Deck 8: Molecular Biology of Transcription and Rna Processing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Molecular Biology of Transcription and Rna Processing
1
What are two distinguishing features of RNA?
A) RNA has a ribose sugar and uracil nitrogenous base.
B) RNA contains phophodiester bonds as part of its sugar backbone.
C) RNA forms a double helix of reverse complementary strands.
D) RNA contains a methylated form of thymine.
E) RNA contains a pyrophosphate group bound to the ribose.
A) RNA has a ribose sugar and uracil nitrogenous base.
B) RNA contains phophodiester bonds as part of its sugar backbone.
C) RNA forms a double helix of reverse complementary strands.
D) RNA contains a methylated form of thymine.
E) RNA contains a pyrophosphate group bound to the ribose.
A
2
Which region(s) of a gene are NOT found within the mRNA transcript?
A) promoter and termination region
B) promoter region
C) stop codon
D) termination region
E) promoter and stop codon
A) promoter and termination region
B) promoter region
C) stop codon
D) termination region
E) promoter and stop codon
A
3
You want to design a drug that prevents transcription of eukaryotic mRNAs but does not affect transcription of other RNAs. What enzyme would you target?
A) RNA polymerase III
B) RNA polymerase I
C) ribozyme
D) methyl transferase
E) RNA polymerase II
A) RNA polymerase III
B) RNA polymerase I
C) ribozyme
D) methyl transferase
E) RNA polymerase II
E
4
What is the type of each eukaryotic protein that primarily transcribes mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA, respectively?
A) RNA Polymerase I, II, III
B) RNA Polymerase II, III, I
C) RNA Polymerase I, III, II
D) RNA Polymerase II, I, III
E) RNA Polymerase III, II, I
A) RNA Polymerase I, II, III
B) RNA Polymerase II, III, I
C) RNA Polymerase I, III, II
D) RNA Polymerase II, I, III
E) RNA Polymerase III, II, I

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements accurately describes tRNA?
A) tRNAs are a variety of lengths and fold into a variety of shapes.
B) Amino acids are bound to the 5' end of the tRNA.
C) Wobble in the anticodon allows a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons.
D) Post- transcriptional modifications of tRNAs are not necessary for their function.
E) All organisms produce tRNAs corresponding to the 61 amino- acid coding codons.
A) tRNAs are a variety of lengths and fold into a variety of shapes.
B) Amino acids are bound to the 5' end of the tRNA.
C) Wobble in the anticodon allows a single tRNA to bind to multiple codons.
D) Post- transcriptional modifications of tRNAs are not necessary for their function.
E) All organisms produce tRNAs corresponding to the 61 amino- acid coding codons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the consensus sequence for the Pribnow box from these sequences? 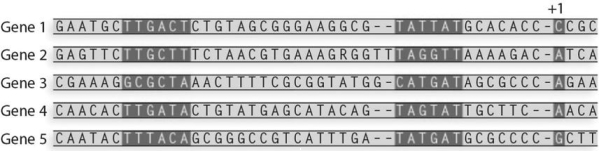
A) TATGAT
B) TATTAT
C) TAGTAT
D) ACCA
E) TTGATA

A) TATGAT
B) TATTAT
C) TAGTAT
D) ACCA
E) TTGATA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
RNA polymerase I transcribes which tandem- repeat genes in nucleoli?
A) mRNA
B) tRNA
C) siRNA
D) rRNA
E) all types of RNA
A) mRNA
B) tRNA
C) siRNA
D) rRNA
E) all types of RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes produce which of the following types of RNA?
A) siRNA, tRNA, miRNA
B) rRNA, siRNA, snRNA
C) mRNA, gRNA, siRNA
D) miRNA, rRNA, snRNA
E) mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
A) siRNA, tRNA, miRNA
B) rRNA, siRNA, snRNA
C) mRNA, gRNA, siRNA
D) miRNA, rRNA, snRNA
E) mRNA, tRNA, rRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a given bacterium, transcription of housekeeping genes is normal, but genes involved in nitrogen metabolism, stress, and chemotaxis are disrupted. Which sigma subunit is INTACT?
A) a32
B) a28
C) a70
D) a54
E) a35
A) a32
B) a28
C) a70
D) a54
E) a35

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which type of research technique was used to track newly synthesized RNA within a eukaryotic cell?
A) DNA footprint protection assay
B) in situ hybridization
C) pulse- chase
D) Southern blotting
E) band shift assay
A) DNA footprint protection assay
B) in situ hybridization
C) pulse- chase
D) Southern blotting
E) band shift assay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the significance of the open complex when the RNA Polymerase binds the DNA?
A) The growing RNA molecule can now fit inside the active site of the RNA Polymerase.
B) It permits transcription factors to bind to the RNA Polymerase.
C) It assists with propagation of the RNA Polymerase along the DNA helix.
D) The RNA Polymerase binds the single- stranded coding strand in its active site.
E) The RNA Polymerase binds the single- stranded template strand in its active site.
A) The growing RNA molecule can now fit inside the active site of the RNA Polymerase.
B) It permits transcription factors to bind to the RNA Polymerase.
C) It assists with propagation of the RNA Polymerase along the DNA helix.
D) The RNA Polymerase binds the single- stranded coding strand in its active site.
E) The RNA Polymerase binds the single- stranded template strand in its active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which assay allows you to identify the exact location of the protein- binding sequence within a promoter?
A) DNA footprint protection assay
B) pulse- chase assay
C) western/immuno blotting
D) in situ hybridization
E) Southern blotting
A) DNA footprint protection assay
B) pulse- chase assay
C) western/immuno blotting
D) in situ hybridization
E) Southern blotting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the role of a promoter region of a gene?
A) Protect the gene from mutations in intergenic regions.
B) Recruit transcription factors that form the initiation complex.
C) Recruit RNA Polymerase to the transcriptional start site.
D) Recruit rho protein to assist in transcription.
E) Serve as the original region of transcription of a gene.
A) Protect the gene from mutations in intergenic regions.
B) Recruit transcription factors that form the initiation complex.
C) Recruit RNA Polymerase to the transcriptional start site.
D) Recruit rho protein to assist in transcription.
E) Serve as the original region of transcription of a gene.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is part of a DNA molecule?
A) sigma
B) activator
C) RNA polymerase
D) promoter
E) transcription factor
A) sigma
B) activator
C) RNA polymerase
D) promoter
E) transcription factor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What must eukaryotes do to initiate transcription of a gene?
A) Recruit general transcription factors to produce an open complex and then recruit RNA Polymerase.
B) Bind RNA Polymerase to displace histone proteins that binding DNA in the promoter region.
C) Bind transcription factors from enhancer sequences to the RNA Polymerase.
D) Recruit the transcription factors and RNA Polymerase that compose the pre- initiation complex.
E) Open the DNA template and then bind RNA Polymerase at the transcriptional initiation site.
A) Recruit general transcription factors to produce an open complex and then recruit RNA Polymerase.
B) Bind RNA Polymerase to displace histone proteins that binding DNA in the promoter region.
C) Bind transcription factors from enhancer sequences to the RNA Polymerase.
D) Recruit the transcription factors and RNA Polymerase that compose the pre- initiation complex.
E) Open the DNA template and then bind RNA Polymerase at the transcriptional initiation site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following are present in your liver cells?
A) enhancers of genes expressed in the kidney
B) promoters of genes expressed in the kidney
C) promoters of genes expressed in the liver
D) enhancers of genes expressed in the liver
E) All enhancers and promoters are present in liver cells
A) enhancers of genes expressed in the kidney
B) promoters of genes expressed in the kidney
C) promoters of genes expressed in the liver
D) enhancers of genes expressed in the liver
E) All enhancers and promoters are present in liver cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the - 35 consensus sequence for the following sequences? 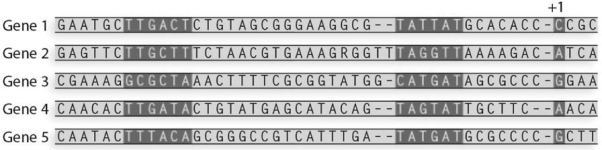
A) ACAA
B) TTGATA
C) TATGAT
D) TATTAT
E) TAGTAT

A) ACAA
B) TTGATA
C) TATGAT
D) TATTAT
E) TAGTAT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A gene has acquired a mutation in which the protein product has 50 additional amino acids at the end. Which region of the gene was likely mutated?
A) coding region
B) stop colon
C) terminator sequence
D) promoter sequence
E) start codon
A) coding region
B) stop colon
C) terminator sequence
D) promoter sequence
E) start codon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why does rho- dependent transcriptional termination in bacteria require the rho protein?
A) The rho protein assists in formation of the termination stem- loop that pauses the RNA Polymerase.
B) RNA Polymerase stalls at various sites in the gene and rho helps push RNA Polymerase to the end of the gene.
C) The rho protein helps unwind the stem- loop structure after the RNA has been released by RNA Polymerase.
D) The stem- loop is insufficiently stable to displace the RNA Polymerase by itself and needs rho protein to assist.
E) RNA Polymerase stalls on the termination stem- loop and rho is needed to displace the RNA Polymerase.
A) The rho protein assists in formation of the termination stem- loop that pauses the RNA Polymerase.
B) RNA Polymerase stalls at various sites in the gene and rho helps push RNA Polymerase to the end of the gene.
C) The rho protein helps unwind the stem- loop structure after the RNA has been released by RNA Polymerase.
D) The stem- loop is insufficiently stable to displace the RNA Polymerase by itself and needs rho protein to assist.
E) RNA Polymerase stalls on the termination stem- loop and rho is needed to displace the RNA Polymerase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
You wish to create a mutation that prevents access of RNA polymerase to the gene. Which region of a gene would you mutate?
A) terminator sequence
B) stop codon
C) coding region
D) start codon
E) promoter sequence
A) terminator sequence
B) stop codon
C) coding region
D) start codon
E) promoter sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
miRNA regulates protein production through which process?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Using the accompanying diagram, which of the following corresponds to the 3' untranslated region? 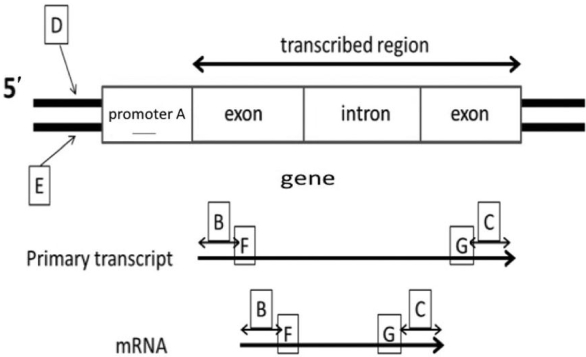
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) G
E) F

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) G
E) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the purpose of alternative splicing in eukaryotic cells?
A) Improve the efficiency of transcription and translation.
B) Regulate the quantity of any single protein being produced in the cell.
C) Increase the number of genes that do not have to contain introns.
D) Produce multiple types of tRNAs that can bind to different codons.
E) Produce multiple polypeptide sequences from a single primary transcript.
A) Improve the efficiency of transcription and translation.
B) Regulate the quantity of any single protein being produced in the cell.
C) Increase the number of genes that do not have to contain introns.
D) Produce multiple types of tRNAs that can bind to different codons.
E) Produce multiple polypeptide sequences from a single primary transcript.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
One type of RNA editing involves inserting uracils into edited mRNA with the assistance of which type of specialized RNA?
A) telomerase RNA
B) guide RNA
C) post- transcriptional editor RNA
D) transposon RNA
E) small nucleolar RNA
A) telomerase RNA
B) guide RNA
C) post- transcriptional editor RNA
D) transposon RNA
E) small nucleolar RNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A cell has a defect in polyadenylation of mRNA. The RNA transcripts encoding which type of protein would NOT be affected by this defect because they are not polyadenylated?
A) SR proteins
B) histone proteins
C) DNA binding proteins
D) transcription factors
E) transmembrane proteins
A) SR proteins
B) histone proteins
C) DNA binding proteins
D) transcription factors
E) transmembrane proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which three types of RNAs are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If transcription of this gene occurs from left to right in the accompanying diagram, which DNA strand is the CODING (non- template) strand? 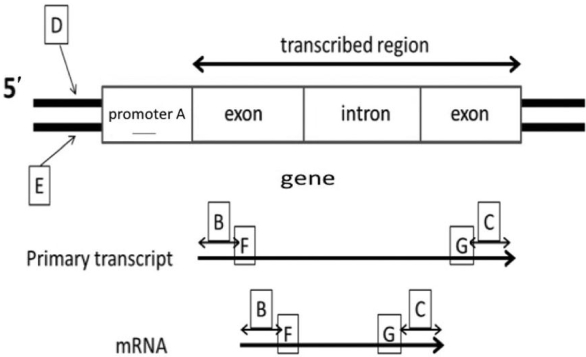
A) impossible to determine
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) impossible to determine
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What are the two chemical structures found in RNA but not DNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In humans, the 30S pre- RNA transcript yields three rRNA segments following transcription and RNA cleavage. Which RNA transcripts are generated by the 30S pre- RNA transcript in E. coli?
A) two tRNA transcripts
B) three rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S) and two tRNA transcripts
C) three rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S)
D) three rRNAs (5.8S, 18S, and 28S) and two tRNA transcripts
E) two rRNAs (15S each)
A) two tRNA transcripts
B) three rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S) and two tRNA transcripts
C) three rRNAs (5S, 16S, and 23S)
D) three rRNAs (5.8S, 18S, and 28S) and two tRNA transcripts
E) two rRNAs (15S each)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You wish to prevent transcription of all three types of RNA in bacteria. How many different types of RNA polymerase would you need to inhibit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What are the mechanisms for transcription termination in bacteria?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What are catalytically active RNAs that can activate processes such as self- splicing?
A) snRNAs
B) ribosomes
C) pre- mRNAs
D) rnzymes
E) ribozymes
A) snRNAs
B) ribosomes
C) pre- mRNAs
D) rnzymes
E) ribozymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A plant cell exhibits defects in transcription of transfer RNA genes. The gene encoding which polymerase is likely to be mutated in this cell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Eukaryotes have how many different RNA polymerases?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the general name for the components of the spliceosome, which removes introns from mRNAs?
A) small interfering RNA enhancers
B) small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
C) lariat intronic nucleolar proteins
D) microRNA activators
E) branch point adenine recognition proteins
A) small interfering RNA enhancers
B) small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
C) lariat intronic nucleolar proteins
D) microRNA activators
E) branch point adenine recognition proteins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What defines the end of a eukaryotic gene?
A) A 3' UTR of at least 25 nucleotides recruits an RNase that cleaves the pre- mRNA.
B) Presence of a polyadenylation signal sequence leads to cleavage of the pre- mRNA.
C) A stem- loop structure in the transcriptional terminator region stalls the RNA polymerase.
D) There is no clearly defined end to eukaryotic genes, unlike for bacterial genes.
E) Presence of a stop codon leads to RNA polymerase stalling and ceasing transcription.
A) A 3' UTR of at least 25 nucleotides recruits an RNase that cleaves the pre- mRNA.
B) Presence of a polyadenylation signal sequence leads to cleavage of the pre- mRNA.
C) A stem- loop structure in the transcriptional terminator region stalls the RNA polymerase.
D) There is no clearly defined end to eukaryotic genes, unlike for bacterial genes.
E) Presence of a stop codon leads to RNA polymerase stalling and ceasing transcription.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which type of RNA interacts with nuclear proteins to form a ribonucleoprotein complex responsible for intron removal?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The rat a- tropomyosin (a- Tm) gene produces nine different mature mRNA proteins from a single gene using which three "alternative" mechanisms?
A) 5' cap, branch points, polyadenylation
B) 5' cap, self- splicing, polyadenylation
C) splicing, start codon, stop codon
D) promoters, start codon, poly(A) signal sequences
E) splicing, promoters, and polyadenylation
A) 5' cap, branch points, polyadenylation
B) 5' cap, self- splicing, polyadenylation
C) splicing, start codon, stop codon
D) promoters, start codon, poly(A) signal sequences
E) splicing, promoters, and polyadenylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which enzyme is required to initiate 5' capping of eukaryotic mRNA transcripts by removing the terminal phosphate group?
A) phosphodiesterase
B) adenylyl cyclase
C) ribozyme
D) methyl transferase
E) guanylyl transferase
A) phosphodiesterase
B) adenylyl cyclase
C) ribozyme
D) methyl transferase
E) guanylyl transferase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Transcription of inverted repeats produces an mRNA with complementary segments that fold to form what type of secondary structure?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What proteins bind to silencer sequences, forming a protein "bridge" that bends the DNA over the promoter and prevents transcription?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the mechanism(s) used by bacteria and eukaryotes for transcription termination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What proteins are bound to enhancers, forming a protein "bridge" that bends the DNA over the promoter to initiate transcription?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
RNA polymerase is called a , meaning it is an intact complex with full enzymatic capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Prokaryotes have a - 10 and - 35 consensus sequence in their promoter. What are the three eukaryotic promoter sequence elements (or "boxes")?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Intron self- splicing occurs when two reactions excise the intron and allow exons to ligate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Processing of the 30S pre- RNA transcript in humans produces which three rRNAs after enzymatic cleavage?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Polyadenylation begins with the binding of near a six- nucleotide mRNA sequence, AAUAAA, downstream of the stop codon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What are the three types of posttranscriptional processing, and what are the consequences of preventing each of these modifications in terms of gene expression?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What proteins aid in the recognition of the promoter sequence and binding of RNA polyme in eukaryotes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Describe the three main differences between bacterial and eukaryotic mRNA transcripts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the following prokaryotic DNA sequence, label the highlighted regions.
 Using the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, describe the relationship between the highlighted regions and how mutations in each region may affect gene expression.
Using the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, describe the relationship between the highlighted regions and how mutations in each region may affect gene expression.
 Using the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, describe the relationship between the highlighted regions and how mutations in each region may affect gene expression.
Using the prokaryotic DNA sequence above, describe the relationship between the highlighted regions and how mutations in each region may affect gene expression.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Describe how band/mobility shift assays and DNA footprint protection assays can be used to identify promoter regions in DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In intrinsic termination, inverted repeat DNA sequences followed immediately by a string of _ produce an mRNA stem- loop, followed by a string of .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



