Deck 7: Monopoly and Price Discrimination
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/180
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Monopoly and Price Discrimination
1
A firm that has market power has the ability:
A)to affect the price of its own product.
B)to conduct illegal activities without fear of prosecution.
C)to command consumer to buy any quantity from them.
D)to drive its competition out of the market.
A)to affect the price of its own product.
B)to conduct illegal activities without fear of prosecution.
C)to command consumer to buy any quantity from them.
D)to drive its competition out of the market.
to affect the price of its own product.
2
Which of the following is NOT a barrier to entry for monopoly?
A)a patent
B)government licensing
C)large economies of scale
D)a large number of existing firms in a market
A)a patent
B)government licensing
C)large economies of scale
D)a large number of existing firms in a market
a large number of existing firms in a market
3
Which of the following is NOT an artificial barrier to entry?
A)a patent
B)government franchise
C)large economies of scale
D)government licensing
A)a patent
B)government franchise
C)large economies of scale
D)government licensing
large economies of scale
4
When economists say a market has ʺbarriers to entryʺ they refer to:
A)monopolists being prohibited from selling their products to certain customers.
B)a policy that some countries establish to reduce imports from other countries.
C)factors that prevent other firms from challenging a firm with market power.
D)economic profits that are positive, but too high to encourage entry.
A)monopolists being prohibited from selling their products to certain customers.
B)a policy that some countries establish to reduce imports from other countries.
C)factors that prevent other firms from challenging a firm with market power.
D)economic profits that are positive, but too high to encourage entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an example of a barrier to entry?
A)A firm is open for business only at certain hours of the day, and has its doors locked at other times.
B)The government grants licenses to taxicab drivers, without which it is illegal to operate a taxicab.
C)A newspaper sells advertising space to businesses.
D)Lack of a Web site.
A)A firm is open for business only at certain hours of the day, and has its doors locked at other times.
B)The government grants licenses to taxicab drivers, without which it is illegal to operate a taxicab.
C)A newspaper sells advertising space to businesses.
D)Lack of a Web site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following firms have market power?
A)private universities
B)fast food chains such as McDonaldʹs
C)theme parks
D)All of the above have market power.
A)private universities
B)fast food chains such as McDonaldʹs
C)theme parks
D)All of the above have market power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
_______ is a monopoly that exists in an industry where the large economies of scale acts as its barrier to entry.
A)A natural monopoly
B)A monopolistic competitor
C)A regulated monopoly
D)A price discriminator
A)A natural monopoly
B)A monopolistic competitor
C)A regulated monopoly
D)A price discriminator

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A network externality occurs when:
A)a firm has a patent.
B)the value of a product to a consumer increase with the number of other consumers who use it.
C)a firm has large economies of scale.
D)the value of a product to a consumer requires another product.
A)a firm has a patent.
B)the value of a product to a consumer increase with the number of other consumers who use it.
C)a firm has large economies of scale.
D)the value of a product to a consumer requires another product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following firms have no market power?
A)clothing companies
B)fast food chains such as McDonaldʹs
C)theme parks
D)gold panners during the gold rush
A)clothing companies
B)fast food chains such as McDonaldʹs
C)theme parks
D)gold panners during the gold rush

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a firm is awarded a patent, it is given monopoly rights to the production of that product for _______ years.
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)50
A)10
B)20
C)30
D)50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monopoly may arise due to:
A)a patent.
B)net work externalities.
C)large economies of scale.
D)all of the above
A)a patent.
B)net work externalities.
C)large economies of scale.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
-Refer to Table 7.1, which shows the relationship between the price that Gladys charges for a product and the quantity of that product that Gladys sells. Gladysʹ marginal revenue becomes negative starting with the production of which unit?
A)2
B)4
C)6
D)None of the above; marginal revenue is always positive or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a monopoly?
A)There is only one seller.
B)A monopolist is a price-taker.
C)There exist barriers to entry.
D)A monopolistʹs sales revenue is constrained by the market demand.
A)There is only one seller.
B)A monopolist is a price-taker.
C)There exist barriers to entry.
D)A monopolistʹs sales revenue is constrained by the market demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
-Refer to Table 7.1, which shows the relationship between the price that Gladys charges for a product and the quantity of that product that Gladys sells. The marginal revenue that Gladys receives from selling the fourth unit of output is:
A)$3.
B)$6.
C)$10.
D)$24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The demand curve that a monopolist faces is:
A)the market demand curve.
B)the same as the demand curve that faces a perfectly competitive firm.
C)not affected by changes in the prices of other goods.
D)generally flatter than the demand curve that faces a perfectly competitive firm.
A)the market demand curve.
B)the same as the demand curve that faces a perfectly competitive firm.
C)not affected by changes in the prices of other goods.
D)generally flatter than the demand curve that faces a perfectly competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A market served by only one firm is called a:
A)perfectly competitive market.
B)monopoly.
C)oligopoly.
D)Any of the above could be correct.
A)perfectly competitive market.
B)monopoly.
C)oligopoly.
D)Any of the above could be correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Facebook is a social networking Web site that is used by a growing number of individuals. Because of its popularity, it is now more difficult for new networking websites to enter and compete with Facebook. Facebook enjoys _______ as a barrier for others to enter the market.
A)a network externality
B)price discrimination
C)a negative externality
D)economies of scale
A)a network externality
B)price discrimination
C)a negative externality
D)economies of scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
-Refer to Table 7.1, which shows the relationship between the price that Gladys charges for a product and the quantity of that product that Gladys sells. The marginal revenue that Gladys receives from selling the fifth unit of output is:
A)$5, because that is the price per unit of output that Gladys receives.
B)$5, because that is the quantity that Gladys sells.
C)$25, because Gladys sells five unit of output at a price of $5.
D)$1, because Gladys earns $1 more in revenues by increasing her output to five units from four units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following firms rely on patents the most as the barrier to keep other firms from entering the industry?
A)pharmaceutical firms
B)textbook publishers
C)law firms
D)wine makers
A)pharmaceutical firms
B)textbook publishers
C)law firms
D)wine makers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
-Refer to Table 7.1, which shows the relationship between the price that Gladys charges for a product and the quantity of that product that Gladys sells. The total revenue that Gladys receives from selling four units of output is:
A)$4.
B)$6.
C)$10.
D)$24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
At a price of $20, the marginal revenue of a monopolist is $12. If the marginal cost of production is $10, what should the monopolist do in order to maximize profits?
A)Increase its price.
B)Decrease its price.
C)Keep its price at the same level.
D)not enough information to solve
A)Increase its price.
B)Decrease its price.
C)Keep its price at the same level.
D)not enough information to solve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
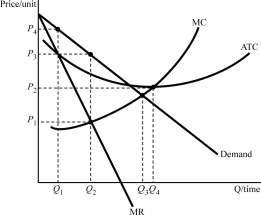 Figure 7.3
Figure 7.3The firm in Figure 7.3 will produce:
A)Q1.
B)Q2.
C)Q3.
D)Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a monopoly?
A)A monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)There are no close substitutes for a monopolistʹs product.
C)After the first unit, the monopolistʹs marginal revenue is always less than its price.
D)A monopolist is a price-taker.
A)A monopolist faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
B)There are no close substitutes for a monopolistʹs product.
C)After the first unit, the monopolistʹs marginal revenue is always less than its price.
D)A monopolist is a price-taker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
How do monopoly prices and quantities produced differ from perfectly competitive outcomes, all other things equal?
A)Monopoly prices and quantities are both lower than competitive outcomes.
B)Monopoly prices and quantities are both higher than competitive outcomes.
C)Monopoly prices are lower than competitive prices but monopoly quantities are higher than competitive quantities.
D)Monopoly prices are higher than competitive prices but monopoly quantities are lower than competitive quantities.
A)Monopoly prices and quantities are both lower than competitive outcomes.
B)Monopoly prices and quantities are both higher than competitive outcomes.
C)Monopoly prices are lower than competitive prices but monopoly quantities are higher than competitive quantities.
D)Monopoly prices are higher than competitive prices but monopoly quantities are lower than competitive quantities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
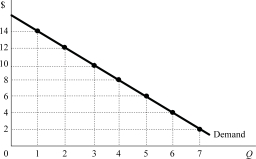 Figure 7.2
Figure 7.2Figure 7.2 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. Suppose that the marginal cost is $6 for all units and the current output level is 4 units. Then which of the following is true?
A)The marginal revenue is less than the marginal cost.
B)The price is greater than the average total cost.
C)The firm is producing the profit maximizing level of output.
D)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following best characterizes the tradeoff faced by a monopolist when deciding what quantity to produce?
A)The firm can increase its output, but needs to lower its price for only the marginal unit of output.
B)The firm can increase its output, but to do so it must charge a higher price to all customers.
C)The firm gets more revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets less revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
D)The firm gets less revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets more revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
A)The firm can increase its output, but needs to lower its price for only the marginal unit of output.
B)The firm can increase its output, but to do so it must charge a higher price to all customers.
C)The firm gets more revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets less revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.
D)The firm gets less revenue from new customers by increasing output, but gets more revenue from existing customers given that it lowered its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
 Figure 7.2
Figure 7.2Figure 7.2 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. Suppose that the marginal cost is $6 for all units and the current output level is 4 units. Then what would you recommend to the firm?
A)Lower the price to sell more units.
B)Raise the price and sell fewer units.
C)Maintain the current price and output level.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
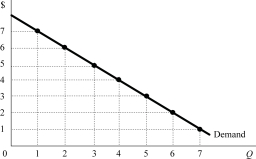 Figure 7.1
Figure 7.1Figure 7.1 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. If the monopolist were to maximize its total revenue, it would produce _______ units of output and charge a price of _______.
A)3; $5
B)4; $4
C)5; $3
D)6; $2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When a monopolist sells two units of output its total revenues are $100. When the monopolist sells three units of output its total revenues are $120. When the monopolist sells three units of output, the price per unit is:
A)$6.67.
B)$20.
C)$33.33.
D)$40.
A)$6.67.
B)$20.
C)$33.33.
D)$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
 Figure 7.1
Figure 7.1Figure 7.1 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. If the monopolist increases output from four to five units, what is its marginal revenue?
A)$16
B)$15
C)$3
D)-$1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
 Figure 7.1
Figure 7.1Figure 7.1 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. If the monopolist increases output from two to three units, what is its marginal revenue?
A)$3
B)$5
C)$12
D)$15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When a monopolist sells two units of output its total revenues are $100. When the monopolist sells three units of output, its price per unit is $35. The monopolistʹs marginal revenue from selling the third unit of output is:
A)$5.
B)$33.33.
C)$35.
D)$105.
A)$5.
B)$33.33.
C)$35.
D)$105.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a monopolist is maximizing its profits, we know that it has:
A)maximized total revenue.
B)maximized marginal revenue.
C)minimized total cost.
D)equated marginal cost and marginal revenue.
A)maximized total revenue.
B)maximized marginal revenue.
C)minimized total cost.
D)equated marginal cost and marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
For a monopolist, marginal revenue _______ for all units of output except the first unit.
A)is greater than the price of output
B)is less than the price of output
C)is equal to the price of output
D)may be either greater than or less than the price of output
A)is greater than the price of output
B)is less than the price of output
C)is equal to the price of output
D)may be either greater than or less than the price of output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
At a price of $10, the marginal revenue of a monopolist is $6. If the marginal cost of production is $8, what should the monopolist do in order to maximize profits?
A)Increase its price.
B)Decrease its price.
C)Keep its price at the same level.
D)not enough information to solve
A)Increase its price.
B)Decrease its price.
C)Keep its price at the same level.
D)not enough information to solve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
 Figure 7.2
Figure 7.2Figure 7.2 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. The marginal revenue from selling the fourth unit is:
A)$8.
B)$6.
C)$4.
D)$2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A monopolist will never produce at a quantity where the:
A)MR < 0.
B)MR > 0.
C)P > MR.
D)MR= MC.
A)MR < 0.
B)MR > 0.
C)P > MR.
D)MR= MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A monopolist maximizes profits by setting the quantity where:
A)marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
B)marginal revenue greater than marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue less than marginal cost.
D)total revenue as high as possible.
A)marginal revenue equal to marginal cost.
B)marginal revenue greater than marginal cost.
C)marginal revenue less than marginal cost.
D)total revenue as high as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
 Figure 7.2
Figure 7.2Figure 7.2 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve. The marginal revenue from selling the third unit is:
A)$6.
B)$8.
C)$10.
D)$44.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a monopolist charges the same price for all of the units of the good that it sells, then beyond the first unit sold:
A)P = MR because the firm maximizes profit.
B)P = MR because the monopolist holds price constant.
C)P < MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units in order to sell another unit.
D)P > MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units in order to sell another unit.
A)P = MR because the firm maximizes profit.
B)P = MR because the monopolist holds price constant.
C)P < MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units in order to sell another unit.
D)P > MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units in order to sell another unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why do some markets have more firms than others?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
 Figure 7.3
Figure 7.3The firm in Figure 7.3 will charge:
A)P1.
B)P2.
C)P3.
D)P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why do barriers to entry create market power?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A monopolistʹs marginal cost is less than the price it charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Should a monopolist charge the highest price for its good that anyone in the market will pay?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is most accurate?
A)In all cases, competitive markets yield more consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
B)In all cases, competitive markets yield less consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
C)In some cases, competitive markets can yield less consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
D)In all cases, competitive markets yield the same consumer surplus that would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
A)In all cases, competitive markets yield more consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
B)In all cases, competitive markets yield less consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
C)In some cases, competitive markets can yield less consumer surplus than would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.
D)In all cases, competitive markets yield the same consumer surplus that would be enjoyed in a monopoly market with the same cost structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
After the first unit, a monopolistʹs marginal revenue is less than the price it charges because to sell an additional unit it needs to lower its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A network externality acts as a barrier to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A monopolist picks the quantity of output at which price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A monopolist will never produce a level of output where MR < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the long run, the main reason that a monopolist can earn positive economic profits while a perfectly competitive firm cannot is:
A)monopolists enjoy greater economies of scale.
B)there are no barriers to entry in a perfectly competitive market.
C)the monopolist faces an inelastic demand for its product.
D)perfectly competitive firms face greater opportunity costs.
A)monopolists enjoy greater economies of scale.
B)there are no barriers to entry in a perfectly competitive market.
C)the monopolist faces an inelastic demand for its product.
D)perfectly competitive firms face greater opportunity costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
How does a monopolistʹs marginal revenue change as output increases? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
At a price of $18, the marginal revenue of a movie seller is $12. If the marginal cost of a movie is
$9, the firm should increase its price.
$9, the firm should increase its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is a network externality?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Will a profit maximizing monopolist who is not subject to government regulation produce a quantity where the MR < 0?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Monopolist marginal revenue rises with output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A monopolist maximizes profit by producing the output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Figure 7.3
Figure 7.3Where it wants to produce the firm in Figure 7.3 will:
A)make a zero economic profit.
B)suffer a loss.
C)make a positive economic profit.
D)break even.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why is a monopolistʹs marginal revenue less than the price?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
At a price of $15, a firm sells 80 CDs per day. If the slope of the demand curve is 0.10, marginal revenue is $5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
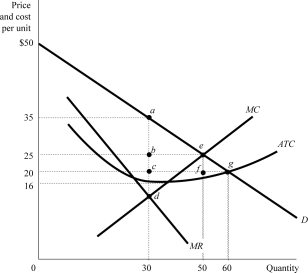 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve, marginal revenue, and its costs. The monopolist would maximize its profit by charging a price of:
A)$35.
B)$25.
C)$20.
D)$16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is true in the long run for both monopoly and perfectly competitive industries?
A)There are low barriers to entry.
B)Firms can earn positive economic profits in the long run.
C)Firms produce at levels that are economically efficient.
D)Firms will go out of business if they cannot charge a price that is at least equal to average total cost.
A)There are low barriers to entry.
B)Firms can earn positive economic profits in the long run.
C)Firms produce at levels that are economically efficient.
D)Firms will go out of business if they cannot charge a price that is at least equal to average total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
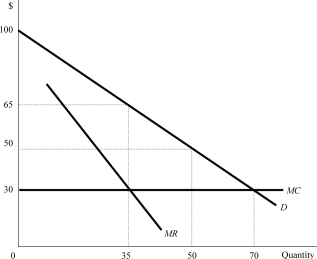 Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5Suppose that Figure 7.5 shows an industryʹs market demand, its marginal revenue, and the production costs of a representative firm. If the industry was perfectly competitive, it will produce a quantity of _______ and charge a price of _______.
A)35; $65
B)50; $50
C)70; $30
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Refer to Figure 7.4. If the market was a monopoly, the consumer surplus would be:
A)$625.
B)$450.
C)$300
D)$225.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows an industryʹs market demand, its marginal revenue, and the production costs of a representative firm. If the industry was perfectly competitive, it would produce a quantity of:
A)30 units.
B)50 units.
C)60 units.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When a local casino spends millions in TV ads convincing town residents to reject another casinoʹs bid to operate in the area, the casino is:
A)rent seeking.
B)seeking rent controls.
C)acting fraudulently.
D)allocating resources efficiently.
A)rent seeking.
B)seeking rent controls.
C)acting fraudulently.
D)allocating resources efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The term ʺrent seekingʺ best describes a situation in which:
A)individuals expend effort searching for a good price on an apartment.
B)consumers compete for a limited quantity of the good.
C)firms use resources to secure or preserve a monopoly in providing a good or service.
D)None of the above are good descriptions of rent -seeking behavior.
A)individuals expend effort searching for a good price on an apartment.
B)consumers compete for a limited quantity of the good.
C)firms use resources to secure or preserve a monopoly in providing a good or service.
D)None of the above are good descriptions of rent -seeking behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
 Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5Refer to Figure 7.5. The deadweight loss associated with the monopoly would be:
A)$787.5.
B)$612.5.
C)$262.5.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When a local casino spends millions in TV ads convincing town residents to reject another casinoʹs bid to operate in the area, the most that the casino would be willing to spend is:
A)the producer surplus gained by being a monopoly.
B)the consumer surplus gained by being a monopoly.
C)deadweight loss.
D)total economic surplus.
A)the producer surplus gained by being a monopoly.
B)the consumer surplus gained by being a monopoly.
C)deadweight loss.
D)total economic surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
 Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5Suppose that Figure 7.5 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve, marginal revenue, and its cost. The monopolist would maximize its profit by producing a quantity of _______ and by charging a price of _______.
A)35; $65
B)50; $50
C)70; $30
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Relative to a competitive market equilibrium, the profit maximizing quantity chosen by a monopolist will result in a deadweight loss because:
A)the monopolist will produce at a quantity lower than the competitive equilibrium.
B)the monopolist will produce at a quantity higher than the competitive equilibrium.
C)the monopolist will charge a price lower than the competitive equilibrium.
D)the monopolist will keep producing at a quantity even though the MR < MC.
A)the monopolist will produce at a quantity lower than the competitive equilibrium.
B)the monopolist will produce at a quantity higher than the competitive equilibrium.
C)the monopolist will charge a price lower than the competitive equilibrium.
D)the monopolist will keep producing at a quantity even though the MR < MC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows an industryʹs market demand, its marginal revenue, and the production costs of a representative firm. If the industry was perfectly competitive, a representative firmʹs profit would be:
A)$1,250.
B)$450.
C)$250.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows an industryʹs market demand, its marginal revenue, and the production costs of a representative firm. If the industry was perfectly competitive, a representative firm would charge a price of:
A)$35.
B)$25.
C)$20.
D)$16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
 Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5Suppose that Figure 7.5 shows an industryʹs market demand, its marginal revenue, and the production costs of a representative firm. If the industry was perfectly competitive, the consumer surplus would be:
A)$2,450.
B)$1,225.
C)$612.5.
D)$262.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Refer to Figure 7.4. The deadweight loss associated with the monopoly would be represented by the area:
A)△abe.
B)△ace.
C)△ade.
D)△efg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Refer to Figure 7.4. If the market was perfectly competitive, the consumer surplus would be:
A)$850.
B)$625.
C)$300.
D)$100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve, marginal revenue, and its costs. The monopolist would maximize its profit by producing a quantity of:
A)30 units.
B)50 units.
C)60 units.
D)There is not sufficient information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
 Figure 7.5
Figure 7.5Suppose that Figure 7.5 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve, marginal revenue, and its cost. At the profit maximizing output level and price, the consumer surplus would be:
A)$2,450.
B)$1,225.
C)$612.5.
D)$262.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
 Figure 7.4
Figure 7.4Suppose that Figure 7.4 shows a monopolistʹs demand curve, marginal revenue, and its costs. At the profit maximizing output level, the monopolistʹs profit would be:
A)$730.
B)$570.
C)$320.
D)$150.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When a pharmaceutical firm spends millions of dollars to lobby and convince Congress to extend the number of years a firm is awarded patent protection, then the pharmaceutical firm is engaging in:
A)rent seeking.
B)fraud.
C)price discrimination.
D)marginal cost pricing.
A)rent seeking.
B)fraud.
C)price discrimination.
D)marginal cost pricing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 180 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



