Deck 3: Growth, Slavery, and Conflict: Colonial America, 1710-176
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Growth, Slavery, and Conflict: Colonial America, 1710-176
1
As illustrated in William Hogarth's painting The Gaols Committee of the House of Commons,
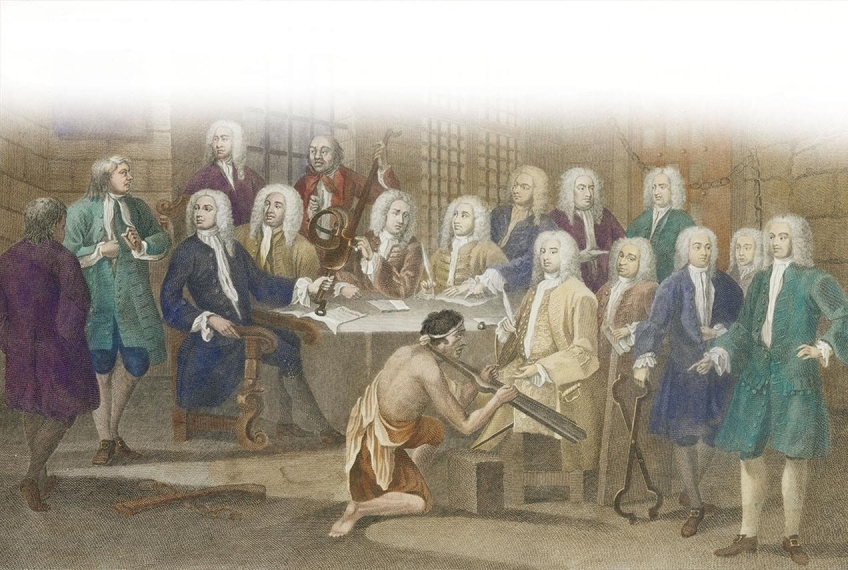

Georgia proprietor James Oglethorpe primarily viewed that colony as .
A) a buffer against the Spanish in Florida
B) a way to prove that prisoners could be rehabilitated
C) a laboratory for political experimentation
D) an opportunity to enrich himself
a way to prove that prisoners could be rehabilitated
2

Why were colonial governors so weak?
A) The voting population was larger in Britain, which meant that Americans were not politically active.
B) Royal governors depended on the colonial assemblies for their salaries.
C) The governors' councils were too powerful, thus making the assemblies reluctant to work with the governors.
D) Royal governors had to be born in the colonies so they lacked the educational opportunities available to English-born assemblymen.
Royal governors depended on the colonial assemblies for their salaries.
3
James Oglethorpe designed the city of Savannah, Georgia, in the style of a Roman military encampment mainly to .
A) prevent an attack from hostile Indians living on the coast
B) defend the city against the possibility of a slave rebellion
C) protect the coastline from pirate raids
D) launch an attack against the Spanish in Florida
launch an attack against the Spanish in Florida
4
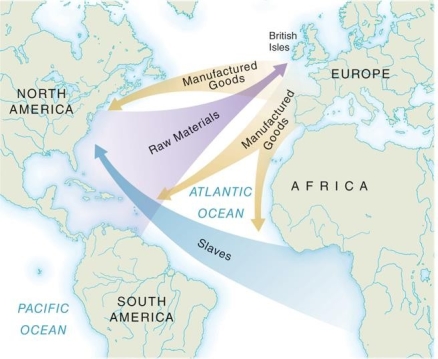
The increase of wealthy colonists and the flood of new luxury goods to the American colonies was most impacted by .
A) greater reliance on goods traded with Indians
B) the self-sufficiency developed by American colonists
C) expanded trade with the British empire
D) the greater role American colonial assemblies took in developing trade policies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

The Hart Room, representing the home of a prosperous colonist, indicates that affluent colonists in the early eighteenth century .
A) lived in primitive conditions much like those of the earliest settlers
B) had simple homes that lacked ornamentation and were sparsely furnished
C) demonstrated the fine furnishings and carpets imported from England
D) used highly specialized construction techniques

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6

This portrait of Benjamin Franklin with a lightning storm in the background depicts him as a champion of the Enlightenment because of his role as a .
A) scientist
B) diplomat
C) printer
D) reformer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Which of the following best characterizes the portrait of the young Henry Darnall III?
A) The portrait shows that most colonists wore homespun clothing.
B) The portrait places young Darnall in surroundings that the English gentry aspired to but had not yet attained.
C) The portrait indicates that African Americans lived freely among wealthy planter families.
D) The portrait shows that wealthy families in the South were extremely religious.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

How did the Great Awakening encourage the growth of democracy in the colonies?
A) Individuals were urged to keep the status quo by remaining in their current congregations.
B) Groups who had been previously excluded from colonial society such as Quakers, women, Indians, and blacks had greater voices in this religious movement.
C) Preachers of the Great Awakening inspired colonists to pursue greater economic opportunities.
D) Followers of the Great Awakening began to focus on the abolition of slavery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

The term Anglicization refers to the .
A) attempt to take over Indian lands
B) development of a unique political system established in the colonies
C) enslavement of non-white peoples
D) emulation of British customs and style

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

How did the establishment of the colony of Georgia reflect Enlightenment ideals?
A) The importation of rum to this colony strengthened the system of triangular trade.
B) The arrival of African slaves in Georgia created a wider gap between rich and poor.
C) The poor of England had an opportunity to earn a living in Georgia and avoid impoverishment.
D) The Georgia assembly supported ideas that promoted greater equality between the races.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

How did drop-leaf bookcases with writing surfaces such as the one shown on the left side of this image reflect deeper changes in colonial society and economy?
A) New pieces of this type of furniture were symbolic of the expanding trade networks in the British Empire and the growing wealth of the merchant class in the colonies.
B) Writers and poets now had resources to develop a unique American literary style.
C) Furniture with writing surfaces promoted a higher level of educational advancement available to all levels of colonial society.
D) Members of colonial assemblies had greater opportunities to develop local legislation from their homes instead of having to travel to distant cities where the assemblies met.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

How does this mural from the eighteenth-century home of Captain Archibald Macpheadris represent an artistic style that is more European than American Indian?
A) The Indian chiefs are posing with their hands on their hips, a style common to European aristocrats.
B) Weapons typical in European warfare like a tomahawk are featured in the mural.
C) Lighter European skin tones rather than darker American Indian skin tones are used to depict the Indian chiefs.
D) The Indian chiefs are in powdered wigs that were commonly worn by wealthy Europeans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

The Great Awakening was a movement that reflected a renewed interest in .
A) Enlightenment ideals
B) trade with England
C) spirituality and religion
D) the abolition of slavery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

Who were the Old Lights?
A) Ministers who rejected the emotionalism of the Great Awakening.
B) Opponents to the Great Awakening who the revivalists claimed were damned.
C) Religious leaders who favored leaving the Anglican Church.
D) Those who believed that terror of hell was the best motivator of spirituality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

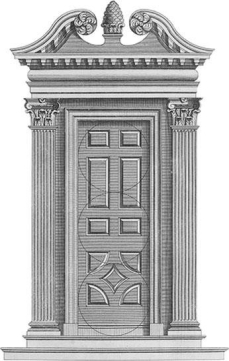
The carved pineapple found at the top of this doorway from the main entrance of Westover Plantation symbolized .
A) the importance of locally grown crops in the lower South
B) an architectural style unique to the American colonies
C) affluent hospitality
D) the dependence on African slave labor for agricultural production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

Under the policy of "salutary neglect," Parliament .
A) allowed colonial assemblies to appoint royal governors
B) banned the importation of African slaves to the North American mainland
C) did not meddle in colonial affairs
D) granted American colonists titles of nobility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

Although American colonists sent no representatives to the British Parliament, the Whig theory of virtual representation stated that their interests were protected because members of Parliament stood for .
A) the interests of landowners
B) local interests
C) the will of the crown
D) the greater public good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

The focus of Newtonianism was on .
A) observations of the natural world
B) the perception of equality between different racial groups
C) belief in the supernatural
D) viewing God as a patriarch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19

Goods coming from the American colonies such as tobacco and beaver furs that were involved in triangle trade were known as .
A) raw materials
B) luxury goods
C) manufactured goods
D) cash crops

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

How does this image of the Pennsylvania State House reflect the paradox between wealth and political power in the colonies?
A) The windows and brick exterior symbolized a desire for orderliness while the lack of order within the Pennsylvania assembly showed how chaotic affairs were in the colonies.
B) The design of the State House reflected the growing wealth of the colonies that was supported by the pro-slavery agenda of the Pennsylvania assembly.
C) The architectural style of the State House was typical of local architecture and represented the local interests of the Pennsylvania assembly.
D) The architecture denoted the influence of Anglicization while the role of the Pennsylvania assembly demonstrated the growing power of the American-born elite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

American colleges founded in the eighteenth century such as those that later became Princeton, Brown, and Rutgers were established in order to .
A) strengthen connections to commerce with England
B) educate new ministers associated with the Great Awakening
C) establish a generation of American scientists
D) instruct colonists on British views of government and politics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

How did the Great Awakening affect women in the colonies?
A) Colonial women gained opportunities to become ordained ministers.
B) Colonial women were able to establish their own congregations.
C) Colonial women were empowered to lead religious revivals.
D) Colonial women gained a forum to testify publicly about their spiritual lives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Under the slave codes of the mainland British colonies, children born to slave mothers and free white fathers were _ .
A) born free
B) guaranteed the rights to vote and own property as adults
C) allowed to purchase their freedom once they reached adulthood
D) slaves themselves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
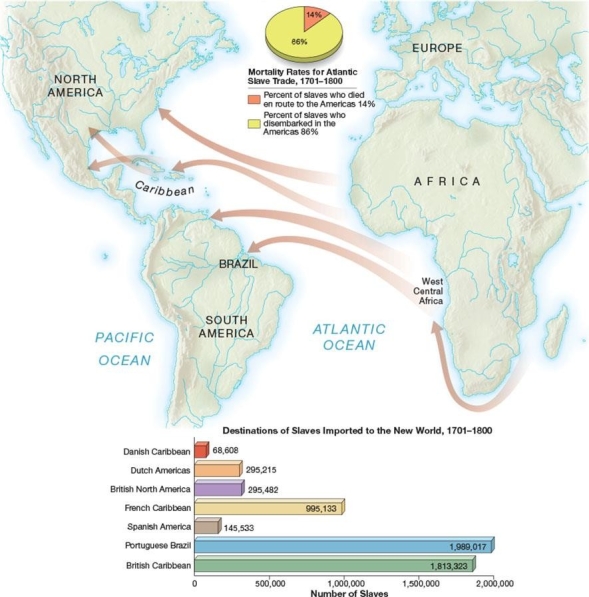
Most African slaves imported to the New World during the eighteenth century were sent to
A) Brazil and the Caribbean
B) British North America
C) Spanish America
D) Dutch America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

By the 1730s, Indian prophets like Neolin began preaching that Indians should .
A) abandon their traditional religious customs
B) reject European influences and revive traditional beliefs
C) encourage trade with the American colonists
D) consume greater quantities of alcohol during religious ceremonies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

The preaching style of New Light ministers could be best described as .
A) calming
B) optimistic
C) intellectual
D) emotional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

In New York, the African-American festival called "Pinkster" was adapted from the
A) Dutch religious holiday of Pentecost
B) Catholic traditions associated with Lent
C) English traditions connected to Christmas
D) fiery religious sermons from the Great Awakening

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Who was the leading intellectual champion of the Great Awakening and offered parishioners a view of a fiery hell in the sermon "Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God"?
A) George Whitefield
B) Gilbert Tennent
C) Jonathan Edwards
D) Bathsheba Kingsley

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

What evidence found in this illustration shows how American slaves used African customs and traditions as a form of cultural expression?
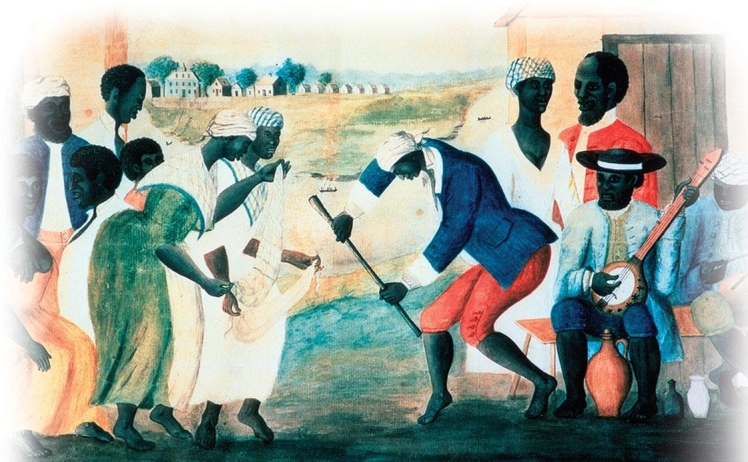

A) Both the style of dance and the use of the banjo had their roots in African musical traditions.
B) Clothing was based on traditional styles of African outfits.
C) The slave quarters were laid out in a pattern unique to African settlements.
D) The application of vibrant colors was an exclusive practice related to African artwork.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

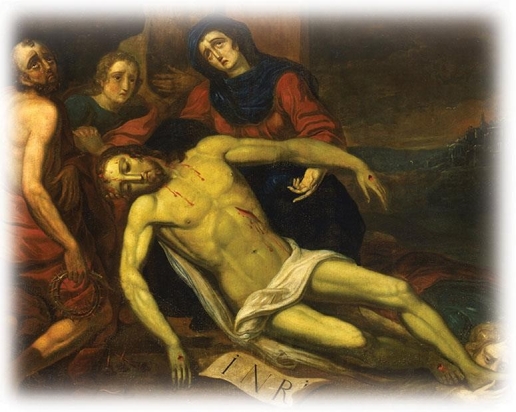
How did artwork such as Lamentation help Moravian missionaries convert American Indians to Christianity?
A) The crucified Jesus appealed to young male Indians who viewed him as a brave warrior.
B) Christianity attracted Indians because images of Jesus were pleasant and peaceful.
C) Indian women took pity on the images of a crucified Jesus.
D) Indians believed that Christianity would revitalize their native traditions and customs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

Which two cash crops introduced in the lower South before 1750 led to a higher population of slaves in that region?
A) cotton and tobacco
B) rice and indigo
C) corn and flax
D) sugar cane and wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

What factor contributed most in making South Carolina's Stono Rebellion of 1739 the largest slave uprising of the colonial era?
A) Slaves could hide in the swamps of the low country and evade capture.
B) Slaves were adept at making and seizing weapons that were used against whites.
C) Slaves hoped to find refuge in nearby Spanish Florida.
D) Slaves joined forces with the neighboring Seminole Indians to defeat their white owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

Slaves had more autonomy and free time under .
A) the gang system
B) the Great Awakening
C) tight packing
D) the task system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

In the Atlantic slave trade, the journey from Africa to the Americas was called the
A) Middle Passage
B) Great Awakening
C) task system
D) "seasoning" process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
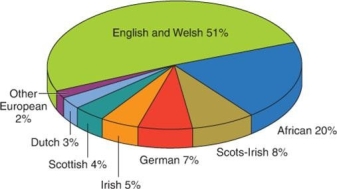
The chief labor force in the mid-Atlantic colonies during the eighteenth century was made up of .
A) African slaves
B) indentured servants
C) captured Indians
D) large landowners

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

As the demand for slave labor grew during the eighteenth century in colonial America, "saltwater slaves" were directly imported from .
A) the Caribbean
B) Africa
C) Brazil
D) Spanish America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

How was the slave population in the lower South different from that of other regions in the American colonies?
A) Slaves mostly harvested tobacco while working in gang systems.
B) Higher mortality rates for slaves occurred because they lacked immunity to malaria.
C) African slaves outnumbered the white population in this region.
D) More slaves worked in seaports than on plantations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

Which region of colonial America was the most ethnically homogenous?
A) New England
B) the mid-Atlantic
C) the upper South
D) the lower South

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

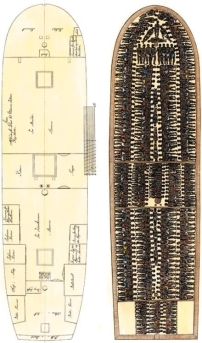
The depiction of tight packing of Africans on this slave ship demonstrates which of the following views that Europeans and colonists had toward enslaved Africans?
A) Slaves were regarded to be valuable property.
B) Slaves were thought to prefer living in close proximity to each other.
C) Slaves were treated more like objects than people.
D) Slaves were tenderly cared for so that they could remain healthy during the voyage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

What conclusion can be made about the ethnic composition of the British North American colonies during the eighteenth century?
A) Immigrants from other parts of the British Empire besides England and Wales made up the majority of settlers in these colonies.
B) Over 20 percent of settlers in these colonies came from continental Europe.
C) Non-European and non-African immigrants to these colonies comprised a quarter of the population.
D) One-fifth of the immigrants in these colonies were of African descent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

Britain's desire to seize Fort Duquesne was part of its military goal to gain control of
A) Montreal
B) the Great Lakes region
C) the Gulf of St. Lawrence
D) the Ohio Valley

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42

What prediction can be formulated from the interaction between population groups in the colonies and the line fixed by the Proclamation of 1763?
A) Emigration would likely result, as colonists decided to return to Europe.
B) Displacement would likely result, as colonists abandoned farming for life in the cities.
C) Peace would likely result, as colonists and Indians found ways to live in prosperity in the lands allotted to each.
D) Conflict would likely result, as colonists pushed for settlement in the land reserved for Indians.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

How did the French and Indian War transform the map of North America?
A) Spain acquired control of East and West Florida.
B) Indians lost control of their reserve between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River.
C) Britain gained control of Canada and lands to the west of the Appalachian Mountains.
D) France took over ownership of Spanish Louisiana.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44

Which of these factors made the upper and lower South two distinct regions?
A) The population of the upper South was more diverse and came from different parts of Europe.
B) The lower South depended on a cash crop economy based on tobacco and grains.
C) People in the upper South had access to prestigious colleges like William and Mary while those in the lower South lacked access to such institutions.
D) The economy of the lower South was based on indentured servitude rather than slave labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
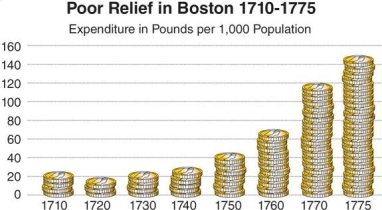
The graph "Poor Relief in Boston 1710-1775" demonstrates that .
A) the public lacked interest in assisting the poor
B) poverty among urban dwellers was successfully contained due to financial relief
C) the population of the urban poor continued to increase throughout the eighteenth century
D) living conditions between the urban poor and other economic classes were equitable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

Benjamin West's depiction of the death of General James Wolfe at the battle of Quebec reveals .
A) the consequences of collusion between the British and the Indians
B) religious imagery comparing the dying general to a crucified Christ
C) the massacre of British forces during the Seven Years War
D) a departure from European influence on American art

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47

The Quakers of Pennsylvania opposed the formation of a militia in that colony during the French and Indian War because they .
A) were pacifists
B) lacked the resources to manufacture rifles
C) preferred to pay a fine instead of bearing arms
D) were currently at peace with Indian tribes near their western settlements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The growth of power for the merchant class in the New England and mid-Atlantic colonies during the eighteenth century demonstrated that _ .
A) commerce became increasingly important in these regions
B) religious interests began to decline in these regions
C) the importation of African slaves to these regions increased significantly
D) a growing availability of farmland in these regions led to greater agricultural production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49

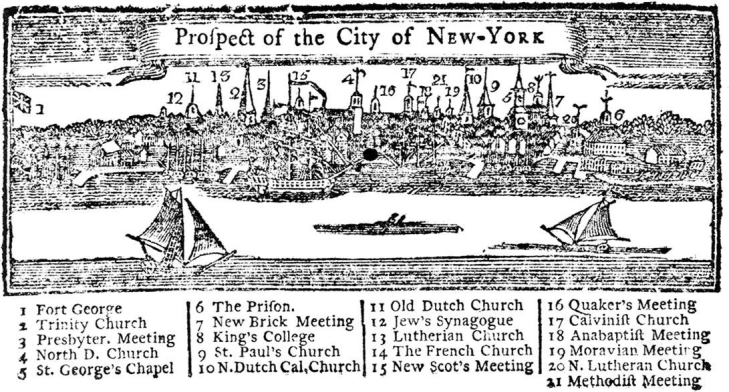
This engraving of the New York skyline revealed that this city .
A) lacked a seaport
B) depended on walled fortifications to defend itself
C) was divided along ethnic lines
D) tolerated different forms of religion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

What made the middle ground a distinctive region of North America?
A) The Indians of the middle ground remained isolated from European settlers.
B) Indians living here established deep-seated economic and cultural ties with French traders.
C) Indians in this region often allied themselves with the English in conflicts against the French.
D) Indian chiefs in this region ran their societies through a powerful patriarchal system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



