Deck 16: Understanding Options
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Understanding Options
1
In June 2007, an investor buys a call option on Amgen stock with an exercise of price of $65 and expiring in January 2009. If the stock price in June 2003 is $60, then this option is:
I. in-the-money
II. out-of-the-money
III. a LEAPS
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
I. in-the-money
II. out-of-the-money
III. a LEAPS
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
II and III only
2
The writer (seller) of a regular exchange-listed call-option on the stock:
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
3
Figure-4 depicts the:
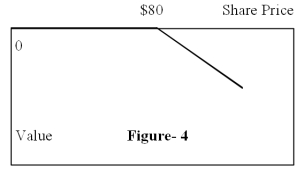
A) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
B) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
C) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option
D) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option

A) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
B) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
C) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option
D) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option
position diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
4
Firms regularly use the following to reduce risk:
I. Currency options
II. Interest-rate options
III. Commodity options
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III
I. Currency options
II. Interest-rate options
III. Commodity options
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The Position diagram for a put with the same exercise price and premium as the call on the same underlying asset with the same maturity is (like):
A) the inverse of the call diagram along the put price
B) unrelated to the call diagram no matter what the exercise price
C) the mirror image of the call diagram around the exercise price
D) exactly the same as the call diagram for the given exercise price
A) the inverse of the call diagram along the put price
B) unrelated to the call diagram no matter what the exercise price
C) the mirror image of the call diagram around the exercise price
D) exactly the same as the call diagram for the given exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure-1 depicts the:
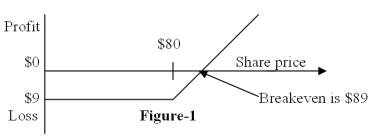
A) position diagram for the buyer of a call option
B) profit diagram for the buyer of a call option
C) position diagram for the buyer of a put option
D) profit diagram for the buyer of a put option

A) position diagram for the buyer of a call option
B) profit diagram for the buyer of a call option
C) position diagram for the buyer of a put option
D) profit diagram for the buyer of a put option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An investor, in practice, can buy:
I. an option on a single share of stock
II. options that are in multiples of 100
III. a minimum order of 100 options on a share of stock
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) II only
D) III only
I. an option on a single share of stock
II. options that are in multiples of 100
III. a minimum order of 100 options on a share of stock
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) II only
D) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The writer (seller) of a regular exchange-listed put-option on the stock:
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An option that can be exercised any time before expiration date is called:
A) an European option
B) an American option
C) a call option
D) a put option
A) an European option
B) an American option
C) a call option
D) a put option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A put option gives the owner the right:
A) and the obligation to buy an asset at a given price
B) and the obligation to sell an asset at a given price
C) but not the obligation to buy an asset at a given price
D) but not the obligation to sell an asset at a given price
A) and the obligation to buy an asset at a given price
B) and the obligation to sell an asset at a given price
C) but not the obligation to buy an asset at a given price
D) but not the obligation to sell an asset at a given price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The two principal options exchanges in the U.S.A. are:
I. International Securities Exchange
II. New York Stock Exchange
III. NASDAQ
IV. Chicago Board of Options Exchange
A) II and III only
B) I and II only
C) I and IV only
D) III and IV only
I. International Securities Exchange
II. New York Stock Exchange
III. NASDAQ
IV. Chicago Board of Options Exchange
A) II and III only
B) I and II only
C) I and IV only
D) III and IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The following are examples of disguised options for firms:
I. acquiring growth opportunities
II. ability of the firm to terminate a project when it is no longer profitable
III. options that are associated with corporate securities that provide flexibility to change the terms of the issues
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
I. acquiring growth opportunities
II. ability of the firm to terminate a project when it is no longer profitable
III. options that are associated with corporate securities that provide flexibility to change the terms of the issues
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The buyer of a call option has the right to exercise, but the writer of the call option has:
A) The choice to offset with a put option
B) The obligation to deliver the shares at exercise price
C) The choice to deliver shares or take a cash payoff
D) The choice of exercising the call or not
A) The choice to offset with a put option
B) The obligation to deliver the shares at exercise price
C) The choice to deliver shares or take a cash payoff
D) The choice of exercising the call or not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The value of a put option at expiration is:
A) market price of the share minus the exercise price
B) higher of the exercise price minus market price of the share and zero
C) the exercise price
D) none of the above
A) market price of the share minus the exercise price
B) higher of the exercise price minus market price of the share and zero
C) the exercise price
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The owner of a regular exchange-listed put-option on the stock:
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Figure-3 depicts the:
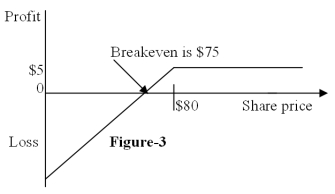
A) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
B) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
C) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option
D) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option

A) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
B) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a call option
C) position diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option
D) profit diagram for the writer (seller) of a put option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In June 2007, an investor buys a put option on Genentech stock with an exercise of price Of $75 and expiring in January 2009. If the stock price in June 2007 is $80, then this option is:
I. in-the-money
II. out-of-the-money
III. a LEAPS
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III only
I. in-the-money
II. out-of-the-money
III. a LEAPS
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure-2 depicts the:
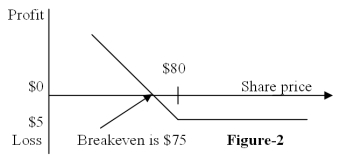
A) position diagram for the buyer of a call option
B) profit diagram for the buyer of a call option
C) position diagram for the buyer of a put option
D) profit diagram for the buyer of a put option

A) position diagram for the buyer of a call option
B) profit diagram for the buyer of a call option
C) position diagram for the buyer of a put option
D) profit diagram for the buyer of a put option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose an investor sells (writes) a put option. What will happen if the stock price on the exercise date exceeds the exercise price?
A) The seller will need to deliver stock to the owner of the option
B) The seller will be obliged to buy stock from the owner of the option
C) The owner will not exercise his option
D) None of the above
A) The seller will need to deliver stock to the owner of the option
B) The seller will be obliged to buy stock from the owner of the option
C) The owner will not exercise his option
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The owner of a regular exchange-listed call-option on the stock:
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
A) has the right to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
B) has the right to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
C) has the obligation to buy 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price
D) has the obligation to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the volatility of the underlying asset decreases, then the:
A) Value of the put option will increase, but the value of the call option will decrease
B) Value of the put option will decrease, but the value of the call option will increase
C) Value of both the put and call option will increase
D) Value of both the put and call option will decrease
A) Value of the put option will increase, but the value of the call option will decrease
B) Value of the put option will decrease, but the value of the call option will increase
C) Value of both the put and call option will increase
D) Value of both the put and call option will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose an investor buys one share of stock and a put option on the stock. What will be the value of her investment on the final exercise date if the stock price is below the exercise price? (Ignore transaction costs)
A) The value of two shares of stock
B) The value of one share of stock plus the exercise price
C) The exercise price
D) The value of one share of stock minus the exercise price
A) The value of two shares of stock
B) The value of one share of stock plus the exercise price
C) The exercise price
D) The value of one share of stock minus the exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A call option has an exercise price of $150. At the final exercise date, the stock price could be either $100 or $200. Which investment would combine to give the same payoff as the stock?
A) Lend PV of $100 and buy two calls
B) Lend PV of $100 and sell two calls
C) Borrow $100 and buy two calls
D) Borrow $100 and sell two calls
A) Lend PV of $100 and buy two calls
B) Lend PV of $100 and sell two calls
C) Borrow $100 and buy two calls
D) Borrow $100 and sell two calls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following investors would be happy to see the stock price rise sharply?
I. Investor who owns the stock and a put option
II. Investor who has sold a put option and bought a call option
III. Investor who owns the stock and has sold a call option
IV. Investor who has sold a call option
A) I and II only
B) III and IV only
C) III only
D) IV only
I. Investor who owns the stock and a put option
II. Investor who has sold a put option and bought a call option
III. Investor who owns the stock and has sold a call option
IV. Investor who has sold a call option
A) I and II only
B) III and IV only
C) III only
D) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the risk-free interest rate increases:
A) the direct effect of it on the call option price is positive
B) the direct effect of it on the call option price is negative
C) the direct effect of it on the call option price is unknown
D) none of the above
A) the direct effect of it on the call option price is positive
B) the direct effect of it on the call option price is negative
C) the direct effect of it on the call option price is unknown
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For European options, the value of a call minus the value of a put is equal to:
A) The present value of the exercise price minus the value of a share
B) The present value of the exercise price plus the value of a share
C) The value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
D) The value of a share minus the present value of the exercise price
A) The present value of the exercise price minus the value of a share
B) The present value of the exercise price plus the value of a share
C) The value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
D) The value of a share minus the present value of the exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Put-call parity can be used to show:
A) How far in-the-money put options can get
B) How far in-the-money call options can get
C) The precise relationship between put and call option prices given equal exercise prices and equal expiration dates
D) That the value of a call option is always twice that of a put given equal exercise prices and equal expiration dates
A) How far in-the-money put options can get
B) How far in-the-money call options can get
C) The precise relationship between put and call option prices given equal exercise prices and equal expiration dates
D) That the value of a call option is always twice that of a put given equal exercise prices and equal expiration dates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose you buy a call and lend the present value of its exercise price. You could match the payoffs of this strategy by:
A) Buying the underlying stock and selling a call
B) Selling a put and lending the present value of the exercise price
C) Buying the underlying stock and buying a put
D) Buying the underlying stock and selling a put
A) Buying the underlying stock and selling a call
B) Selling a put and lending the present value of the exercise price
C) Buying the underlying stock and buying a put
D) Buying the underlying stock and selling a put

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If the stock makes a dividend payment before the expiration date then the put-call parity is:
A) Value of call = value of put + share price - present value (PV) of dividend -PV of exercise price
B) Value of call = value of put - share price + PV of dividend - PV of exercise price
C) Value of call = value of put + share price + PV of dividend + PV of exercise price
D) Value of call = value of put + share price + PV of dividend - PV of exercise price
A) Value of call = value of put + share price - present value (PV) of dividend -PV of exercise price
B) Value of call = value of put - share price + PV of dividend - PV of exercise price
C) Value of call = value of put + share price + PV of dividend + PV of exercise price
D) Value of call = value of put + share price + PV of dividend - PV of exercise price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Buying the stock and the put option on the stock provides the same payoff as:
A) investing the present value of the exercise price in T-bills and buying the call option
B) on the stock
C) short selling the stock and buying a call option on the stock
D) writing (selling) a put option and buying a call option on the stock
E) none of above
A) investing the present value of the exercise price in T-bills and buying the call option
B) on the stock
C) short selling the stock and buying a call option on the stock
D) writing (selling) a put option and buying a call option on the stock
E) none of above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For European options, the value of a call plus the present value of the exercise price is equal to:
A) The value of a put minus the value of a share
B) The value of a share minus the value of a call
C) The value of a put plus the value of a share
D) The value of a share minus the value of a put
A) The value of a put minus the value of a share
B) The value of a share minus the value of a call
C) The value of a put plus the value of a share
D) The value of a share minus the value of a put

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Given the following data: Expiration = 6 months; Stock price = $80; exercise price = $75; call option price = $12; risk-free rate = 5% per year. Calculate the price of an equivalent put option using put-call parity:
A) $3.07
B) $5.19
C) $11.43
D) none of the above
A) $3.07
B) $5.19
C) $11.43
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Buying a call option, investing the present value of the exercise price in T-bills, and short selling the underlying share is the same as:
A) Buying a call and a put
B) Buying a put and a share
C) Buying a put
D) Selling a call
A) Buying a call and a put
B) Buying a put and a share
C) Buying a put
D) Selling a call

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The higher the underlying stock price: (everything else remaining the same)
A) higher the put price
B) lower the put price
C) has no effect on put price
D) none of the above
A) higher the put price
B) lower the put price
C) has no effect on put price
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Relative to the underlying stock, a call option always has:
A) A higher beta and a higher standard deviation of return
B) A lower beta and a higher standard deviation of return
C) A higher beta and a lower standard deviation of return
D) A lower beta and a lower standard deviation of return
A) A higher beta and a higher standard deviation of return
B) A lower beta and a higher standard deviation of return
C) A higher beta and a lower standard deviation of return
D) A lower beta and a lower standard deviation of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For European options, the value of a put is equal to:
A) The value of a call minus the value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
B) The value of a call plus the value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
C) The value of the share minus the value of a call plus the present value of the exercise price
D) The value of the share minus the present value of the exercise price plus the valued of a call
A) The value of a call minus the value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
B) The value of a call plus the value of a share plus the present value of the exercise price
C) The value of the share minus the value of a call plus the present value of the exercise price
D) The value of the share minus the present value of the exercise price plus the valued of a call

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The higher the underlying stock price: (everything else remaining the same)
A) higher the call price
B) lower the call price
C) has no effect on call price
D) none of the above
A) higher the call price
B) lower the call price
C) has no effect on call price
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Suppose an investor buys one share of stock and a put option on the stock and simultaneously sells a call option on the stock with the same exercise price. What will be the value of his investment on the final exercise date?
A) Above the exercise price if the stock price rises and below the exercise price if it falls
B) Equal to the exercise price regardless of the stock price
C) Equal to zero regardless of the stock price
D) Below the exercise price if the stock price rises and above if it falls
A) Above the exercise price if the stock price rises and below the exercise price if it falls
B) Equal to the exercise price regardless of the stock price
C) Equal to zero regardless of the stock price
D) Below the exercise price if the stock price rises and above if it falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following features increase(s) the value of a call option?
A) A high interest rate
B) A long time to maturity
C) A higher volatility of the underlying stock price
D) All of the above
A) A high interest rate
B) A long time to maturity
C) A higher volatility of the underlying stock price
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the underlying stock pays a dividend before the expiration of the options that will have the following effect on the price of the options:
I. increase the value of the call option
II. increase the value of the put option
III. decrease the value of the call option
IV. decrease the value of the put option
A) I and II only
B) III and IV only
C) I and IV only
D) II and III only
I. increase the value of the call option
II. increase the value of the put option
III. decrease the value of the call option
IV. decrease the value of the put option
A) I and II only
B) III and IV only
C) I and IV only
D) II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If you write a put option, you acquire the right to buy stock at a fixed strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The value of a call option is negatively related to: I) Exercise price
II) Risk-free rate
III) Time to expiration
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only
II) Risk-free rate
III) Time to expiration
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Position diagrams and profit diagrams are one and the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A call options gives its owner the right to buy stock at a fixed strike price during a specified period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The value of a put option is positively related to:
I. Exercise price
II. Time to expiration
III. Volatility of the underlying stock price
IV. Risk-free rate
A) I, II, and III only
B) II, III, and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) IV only
I. Exercise price
II. Time to expiration
III. Volatility of the underlying stock price
IV. Risk-free rate
A) I, II, and III only
B) II, III, and IV only
C) I, II, and IV only
D) IV only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
It is possible to replicate an investment in a call option by a levered investment in the underlying asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Buying a stock and a put option, and depositing the present value of the exercise price in a bank account and buying a call provide the same payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The value of a call option increases with higher volatility of the stock prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For an European option: Value of call + PV(exercise price) = Value of put + share price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The writer of a put option loses if the stock price declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The value of a call option, beyond the stock price less the exercise price, is most likely to be realized when the option is:
A) out of the money.
B) in the money.
C) at the money.
D) cannot be determined.
A) out of the money.
B) in the money.
C) at the money.
D) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The value of a put option is negatively related to:
I. stock price
II. risk-free rate III) exercise price
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) III only
I. stock price
II. risk-free rate III) exercise price
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The value of an option (both call and put) is positively related to:
I. volatility of the underlying stock price
II. time to expiration
III. risk-free rate
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) III only
I. volatility of the underlying stock price
II. time to expiration
III. risk-free rate
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The value of a call option is positively related to the following:
I. underlying stock price
II. risk-free rate
III. time to expiration
IV. volatility of the underlying stock price
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, III, and IV
I. underlying stock price
II. risk-free rate
III. time to expiration
IV. volatility of the underlying stock price
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Options can have a value even when the stock is worthless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the stock price follows a random walk successive price changes are statistically independent. If σ2 is the variance of daily price change, and there are t days until expiration, the variance of the cumulative price changes is:
A) σ2
B) (σ2) * (t)
C) (σ2)/t
D) none of the above
A) σ2
B) (σ2) * (t)
C) (σ2)/t
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An increase in the exercise price results in an equal increase in the call option price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An investor can get downside protection by buying a stock and a put option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An increase in the stock price results in an increase in the call option price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An European option gives its owner the right to exercise the option at any time before expiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Briefly explain the relationship between risk and option values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Options written on volatile assets are worth more than options written on safer assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All things being equal, the closer an option gets to expiration, the lower the option price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Briefly explain what is meant by put-call parity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Briefly explain what is meant by "protective put."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Briefly explain how position diagrams are useful?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Discuss the factors that determine the value of a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



