Deck 5: Special Applications Diodes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Special Applications Diodes
1
When forward biased, the PIN diode acts as a
A) current-controlled resistance.
B) current-controlled capacitance.
C) voltage-controlled resistance.
D) voltage-controlled capacitance.
A) current-controlled resistance.
B) current-controlled capacitance.
C) voltage-controlled resistance.
D) voltage-controlled capacitance.
current-controlled resistance.
2
The capacitance of a varactor varies
A) inversely with the width of its depletion layer.
B) directly with the width of its depletion layer.
A) inversely with the width of its depletion layer.
B) directly with the width of its depletion layer.
inversely with the width of its depletion layer.
3
A tuned amplifier contains a 2.2 mH inductor in its tank circuit, along with a varactor with the following ratings: Ct = 80 pF when Vr = 3 Vdc and CR = 3 for V = 3 Vdc to 6 Vdc. What is the resonant frequency of the circuit when VR = 3 Vdc?
A) 904.3 GHz
B) 758.7 kHz
C) 379.4 kHz
D) 189.9 MHz
A) 904.3 GHz
B) 758.7 kHz
C) 379.4 kHz
D) 189.9 MHz
379.4 kHz
4
A tuned amplifier has a 2.2 mH inductor and a varactor in its tank. The varactor has the ratings Ct = 72 pf when Vr = 3 Vdc and a Cr = 2.7 for V = 3 Vdc to 6 Vdc. What is the resonant frequency of the circuit described when VR = 6 Vdc?
A) 599.8 kHz
B) 479.9 kHz
C) 657 kHz
D) 1.20 MHz
A) 599.8 kHz
B) 479.9 kHz
C) 657 kHz
D) 1.20 MHz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The clamping voltage Vc) rating of a transient suppressor indicates
A) the maximum voltage across the device at a given value of reverse surge current.
B) the maximum reverse voltage that will not drive the component into its zener operating region.
A) the maximum voltage across the device at a given value of reverse surge current.
B) the maximum reverse voltage that will not drive the component into its zener operating region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following are characteristics of an effective surge protection circuit?
A) High power dissipation capability and rapid turn-on time
B) High power dissipation capability and slow turn-on time
C) High voltage capability and rapid turn-on time
D) High voltage capability and slow turn-on time
A) High power dissipation capability and rapid turn-on time
B) High power dissipation capability and slow turn-on time
C) High voltage capability and rapid turn-on time
D) High voltage capability and slow turn-on time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The maximum reverse standoff voltage VRWM) rating of a transient suppressor indicates
A) the voltage across the device while in its zener operating region.
B) the maximum reverse voltage that will not drive the component into its zener operating region.
A) the voltage across the device while in its zener operating region.
B) the maximum reverse voltage that will not drive the component into its zener operating region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A series current regulator is used to
A) provide a constant input current to a load over a wide range of input voltages.
B) provide a load with an input current that equals the difference between the source current and the regulator current.
A) provide a constant input current to a load over a wide range of input voltages.
B) provide a load with an input current that equals the difference between the source current and the regulator current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When reverse biased, the capacitance of a PIN diode can be varied like that of the varactor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The PIN diode actually contains pn junctions).
A) zero
B) one
C) two
D) three
A) zero
B) one
C) two
D) three

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Forward voltage and current are directly proportional for a tunnel diode that is operated between its peak voltage VP ) and its valley voltage VV ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Schottky diodes have extremely low
A) VF, VRRM, and junction capacitance ratings.
B) IF, VRRM, and junction capacitance ratings.
C) VF, VK, and junction capacitance ratings.
D) fmax, VRRM, and VF ratings.
A) VF, VRRM, and junction capacitance ratings.
B) IF, VRRM, and junction capacitance ratings.
C) VF, VK, and junction capacitance ratings.
D) fmax, VRRM, and VF ratings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The tunnel diode is a
A) lightly doped diode that is used in high-frequency communications applications.
B) lightly doped diode that is used in low-frequency communications applications.
C) heavily doped diode that is used in high-frequency communications applications.
D) heavily doped diode that is used in low-frequency communications applications.
A) lightly doped diode that is used in high-frequency communications applications.
B) lightly doped diode that is used in low-frequency communications applications.
C) heavily doped diode that is used in high-frequency communications applications.
D) heavily doped diode that is used in low-frequency communications applications.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Constant-current diodes are also known as
A) current-restricting diodes.
B) current suppressors.
C) current regulator diodes.
D) All of the above.
A) current-restricting diodes.
B) current suppressors.
C) current regulator diodes.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The tunnel diode region of operation between VP and VV is called the
A) constant resistance region.
B) constant current region.
C) negative resistance region.
D) negative current region.
A) constant resistance region.
B) constant current region.
C) negative resistance region.
D) negative current region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Constant-current diodes have
A) extremely low internal impedance values.
B) extremely high breakdown current ratings.
C) extremely high internal impedance values.
D) extremely low breakdown voltage ratings.
A) extremely low internal impedance values.
B) extremely high breakdown current ratings.
C) extremely high internal impedance values.
D) extremely low breakdown voltage ratings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A varactor with a high capacitance ratio CR) rating would be well suited for use in
A) a fine-tuning circuit.
B) a course-tuning circuit.
C) a crystal-controlled oscillator.
D) any of the circuits listed here.
A) a fine-tuning circuit.
B) a course-tuning circuit.
C) a crystal-controlled oscillator.
D) any of the circuits listed here.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Back-to-back suppressors contain two components that are connected
A) anode-to-cathode.
B) anode-to-anode.
C) cathode-to-cathode.
D) either anode-to-anode or cathode-to-cathode.
A) anode-to-cathode.
B) anode-to-anode.
C) cathode-to-cathode.
D) either anode-to-anode or cathode-to-cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The varactor can be used as a
A) current-controlled capacitance when forward biased.
B) voltage-controlled capacitance when forward biased.
C) current-controlled capacitance when reverse biased.
D) voltage-controlled capacitance when reverse biased.
A) current-controlled capacitance when forward biased.
B) voltage-controlled capacitance when forward biased.
C) current-controlled capacitance when reverse biased.
D) voltage-controlled capacitance when reverse biased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The tunnel diode can be used as the active device in a
A) constant resistance amplifier.
B) negative resistance oscillator.
C) negative current rectifier.
D) negative resistance linear amplifier.
A) constant resistance amplifier.
B) negative resistance oscillator.
C) negative current rectifier.
D) negative resistance linear amplifier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

This is the schematic symbol of a .
A) back to back suppressor
B) constant current diode
C) tunnel diode
D) Schottky diode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The is sometimes referred to as a barrier diode, hot-carrier diode, or surface-barrier diode.
A) Tunnel diode
B) PIN diode
C) Step recovery diode
D) Schottky diode
A) Tunnel diode
B) PIN diode
C) Step recovery diode
D) Schottky diode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A tunnel diode has the following values: IP = 10 mA at VP = 250 mV and IV = 200 μA at VV = 480 mV
Calculate the dynamic resistance of the component.
A) -2.4 kΩ to -25 Ω
B) -23.5 Ω
C) +23.5 Ω
D) 25 Ω to 2.4 kΩ
Calculate the dynamic resistance of the component.
A) -2.4 kΩ to -25 Ω
B) -23.5 Ω
C) +23.5 Ω
D) 25 Ω to 2.4 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The doping level of a step-recovery diode
A) is extremely high.
B) is extremely low.
C) decreases as the distance from the junction increases.
D) increases as the distance from the junction increases.
A) is extremely high.
B) is extremely low.
C) decreases as the distance from the junction increases.
D) increases as the distance from the junction increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
diodes are used in the manufacture of integrated circuit chips to decrease the propagation delay time of the internal circuits.
A) Constant current
B) Step recovery
C) Schottky
D) Tunnel
A) Constant current
B) Step recovery
C) Schottky
D) Tunnel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
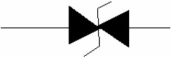
Figure shows the schematic symbol for a
A) back to back suppressor.
B) constant current diode.
C) tunnel diode.
D) Schottky diode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
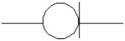
Figure shows the schematic symbol for a
A) back to back suppressor.
B) constant current diode.
C) tunnel diode.
D) Schottky diode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

Figure shows the schematic symbol for a
A) back to back suppressor.
B) constant current diode.
C) tunnel diode.
D) Schottky diode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The step-recovery diode is a/an
A) high-current diode.
B) high-voltage diode.
C) high-power diode.
D) ultra-fast diode.
A) high-current diode.
B) high-voltage diode.
C) high-power diode.
D) ultra-fast diode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An engineer is designing a television tuner circuit. Which diode would you expect to see in the design?
A) A constant-current diode.
B) A tunnel diode.
C) A varactor diode.
D) A PIN diode.
Chapter 5 Special Applications Diodes Answer Key
A) A constant-current diode.
B) A tunnel diode.
C) A varactor diode.
D) A PIN diode.
Chapter 5 Special Applications Diodes Answer Key

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



