Deck 6: Bipolar Junction Transistors
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/32
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Bipolar Junction Transistors
1
Which of the following biasing combinations is not normally associated with any of the three transistor operating regions?
A) A forward biased E-B junction and a reverse biased C-B junction
B) A reverse biased E-B junction and a reverse biased C-B junction.
C) A reverse biased E-B junction and a forward biased C-B junction.
D) A forward biased E-B junction and a forward biased C-B junction.
A) A forward biased E-B junction and a reverse biased C-B junction
B) A reverse biased E-B junction and a reverse biased C-B junction.
C) A reverse biased E-B junction and a forward biased C-B junction.
D) A forward biased E-B junction and a forward biased C-B junction.
A reverse biased E-B junction and a forward biased C-B junction.
2
A BJT has values of IE = 12 mA and IB = 600 μA. What is the exact value of beta?
A) 20
B) 21
C) 19
D) None of these are correct.
A) 20
B) 21
C) 19
D) None of these are correct.
19
3
Ideally, the total collector current through a saturated transistor is determined by
A) The voltage source and the total resistance in the collector and emitter circuits.
B) VCE and VCC.
C) VCC, VCE, and the total base circuit resistance.
D) the transistor.
A) The voltage source and the total resistance in the collector and emitter circuits.
B) VCE and VCC.
C) VCC, VCE, and the total base circuit resistance.
D) the transistor.
The voltage source and the total resistance in the collector and emitter circuits.
4
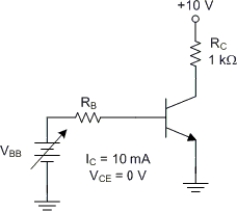
The transistor in Figure is operating in
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) the active region.
D) the limited region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Beta β) is the ratio of
A) collector current to emitter current.
B) base current to collector current.
C) collector current to base current.
D) emitter current to collector current.
A) collector current to emitter current.
B) base current to collector current.
C) collector current to base current.
D) emitter current to collector current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
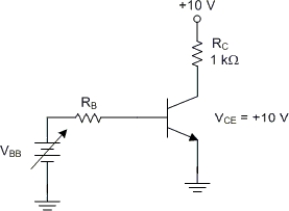
The transistor in Figure is operating in
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) the active region.
D) the limited region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A BJT has values of IE = 15 mA and IC = 14.95 mA. What is the exact value of beta?
A) 300
B) 299
C) 1.003
D) 250
A) 300
B) 299
C) 1.003
D) 250

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
VCE is measured
A) from the collector terminal to ground.
B) from the collector terminal to the emitter terminal.
C) from the emitter terminal to ground.
D) from the collector-emitter junction to ground.
A) from the collector terminal to ground.
B) from the collector terminal to the emitter terminal.
C) from the emitter terminal to ground.
D) from the collector-emitter junction to ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a transistor is in saturation, VCE is approximately equal to
A) VCC.
B) ICRC.
C) 0 V.
D) VE.
A) VCC.
B) ICRC.
C) 0 V.
D) VE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under normal circumstances, which BJT terminal currents are approximately equal in value?
A) IC and IB
B) IC and IE
C) IE and IB
D) No two currents are ever approximately equal in value
A) IC and IB
B) IC and IE
C) IE and IB
D) No two currents are ever approximately equal in value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a BJT is in cutoff, VCE is approximately equal to
A) VCC.
B) ICRC.
C) 0 V.
D) VE.
A) VCC.
B) ICRC.
C) 0 V.
D) VE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bipolar junction transistors BJTs) are commonly used in
A) linear amplifiers.
B) high-speed electronic switches.
C) rectifiers.
D) all of the above.
E) both A and B above.
A) linear amplifiers.
B) high-speed electronic switches.
C) rectifiers.
D) all of the above.
E) both A and B above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

The value of IC in a transistor amplifier is determined by
A) the values of VCC, RC, and VCE.
B) the value of IB for any operating region other than saturation).
C) the value of VCE only.
D) the value of VB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A BJT has values of α = 0.9985 and IC = 15 mA. What is the value of IB for the component?
A) 22.5 μA
B) 15.15 mA
C) 14.85 mA
D) None of these are correct.
A) 22.5 μA
B) 15.15 mA
C) 14.85 mA
D) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The condition where increases in IB will not cause further increases in IC is called
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) active operation.
D) limit operation.
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) active operation.
D) limit operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The arrow on the BJT schematic symbol identifies
A) the emitter terminal and the type of BJT.
B) the collector terminal and the type of BJT.
C) the base terminal and the type of BJT.
D) none of the above.
A) the emitter terminal and the type of BJT.
B) the collector terminal and the type of BJT.
C) the base terminal and the type of BJT.
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The BJT is a
A) voltage-controlled device.
B) current-controlled device.
C) frequency-controlled device.
D) power-controlled device.
A) voltage-controlled device.
B) current-controlled device.
C) frequency-controlled device.
D) power-controlled device.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When both BJT junctions are reverse biased, the component is said to be in
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) active operation.
D) limit operation.
A) cutoff.
B) saturation.
C) active operation.
D) limit operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
IC and VCE are directly proportional.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A BJT has a beta rating of 400. What is the value of alpha for the device?
A) 1.0025
B) 0.0025
C) 0.9975
D) None of these are correct.
A) 1.0025
B) 0.0025
C) 0.9975
D) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An integrated transistor is:
A) a single transistor that is packaged in its own casing.
B) one of a group of transistors contained in an IC package.
C) an IC containing transistors that have extremely high power dissipation ratings.
D) a special device that uses both solid state and steady-state electronics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As temperature increases, beta
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains unchanged.
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) remains unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
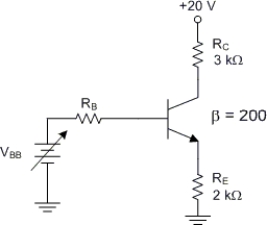
Assuming that IB = 25 μA, what is the exact value of IC?
A) 4 mA
B) 4.975mA
C) 5 mA
D) Canʹt be determined without knowing the value of RB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24

An engineer is designing a television CRT control circuit. What type of transistor do you expect to see in the design?
A) High-voltage
B) High-current
C) High-power
D) General purpose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A transistor has ratings of ICmax) = 200 mA and β = 150 to 200. What is the maximum allowable value of IB for the device?
A) 1 mA
B) 4 mA
C) 1.33 mA
D) None of these are correct.
A) 1 mA
B) 4 mA
C) 1.33 mA
D) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The higher the value of beta for a transistor, the greater the difference between the values of IC and IE.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

Assuming that IB = 10 μA, what is the value of IC?
A) 2 mA
B) 2.01 mA
C) 0.4 mA
D) Canʹt be determined without knowing the value of RB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Assuming that IB = 5 μA, what is the exact value of VC?
A) 3 V
B) 3.015 V
C) 16.985 V
D) 17 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

What is the value of ICsat)) for the circuit?
A) 3.3 mA
B) 4 mA
C) 10 mA
D) Canʹt be determined without knowing the value of IBsat)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
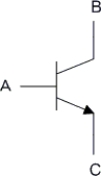
. Which of the following correctly identifies the transistor terminals?
A) A = collector, B = Base, C = Emitter
B) A = Base, B = Emitter, C = collector
C) A = Base, B = collector, C = Emitter
D) A = collector, B = Emitter, C = Base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following labels is generally used to represent dc beta on specification sheets?
A) β
B) βdc
C) hFE
D) hDC
A) β
B) βdc
C) hFE
D) hDC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

The circuit in Figure wonʹt work. Why not?
A) RB is open.
B) The transistor is in saturation.
C) RC is open.
D) The polarities of VCC and VBB are incorrect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 32 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



