Deck 6: Perfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/218
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Perfect Competition
1
Who are the price takers in a perfectly competitive market?
A)both the buyers and the sellers
B)the buyers
C)neither the buyers nor the sellers
D)the sellers
A)both the buyers and the sellers
B)the buyers
C)neither the buyers nor the sellers
D)the sellers
both the buyers and the sellers
2
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)a small number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)an individual firm having no control over price
A)a small number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)an individual firm having no control over price
a small number of firms in a market
3
In a market for a homogeneous good, if sellers and buyers can enter or exit a market freely , the market is most likely:
A)an oligopoly.
B)a monopolistically competitive market.
C)a monopoly.
D)a perfectly competitive market.
A)an oligopoly.
B)a monopolistically competitive market.
C)a monopoly.
D)a perfectly competitive market.
a perfectly competitive market.
4
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)a large number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)substantial barriers to entry
D)an individual firm having no control over price
A)a large number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)substantial barriers to entry
D)an individual firm having no control over price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consumers do not have a strong preference for the output of one seller over that of another in a perfectly competitive market because:
A)there a large number of firms in the market.
B)the firms sell a standardized product.
C)there are no barriers to entry.
D)an individual firm has control over price.
A)there a large number of firms in the market.
B)the firms sell a standardized product.
C)there are no barriers to entry.
D)an individual firm has control over price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A market where individual firms cannot affect the market price of their good is most likely:
A)a monopoly market.
B)an oligopoly market.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)a perfectly competitive market.
A)a monopoly market.
B)an oligopoly market.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)a perfectly competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In which of the following market structures do you no barriers to entry?
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A)a large number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)all of the above
A)a large number of firms in a market
B)selling a standardized product
C)no barriers to entry
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How does the firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market compare to that in a monopoly?
A)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is horizontal. The demand curve in a monopoly is downward sloping.
B)They are the same.
C)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is horizontal. The demand curve in a monopoly is upward sloping.
D)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is vertical. The demand curve in a monopoly is horizontal.
A)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is horizontal. The demand curve in a monopoly is downward sloping.
B)They are the same.
C)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is horizontal. The demand curve in a monopoly is upward sloping.
D)The firm-specific demand curve in a perfectly competitive market is vertical. The demand curve in a monopoly is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Firms in a perfectly competitive market:
A)sell a differentiated product.
B)sell homogeneous products.
C)usually have large advertising budgets.
D)try to attract customers away from their competitors.
A)sell a differentiated product.
B)sell homogeneous products.
C)usually have large advertising budgets.
D)try to attract customers away from their competitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In which of the following market structures do you find many sellers?
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)monopolistic competition
D)monopolistic competition and perfect competition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A perfectly competitive firm can:
A)affect the market price for its good.
B)sell as much as it can produce at the market price.
C)prevent entry of other firms into their market.
D)collude with its competitors to set prices.
A)affect the market price for its good.
B)sell as much as it can produce at the market price.
C)prevent entry of other firms into their market.
D)collude with its competitors to set prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements about a perfectly competitive market is INCORRECT?
A)There are many sellers, each supplying a small quantity.
B)There are many buyers, each purchasing a small quantity.
C)The market sell homogeneous products.
D)Buyers and sellers cannot enter exit the market freely.
A)There are many sellers, each supplying a small quantity.
B)There are many buyers, each purchasing a small quantity.
C)The market sell homogeneous products.
D)Buyers and sellers cannot enter exit the market freely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A perfectly competitive market:
A)is dominated by one firm.
B)consists of at most five firms.
C)is made up of a large number of firms.
D)consists of only one firm.
A)is dominated by one firm.
B)consists of at most five firms.
C)is made up of a large number of firms.
D)consists of only one firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the best example of a perfectly competitive firm?
A)DeBeers Diamond Company
B)your local cable T.V. company
C)Tinoʹs Italian Eatery, a local restaurant
D)Jonesʹs wheat farm in eastern Washington
A)DeBeers Diamond Company
B)your local cable T.V. company
C)Tinoʹs Italian Eatery, a local restaurant
D)Jonesʹs wheat farm in eastern Washington

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A firm that can sell as much as it can produce at the market price is likely operating in:
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly market.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)an oligopoly market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)a monopoly market.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)an oligopoly market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A market in which firms sell a homogeneous product and cannot influence market price is most likely:
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)an oligopoly.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)a monopoly market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)an oligopoly.
C)a monopolistically competitive market.
D)a monopoly market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A price taker is a buyer or a seller who:
A)takes the market price as given.
B)buys or sells only at a price where profits can be made.
C)accepts whatever price that the government legislates as the price of the good or service.
D)has the ability to influence the equilibrium price in the market.
A)takes the market price as given.
B)buys or sells only at a price where profits can be made.
C)accepts whatever price that the government legislates as the price of the good or service.
D)has the ability to influence the equilibrium price in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the characteristic of a perfectly competitive firm that causes it to be a price taker?
A)many buyers and sellers
B)homogeneous product
C)free entry and exit
D)A and B are correct.
A)many buyers and sellers
B)homogeneous product
C)free entry and exit
D)A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A price maker is a buyer or a seller who:
A)takes the market price as given.
B)buys or sells only at a price where profits can be made.
C)accepts whatever price that the government legislates as the price of the good or service.
D)has the ability to influence the equilibrium price in the market.
A)takes the market price as given.
B)buys or sells only at a price where profits can be made.
C)accepts whatever price that the government legislates as the price of the good or service.
D)has the ability to influence the equilibrium price in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the demand curve faced by a firm is horizontal, then the firm is _______ and a _______.
A)perfectly competitive; price taker
B)perfectly competitive; price maker
C)a monopoly; price taker
D)monopoly; price maker
A)perfectly competitive; price taker
B)perfectly competitive; price maker
C)a monopoly; price taker
D)monopoly; price maker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
You sell your good in a perfectly competitive market where the market price is $7.00. When you sell 100 units your total revenue is $700. When you sell 101 units:
A)total revenue increases by less than $7.
B)total revenue increases by exactly $7.
C)total revenue increases by more than $7.
D)total revenue may increase or decrease.
A)total revenue increases by less than $7.
B)total revenue increases by exactly $7.
C)total revenue increases by more than $7.
D)total revenue may increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Perfect competition is characterized by many firms and no barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Monopolies are characterized by a firm demand curve that is more elastic than the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Oligopolies are characterized by many firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You sell your good in a perfectly competitive market where the market price is $33.00. When you sell 100 units your total revenue is $3,300. When you sell 101 units:
A)total revenue increases by less than $33.
B)total revenue increases by exactly $33.
C)total revenue increases by more than $33.
D)total revenue may increase or decrease.
A)total revenue increases by less than $33.
B)total revenue increases by exactly $33.
C)total revenue increases by more than $33.
D)total revenue may increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A perfectly competitive firm has no control over the price that it charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What are the characteristics of perfect competition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What are the characteristics of monopolies?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Monopolistically competitive industries are characterized by no barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Brodie sells fish in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose the current market price of fish is $4.50 per pound.
A)Brodie can sell as many fish as he can catch at $4.50 per pound.
B)Brodie can charge any price he likes for his fish, but will maximize profit if he sells for less than $4.50.
C)Brodie should charge more than $4.50.
D)Brodie can charge more than $4.50 and still sell some fish.
A)Brodie can sell as many fish as he can catch at $4.50 per pound.
B)Brodie can charge any price he likes for his fish, but will maximize profit if he sells for less than $4.50.
C)Brodie should charge more than $4.50.
D)Brodie can charge more than $4.50 and still sell some fish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What are the characteristics of monopolistic competition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Toby sells wheat in a perfectly competitive market. The demand curve for Tobyʹs wheat is:
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)downward sloping.
D)U-shaped.
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)downward sloping.
D)U-shaped.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a firm is a price taker, the demand curve faced by the firm is:
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)downward sloping.
D)upward sloping.
A)horizontal.
B)vertical.
C)downward sloping.
D)upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A perfectly competitive market is one where:
A)each firm controls the price charged for its product by changing the quantity they produce.
B)each firm sells at the government mandated price.
C)each firm within the market must sell its good at the market price.
D)a firm can affect market price by increasing output.
A)each firm controls the price charged for its product by changing the quantity they produce.
B)each firm sells at the government mandated price.
C)each firm within the market must sell its good at the market price.
D)a firm can affect market price by increasing output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Farmer Brown sells her wheat in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose the current market price of wheat is $2.50 per bushel.
A)Farmer Brown can sell as much wheat as she likes at $2.50 per bushel.
B)Farmer Brown can charge any price for her wheat, but will maximize profit if she sells for less than $2.50.
C)Farmer Brown should charge more than $2.50.
D)Farmer Brown can charge more than $2.50 and still sell some wheat.
A)Farmer Brown can sell as much wheat as she likes at $2.50 per bushel.
B)Farmer Brown can charge any price for her wheat, but will maximize profit if she sells for less than $2.50.
C)Farmer Brown should charge more than $2.50.
D)Farmer Brown can charge more than $2.50 and still sell some wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What are the characteristics of oligopoly?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In which of the following market structures can you find differentiated products?
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition and oligopoly
A)monopoly
B)perfect competition
C)oligopoly
D)monopolistic competition and oligopoly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What are the four types of market structure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What are the similarities between perfect competition and monopolistic competition?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price = marginal cost > average total cost, the firm is:
A)earning a positive profit.
B)earning a zero profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)all of the above
A)earning a positive profit.
B)earning a zero profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If individual firms face a horizontal demand curve at a given market price,
A)price is equal to average total cost.
B)price is equal to marginal cost.
C)price is equal to marginal revenue.
D)price is equal to average variable cost.
A)price is equal to average total cost.
B)price is equal to marginal cost.
C)price is equal to marginal revenue.
D)price is equal to average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Jerryʹs Quarry sells building stone in a perfectly competitive market. At its current level of building stone production, Jerryʹs Quarry has marginal costs equal to $45, and AVC is rising. If the market price of building stone is $50, Jerryʹs Quarry should:
A)decrease its level of building stone production.
B)continue producing its current level of production.
C)increase its production of building stone.
D)shut down and produce no building stone.
A)decrease its level of building stone production.
B)continue producing its current level of production.
C)increase its production of building stone.
D)shut down and produce no building stone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For the perfectly competitive firm:
A)price always equals average cost.
B)price always equals marginal cost.
C)price always equals marginal revenue.
D)price always equals average variable cost.
A)price always equals average cost.
B)price always equals marginal cost.
C)price always equals marginal revenue.
D)price always equals average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
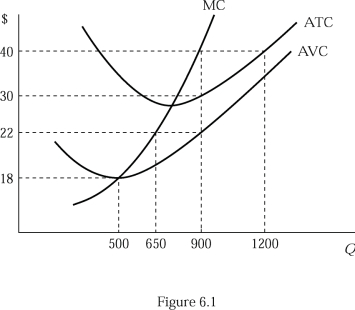
Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40, the firmʹs profit maximizing output level is:
A)500.
B)650.
C)900.
D)1,200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
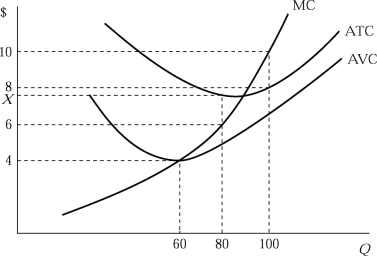 Figure 6.2
Figure 6.2Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose the current market price is $10 and the firm produces the profit maximizing output level. If the firmʹs total fixed cost increases due to a new government regulation, the short-run response of the firm should be to: Note: since the question does not restrict the firmʹs response to the short-run, we canʹt rule out that the rise in fixed cost will push the firm below the breakeven point and that the firm will exit the industry in the long run, thus decreasing its current output level.
A)produce its current output level.
B)increase its current output level.
C)decrease its current output level.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Compact discs are sold in a perfectly competitive market. The current market price of compact discs is $15. If at the current level of production of compact discs you calculate that the marginal cost to your company is also $15, and that AVC is rising, in the short run your company should:
A)produce more compact discs.
B)produce fewer compact discs.
C)continue producing the current level of compact discs.
D)raise the price of its compact discs.
A)produce more compact discs.
B)produce fewer compact discs.
C)continue producing the current level of compact discs.
D)raise the price of its compact discs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Kevinʹs Golf-a-Rama sells golf balls in a perfectly competitive market. At its current level of golf ball production, Kevin has marginal costs equal to $2. If the market price of golf balls is $1, Kevin should:
A)decrease the level of golf ball production.
B)continue producing the current level of production.
C)increase the production of golf balls.
D)raise the price of its golf balls.
A)decrease the level of golf ball production.
B)continue producing the current level of production.
C)increase the production of golf balls.
D)raise the price of its golf balls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
 Figure 6.2
Figure 6.2Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $10 and the firm chooses the profit maximizing output level, its profit is:
A)$1,000.
B)$800.
C)$720.
D)$200.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the firmʹs fixed cost increases by 3,000 due to a new government regulation,
A)the marginal cost curve shifts upward.
B)the average variable cost curve shifts upward.
C)the average total cost curve shifts upward.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Marginal revenue is equal to price for a perfectly competitive firm because:
A)total revenue increases by the price of the good when an additional unit is sold.
B)total revenue increases by less than the price of the good when an additional unit is sold.
C)firms need to lower price to increase the quantity sold.
D)firms can increase price and still increase the quantity sold.
A)total revenue increases by the price of the good when an additional unit is sold.
B)total revenue increases by less than the price of the good when an additional unit is sold.
C)firms need to lower price to increase the quantity sold.
D)firms can increase price and still increase the quantity sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If a firm suffers an economic loss, its:
A)price is less than its marginal cost.
B)price is less than its marginal revenue.
C)price is less than its average total cost.
D)none of the above
A)price is less than its marginal cost.
B)price is less than its marginal revenue.
C)price is less than its average total cost.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53

Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total fixed cost is:
A)$2,800.
B)$5,200.
C)$7,200.
D)$9,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Alexʹs Furniture Mart produces and sells tables in a perfectly competitive market. When Alexʹs Furniture Mart produces and sells 250 tables, its marginal cost is equal to $200, and AVC is rising. If the market price of tables is equal to $150, Alexʹs Furniture Mart should:
A)decrease its level of table production.
B)increase its level of table production.
C)continue producing 250 tables.
D)raise the price of its tables.
A)decrease its level of table production.
B)increase its level of table production.
C)continue producing 250 tables.
D)raise the price of its tables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Kevinʹs Golf-a-Rama sells golf balls in a perfectly competitive market. At its current level of golf ball production, Kevin has marginal costs equal to $1, and AVC is rising. If the market price of golf balls is $2, Kevin should:
A)decrease the level of golf ball production.
B)continue producing the current level of production.
C)increase the production of golf balls.
D)shut down and produce no golf balls.
A)decrease the level of golf ball production.
B)continue producing the current level of production.
C)increase the production of golf balls.
D)shut down and produce no golf balls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
A)$12,500.
B)$14,300.
C)$19,800.
D)$27,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If a firm can maximize its profit by producing the output where price is equal to its marginal cost, the firm is operating in:
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)an oligopolistic market.
C)a monopolistic market.
D)in a monopolistically competitive market.
A)a perfectly competitive market.
B)an oligopolistic market.
C)a monopolistic market.
D)in a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price = marginal cost = average total cost, the firm is:
A)earning a positive economic profit.
B)earning a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)all of the above
A)earning a positive economic profit.
B)earning a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Marginal revenue is equal to:
A)the change in total revenue from selling one more unit of a good.
B)the number of units sold times the price of the good.
C)the change in average revenue from selling one more unit of a good.
D)all of the above
A)the change in total revenue from selling one more unit of a good.
B)the number of units sold times the price of the good.
C)the change in average revenue from selling one more unit of a good.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

Figure 6.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, the firmʹs profit is:
A)$7,200.
B)$9,000.
C)$27,000.
D)$36,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In short-run equilibrium for a competitive firm:
A)price will not equal marginal revenue.
B)marginal revenue will be greater than marginal cost.
C)price will equal marginal cost.
D)price will be greater than marginal cost.
A)price will not equal marginal revenue.
B)marginal revenue will be greater than marginal cost.
C)price will equal marginal cost.
D)price will be greater than marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the price a firm charges in a perfectly competitive industry is greater than average total cost:
A)the firm is earning an economic profit equal to zero.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about profits.
A)the firm is earning an economic profit equal to zero.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If your firm is producing a good at a level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, and price is greater than average total cost, your firm:
A)should shut down and suffer a loss equal to your fixed costs.
B)is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)should decrease output.
D)should increase output.
A)should shut down and suffer a loss equal to your fixed costs.
B)is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)should decrease output.
D)should increase output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
 Figure 6.2
Figure 6.2Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose the current market price is $6 and the firm produces at a given output level. If the firmʹs total fixed cost increases due to a new government regulation, the short-run response of the firm should be to:
A)produce its current output level.
B)decrease its current output level.
C)increase its current output level.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 Figure 6.2
Figure 6.2Figure 6.2 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose that market price falls to $6. If the firm produces at an output level that causes it to suffer an economic loss of $120, its average total cost X)is:
A)$8.
B)$7.5.
C)$6.5.
D)$4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A perfectly competitive firm that is maximizing profit produces the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In a perfectly competitive market, if price is greater than average total cost at the level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue:
A)the firm must be in long-run equilibrium.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)we cannot determine whether the firm is earning positive or negative profits.
A)the firm must be in long-run equilibrium.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)we cannot determine whether the firm is earning positive or negative profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium, then:
A)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
B)price is greater than marginal cost.
C)price is equal to average variable cost.
D)price is greater than marginal revenue.
A)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
B)price is greater than marginal cost.
C)price is equal to average variable cost.
D)price is greater than marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For a perfectly competitive firm, price always equals marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the price a firm charges in a perfectly competitive industry is less than average total cost:
A)the firm is earning positive economic profit.
B)the firm is earning zero economic profit.
C)the firm is earning negative economic profit.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about profits.
A)the firm is earning positive economic profit.
B)the firm is earning zero economic profit.
C)the firm is earning negative economic profit.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In short-run equilibrium for a competitive firm economic profits:
A)will be positive.
B)will be negative.
C)will be zero.
D)may be positive, negative, or zero.
A)will be positive.
B)will be negative.
C)will be zero.
D)may be positive, negative, or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price - average variable cost)= average fixed cost, the firm is:
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If a perfectly competitive firm charges a price that is equal to its average total cost:
A)the firm is earning an economic profit equal to zero.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about the firmʹs profits.
A)the firm is earning an economic profit equal to zero.
B)the firm is earning an economic profit greater than zero.
C)the firm is earning an economic profit less than zero.
D)it is not possible to determine anything about the firmʹs profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Suppose that the market price of sugar is 25 cents per pound and a farmerʹs marginal cost of producing sugar is 28 cents per pound. The farmer should increase her sugar production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price - average variable cost)< average fixed cost, the firm is:
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If a profit-maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive market is currently producing the output where price - average variable cost)> average fixed cost, the firm is:
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above
A)making a positive economic profit.
B)making a zero economic profit.
C)suffering an economic loss.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the firm is incurring losses in the short run, then which of the following is true?
A)P < ATC
B)P > ATC
C)P > MC
D)MC > ATC
A)P < ATC
B)P > ATC
C)P > MC
D)MC > ATC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If the market demand increases for a good sold in a perfectly competitive market, individual firms in the market:
A)will be able to charge a higher price for their product.
B)will need to lower price in order to remain competitive.
C)will not be able to change their price.
D)will begin earning economic losses.
A)will be able to charge a higher price for their product.
B)will need to lower price in order to remain competitive.
C)will not be able to change their price.
D)will begin earning economic losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In long-run equilibrium for a competitive firm economic profits:
A)will be positive.
B)will be negative.
C)will be zero.
D)may be positive, negative, or zero.
A)will be positive.
B)will be negative.
C)will be zero.
D)may be positive, negative, or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
In a perfectly competitive market, if price is less than average total cost, but greater than average variable cost at the level of output where marginal cost equals marginal revenue:
A)the firm is earning positive economic profit.
B)the firm is earning negative economic profit.
C)the firm should shut down.
D)we cannot determine whether the firm is earning positive or negative profits.
A)the firm is earning positive economic profit.
B)the firm is earning negative economic profit.
C)the firm should shut down.
D)we cannot determine whether the firm is earning positive or negative profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



