Deck 11: Introduction to Alternating Current and Voltage
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/58
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Introduction to Alternating Current and Voltage
1
A sine wave reaches its rms value of 70.7% of the peak voltage at an angle of how many radians?
A) 2n rad
B) n rad
C) n/4 rad
D) n/2 rad
A) 2n rad
B) n rad
C) n/4 rad
D) n/2 rad
n/4 rad
2
A harmonic frequency is always an integral odd or even) multiple of the fundamental frequency.
True
3
A sine wave is the only waveform that contains no harmonics. All other waveforms are composed of a fundamental sine wave and harmonically related sine waves.
True
4
The rate of change of a voltage sine wave is due to the change in flux density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A given rms value of a sine wave is equal to the same value of DC voltage with respect to the heat produced in a resistor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Increasing positive angles of a phasor move clockwise from the reference point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Refer to Figure 11-3. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Waveform A lags Waveform B
B) Waveform A leads Waveform B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A sawtooth voltage waveform has a linear ramp changing voltage level with respect to time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
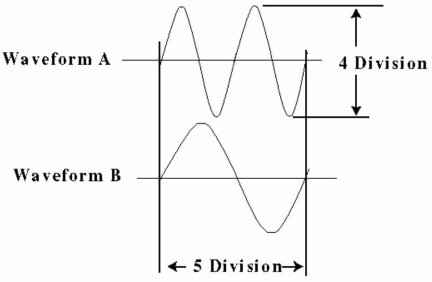
Given the drawing in Figure 11-2, and the Time-per-division knob is set to 1.0 ms/Div, what is the frequency of Waveform A?
A) 2 kHz
B) 400 Hz
C) 100 Hz
D) 5 kHz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A complete sine wave contains:
A) 3n/2 radians
B) n radians
C) n/2 radians
D) 2n radians
A) 3n/2 radians
B) n radians
C) n/2 radians
D) 2n radians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11

Refer to Figure 11-3. Waveforms A and B have the same frequency, but appear to have different amplitudes. Is this possible?
A) No
B) Yes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

Refer to Figure 11-3. The phase shift between Waveform A and Waveform B expressed in Radians is:
A) n/4 rad
B) 2n/6 rad
C) 2n rad
D) n/2 rad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

Given the drawing in Figure 11-3, the phase shift between Waveform A and Waveform B is:
A) 180°
B) 60°
C) 90°
D) 45°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14

You count 5 divisions on the horizontal axis on the scope. The Time-per-division knob is set to 1.0 ms/Div. Given the drawing in Figure 11-2, what is the frequency of Waveform B?
A) 0.2 kHz
B) 0.5 kHz
C) 1 kHz
D) 5 kHz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
One radian equals:
A) 90°
B) 57.3°
C) 45°
D) 114.6°
A) 90°
B) 57.3°
C) 45°
D) 114.6°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Frequency is the reciprocal of the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The average value of a sine wave is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

For Waveform A, you count 4 divisions on the Vertical axis on the scope. The Volts-per-division knob is set to 50 mV/Div. Given the drawing in Figure 11-2, what is the Peak-to-peak amplitude of Waveform A?
A) 500 mV
B) 250 mV
C) 0.2 V
D) 50 mV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
There are 360 degrees in a complete cycle of a sine wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When the phasor moves in the clockwise direction, the various angle positions are labeled as negative values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Find the frequency of a periodic wave that has a period of one hour.
A) 0.278 mHz
B) 27.8 mHz
C) 2.78 mHz
D) 278 mHz
A) 0.278 mHz
B) 27.8 mHz
C) 2.78 mHz
D) 278 mHz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
On an oscilloscope display:
A) a flat horizontal trace means voltage is constant.
B) a straight diagonal trace means voltage is changing at a steady rate.
C) all the above
D) voltage is on the vertical axis and time is on the horizontal axis.
A) a flat horizontal trace means voltage is constant.
B) a straight diagonal trace means voltage is changing at a steady rate.
C) all the above
D) voltage is on the vertical axis and time is on the horizontal axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What angle in degrees is equivalent to n/3 radians?
A) 60°
B) 90°
C) 120°
D) 30°
A) 60°
B) 90°
C) 120°
D) 30°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The negative alternation of a sine wave of current indicates that:
A) power in the circuit will be less during this time.
B) the current has changed direction.
C) the current is the opposite direction and polarity across components changes.
D) it is different in amplitude from its positive alternation.
A) power in the circuit will be less during this time.
B) the current has changed direction.
C) the current is the opposite direction and polarity across components changes.
D) it is different in amplitude from its positive alternation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The phase difference between sine waves of different frequencies is:
A) the same throughout time
B) constantly changing.
C) the difference in their fixed time displacement
D) equal to their frequency differences.
A) the same throughout time
B) constantly changing.
C) the difference in their fixed time displacement
D) equal to their frequency differences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A sine wave reaches half of its peak value at:
A) 90°
B) 30°
C) 60°
D) 45°
A) 90°
B) 30°
C) 60°
D) 45°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The frequency of the waveform in Figure 11-4 is:
A) 1 Hz
B) 1 kHz
C) 1000 cycles per second
D) Both B and C are correct.
A) 1 Hz
B) 1 kHz
C) 1000 cycles per second
D) Both B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the period of a 50 kHz sine wave?
A) 5 × 104 s
B) 5 µs
C) 20 µs
D) 50 µs
A) 5 × 104 s
B) 5 µs
C) 20 µs
D) 50 µs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The equation for finding the frequency, when the period is known is:
A) f = 1/T
B) T = 0.707f
C) T = 1/f
D) T = n/2f)
A) f = 1/T
B) T = 0.707f
C) T = 1/f
D) T = n/2f)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the effective voltage of an ac receptacle is 120 V, what is the peak-to-peak voltage?
A) 84.8 V
B) 169.7 V
C) 339.4 V
D) 240 V
A) 84.8 V
B) 169.7 V
C) 339.4 V
D) 240 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Period of the waveform in Figure 11-4 is:
A) 0.5 mS
B) 1 kHz
C) 1.0 mS
D) 100 Hz
A) 0.5 mS
B) 1 kHz
C) 1.0 mS
D) 100 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The equation for finding the Period, when the frequency is known is:
A) T = 1/f
B) T = n/2f)
C) T = 0.707f
D) f = 1/T
A) T = 1/f
B) T = n/2f)
C) T = 0.707f
D) f = 1/T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a sine wave signal measured 100 mV peak-to-peak, how many volts would be read by a voltmeter?
A) 63.7 mV
B) 14.14 mV
C) 70.7 mV
D) 35.4 mV
A) 63.7 mV
B) 14.14 mV
C) 70.7 mV
D) 35.4 mV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The instantaneous value of a sine wave is:
A) constantly changing
B) 0.707 of its peak value.
C) equivalent to a like DC value
D) equal to 1.414 of the rms value.
A) constantly changing
B) 0.707 of its peak value.
C) equivalent to a like DC value
D) equal to 1.414 of the rms value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the rms value of the waveform in Figure 11-4 is 100 V rms, what is the peak voltage?
A) 70.07 V
B) 288.28 V
C) 200 V
D) 141.4 V
A) 70.07 V
B) 288.28 V
C) 200 V
D) 141.4 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The is defined as the time the output is active divided by the total period it could possibly be active.
A) active ratio
B) duty cycle
C) pulse width
D) on time
A) active ratio
B) duty cycle
C) pulse width
D) on time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the rms value of the waveform in Figure 11-4 is 10 V rms, what is the peak voltage?
A) 7.07 V
B) 20 V
C) 28.28 V
D) 14.14 V
A) 7.07 V
B) 20 V
C) 28.28 V
D) 14.14 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the rms value of the waveform in Figure 11-4 is 12 V rms, what is the peak voltage?
A) 16.97 V
B) 8.48 V
C) 33.94 V
D) 15.3 V
A) 16.97 V
B) 8.48 V
C) 33.94 V
D) 15.3 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The coordinate system consists of:
A) four quadrants
B) two perpendicular lines.
C) two axes, x and y
D) all of the above.
A) four quadrants
B) two perpendicular lines.
C) two axes, x and y
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
How much time has elapsed when the waveform in Figure 11-4 reaches its rms value?
A) 0.25 mS
B) 0.707 mS
C) 0.5 mS
D) 0.125 mS
A) 0.25 mS
B) 0.707 mS
C) 0.5 mS
D) 0.125 mS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Phasor algebra for sinusoidal quantities is applicable only for waveforms which have different frequencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The length of a phasor is called the magnitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The length of a phasor represents the amplitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Determine the instantaneous value of a sine wave whose rms is 20 V, and phase angle is -297 degrees.
A) -17.8 V
B) -25.2 V
C) +17.8 V
D) +25.2 V
A) -17.8 V
B) -25.2 V
C) +17.8 V
D) +25.2 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The length of the phasor "arrow" represents the of a quantity.
A) amplitude
B) frequency
C) angle
D) direction
A) amplitude
B) frequency
C) angle
D) direction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A phasor represents a time-varying quantity in terms of both magnitude and direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The instantaneous value of a sine wave voltage, at any point, is equal to the vertical distance from the tip of the phasor to the:
A) horizontal axis
B) negative peak
C) positive peak
D) vertical axis
A) horizontal axis
B) negative peak
C) positive peak
D) vertical axis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The time base control of the oscilloscope does which of the following?
A) adjusts the vertical scale
B) shows you the current time of day
C) sends a clock pulse to the probe
D) sets the amount of time represented by the horizontal width of the screen
A) adjusts the vertical scale
B) shows you the current time of day
C) sends a clock pulse to the probe
D) sets the amount of time represented by the horizontal width of the screen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The equivalent negative angle for a positive angle of 30 degrees is:
A) 330 degrees
B) -330 degrees
C) -60 degrees
D) -150 degrees
A) 330 degrees
B) -330 degrees
C) -60 degrees
D) -150 degrees

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In a circuit that contains a dc voltage source of 15 V and an ac voltage source of 50 Vp and a resistive load, what would be the maximum and minimum voltage measured across the resistive load?
A) VMAX = zero V, VMIN = 35 V
B) VMAX = 65 V, VMIN = zero V
C) VMAX = 35 V, VMIN = 65 V
D) VMAX = 65 V, VMIN = 35 V
A) VMAX = zero V, VMIN = 35 V
B) VMAX = 65 V, VMIN = zero V
C) VMAX = 35 V, VMIN = 65 V
D) VMAX = 65 V, VMIN = 35 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Phasors are a convenient graphic way of representing sine wave voltages in terms of their:
A) magnitude and frequency
B) magnitude and amplitude
C) magnitude and period
D) magnitude and phase
A) magnitude and frequency
B) magnitude and amplitude
C) magnitude and period
D) magnitude and phase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The angular position of a phasor represents the amplitude of a sine wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following expresses angular velocity?
A) 2n/T
B) f/T
C) n/T
D) 2n × T
A) 2n/T
B) f/T
C) n/T
D) 2n × T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The opposite side of a right triangle is equal to the hypotenuse times the sine of the angle 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The velocity of rotation is called:
A) the frequency
B) the angular velocity
C) the wavelength
D) the speed
A) the frequency
B) the angular velocity
C) the wavelength
D) the speed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What is the angular velocity of a phasor representing a sine wave with a frequency of 1.4 kHz?
A) 440 rad/s
B) 4398 rad/s
C) 8796 rad/s
D) 880 rad/s
A) 440 rad/s
B) 4398 rad/s
C) 8796 rad/s
D) 880 rad/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The length of a phasor is represented by the formula v = Vpsin 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A four-pole generator has a rotation speed of 400 rps. Determine the frequency of the output voltage.
A) 200 Hz
B) 400 Hz
C) 800 Hz
D) 1600 Hz
A) 200 Hz
B) 400 Hz
C) 800 Hz
D) 1600 Hz

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 58 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



