Deck 2: Diodes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Diodes
1
The ideal model of a pn-junction diode represents the device as a
A) switch.
B) switch in series with a battery.
C) switch in series with a battery and a resistor.
A) switch.
B) switch in series with a battery.
C) switch in series with a battery and a resistor.
switch.
2
The diode model is typically used in circuit calculations.
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete
practical
3
A zener diode has the following ratings: VZ = 9.1 V and IZT = 20 mA. The measured value of VZ changes by 30 mV when Izt = 2 mA. What is the value of ZZ for the device?
A) 1.5 Ω
B) 15 Ω
C) 30 Ω
D) 3.0 Ω
A) 1.5 Ω
B) 15 Ω
C) 30 Ω
D) 3.0 Ω
15 Ω
4
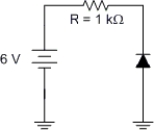
The voltage across the resistor in Figure is
A) 6 V.
B) 5.3 V.
C) 0.7 V.
D) 0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
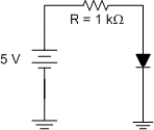
The voltage across a resistor is calculated as being 4 V. The measured value of the voltage is 4.3 V. What is the percent of error between the two values?
A) 6.98%
B) 7.5%
C) 0.698%
D) 0.075%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The diode model is typically used in the initial stages of troubleshooting.
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A zener diode is designed to operate in the region of its characteristic curve.
A) forward operating
B) reverse breakdown
C) zero bias
A) forward operating
B) reverse breakdown
C) zero bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A maximum rating on a spec sheet is a
A) quality.
B) limit.
C) average value.
D) ac characteristic.
A) quality.
B) limit.
C) average value.
D) ac characteristic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When substituting one diode for another, you must consider the
A) average forward current and bulk resistance ratings.
B) peak reverse voltage and diode capacitance ratings.
C) average forward current and peak reverse voltage ratings.
D) bulk resistance and diode capacitance ratings.
A) average forward current and bulk resistance ratings.
B) peak reverse voltage and diode capacitance ratings.
C) average forward current and peak reverse voltage ratings.
D) bulk resistance and diode capacitance ratings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The p-type material of a diode is called the
A) anode.
B) cathode.
A) anode.
B) cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

The voltage across the diode in Figure is
A) 5 V.
B) 4.3 V.
C) 0.7 V.
D) 0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The diode model is typically used in circuit development applications.
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete
A) ideal
B) practical
C) complete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Electron flow through a forward-biased pn junction is
A) from cathode to anode.
B) from anode to cathode.
A) from cathode to anode.
B) from anode to cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A pn-junction diode conducts when the arrow in the schematic symbol
A) points to the more negative diode potential.
B) points to the more positive diode potential.
A) points to the more negative diode potential.
B) points to the more positive diode potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Conventional current through a forward-biased pn junction is
A) from cathode to anode.
B) from anode to cathode.
A) from cathode to anode.
B) from anode to cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16

The voltage across the resistor in Figure is
A) 5 V.
B) 4.3 V.
C) 0.7 V.
D) 0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

The voltage across the diode in Figure is
A) 6 V.
B) 5.3 V.
C) 0.7 V.
D) 0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A calculated value is generally considered to be accurate enough when it is within
A) 20% of the measured value.
B) 15% of the measured value.
C) 10% of the actual value.
D) 5% of the actual value.
Figure 2-1
A) 20% of the measured value.
B) 15% of the measured value.
C) 10% of the actual value.
D) 5% of the actual value.
Figure 2-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The n-type material of a diode is called the
A) anode.
B) cathode.
A) anode.
B) cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A silicon diode has a bulk resistance of 12 Ω and a forward current of 7 mA. The forward voltage drop across the diode is approximately
A) 700 mV.
B) 784 mV.
C) 84 mV.
D) 884 mV.
A) 700 mV.
B) 784 mV.
C) 84 mV.
D) 884 mV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A given LED has a maximum forward current rating of 30 mA. You should use IF = to calculate the value of the current-limiting resistor.
A) 30 mA
B) 24 mA
C) 36 mA
D) 20 mA
Chapter 2 Diodes Answer Key
A) 30 mA
B) 24 mA
C) 36 mA
D) 20 mA
Chapter 2 Diodes Answer Key

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
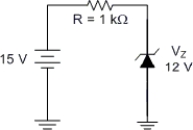
What is the value of IT for the circuit in Figure ?
A) 3 mA
B) 1 mA
C) 5 mA
D) 12 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An LED is typically wired in series with a current-limiting resistor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The color of an LED is typically determined by the magnitude of the diode current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When tested with an ohmmeter, a diode should have forward resistance and reverse resistance.
A) low; high
B) high; low
C) high; high
D) low; low
A) low; high
B) high; low
C) high; high
D) low; low

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which diode type can be best utilized as a panel indicator?
A) A pn-junction diode
B) A zener diode
C) A light-emitting diode LED)
D) None of the above.
A) A pn-junction diode
B) A zener diode
C) A light-emitting diode LED)
D) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The stripe on the body of a pn-junction diode is used to identify the .
A) cathode
B) anode
A) cathode
B) anode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following steps should be taken when testing a diode with an ohmmeter?
A) The ohmmeter should be calibrated using the zero adjust when applicable).
B) The relative polarity of the meter leads should be checked.
C) The meter output current level for each resistance scale should be verified as being safe for the diode under test.
D) All of the above.
A) The ohmmeter should be calibrated using the zero adjust when applicable).
B) The relative polarity of the meter leads should be checked.
C) The meter output current level for each resistance scale should be verified as being safe for the diode under test.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The anode and cathode leads on an LED are usually identified by
A) their color.
B) their lengths.
C) a marking on the LED case.
D) their lengths and/or a marking on the LED case.
A) their color.
B) their lengths.
C) a marking on the LED case.
D) their lengths and/or a marking on the LED case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
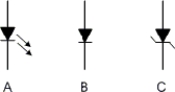
Symbols A, B, and C represent the , respectively.
A) LED, zener diode, and pn-junction diode
B) zener diode, pn-junction diode, and LED
C) photo diode, zener diode, and LED
D) LED, pn-junction diode, and zener diode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
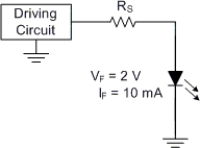
The driving circuit has a peak output of 6 V. What value of RS will protect the LED from excessive forward current?
A) 470 Ω
B) 560 Ω
C) 680 Ω
D) Any of the resistors listed will protect the LED.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

Which of the following is most likely to destroy a zener diode?
A) Exceeding VBR
B) Exceeding IZM

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



