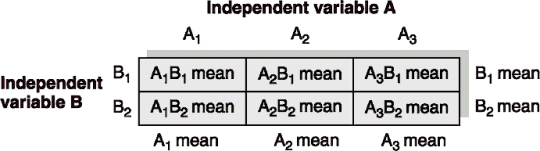
The A1 mean, A2 mean, and A3 mean represent the main effect of IVA and can also be called means.
A) cell
B) marginal
C) summary
D) variable

The A1 mean, A2 mean, and A3 mean represent the main effect of IVA and can also be called means.
A) cell
B) marginal
C) summary
D) variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
This is a design.
A) 2X3 factorial
B) 2X2 factorial
C) simple randomized
D) 3X3 factorial
A) 2X3 factorial
B) 2X2 factorial
C) simple randomized
D) 3X3 factorial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
There are many good reasons for pretesting participants before introducing the independent variable. Perhaps the most common of these is that pretesting
A) gives the experimenter direct evidence of change in performance.
B) is a prerequisite for posttesting.
C) eliminates the need for random assignment of participants to groups.
D) increases the sensitivity of the experiment.
A) gives the experimenter direct evidence of change in performance.
B) is a prerequisite for posttesting.
C) eliminates the need for random assignment of participants to groups.
D) increases the sensitivity of the experiment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Any experimental design that incorporates more than one independent variable is called an) design. 
A) complex
B) interaction
C) simple randomized
D) factorial

A) complex
B) interaction
C) simple randomized
D) factorial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In all repeated-measures designs
A) participants will be matched on at least one variable.
B) participants will be tested more than once per condition.
C) there is less control than between participants designs.
D) every participant will be tested in each of the conditions of the study.
A) participants will be matched on at least one variable.
B) participants will be tested more than once per condition.
C) there is less control than between participants designs.
D) every participant will be tested in each of the conditions of the study.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the major advantage of a within-participants design?
A) the data are easier to interpret than are data from between-participants designs
B) it does not carry the risk of carryover or sequencing effects
C) the experimenter doesn't have to worry about whether the groups of participants are equivalent to each other
D) it is not subject to the influence of expectancy effects
A) the data are easier to interpret than are data from between-participants designs
B) it does not carry the risk of carryover or sequencing effects
C) the experimenter doesn't have to worry about whether the groups of participants are equivalent to each other
D) it is not subject to the influence of expectancy effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the factor that makes the between-participants posttest-only design a "strong" experimental design and the nonequivalent posttest-only design a weak design?
A) the between-participants posttest-only design involves manipulating variables and the nonequivalent posttest-only design does not
B) testing participants twice changes their performance in the nonequivalent posttest- only design
C) the between participants posttest-only design uses two groups of different participants and the nonequivalent posttest-only design used the same participants
D) random assignment helps insure that the two experimental groups are essentially Equivalent at the outset
A) the between-participants posttest-only design involves manipulating variables and the nonequivalent posttest-only design does not
B) testing participants twice changes their performance in the nonequivalent posttest- only design
C) the between participants posttest-only design uses two groups of different participants and the nonequivalent posttest-only design used the same participants
D) random assignment helps insure that the two experimental groups are essentially Equivalent at the outset

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the experimenter wanted 8 participants per group, she would need a total of participants.
A) 16
B) 32
C) 48
D) 72
A) 16
B) 32
C) 48
D) 72

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The posttest-only control group design requires
A) random selection of participants.
B) a control condition.
C) matching on at least one extraneous variable.
D) all of the above.
A) random selection of participants.
B) a control condition.
C) matching on at least one extraneous variable.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the following table to answer questions

This table contains 6 groups each represented by a .
A) row
B) column
C) cell
D) table

This table contains 6 groups each represented by a .
A) row
B) column
C) cell
D) table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The major disadvantage of a within-participants design is that
A) it is very susceptible to order and carryover effects.
B) it is unusually vulnerable to influence of expectancy effects.
C) it is difficult to interpret the data it produces.
D) it does not guarantee equivalence across groups of participants.
A) it is very susceptible to order and carryover effects.
B) it is unusually vulnerable to influence of expectancy effects.
C) it is difficult to interpret the data it produces.
D) it does not guarantee equivalence across groups of participants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
This is a design.
A) between-participants
B) within-participants
C) mixed model
D) one-group
A) between-participants
B) within-participants
C) mixed model
D) one-group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following table to answer questions

The B1 mean and B2 mean represent the main effect of IVB and can also be called means.
A) cell
B) marginal
C) summary
D) variable

The B1 mean and B2 mean represent the main effect of IVB and can also be called means.
A) cell
B) marginal
C) summary
D) variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the important difference between the between-participants posttest-only design and the flawed non-equivalent posttest-only design?
A) the former uses random assignment of participants to groups
B) the former uses two groups of participants
C) the latter involves testing participants twice
D) the latter does not manipulate an independent variables
A) the former uses random assignment of participants to groups
B) the former uses two groups of participants
C) the latter involves testing participants twice
D) the latter does not manipulate an independent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the following table to answer questions

is the combination of levels of two or more independent variables.
A) Mean
B) Cell
C) Marginal mean
D) Cell mean
Use the following to answer questions 38-43:
An experiment was designed to determine if gender of the interviewer and the amount of eye contact by the interviewer will influence the participant's liking of an interviewer. Thus participants were randomly assigned to groups that had either a male or female interviewer who made little, moderate, or sustained eye contact. At the end of the sessions, the participants were asked to rate their liking of the interviewer.

is the combination of levels of two or more independent variables.
A) Mean
B) Cell
C) Marginal mean
D) Cell mean
Use the following to answer questions 38-43:
An experiment was designed to determine if gender of the interviewer and the amount of eye contact by the interviewer will influence the participant's liking of an interviewer. Thus participants were randomly assigned to groups that had either a male or female interviewer who made little, moderate, or sustained eye contact. At the end of the sessions, the participants were asked to rate their liking of the interviewer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following table to answer questions

A2B2 is the average score of participants in one group which is called a
A) cell sum
B) marginal mean
C) cell mean
D) marginal cell

A2B2 is the average score of participants in one group which is called a
A) cell sum
B) marginal mean
C) cell mean
D) marginal cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The defining characteristic of a factorial experimental design is
A) the manipulation of one independent variable.
B) the manipulation of more than one independent variable.
C) the measurement of more than one dependent variable.
D) inclusion of more than two cells.
A) the manipulation of one independent variable.
B) the manipulation of more than one independent variable.
C) the measurement of more than one dependent variable.
D) inclusion of more than two cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is the difference between a within-participants design and a between-participants design?
A) the former exposes the participants to more than one level of the independent variable
B) the former involves all participants experiencing all levels of the independent variable
C) the latter exposes all participants to all levels of the independent variable
D) the latter involves research participants testing each other, rather than the experimenter testing them
A) the former exposes the participants to more than one level of the independent variable
B) the former involves all participants experiencing all levels of the independent variable
C) the latter exposes all participants to all levels of the independent variable
D) the latter involves research participants testing each other, rather than the experimenter testing them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In a between-participants posttest-only design
A) each participant is tested in only one treatment condition.
B) each participant experiences all treatment conditions.
C) pairs of matched participants experience the same treatment conditions.
D) all of the above.
A) each participant is tested in only one treatment condition.
B) each participant experiences all treatment conditions.
C) pairs of matched participants experience the same treatment conditions.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A research design that contains both between participants and within participants variables is called a
A) mixed design
B) factorial design
C) combination design
D) double variable design
A) mixed design
B) factorial design
C) combination design
D) double variable design

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Rhonda designs an experiment in which half of her participants are randomly assigned to view a sad movie and half view a comedy, but all participants fill out three mood surveys at one, two, and three weeks after the movie. This is an example of
A) a between-participants design.
B) a within-participants design.
C) a non-equivalent posttest-only design.
D) a mixed-model, factorial design.
A) a between-participants design.
B) a within-participants design.
C) a non-equivalent posttest-only design.
D) a mixed-model, factorial design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an advantage of within-participant designs over between- participant designs?
A) a reduction in the potential for differential carryover effects
B) reduced potential for practice and fatigue effects
C) a reduction in the number of research participants needed
D) reduced potential for guessing the hypothesis
A) a reduction in the potential for differential carryover effects
B) reduced potential for practice and fatigue effects
C) a reduction in the number of research participants needed
D) reduced potential for guessing the hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In a 4x2 factorial design, there are
A) two independent variables with 4 levels on one and 2 levels on the other.
B) four independent variables with 2 levels each.
C) two independent variables with 4 levels each.
D) eight independent variables.
A) two independent variables with 4 levels on one and 2 levels on the other.
B) four independent variables with 2 levels each.
C) two independent variables with 4 levels each.
D) eight independent variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A researcher predicts that tennis professionals will play better in front of an audience. Less capable tennis players, however, are expected to do better without an audience. The researcher
A) is predicting a main effect for the audience variable.
B) is predicting a main effect for ability of the tennis player.
C) expects an interaction effect to occur.
D) is using a mixed design.
A) is predicting a main effect for the audience variable.
B) is predicting a main effect for ability of the tennis player.
C) expects an interaction effect to occur.
D) is using a mixed design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
This experimental design allows for testing
A) the effect of interviewer gender on liking.
B) the effect of interviewer gender on liking and the effect of eye contact on liking.
C) the effect of eye contact on liking and the interaction effects of interviewer gender and eye contact on liking.
D) the effect of interviewer gender on liking, the effect of eye contact on liking, and the interaction effects of interviewer gender and eye contact on liking.
A) the effect of interviewer gender on liking.
B) the effect of interviewer gender on liking and the effect of eye contact on liking.
C) the effect of eye contact on liking and the interaction effects of interviewer gender and eye contact on liking.
D) the effect of interviewer gender on liking, the effect of eye contact on liking, and the interaction effects of interviewer gender and eye contact on liking.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Factorial designs are very frequently used because they have many advantages. Which of the following is NOT among them?
A) more than one hypothesis can be tested
B) the results are easy to interpret
C) potentially confounding extraneous variables can be incorporated into the experiment
D) possible interactions among independent variables can be explored
A) more than one hypothesis can be tested
B) the results are easy to interpret
C) potentially confounding extraneous variables can be incorporated into the experiment
D) possible interactions among independent variables can be explored

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The difference between a factorial experimental design and a one-way design is that
A) a stronger case for causality can be made with a factorial design.
B) there is more than one independent variable in a factorial design.
C) factorial designs always incorporate both within and between participants.
D) greater external validity is gained in a factorial design.
A) a stronger case for causality can be made with a factorial design.
B) there is more than one independent variable in a factorial design.
C) factorial designs always incorporate both within and between participants.
D) greater external validity is gained in a factorial design.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the interaction between interviewer gender and duration of eye contact were significant,
A) the effect of eye contact on liking would differ for the male and female interviewers.
B) the main effects will be significant, too.
C) the main effects will not be significant.
D) the male interviewers will be liked less than the female interviewers.
A) the effect of eye contact on liking would differ for the male and female interviewers.
B) the main effects will be significant, too.
C) the main effects will not be significant.
D) the male interviewers will be liked less than the female interviewers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A mixed factorial design has
A) at least one between-subjects factor and at least one within-subjects factor.
B) a yoked control.
C) one independent variable and two dependent variables.
D) one main effect and one interaction.
A) at least one between-subjects factor and at least one within-subjects factor.
B) a yoked control.
C) one independent variable and two dependent variables.
D) one main effect and one interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose a researcher were reporting on a factorial experiment in which she simultaneously manipulated two independent variables. One of the independent variables was presented between participants and the other was presented within participants. This is an example of a design.
A) mixed model
B) simple randomized participants
C) complex
D) interactive
A) mixed model
B) simple randomized participants
C) complex
D) interactive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is a clear example of an interaction?
A) rats given a drug in the morning are more active than rats given placebo and rats given placebo in the evening are more active than rats given drug.
B) larger print is read faster in bright light than smaller print and smaller print is read slower in dim light than larger print.
C) compared to drinking non-alcoholic beverages, drinking alcohol makes men more aggressive in a hot room and drinking alcohol also makes men more aggressive in a cool room.
D) performance on a proofreading task is impaired when others are present rather than alone. The effect is the same whether the others are men or women.
A) rats given a drug in the morning are more active than rats given placebo and rats given placebo in the evening are more active than rats given drug.
B) larger print is read faster in bright light than smaller print and smaller print is read slower in dim light than larger print.
C) compared to drinking non-alcoholic beverages, drinking alcohol makes men more aggressive in a hot room and drinking alcohol also makes men more aggressive in a cool room.
D) performance on a proofreading task is impaired when others are present rather than alone. The effect is the same whether the others are men or women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Suppose you are conducting a factorial study with variables A and B. Your results reveal an interaction effect. This means that
A) variable A is effective in changing performance only if variable B is also effective.
B) the effect of independent variable A depends on what level of independent variable B they experience.
C) one of the variables, A or B, can have an effect on performance only if the other does not.
D) the effects of variable A and of variable B cancel each other out.
A) variable A is effective in changing performance only if variable B is also effective.
B) the effect of independent variable A depends on what level of independent variable B they experience.
C) one of the variables, A or B, can have an effect on performance only if the other does not.
D) the effects of variable A and of variable B cancel each other out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Factorial designs present many problems. Which of the following is NOT among them?
A) they often require a large number of participants
B) if the design incorporates more than two factors, the higher-order interactions may be difficult to interpret
C) simultaneous manipulation of all the factors can be difficult
D) they can be used with one or more factors or independent variables
A) they often require a large number of participants
B) if the design incorporates more than two factors, the higher-order interactions may be difficult to interpret
C) simultaneous manipulation of all the factors can be difficult
D) they can be used with one or more factors or independent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following outcomes would indicate an interaction effect?
A) female and male interviewers are liked more with longer eye contact.
B) female and male interviewers are liked less with longer eye contact.
C) female interviewers are liked more with longer eye contact while duration of eye contact has no effect on liking of male interviewers.
D) all of the above are interaction effects.
A) female and male interviewers are liked more with longer eye contact.
B) female and male interviewers are liked less with longer eye contact.
C) female interviewers are liked more with longer eye contact while duration of eye contact has no effect on liking of male interviewers.
D) all of the above are interaction effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When choosing between a within-participants design and a between-participants design, one is often considering a tradeoff between
A) a more sensitive design with the former and a more controlled design with the latter.
B) internal validity with the former and an ability to generalize results to a larger population with the latter.
C) a more sensitive design with the former and a more economical design with the latter.
D) controlling for more extraneous variables with the former and having results that are more applicable to the "real world" with the latter.
A) a more sensitive design with the former and a more controlled design with the latter.
B) internal validity with the former and an ability to generalize results to a larger population with the latter.
C) a more sensitive design with the former and a more economical design with the latter.
D) controlling for more extraneous variables with the former and having results that are more applicable to the "real world" with the latter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The pretest-posttest control group design is also considered a design.
A) weak
B) mixed
C) within participants
D) between participants
A) weak
B) mixed
C) within participants
D) between participants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a 2 age) x 2 type of therapy) factorial design, which of the following outcomes would be an example of an interaction?
A) young adults do better in therapy A; older adults also do better with this therapy
B) therapy A works better for young adults, while therapy B works better for older adults
C) therapy B works better overall, and this is true for both young and old adults
D) older adults improve more than younger adults, regardless of type of therapy
A) young adults do better in therapy A; older adults also do better with this therapy
B) therapy A works better for young adults, while therapy B works better for older adults
C) therapy B works better overall, and this is true for both young and old adults
D) older adults improve more than younger adults, regardless of type of therapy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a 4x2 factorial design, there are independent variables.
A) 8
B) 6
C) 4
D) 2
A) 8
B) 6
C) 4
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In a 4X2 factorial design there are cells.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A research study examined the effects of playing violent or non-violent video games on the aggressive behavior of children of two different ages 10 year olds and 13 year olds). The researchers found that, regardless of age, children who played violent video games were more aggressive than those who played non-violent video games. This finding represents an)
A) interaction.
B) main effect.
C) two-way interaction.
D) mixed interaction.
A) interaction.
B) main effect.
C) two-way interaction.
D) mixed interaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A occurs in a factorial design when there are differences on the dependent variable in the different levels of one condition, that are consistent across the levels of the other independent variable .
A) main effect
B) confound
C) interaction
D) marginal mean
A) main effect
B) confound
C) interaction
D) marginal mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 62 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



