Deck 4: Descriptive Statistics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/109
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Descriptive Statistics
1
To construct a frequency distribution for categorical data, the
A) observations that appear in each category must be summed up.
B) number of observations that appear in each category must be counted.
C) observations in each category must be multiplied by observations in the corresponding category.
D) number of observations in each category must be divided by the total number of observations in all categories.
A) observations that appear in each category must be summed up.
B) number of observations that appear in each category must be counted.
C) observations in each category must be multiplied by observations in the corresponding category.
D) number of observations in each category must be divided by the total number of observations in all categories.
number of observations that appear in each category must be counted.
2
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-A graphical depiction of a frequency distribution for numerical data in the form of a column chart is called a .
A) cartogram
B) correlogram
C) histogram
D) dendogram
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-A graphical depiction of a frequency distribution for numerical data in the form of a column chart is called a .
A) cartogram
B) correlogram
C) histogram
D) dendogram
histogram
3
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-What is the cumulative relative frequency of employees on a 'A to D' pay scale?
A) 1.00
B) 0.80
C) 0.30
D) 0.60
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-What is the cumulative relative frequency of employees on a 'A to D' pay scale?
A) 1.00
B) 0.80
C) 0.30
D) 0.60
0.80
4
Which of the following allow meaningful comparison of ranges, averages and other statistics?
A) interval data
B) categorical data
C) ratio data
D) ordinal data
A) interval data
B) categorical data
C) ratio data
D) ordinal data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).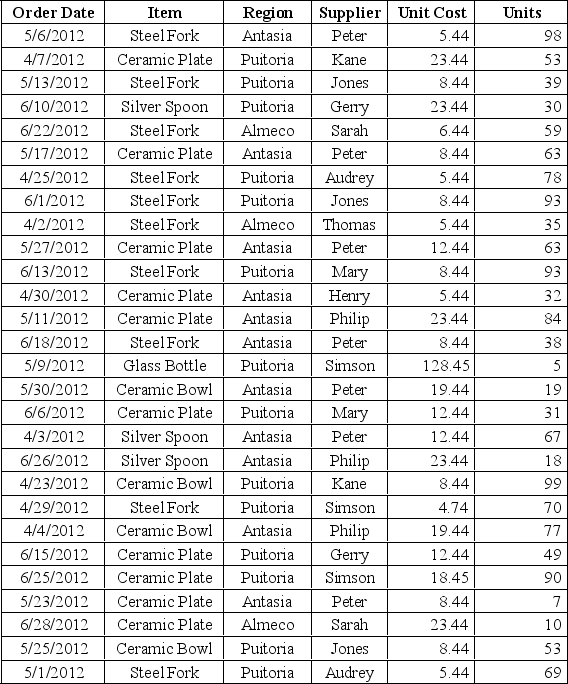
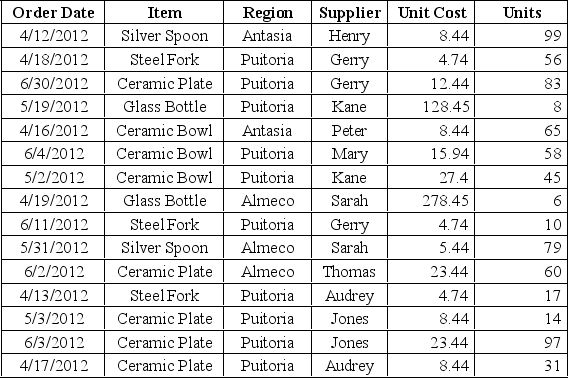
Construct a relative frequency distribution for items in the purchase order database and show the proportions of the frequencies visually using a pie chart.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).


Construct a relative frequency distribution for items in the purchase order database and show the proportions of the frequencies visually using a pie chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-While constructing a histogram, how is group width calculated?
A) number of groups × lower limit of the last group + upper limit of the first group)
B) upper limit of the last group - lower limit of the first group) / number of groups
C) upper limit of the first group + number of groups) × lower limit of the last group + number of groups)
D) lower limit of the first group - number of groups) × upper limit of the last group
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-While constructing a histogram, how is group width calculated?
A) number of groups × lower limit of the last group + upper limit of the first group)
B) upper limit of the last group - lower limit of the first group) / number of groups
C) upper limit of the first group + number of groups) × lower limit of the last group + number of groups)
D) lower limit of the first group - number of groups) × upper limit of the last group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Fewer groups provide a "coarser" histogram.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Fewer groups provide a "coarser" histogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When constructing frequency distributions for numerical data, SUMIF is used to count the frequencies of each discrete value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Following are the components of a data set containing purchase details of a shoe manufacturing company. Identify the ratio data.
A) Item Number
B) Rank of suppliers
C) Item cost
D) Arrival Date
A) Item Number
B) Rank of suppliers
C) Item cost
D) Arrival Date

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Not specifying a Bin Range will not allow Excel to automatically determine bin values for the frequency distribution and histogram.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Not specifying a Bin Range will not allow Excel to automatically determine bin values for the frequency distribution and histogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When data are classified by the type of measurement scale, which is the strongest form of measurement?
A) nominal
B) interval
C) ordinal
D) ratio
A) nominal
B) interval
C) ordinal
D) ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Nominal data:
A) are ranked according to some relationship to one another.
B) have constant differences between observations.
C) are continuous and have a natural zero.
D) are sorted into categories according to specified characteristics.
A) are ranked according to some relationship to one another.
B) have constant differences between observations.
C) are continuous and have a natural zero.
D) are sorted into categories according to specified characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a data set has 'c' number of observations, the relative frequency of category 'l' is computed as .
A) frequency of category 'l') / 'c'
B) 'c' × number of observations in category 'l')
C) sum of all observations in category 'l') / 'c'
D) sum of 'c' + each observation in category 'l')
A) frequency of category 'l') / 'c'
B) 'c' × number of observations in category 'l')
C) sum of all observations in category 'l') / 'c'
D) sum of 'c' + each observation in category 'l')

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Explain statistics as defined by David Hand. What are the two ways in which Microsoft Excel supports statistical analysis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-What is the relative frequency of Grade 3 employees?
A) 4
B) 0.55
C) 0.20
D) 5
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-What is the relative frequency of Grade 3 employees?
A) 4
B) 0.55
C) 0.20
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How is a frequency distribution calculated for categorical and numerical data?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-What is the relative frequency of Female employees?
A) 0.65
B) 0.75
C) 0.25
D) 0.35
Following is an extract from the Employee Payroll Database of HFR Informatics Inc.
-What is the relative frequency of Female employees?
A) 0.65
B) 0.75
C) 0.25
D) 0.35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Measure is the act of obtaining data associated with a metric. Measurements are the numerical values associated with a metric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is an example of a measure of continuous metrics?
A) four errors revealed in an invoice
B) a delivery delayed by seven days
C) weight and volume of a sheet of steel
D) three incomplete orders on a day
A) four errors revealed in an invoice
B) a delivery delayed by seven days
C) weight and volume of a sheet of steel
D) three incomplete orders on a day

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a disadvantage of ordinal data?
A) They bear no relationship to one another.
B) They have no fixed units of measurement.
C) They have no natural zero.
D) They are not comparable with each other.
A) They bear no relationship to one another.
B) They have no fixed units of measurement.
C) They have no natural zero.
D) They are not comparable with each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following measures of location is calculated using the formula , where n is the number of observations?
A) midrange
B) sample mean
C) mode
D) median
A) midrange
B) sample mean
C) mode
D) median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following observations is closest to the 87th percentile of costs per order?
A) 75 SD104 screwdrivers for $183.00
B) 66 N103 nuts for $114.84
C) 73 B101 bolts for $1,200.12
D) 49 S101 screws for $1,001.56
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following observations is closest to the 87th percentile of costs per order?
A) 75 SD104 screwdrivers for $183.00
B) 66 N103 nuts for $114.84
C) 73 B101 bolts for $1,200.12
D) 49 S101 screws for $1,001.56

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is true about cross-tabulation?
A) All subcategories together must constitute the complete data set.
B) A cross-tabulation table is often called a latent class model.
C) Each observation can be classified into many subcategories.
D) The table displays the number of categorical variables between two observations.
A) All subcategories together must constitute the complete data set.
B) A cross-tabulation table is often called a latent class model.
C) Each observation can be classified into many subcategories.
D) The table displays the number of categorical variables between two observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The purpose of sampling is to .
A) enumerate all the values in the population
B) measure all items of interest for a particular interest or investigation
C) obtain sufficient information to draw a valid inference about a population
D) calculate all variables and observations within a population
A) enumerate all the values in the population
B) measure all items of interest for a particular interest or investigation
C) obtain sufficient information to draw a valid inference about a population
D) calculate all variables and observations within a population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is true about quartiles?
A) The 25th percentile is called the fourth quartile.
B) One-fourth of the data fall below the fourth quartile.
C) Three-fourths of the data are below the third quartile.
D) The 50th quartile is the third percentile.
A) The 25th percentile is called the fourth quartile.
B) One-fourth of the data fall below the fourth quartile.
C) Three-fourths of the data are below the third quartile.
D) The 50th quartile is the third percentile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Use the table below to answer the following questions).
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the mode for the cost per order data.
A) $174.17
B) $325
C) $88
D) $206.5
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the mode for the cost per order data.
A) $174.17
B) $325
C) $88
D) $206.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the table below to answer the following questions).
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the median for the cost per order data.
A) $325
B) $154
C) $174.17
D) $88
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the median for the cost per order data.
A) $325
B) $154
C) $174.17
D) $88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-The Excel 2010 function computes the kth percentile of data in the range specified in the array field, where k is in the range 0 to 1, inclusive.
A) PERCENTILE.INCarray, k)
B) PERCENTILEarray + k)
C) PERCENTILE.IFarray, k)
D) PERCENTILESUMarray), k)
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-The Excel 2010 function computes the kth percentile of data in the range specified in the array field, where k is in the range 0 to 1, inclusive.
A) PERCENTILE.INCarray, k)
B) PERCENTILEarray + k)
C) PERCENTILE.IFarray, k)
D) PERCENTILESUMarray), k)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
One of the measures of location is calculated as 88. Which of the following measures of location corresponds to this value?
A) mean
B) mode
C) median
D) midrange
A) mean
B) mode
C) median
D) midrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In statistical notation, the elements of a data set are typically labeled as .
A) summation operators
B) letters in capitals
C) Greek letters
D) subscripted variables
A) summation operators
B) letters in capitals
C) Greek letters
D) subscripted variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to statistical notations, what does Σ stand for?
A) to act as a summation operator
B) to represent sample statistics
C) to represent population measures
D) to represent the number of items in a population
A) to act as a summation operator
B) to represent sample statistics
C) to represent population measures
D) to represent the number of items in a population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following does the second quartile of the costs per order indicate?
A) 2% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $114.84.
B) 20% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $1,200.12.
C) 5% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $229.36.
D) 50% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $286.16.
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following does the second quartile of the costs per order indicate?
A) 2% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $114.84.
B) 20% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $1,200.12.
C) 5% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $229.36.
D) 50% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $286.16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Which of the following represents the proportion of the total number of observations that fall at or below the upper limit of each group?
A) Percentile
B) Pareto chart
C) Frequency distribution
D) Cumulative relative frequency
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-Which of the following represents the proportion of the total number of observations that fall at or below the upper limit of each group?
A) Percentile
B) Pareto chart
C) Frequency distribution
D) Cumulative relative frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-What is the rank of the 42nd percentile of the costs per order ?
A) 17
B) 13.35
C) 19
D) 33.75
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-What is the rank of the 42nd percentile of the costs per order ?
A) 17
B) 13.35
C) 19
D) 33.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Use the data given below to answer the following question.
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-What is the cumulative relative frequency of Ranks 1 and 2?
A) 0.80
B) 0.15
C) 0.30
D) 0.25
Following is the purchase order database of 'The Chef Says So', a restaurant in New York, over the last quarter April-June).
-What is the cumulative relative frequency of Ranks 1 and 2?
A) 0.80
B) 0.15
C) 0.30
D) 0.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following observations is closest to the third quartile?
A) 35 N102 nuts for $190.40
B) 59 S103 screws for $556.96
C) 13 N103 nuts for $22.62
D) 2 NG102 nailgun packs for $550.90
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following observations is closest to the third quartile?
A) 35 N102 nuts for $190.40
B) 59 S103 screws for $556.96
C) 13 N103 nuts for $22.62
D) 2 NG102 nailgun packs for $550.90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true from the equation: = 0, where is the mean of the sample?
A) The sum of the deviations above the mean are the same as the sum of the deviations below the mean
B) Half the data lie above the mean of the values
C) The specific set of values does not have any outliers affecting the mean
D) Half the data lie below the mean of the values
A) The sum of the deviations above the mean are the same as the sum of the deviations below the mean
B) Half the data lie above the mean of the values
C) The specific set of values does not have any outliers affecting the mean
D) Half the data lie below the mean of the values

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the data given below to answer the following questions).
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following does the 38th percentile of the costs per order indicate?
A) 62% of the costs per order are more than or equal to $190.40.
B) 38% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $189.20.
C) 62% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $484.16.
D) 38% of the costs per order are more than or equal to $501.80.
Following is an extract from the Cost per Order Database of Grogtes LLC.
-Which of the following does the 38th percentile of the costs per order indicate?
A) 62% of the costs per order are more than or equal to $190.40.
B) 38% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $189.20.
C) 62% of the costs per order are less than or equal to $484.16.
D) 38% of the costs per order are more than or equal to $501.80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the table below to answer the following questions).
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the mean cost per order.
A) $220.54
B) $174.70
C) $159
D) $88
Below is a table showing the costs per order of items bought by a computer hardware store.
-Calculate the mean cost per order.
A) $220.54
B) $174.70
C) $159
D) $88

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following will give the value for the third quartile?
A) PERCENTILE.INCarray, 0.75)
B) QUARTILE.INCarray, 0.75)
C) DECILE.INCarray, 0.30)
D) QUARTILE.INCarray, 0.25)
A) PERCENTILE.INCarray, 0.75)
B) QUARTILE.INCarray, 0.75)
C) DECILE.INCarray, 0.30)
D) QUARTILE.INCarray, 0.25)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the z-score formula, which of the following is true if the value in the numerator is a negative value?
A) that the xi value lies to the left of the mean
B) that the mean is of lesser value than the xi value
C) that the mean is of negative value
D) that the numerator value cannot be divided by the standard deviation
A) that the xi value lies to the left of the mean
B) that the mean is of lesser value than the xi value
C) that the mean is of negative value
D) that the numerator value cannot be divided by the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The difference between the first and third quartiles is referred to as the .
A) standard deviation
B) variance
C) interquartile range
D) midrange
A) standard deviation
B) variance
C) interquartile range
D) midrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is a difference between a mean and a median?
A) A mean divides the data half above it and half below it; a median does not.
B) A median is not affected by outliers; a mean is affected by outliers.
C) A mean is an observation that occurs most frequently; a median is the average of all observations.
D) A median is not meaningful for ratio data; a mean is meaningful to ratio data.
A) A mean divides the data half above it and half below it; a median does not.
B) A median is not affected by outliers; a mean is affected by outliers.
C) A mean is an observation that occurs most frequently; a median is the average of all observations.
D) A median is not meaningful for ratio data; a mean is meaningful to ratio data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is the z-score equation for the ith observation?
A) zt =
B) zi =
C) z1=
D) zi =
A) zt =
B) zi =
C) z1=
D) zi =

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The measure of location that specifies the middle value when the data are arranged from least to greatest is the .
A) outlier
B) mean
C) median
D) mode
A) outlier
B) mean
C) median
D) mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following describes standard deviation?
A) It is the average of the greatest and least values in the data set.
B) It is the square root of the variance.
C) It is the difference between the first and third quartiles of a data set.
D) It is the average of the squared deviations of the observations from the mean.
A) It is the average of the greatest and least values in the data set.
B) It is the square root of the variance.
C) It is the difference between the first and third quartiles of a data set.
D) It is the average of the squared deviations of the observations from the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is an example of a measure of dispersion?
A) median
B) mode
C) variance
D) midrange
A) median
B) mode
C) variance
D) midrange

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following describes variance?
A) It is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value in the data set.
B) It is the difference between the first and third quartiles of a data set.
C) It is the average of the squared deviations of the observations from the mean.
D) It is the average of the greatest and least values in the data set.
A) It is the difference between the maximum value and the minimum value in the data set.
B) It is the difference between the first and third quartiles of a data set.
C) It is the average of the squared deviations of the observations from the mean.
D) It is the average of the greatest and least values in the data set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following types of conditions is most likely to render a midrange value useless?
A) having repetitious values in the data set
B) having the data arranged from least to greatest in value
C) having a small sample size
D) having extreme values in a data
A) having repetitious values in the data set
B) having the data arranged from least to greatest in value
C) having a small sample size
D) having extreme values in a data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is true for a mode?
A) Modes are the mid values of data arranged from least to greatest.
B) Modes are affected by outliers.
C) Modes cannot be used in data having repetitious values.
D) The highest bar in a histogram is its mode.
A) Modes are the mid values of data arranged from least to greatest.
B) Modes are affected by outliers.
C) Modes cannot be used in data having repetitious values.
D) The highest bar in a histogram is its mode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the equation Cp = upper specification - lower specification)/total variation, what does Cp denote?
A) capacity variation index
B) capability pattern
C) process capability index
D) capability push
A) capacity variation index
B) capability pattern
C) process capability index
D) capability push

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is true of variance?
A) The formula to calculate variance of a population is not the same as the formula to calculate variance of a sample.
B) Its value is inversely proportional to the degree to which the data is spread from the mean.
C) It only requires the middle 50% of data to be calculated.
D) It is the square root of standard deviation.
A) The formula to calculate variance of a population is not the same as the formula to calculate variance of a sample.
B) Its value is inversely proportional to the degree to which the data is spread from the mean.
C) It only requires the middle 50% of data to be calculated.
D) It is the square root of standard deviation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is true of midspread?
A) It is an example of a measure of location.
B) It is calculated by finding the difference between the highest and lowest values in the data set.
C) It is affected by extreme values.
D) It is calculated using only the middle 50% of the data.
A) It is an example of a measure of location.
B) It is calculated by finding the difference between the highest and lowest values in the data set.
C) It is affected by extreme values.
D) It is calculated using only the middle 50% of the data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
states that for any set of data, the proportion of values that lie within k standard deviations k > 1) of the mean is at least 1 - 1/k2.
A) Prime number theorem
B) Bertrand's postulate
C) Oppermann's conjecture
D) Chebyshev's theorem
A) Prime number theorem
B) Bertrand's postulate
C) Oppermann's conjecture
D) Chebyshev's theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is a similarity between a midrange and a mean?
A) Both measures are calculated using all the values in a data set.
B) Both measures are affected by outliers.
C) Both measures divide the data into two equal halves.
D) Both measures can only be used for small sample sizes.
A) Both measures are calculated using all the values in a data set.
B) Both measures are affected by outliers.
C) Both measures divide the data into two equal halves.
D) Both measures can only be used for small sample sizes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following describes dispersion in statistics?
A) the degree of variation in the data
B) the central value in the data
C) the frequency of values in the data
D) the measure of outliers in the data
A) the degree of variation in the data
B) the central value in the data
C) the frequency of values in the data
D) the measure of outliers in the data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Using Chebyshev's theorem for standard deviation, calculate the percentage of data that lie within five standard deviations of the mean.
A) 89%
B) 75%
C) 96%
D) 50%
A) 89%
B) 75%
C) 96%
D) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The is the average of the greatest and least values in the data set.
A) mean
B) median
C) midrange
D) mode
A) mean
B) median
C) midrange
D) mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is true for a median?
A) A median is only meaningful for interval or ordinal data and not for ratio data.
B) Medians can be calculated no matter how the data is arranged.
C) Medians are affected by outliers.
D) For an even number of observations, the median is the mean of the two middle numbers.
A) A median is only meaningful for interval or ordinal data and not for ratio data.
B) Medians can be calculated no matter how the data is arranged.
C) Medians are affected by outliers.
D) For an even number of observations, the median is the mean of the two middle numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The is the observation that occurs most frequently.
A) mode
B) mean
C) outlier
D) median
A) mode
B) mean
C) outlier
D) median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How is the return to risk described in financial statistics?
A) as the relative measure of the distance an observation is from the mean
B) as the reciprocal of coefficient of variation
C) as the square root of variance
D) as the ratio of excess returns to its standard deviation
A) as the relative measure of the distance an observation is from the mean
B) as the reciprocal of coefficient of variation
C) as the square root of variance
D) as the ratio of excess returns to its standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is the equation used for computing the sample correlation coefficient?
A) rxy = cov(X,Y)(sxsy)
B) rxy =
C) rxy =
D) rxy =
A) rxy = cov(X,Y)(sxsy)
B) rxy =
C) rxy =
D) rxy =

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
is a measure of the linear association between two variables, X and Y.
A) Kurtosis
B) Proportion
C) Skewness
D) Covariance
A) Kurtosis
B) Proportion
C) Skewness
D) Covariance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following cases require the mean of a sample to be calculated using the formula = where N represents the sample size?
A) the sample has no mode value
B) there is direct access to the raw data
C) sample data are grouped in a frequency distribution
D) the coefficient of skewness is 1 or less than -1
A) the sample has no mode value
B) there is direct access to the raw data
C) sample data are grouped in a frequency distribution
D) the coefficient of skewness is 1 or less than -1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the spreadsheet below to answer the following questions).
Below is the table showing rate of shoes sold per day and the highest-priced shoe sold that day for a one-week period. The rate of shoes sold per day X) and the price of the shoes Y).
-Use Excel to calculate the variance of X.
A) 271.33
B) 16.47
C) 49.57
D) 7.04
Below is the table showing rate of shoes sold per day and the highest-priced shoe sold that day for a one-week period. The rate of shoes sold per day X) and the price of the shoes Y).
-Use Excel to calculate the variance of X.
A) 271.33
B) 16.47
C) 49.57
D) 7.04

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In finance, the is the ratio of a fund's excess returns annualized total returns minus Treasury bill returns) to its standard deviation.
A) field ratio
B) Sortino ratio
C) Calmar ratio
D) Sharpe ratio
A) field ratio
B) Sortino ratio
C) Calmar ratio
D) Sharpe ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the spreadsheet below to answer the following questions).
Below is the table showing rate of shoes sold per day and the highest-priced shoe sold that day for a one-week period. The rate of shoes sold per day X) and the price of the shoes Y).
-Use Excel to calculate the mean for X.
A) 16.71
B) 7.04
C) 2.67
D) 0.02
Below is the table showing rate of shoes sold per day and the highest-priced shoe sold that day for a one-week period. The rate of shoes sold per day X) and the price of the shoes Y).
-Use Excel to calculate the mean for X.
A) 16.71
B) 7.04
C) 2.67
D) 0.02

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is true of covariance, between two variables, when one of the deviations from the mean is positive and the other is negative?
A) the degree of linear association is high between the two variables
B) there is no covariance between the two variables
C) the covariance will be negative
D) the covariance will be positive
A) the degree of linear association is high between the two variables
B) there is no covariance between the two variables
C) the covariance will be negative
D) the covariance will be positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is true of the coefficient of skewness CS)?
A) If the CS is positive, the distribution of values tails off to the left.
B) If the CS value is between 0.5 and 1, the skewness is considered to be moderate.
C) If the CS is closer to zero, the degree of skewness is considered to be high.
D) If the CS value is between -0.5 and -1, the skewness is considered negligible.
A) If the CS is positive, the distribution of values tails off to the left.
B) If the CS value is between 0.5 and 1, the skewness is considered to be moderate.
C) If the CS is closer to zero, the degree of skewness is considered to be high.
D) If the CS value is between -0.5 and -1, the skewness is considered negligible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A z-score of 1.0 means that .
A) the observation is -1.0 standard deviation to the right of the mean
B) the observation is -1.0 standard deviation to the left of the mean
C) the observation has no deviation from the mean
D) the observation is 1.0 standard deviation to the right of the mean
A) the observation is -1.0 standard deviation to the right of the mean
B) the observation is -1.0 standard deviation to the left of the mean
C) the observation has no deviation from the mean
D) the observation is 1.0 standard deviation to the right of the mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
is a measure of the linear relationship between two variables, X and Y, which does not depend on the units of measurement.
A) Kurtosis
B) Proportion
C) Skewness
D) Correlation
A) Kurtosis
B) Proportion
C) Skewness
D) Correlation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Calculate the coefficient of variation from the following data: z-score = 1.32; standard deviation = 0.173; mean = 4.7; total variation = 0.6
A) 27.16
B) 156.66
C) 0.04
D) -0.5
A) 27.16
B) 156.66
C) 0.04
D) -0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In statistics, refers to the peakedness or flatness of a histogram.
A) Sharpe ratio
B) entropy rate
C) Markov chain
D) kurtosis
A) Sharpe ratio
B) entropy rate
C) Markov chain
D) kurtosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is the equation for calculating the coefficient of variation CV)?
A) CV = standard deviation/mean
B) CV = standard deviation - z-score/mean total variation)
C) CV = value of observation's distance from mean/standard deviation
D) CV = mean/standard deviation)2
A) CV = standard deviation/mean
B) CV = standard deviation - z-score/mean total variation)
C) CV = value of observation's distance from mean/standard deviation
D) CV = mean/standard deviation)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The is a formal statistical measure for categorical data, such as defects or errors in quality control applications or consumer preferences in market research.
A) variance
B) proportion
C) mean
D) skewness
A) variance
B) proportion
C) mean
D) skewness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For two variables, a positive correlation coefficient indicates .
A) a linear relationship exists for which one variable increases as the other also increases
B) a linear relationship exists for one variable that increases while the other decreases
C) that the two variables have no linear relationship with each other
D) a nonlinear relationship with no linear correlation between the two variables
A) a linear relationship exists for which one variable increases as the other also increases
B) a linear relationship exists for one variable that increases while the other decreases
C) that the two variables have no linear relationship with each other
D) a nonlinear relationship with no linear correlation between the two variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following values of the coefficients of variation of stocks represents the least risky stock?
A) 1.0
B) 0.005
C) 0.5
D) 0.045
A) 1.0
B) 0.005
C) 0.5
D) 0.045

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following describes a positively skewed histogram?
A) a histogram that tails off toward the right
B) a histogram that has no fluctuation in mass
C) a histogram where more mass tails off toward the left
D) a histogram where mass is only concentrated in the middle
A) a histogram that tails off toward the right
B) a histogram that has no fluctuation in mass
C) a histogram where more mass tails off toward the left
D) a histogram where mass is only concentrated in the middle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The measures the degree of asymmetry of observations around the mean.
A) coefficient of variation
B) return to risk factor
C) coefficient of skewness
D) coefficient of kurtosis
A) coefficient of variation
B) return to risk factor
C) coefficient of skewness
D) coefficient of kurtosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Describe and construct a cross-tabulation showing the region-wise percentage breakdown of purchase of glass bottles and silver spoons and visually represent the data in a 3-D column chart.
Counts: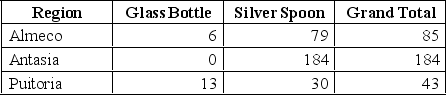 Percentages by Region:
Percentages by Region: 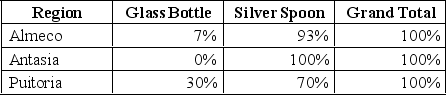
Counts:
 Percentages by Region:
Percentages by Region: 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 109 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



