Deck 10: The Labor Market, Income, and Poverty
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/221
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Labor Market, Income, and Poverty
1
The marginal revenue product of labor is the:
A)change in labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
B)cost of additional labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
C)change in output resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
D)change in revenue resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
A)change in labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
B)cost of additional labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
C)change in output resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
D)change in revenue resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
change in revenue resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
2
When a firm hires a worker for one hour, the marginal benefit to that firm equals the
A)dollar value of the goods produced by that worker in one hour.
B)hourly wage of that worker.
C)number of items the worker produces in that hour.
D)price of each item that the worker produces in that hour.
A)dollar value of the goods produced by that worker in one hour.
B)hourly wage of that worker.
C)number of items the worker produces in that hour.
D)price of each item that the worker produces in that hour.
dollar value of the goods produced by that worker in one hour.
3
The demand for labor is:
A)derived from the demand for the products it is used to produce.
B)determined by the demand for consumer products.
C)determined by the price of consumer products.
D)all of the above
A)derived from the demand for the products it is used to produce.
B)determined by the demand for consumer products.
C)determined by the price of consumer products.
D)all of the above
all of the above
4
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $10 per unit, the marginal revenue product of the third unit of labor is:
A)$50.
B)$60.
C)$500.
D)$600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a perfectly competitive labor market, the firm _______ the price of its product and _______ the wage it pays its workers.
A)takes from the market; takes from the market
B)can freely set; takes from the market
C)takes from the market; can freely set
D)can freely set; can freely set
A)takes from the market; takes from the market
B)can freely set; takes from the market
C)takes from the market; can freely set
D)can freely set; can freely set

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Labor costs account for approximately _______ of total production costs.
A)three-fourths
B)half
C)one-fourth
D)one-third
A)three-fourths
B)half
C)one-fourth
D)one-third

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When a firm hires a worker for one hour, the marginal cost to that firm equals the
A)hourly wage of that worker.
B)diminishing marginal productivity of that worker.
C)price of each item that the worker produces in that hour.
D)average total cost of production at the quantity produced.
A)hourly wage of that worker.
B)diminishing marginal productivity of that worker.
C)price of each item that the worker produces in that hour.
D)average total cost of production at the quantity produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $2 per unit, the marginal revenue product of the eighth unit of labor is:
A)$10.
B)$20.
C)$310.
D)$620.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
-Refer to Table 10.1. The marginal product of the fourth unit of labor is:
A)40.
B)50.
C)52.5.
D)210.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
-Refer to Table 10.1. The marginal product of the fifth unit of labor is:
A)8.
B)40.
C)50.
D)250.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The marginal product of labor is the:
A)change in labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
B)cost of additional labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
C)change in output resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
D)change in revenue resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
A)change in labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
B)cost of additional labor necessary to produce an additional unit of output.
C)change in output resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.
D)change in revenue resulting from adding an additional unit of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Other things being equal, as diminishing marginal returns begin to occur, the marginal revenue product of labor:
A)decreases as more workers are used.
B)increases as more workers are used.
C)remains unchanged as more workers are used.
D)none of the above
A)decreases as more workers are used.
B)increases as more workers are used.
C)remains unchanged as more workers are used.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A curve that shows the relationship between the wage and the quantity of labor demanded in the short-run is:
A)the marginal revenue product of labor curve.
B)the marginal revenue curve.
C)the marginal product of labor curve.
D)none of the above
A)the marginal revenue product of labor curve.
B)the marginal revenue curve.
C)the marginal product of labor curve.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the price of output increases, the marginal revenue product curve will shift _______ and the profit maximizing quantity of labor demanded will _______.
A)up; increase
B)up; decrease
C)down; increase
D)down; decrease
A)up; increase
B)up; decrease
C)down; increase
D)down; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The demand for labor is called a ʺderived demandʺ because it is:
A)derived from the demand for the products it is used to produce.
B)affected by the demand for consumer products workers produce.
C)affected by the price of consumer products workers produce.
D)all of the above
A)derived from the demand for the products it is used to produce.
B)affected by the demand for consumer products workers produce.
C)affected by the price of consumer products workers produce.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
-Refer to Table 10.1. The marginal product of the third unit of labor is:
A)30.
B)50.
C)60.
D)160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the short run, the marginal-revenue product curve is _______ because of
A)downward sloping; diminishing returns.
B)upward sloping; increasing returns.
C)downward sloping; increasing returns.
D)upward sloping; diminishing returns.
A)downward sloping; diminishing returns.
B)upward sloping; increasing returns.
C)downward sloping; increasing returns.
D)upward sloping; diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If labor productivity increases, the marginal revenue product curve will shift _______ and the profit maximizing quantity of labor demanded will _______.
A)up; increase
B)up; decrease
C)down; increase
D)down; decrease
A)up; increase
B)up; decrease
C)down; increase
D)down; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $2 per unit, the marginal revenue product of the fourth unit of labor is:
A)$50.
B)$52.50.
C)$100.
D)$105.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Applied to perfectly competitive labor markets, the marginal principle tells firms to hire workers until
A)marginal revenue product of the last worker hired equals the wage.
B)marginal productivity begins to diminish.
C)average total costs are minimized.
D)the price of the product equals the wage of the worker.
A)marginal revenue product of the last worker hired equals the wage.
B)marginal productivity begins to diminish.
C)average total costs are minimized.
D)the price of the product equals the wage of the worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $2 per unit and we observe the firm hiring four workers, if the firm is maximizing profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$40; $50
B)$50; $90
C)$80; $100
D)$320; $500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
-Refer to Table 10.2. The marginal product of the fifth unit of labor is:
A)50.
B)40.
C)30.
D)20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
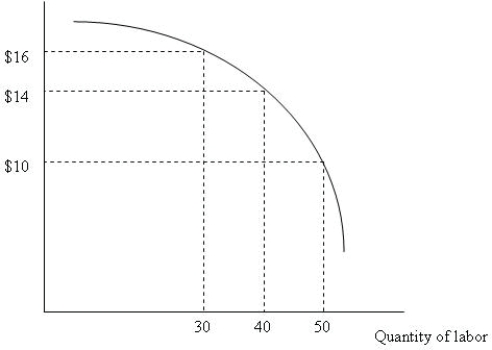 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the firm maximizes its profit and the hourly wage is $12, how many hours of labor will the firm demand?
A)smaller than 30 hours
B)between 30 hours and 40 hours
C)between 40 hours and 50 hours
D)greater than 50 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the firm maximizes its profit and the hourly wage is $15, how many hours of labor will the firm demand?
A)smaller than 30 hours
B)between 30 hours and 40 hours
C)between 40 hours and 50 hours
D)greater than 50 hours

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $2 per unit and we observe the firm hiring six workers, if the firm is maximizing profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$20; $40
B)$30; $50
C)$40; $60
D)$500; $600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. Why does the marginal revenue product of labor decrease faster as the firm increases its use of labor by 10 hours?
A)because the marginal product of labor decreases at an increasing rate
B)because the marginal product of labor decreases at a decreasing rate
C)because the marginal product of labor increases at an increasing rate
D)because the marginal product of labor increases at a decreasing rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $10 per unit, the marginal revenue product of the third unit of labor is:
A)$50.
B)$60.
C)$500.
D)$600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the product price is $4, what is the marginal product of the 40th hour of labor?
A)4 units
B)3.5 units
C)3 units
D)2.5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $2 per unit and the wage rate is $50, how many workers should be hired?
A)three workers
B)four workers
C)five workers
D)six workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the product price decreases, the marginal revenue product curve:
A)shifts downward.
B)shifts upward.
C)remains the same.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the product price is $2, what is the marginal product of the 30th hour of labor?
A)5 units
B)6 units
C)7 units
D)8 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $2 per unit and we observe the firm hiring four workers, if the firm is maximizing profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$25; $45
B)$30; $35
C)$45; $60
D)$60; $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $10 per unit, the marginal revenue product of the sixth unit of labor is:
A)$20.
B)$50.
C)$200.
D)$500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $1 per unit and we observe the firm hiring four workers, if the firm is maximizing profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$35; $40
B)$30; $35
C)$45; $60
D)$80; $90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
-Refer to Table 10.2. The marginal product of the third unit of labor is:
A)25.
B)50.
C)60.
D)160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. The marginal revenue product curve is negatively sloped because _______ decreases as the firm uses more labor.
A)the hourly wage
B)the marginal product of labor
C)the product price
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
-Refer to Table 10.2. The marginal product of the seventh unit of labor is:
A)50.
B)40.
C)30.
D)10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
-Refer to Table 10.1. If the price of output is $2 per unit and the wage rate is $60, _______ workers should be hired.
A)five
B)six
C)seven
D)eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
-Refer to Table 10.2. If the price of output is $2 per unit and the wage rate is $40, how many workers should be hired?
A)six workers
B)five workers
C)four workers
D)three workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
-Refer to Table 10.1. Suppose that this year the wage rate is $30 and the price of the good is $1. If the firm is maximizing profit _______ workers will be hired. Next year the wage rate will increase to $40, but the price of the good will remain at $1. Then _______ workers will be hired.
A)6; 5
B)6; 6
C)7; 6
D)5; 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The short-run labor demand curve is:
A)more elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
B)less elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
C)either more or less elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
D)perfectly elastic horizontal).
A)more elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
B)less elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
C)either more or less elastic than the long-run labor demand curve.
D)perfectly elastic horizontal).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage increases,
A)the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward.
B)the marginal revenue product curve shifts downward.
C)the marginal revenue product curve does not shift but there is a movement upward along the curve.
D)the marginal revenue product curve does not shift but there is a movement downward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
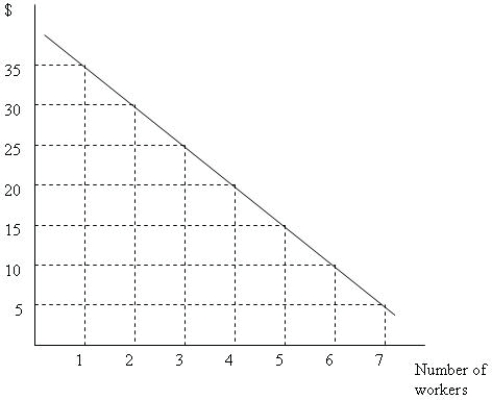 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Figure 10.2 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the wage rate is $15, how many workers does the firm demand?
A)four workers
B)five workers
C)six workers
D)seven workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Figure 10.2 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. Suppose that we observe the firm demanding three workers. If the firm is maximizing its profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$30; $35
B)$25; $30
C)$20; $25
D)$15; $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The change in the quantity of labor demanded resulting from a change in the relative cost of labor is known as the _______ effect.
A)input-substitution
B)price elasticity
C)output
D)derived demand
A)input-substitution
B)price elasticity
C)output
D)derived demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Figure 10.2 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve.If the output price is $5, what is the marginal product of the third worker?
A)four units of output
B)five units of output
C)six units of output
D)seven units of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Figure 10.2 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the marginal product of the second worker is 10 units of output, what is the price of output?
A)$3
B)$4
C)$5
D)$6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In less-developed countries the _______ effect leads to _______.
A)input-substitution; labor intensive production
B)input-substitution; mechanized production
C)output effect; labor intensive production
D)input effect; mechanized production
A)input-substitution; labor intensive production
B)input-substitution; mechanized production
C)output effect; labor intensive production
D)input effect; mechanized production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a long-run impact of an increase in the wage?
A)The quantity demanded of labor increases because there are no diminishing returns.
B)The quantity demanded of labor increases because the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward due to a higher product price.
C)The quantity demanded of labor decreases because firms face a higher degree of diminishing returns.
D)The quantity demanded of labor decreases because firms will have an incentive to use more of other inputs instead of labor.
A)The quantity demanded of labor increases because there are no diminishing returns.
B)The quantity demanded of labor increases because the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward due to a higher product price.
C)The quantity demanded of labor decreases because firms face a higher degree of diminishing returns.
D)The quantity demanded of labor decreases because firms will have an incentive to use more of other inputs instead of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage decreases,
A)the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward.
B)the marginal revenue product curve shifts downward.
C)the marginal revenue product curve does not shift but there is a movement upward along the curve.
D)the marginal revenue product curve does not shift but there is a movement downward along the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Figure 10.2 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. Suppose that we observe the firm demanding five workers. If the firm is maximizing its profit, the wage rate must be between _______ and _______.
A)$5; $10
B)$10; $15
C)$15; $20
D)$25; $30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If principles of economics sections is three credit hours and an instructor teaches two sections with 100 students in each and tuition and fees at your school are $500 per credit hour, then the marginal revenue product for your school from hiring that instructor that semester is:
A)$500.
B)$1500.
C)$150,000.
D)$300,000.
A)$500.
B)$1500.
C)$150,000.
D)$300,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Figure 10.1 depicts a firmʹs marginal revenue product curve. If the product price increases, the marginal revenue product curve:
A)shifts downward.
B)shifts upward.
C)remains the same.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The input-substitution effect of an increase in the wage comes about because higher wages:
A)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, reducing the quantity demanded of the product.
B)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, increasing the quantity demanded of the product.
C)make labor less expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to labor as an input.
D)make labor more expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to other inputs.
A)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, reducing the quantity demanded of the product.
B)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, increasing the quantity demanded of the product.
C)make labor less expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to labor as an input.
D)make labor more expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to other inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The change in the quantity of labor demanded resulting from a change in the quantity produced of the product is known as the _______ effect.
A)input-substitution
B)price elasticity
C)output
D)derived demand
A)input-substitution
B)price elasticity
C)output
D)derived demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The market demand curve for labor is the relationship between the wage and the quantity of labor that:
A)all workers are willing to provide.
B)any given worker is willing to provide.
C)all firms are willing to employ.
D)any given firm is willing to employ.
A)all workers are willing to provide.
B)any given worker is willing to provide.
C)all firms are willing to employ.
D)any given firm is willing to employ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The long-run labor demand curve is:
A)more elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
B)less elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
C)either more or less elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
D)perfectly elastic horizontal).
A)more elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
B)less elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
C)either more or less elastic than the short-run labor demand curve.
D)perfectly elastic horizontal).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Marginal revenue product is the additional revenue for the firm when it hires one additional unit of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The output effect of an increase in the wage comes about because higher wages:
A)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, reducing the quantity demanded of the product.
B)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, increasing the quantity demanded of the product.
C)make labor less expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to labor as an input.
D)make labor more expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to other inputs.
A)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, reducing the quantity demanded of the product.
B)increase production costs, and final good prices will rise, increasing the quantity demanded of the product.
C)make labor less expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to labor as an input.
D)make labor more expensive as an input, leading firms to switch to other inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If principles of economics sections is three credit hours and an instructor teaches two sections with 100 students in each and tuition and fees at your school are $100 per credit hour, then the marginal revenue product for your school from hiring that instructor that semester is:
A)$100.
B)$300.
C)$30,000.
D)$60,000.
A)$100.
B)$300.
C)$30,000.
D)$60,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The price of an hour of leisure time for a successful lawyer is _______ the price of an hour of leisure for an unemployed high school drop-out.
A)greater than
B)the same as
C)less than
D)impossible to compare to
A)greater than
B)the same as
C)less than
D)impossible to compare to

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the output effect?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The price of an hour of leisure time is
A)the income that could have been earned in that hour.
B)zero.
C)the minimum wage rate.
D)determined by the value of the activity the person engages in during that hour of leisure.
A)the income that could have been earned in that hour.
B)zero.
C)the minimum wage rate.
D)determined by the value of the activity the person engages in during that hour of leisure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the input-substitution effect?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to the output effect, a decrease in the wage will decrease production costs, so the price of final goods will decrease and the demand for labor will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The input-substitution effect associated with an increase in the wage implies that as the wage increases, a firm will substitute other inputs for the relatively expensive labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The output effect is the change in labor supply due to a change in the quantity of output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If Jerryʹs demand for leisure increases as the wage increases,
A)the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
B)the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
C)the income effect is completely offset by the substitution effect.
D)There is insufficient information.
A)the income effect dominates the substitution effect.
B)the substitution effect dominates the income effect.
C)the income effect is completely offset by the substitution effect.
D)There is insufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Marginal revenue product equals marginal revenue times the price of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When wages increase, the income effect _______ the supply of labor and the substitution effect _______ the supply of labor.
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases
A)decreases; increases
B)increases; decreases
C)increases; increases
D)decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If Tomʹs demand for leisure decreases as the wage increases,
A)the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
B)the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
C)the income effect is completely offset by the substitution effect.
D)There is insufficient information.
A)the income effect outweighs the substitution effect.
B)the substitution effect outweighs the income effect.
C)the income effect is completely offset by the substitution effect.
D)There is insufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
For a perfectly competitive firm, the marginal-revenue product curve is the same as the firmʹs short run demand for labor curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why is the demand for labor downward sloping in the short-run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The relationship between the wage and the quantity of labor that a given worker is willing to provide is called:
A)individual labor demand.
B)market labor demand.
C)individual labor supply.
D)market labor supply.
A)individual labor demand.
B)market labor demand.
C)individual labor supply.
D)market labor supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to the income effect of labor supply, if leisure is a normal good, then an increase in the wage rate will _______ the quantity of labor _______.
A)increase; supplied
B)decrease; supplied
C)increase; demanded
D)decrease; demanded
A)increase; supplied
B)decrease; supplied
C)increase; demanded
D)decrease; demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
According to the substitution effect of labor supply, when the wage rate goes up:
A)it becomes more costly to consume leisure, so people will work more.
B)it becomes less costly to consume leisure, so people will work more.
C)the opportunity cost of enjoying leisure goes down.
D)firms will hire more workers since people are more willing to work.
A)it becomes more costly to consume leisure, so people will work more.
B)it becomes less costly to consume leisure, so people will work more.
C)the opportunity cost of enjoying leisure goes down.
D)firms will hire more workers since people are more willing to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When wages increase the income effect of labor supply _______ the quantity of labor supplied because
A)reduces; the price of leisure has increased.
B)reduces; workers acquire more of all normal goods when income increases.
C)increases; the value of working has increased.
D)increases; the price of leisure has increased.
A)reduces; the price of leisure has increased.
B)reduces; workers acquire more of all normal goods when income increases.
C)increases; the value of working has increased.
D)increases; the price of leisure has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If leisure is a normal good, as the price of leisure increases the quantity of leisure demanded _______ and the demand for leisure _______.
A)falls; increases
B)falls; is not affected
C)remains the same; decreases
D)increases; is not affected
A)falls; increases
B)falls; is not affected
C)remains the same; decreases
D)increases; is not affected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Explain why the marginal revenue product of labor curve is the firmʹs short-run demand curve for labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The input-substitution effect associated with an increase in the wage implies that as the wage increases, a firm will substitute other inputs for the relatively expensive labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 221 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



