Deck 10: Corporate Bonds: Terms, Issuance, and Valuation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/21
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Corporate Bonds: Terms, Issuance, and Valuation
1
Essentially, a convertible bond is a portfolio of:
A)a bond and an automobile whose top can be removed.
B)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and shares of the issuing firm's stock.
C)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and a call option on the firm's stock.
D)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and a put option on the firm's stock.
A)a bond and an automobile whose top can be removed.
B)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and shares of the issuing firm's stock.
C)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and a call option on the firm's stock.
D)an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and a put option on the firm's stock.
an otherwise equivalent nonconvertible bond and a call option on the firm's stock.
2
The next two problems require the bond yield spread matrix given below:
-Using the bond yield spread matrix above, calculate the fair yield on a 20-year callable corporate bond that is rated "BBB" by S&P, given also that the yield on 20-year Treasuries is 5.55%.
A)1.66%
B)7.21%
C)6.54%
D)8.89%
-Using the bond yield spread matrix above, calculate the fair yield on a 20-year callable corporate bond that is rated "BBB" by S&P, given also that the yield on 20-year Treasuries is 5.55%.
A)1.66%
B)7.21%
C)6.54%
D)8.89%
7.21%
3
The public market for new speculative-grade bonds, also known as high-yield or junk bonds, was created virtually single-handedly by Michael Milken and his firm, Drexel Burnham Lambert, in the late 1970s.Prior to that time, the only corporate bonds that carried a speculative-grade rating were so-called _______, bonds that initially garnered an investment-grade rating, but later the issuer experienced financial distress so that their rating fell into the speculative-grade category.
A)discount bonds
B)concession bonds
C)fallen angels
D)cut rate bonds
A)discount bonds
B)concession bonds
C)fallen angels
D)cut rate bonds
fallen angels
4
Investment banks form a temporary alliance, called a ______, to underwrite a bond issue.
A)selling group
B)syndicate
C)coalition
D)pricing association
A)selling group
B)syndicate
C)coalition
D)pricing association

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Underwriter generally places non-solicitation advertisements in the Wall Street Journal and/or other important newspapers notifying the public of the availability of an issue.These are called _______.
A)tombstone ads
B)headstone ads
C)notifications of availability
D)bond issue schedules
A)tombstone ads
B)headstone ads
C)notifications of availability
D)bond issue schedules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The next two problems require the bond yield spread matrix given below:
-Using the bond yield spread matrix above, calculate the fair yield on a 5-year noncallable corporate bond that is rated "B" by S&P, given also that the yield on 5-year Treasuries is 4.44%.
A)4.15%
B)6.15%
C)8.59%
D)10.59%
-Using the bond yield spread matrix above, calculate the fair yield on a 5-year noncallable corporate bond that is rated "B" by S&P, given also that the yield on 5-year Treasuries is 4.44%.
A)4.15%
B)6.15%
C)8.59%
D)10.59%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In 1982, the SEC adopted Rule 415, also known as the ____rule, which allows qualifying firms to register a bond offering and then sell it either as a whole or piecemeal at any time over several years.
A)delayed registration
B)deferred registration
C)shelf registration
D)piecemeal registration
A)delayed registration
B)deferred registration
C)shelf registration
D)piecemeal registration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Compute the promised yield to maturity and expected return to maturity on a default-risky 3-year pure-discount corporate bond that has a current price of $543.With a probability of 0.6, the issuer will repay the principal of $1,000 at maturity.However, the probability is 0.4 that the issuer will default, in which case bondholders will receive only $200 per bond.
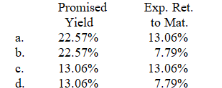
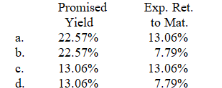

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Bond contracts generally include restrictive covenants, designed to protect the interests of the bondholders.Typical covenants restrict all of the following EXCEPT:
A)the borrowing firm's investment activities.
B)the borrowing firm's ability to issue additional debt.
C)the borrowing firm's dividend policy.
D)the firm's hiring of management personnel.
A)the borrowing firm's investment activities.
B)the borrowing firm's ability to issue additional debt.
C)the borrowing firm's dividend policy.
D)the firm's hiring of management personnel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The _______provision in a corporate bond contract requires the firm to retire a specified percentage of the bonds each year, typically after a deferment period of 5 to 10 years.
A)sinking fund
B)call
C)put
D)conversion
A)sinking fund
B)call
C)put
D)conversion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Underwriter spreads on corporate bonds reflect substantial economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Simulations based on the Black-Scholes model indicate that, for all combinations of leverage (D/V) and firm risk ( ), debt risk:
A)increases as debt maturity increases.
B)decreases as debt maturity increases.
C)remains fairly constant as debt maturity increases.
A)increases as debt maturity increases.
B)decreases as debt maturity increases.
C)remains fairly constant as debt maturity increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Regarding corporate bonds, if the issuing firm does not pledge specific assets as collateral, the bond is called a _______.
A)debenture
B)mortgage
C)chattel mortgage
D)note
A)debenture
B)mortgage
C)chattel mortgage
D)note

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Standard & Poors ratings are grouped into two major categories, investment-grade and speculative- grade.Bonds that are rated (i) are included in the investment-grade group, while speculative-grade bonds are those rated (ii) .



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Conflicts of interest between a borrowing firm and its creditors.This problem is exacerbated in the case of a public bond, because the ownership of public bonds is generally dispersed among many bondholders.For these reasons, the interests of the investors in a public corporate bond are protected in part by the appointment of a _______, who is charged with monitoring the firm's compliance with the various terms, covenants, and provisions in the contract.
A)liaison officer
B)trustee
C)security officer
D)compliance guardian
A)liaison officer
B)trustee
C)security officer
D)compliance guardian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In response to competition from the Eurobond market, the SEC adopted ____in 1990, which allows firms to issue bonds in the U.S.market with minimal regulatory red tape as long as they are sold only to qualified investors (e.g., financial institutions).
A)the Nonregistration Exception
B)Qualified Investors Rule (QIR)
C)Rule 99B
D)Rule 144A
A)the Nonregistration Exception
B)Qualified Investors Rule (QIR)
C)Rule 99B
D)Rule 144A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The probability of a callable bond being called, and thus the yield premium that investors demand for the risk of a call, is directly related to:
A)the volatility of the bond's yield.
B)the deferment period.
C)the call price.
A)the volatility of the bond's yield.
B)the deferment period.
C)the call price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a firm attempts to call an outstanding convertible bond, the bondholders:
A)have the preemptory right to convert the bonds into stock.
B)must tender their bonds immediately and receive the call price.
C)must challenge management's decision to call the bonds via a proxy contest.
D)have the option to keep their bonds outstanding.
A)have the preemptory right to convert the bonds into stock.
B)must tender their bonds immediately and receive the call price.
C)must challenge management's decision to call the bonds via a proxy contest.
D)have the option to keep their bonds outstanding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Compute the promised yield to maturity and expected return to maturity on a default-risky 5-year pure-discount corporate bond that has a current price of $541.With a probability of 0.7, the issuer will repay the principal of $1,000 at maturity.However, the probability is 0.3 that the issuer will default, in which case bondholders will receive only $500 per bond.
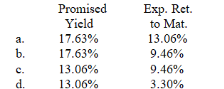
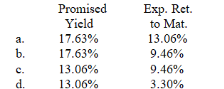

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In _______, an issuing firm solicits bids from among several investment banks for the job of underwriting a bond issue.
A)competitive bidding
B)negotiated underwriting
C)aggressive bidding
D)bargain bidding
A)competitive bidding
B)negotiated underwriting
C)aggressive bidding
D)bargain bidding

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Yield spreads on new convertible bonds generally are negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 21 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



