Deck 2: Fundamentals of Tax Planning
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Fundamentals of Tax Planning
1
Steven James earned $150,000 this year in profits from his proprietorship, which placed him in a 45 bracket. The rate of tax for Canadian-controlled private corporations in his province is 15% on the fi
$500,000 of income. Personal tax rates (federal plus provincial)in James' province are: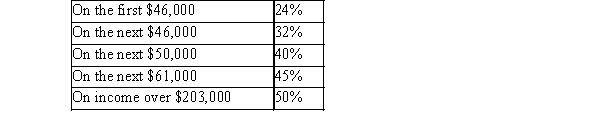 (All rates are assumed for this question.)
(All rates are assumed for this question.)
Steven withdraws $3,000 per month for his personal living expenses. All remaining profits are used t taxes and to expand the business. Steven expects the same business after-tax profits next year.
Steven is considering incorporating his business next year. If he incorporates, he will pay himself a g salary of $48,000.
Required:
A. Determine the increase in Steven's cash flow if he incorporates his company? Show all calculation
B. Name the type of tax planning that Steve would be engaging in if he incorporated his company.
$500,000 of income. Personal tax rates (federal plus provincial)in James' province are:
 (All rates are assumed for this question.)
(All rates are assumed for this question.)Steven withdraws $3,000 per month for his personal living expenses. All remaining profits are used t taxes and to expand the business. Steven expects the same business after-tax profits next year.
Steven is considering incorporating his business next year. If he incorporates, he will pay himself a g salary of $48,000.
Required:
A. Determine the increase in Steven's cash flow if he incorporates his company? Show all calculation
B. Name the type of tax planning that Steve would be engaging in if he incorporated his company.
 Excess cash as a corporation:
Excess cash as a corporation: 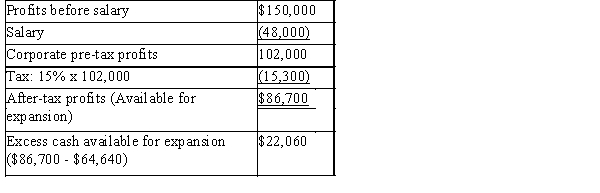 C)Transferring income from one entity to another (individual to corporation)
C)Transferring income from one entity to another (individual to corporation) 2
Certain skills are necessary for successful tax planning. One of these skills is applying the time value of money. Which of the following is FALSE regarding this skill?
A)If a taxpayer invests $1,000 for one year at a rate of return of 14% and is subject to a 45% tax rate, the after-tax value of the investment will be $1,077.
B)If a taxpayer invests $1,000 at 8% and subsequently earns $48 in after-tax income on the investment at the end of the first year, the taxpayer's tax rate is 40%.
C)If a taxpayer earns an annual return of 12% and is subject to a 40% tax rate, the annual after-tax return is 4.8%.
D)Applying the time value of money is a tool used for wealth accumulation.
A)If a taxpayer invests $1,000 for one year at a rate of return of 14% and is subject to a 45% tax rate, the after-tax value of the investment will be $1,077.
B)If a taxpayer invests $1,000 at 8% and subsequently earns $48 in after-tax income on the investment at the end of the first year, the taxpayer's tax rate is 40%.
C)If a taxpayer earns an annual return of 12% and is subject to a 40% tax rate, the annual after-tax return is 4.8%.
D)Applying the time value of money is a tool used for wealth accumulation.
C
3
Match each of the following terms with the most accurate example. Use each example only once.
TERMS:
Tax evasion Tax planning
Tax avoidance
EXAMPLES:
A. An individual is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, applies an application that is not spe prohibited by law.
B. A business is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, does not report a portion of revenue ear during the year.
C. Two unrelated companies take steps to become related in order to shift income from the profitable to the company with losses.
TERMS:
Tax evasion Tax planning
Tax avoidance
EXAMPLES:
A. An individual is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, applies an application that is not spe prohibited by law.
B. A business is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, does not report a portion of revenue ear during the year.
C. Two unrelated companies take steps to become related in order to shift income from the profitable to the company with losses.
An individual is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, applies an application that is not specifically prohibited by law. Tax planning
A business is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, does not report a portion of revenue during the year. Tax evasion
Two unrelated companies take steps to become related in order to shift income from the profita business to the company with losses. Tax avoidance
A business is seeking a beneficial outcome, and therefore, does not report a portion of revenue during the year. Tax evasion
Two unrelated companies take steps to become related in order to shift income from the profita business to the company with losses. Tax avoidance
4
The CEO at Big Company Corporation has decided to sell a piece of capital equipment after the company's year-end in order to avoid paying capital gains tax this year. Which tax planning method will the CEO be using?
A)Shifting income from one time period to another.
B)Converting the nature of income from one type to another.
C)Transferring income to another entity.
D)This is a form of tax evasion and is not allowed.
A)Shifting income from one time period to another.
B)Converting the nature of income from one type to another.
C)Transferring income to another entity.
D)This is a form of tax evasion and is not allowed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following scenarios illustrates a potential tax avoidance scheme?
A)A shareholder owns two corporations and undertakes legal steps in order to permit loss utilization between the two companies.
B)Dividends received from shares transferred from a wife to her husband are taxed in the hands of the wife.
C)A man transfers property to his child at a value less than fair market value.
D)Property transferred between arm's-length parties is valued at fair market value.
A)A shareholder owns two corporations and undertakes legal steps in order to permit loss utilization between the two companies.
B)Dividends received from shares transferred from a wife to her husband are taxed in the hands of the wife.
C)A man transfers property to his child at a value less than fair market value.
D)Property transferred between arm's-length parties is valued at fair market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements regarding GAAR is true?
A)The purpose of GAAR is to catch tax evaders.
B)Individuals who organize their affairs in order to pay as little tax as possible will automatically be subject to GAAR.
C)The Canada Revenue Agency states that "A transaction will not be an avoidance transaction if the taxpayer establishes that it is undertaken primarily for bona fide business, investment or family purposes."
D)When an avoidance transaction takes place, the anti-avoidance rule is automatically applied in all circumstances.
A)The purpose of GAAR is to catch tax evaders.
B)Individuals who organize their affairs in order to pay as little tax as possible will automatically be subject to GAAR.
C)The Canada Revenue Agency states that "A transaction will not be an avoidance transaction if the taxpayer establishes that it is undertaken primarily for bona fide business, investment or family purposes."
D)When an avoidance transaction takes place, the anti-avoidance rule is automatically applied in all circumstances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Andrew has $10,000 to invest. He wants to put his money in a one-year investment earning an annua rate of 12%. Andrew is in a 42% tax bracket.
Required:
a)Calculate the total value of Andrew's investment, after-tax, at the end of the year.
b)Calculate the amount of taxes Andrew will have to pay on his investment.
Required:
a)Calculate the total value of Andrew's investment, after-tax, at the end of the year.
b)Calculate the amount of taxes Andrew will have to pay on his investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The controller of Little Company Ltd. has decided to sell a piece of capital equipment after the company's year-end in order to avoid paying tax on capital gains this year. The controller is engaging in
A)tax planning.
B)tax avoidance.
C)tax evasion.
D)GAAR.
A)tax planning.
B)tax avoidance.
C)tax evasion.
D)GAAR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
For each of the examples listed below, state which of the following three categories of tax planning h applied:
Shifting income from one time period to another Shifting income from one entity to another
Shifting income from one type of income to another.
A. Jack has run a successful proprietorship for the past four years, and has now decided to incorporat company.
B. Karen has decided not to pay herself a dividend from her corporation, (of which she is the sole sha but has chosen to sell a portion of her shares to an associate instead.
C. XYZ Corporation has chosen to delay the recognition of a discretionary reserve until the followin
Shifting income from one time period to another Shifting income from one entity to another
Shifting income from one type of income to another.
A. Jack has run a successful proprietorship for the past four years, and has now decided to incorporat company.
B. Karen has decided not to pay herself a dividend from her corporation, (of which she is the sole sha but has chosen to sell a portion of her shares to an associate instead.
C. XYZ Corporation has chosen to delay the recognition of a discretionary reserve until the followin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Part A: List the three key factors of cash flow.
Part B: List the six skills required for tax planning as suggested in the textbook.
Part B: List the six skills required for tax planning as suggested in the textbook.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



