Deck 7: Coenzymes and Vitamins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Coenzymes and Vitamins
1
The reactive center of coenzyme A is
A) ADP.
B) pantothenate.
C) b-alanine.
D) 2-mercaptoethylamine.
E) serine.
A) ADP.
B) pantothenate.
C) b-alanine.
D) 2-mercaptoethylamine.
E) serine.
2-mercaptoethylamine.
2
The role of zinc in the mechanisms of carbonic anhydrase is to
A) maintain the configuration of the holoenzyme.
B) bind to three histidine residues.
C) produce a nucleophilic attack on the substrate.
D) promote ionization of bound water.
E) produce an electrophilic attack on the substrate.
A) maintain the configuration of the holoenzyme.
B) bind to three histidine residues.
C) produce a nucleophilic attack on the substrate.
D) promote ionization of bound water.
E) produce an electrophilic attack on the substrate.
promote ionization of bound water.
3
Because coenzymes are specific for the chemical groups that they accept and donate, they are referred to as
A) cofactors.
B) reactive centers.
C) activator ions.
D) group-transfer reagents.
E) All of the above
A) cofactors.
B) reactive centers.
C) activator ions.
D) group-transfer reagents.
E) All of the above
group-transfer reagents.
4
Which coenzyme is likely involved in the reaction shown below? 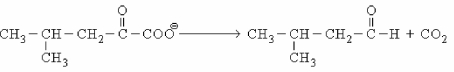
A) TPP
B) biotin
C) coenzyme A
D) FMN

A) TPP
B) biotin
C) coenzyme A
D) FMN

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which coenzyme is composed of a 2-mercaptoethylamine unit, the vitamin pantothenate and an ADP moiety?
A) NADPH
B) biotin
C) coenzyme A
D) ubiquinone
A) NADPH
B) biotin
C) coenzyme A
D) ubiquinone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Active holoenzymes are formed from in the presence of .
A) cofactors; proteins
B) proteins; cofactors
C) apoenzymes; cofactors
D) apoenzymes; proteins
E) apoenzymes; inactive holoenzymes
A) cofactors; proteins
B) proteins; cofactors
C) apoenzymes; cofactors
D) apoenzymes; proteins
E) apoenzymes; inactive holoenzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The products) of lactate dehydrogenase under anaerobic conditions is are)
A) pyruvic acid.
B) NAD+.
C) NADH.
D) A and B
E) A and C
A) pyruvic acid.
B) NAD+.
C) NADH.
D) A and B
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which does not return to its original form after each catalysis?
A) prosthetic groups
B) cosubstrates
C) metalloenzyme
D) None of the above. They all return to their original forms.
A) prosthetic groups
B) cosubstrates
C) metalloenzyme
D) None of the above. They all return to their original forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When NAD+ is reduced, the UV absorbance at 340 nm
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases, then increases.
E) increases, then decreases.
A) decreases.
B) increases.
C) stays the same.
D) decreases, then increases.
E) increases, then decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Vitamin C is a vitamin but not a coenzyme because it
A) does not bind to proteins.
B) is a prosthetic group.
C) is a reducing agent during hydroxylation of collagen.
D) is not required in human diets.
A) does not bind to proteins.
B) is a prosthetic group.
C) is a reducing agent during hydroxylation of collagen.
D) is not required in human diets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The ʺ+ʺ sign in NAD+ indicates that
A) this is the reduced form of the coenzyme.
B) the nitrogen atom has a positive charge.
C) the entire molecule is positively charged.
D) it can bind to negatively charged proteins only.
A) this is the reduced form of the coenzyme.
B) the nitrogen atom has a positive charge.
C) the entire molecule is positively charged.
D) it can bind to negatively charged proteins only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the role of the magnesium ion in kinases that require the magnesium-ATP complex to donate phosphoryl groups?
A) maintain the configuration of the holoenzyme
B) shield the charged phosphate groups of ATP
C) produce an electrophilic attack on the substrate
D) promote ionization of bound water
E) produce ionization of the substrate to be phosphorylated
A) maintain the configuration of the holoenzyme
B) shield the charged phosphate groups of ATP
C) produce an electrophilic attack on the substrate
D) promote ionization of bound water
E) produce ionization of the substrate to be phosphorylated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Unlike NADH and NADPH, FAD and FADH
A) donate one electron at a time.
B) donate one or two electrons at a time.
C) do not become positively charged.
D) A and C
E) B and C
A) donate one electron at a time.
B) donate one or two electrons at a time.
C) do not become positively charged.
D) A and C
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
S-adenosylmethionine SAM) is formed from the amino acid methionine so that
A) methyl groups can be formed.
B) it can react with nucleophilic acceptors.
C) it can donate methyl groups in many biosynthetic reactions.
D) All of the above
E) B and C
A) methyl groups can be formed.
B) it can react with nucleophilic acceptors.
C) it can donate methyl groups in many biosynthetic reactions.
D) All of the above
E) B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An ion commonly found in metalloenzymes and which can undergo reversible oxidation and reduction is
A) Ca++.
B) Mg++.
C) S-.
D) Fe++.
E) All of the above
A) Ca++.
B) Mg++.
C) S-.
D) Fe++.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A nucleotide-sugar coenzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism UDP-glucose) is formed when UTP reacts with a glucose molecule. More UTP is made available for additional reactions by the transfer of a phosphate group from
A) another carbohydrate.
B) ATP.
C) ADP.
D) UTP.
E) UDP.
A) another carbohydrate.
B) ATP.
C) ADP.
D) UTP.
E) UDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Two-electron transfer reactions can be linked to one-electron transfer reactions by
A) formation of semiquinones.
B) a [Fe-S] cluster.
C) NADH and NADPH.
D) B and C
E) A and C
A) formation of semiquinones.
B) a [Fe-S] cluster.
C) NADH and NADPH.
D) B and C
E) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Ca++ or Mg++ are most likely to be part of , while Zn++ or Fe++ are present in .
A) metal-activated enzymes; metalloenzymes
B) metalloenzymes; metal-activated enzymes
C) cofactors; coenzymes
D) coenzymes; cofactors
E) apoenzymes; holoenzymes
A) metal-activated enzymes; metalloenzymes
B) metalloenzymes; metal-activated enzymes
C) cofactors; coenzymes
D) coenzymes; cofactors
E) apoenzymes; holoenzymes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Acyl-group-transfer reactions often involve which coenzyme?
A) Coenzyme A
B) NAD+
C) cytochrome c
D) All of the above
A) Coenzyme A
B) NAD+
C) cytochrome c
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
NAD and NADP dependent dehydrogenases catalyze substrates by transferring to C-4 of NAD+ and NADP+.
A) one electron
B) two electrons
C) one electron and one proton
D) two electrons and one proton
E) two electrons and two protons
A) one electron
B) two electrons
C) one electron and one proton
D) two electrons and one proton
E) two electrons and two protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which atom is the reactive center on biotin? 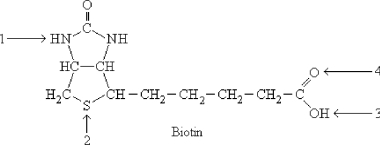
A) Arrow 1
B) Arrow 2
C) Arrow 3
D) Arrow 4

A) Arrow 1
B) Arrow 2
C) Arrow 3
D) Arrow 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which amino acid can form a covalent bond to the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate?
A) aspartate
B) cysteine
C) lysine
D) serine
A) aspartate
B) cysteine
C) lysine
D) serine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which functional group is shown below? 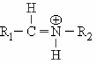
A) Schiff base
B) secondary amine
C) amide
D) peptide bond
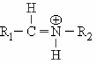
A) Schiff base
B) secondary amine
C) amide
D) peptide bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Pyridoxal phosphate is involved in which type of reaction?
A) oxidation of pyruvate
B) production of new amino acids by transamination
C) phosphate-transfer to produce ATP from ADP
D) the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine
A) oxidation of pyruvate
B) production of new amino acids by transamination
C) phosphate-transfer to produce ATP from ADP
D) the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
We use the term tetrahydrofolate to designate a family of related compounds. What is the main difference between members of this family?
A) degree of protonation
B) number of methyl groups on the heterocylic rings
C) number of phosphate groups
D) length of the polyglutamate tail group
A) degree of protonation
B) number of methyl groups on the heterocylic rings
C) number of phosphate groups
D) length of the polyglutamate tail group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Why has dihydrofolate reductase been identified as a potential target for chemotherapy in the treatment of cancer?
A) It is a hormone that is a primary control agent of the rate of mitosis.
B) It is a DNA binding protein that activates a cancer oncogene.
C) It is essential in DNA synthesis. Cell division will not occur without it.
D) It selectively binds to a receptor on the surface of cancer cells and inactivates them.
A) It is a hormone that is a primary control agent of the rate of mitosis.
B) It is a DNA binding protein that activates a cancer oncogene.
C) It is essential in DNA synthesis. Cell division will not occur without it.
D) It selectively binds to a receptor on the surface of cancer cells and inactivates them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The degradation of aspartic acid to oxaloacetic acid and NH4+ is catalyzed by an enzyme with as its prosthetic group.
A) thiamine
B) biotin
C) pyridoxal phosphate
D) vitamin B12
A) thiamine
B) biotin
C) pyridoxal phosphate
D) vitamin B12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which substance would make a good ligand for biotin on the matrix of an affinity chromatography column?
A) ubiquinone
B) avidin
C) oxaloacetate
D) any molecule with an -SH group
A) ubiquinone
B) avidin
C) oxaloacetate
D) any molecule with an -SH group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The structure shown below is which coenzyme? 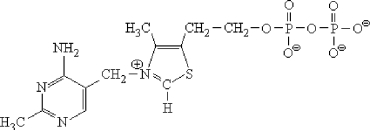
A) QH2
B) Vitamin B12
C) Biotin
D) Thiamine pyrophosphate

A) QH2
B) Vitamin B12
C) Biotin
D) Thiamine pyrophosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which coenzyme links to a lysine residue in a proteinʹs active site?
A) biotin
B) lipoic acid lipoamide)
C) pyridoxal phosphate
D) biotin and pyridoxal phosphate only
E) All three; biotin, lipoic acid and pyridoxal phosphate
A) biotin
B) lipoic acid lipoamide)
C) pyridoxal phosphate
D) biotin and pyridoxal phosphate only
E) All three; biotin, lipoic acid and pyridoxal phosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which structure is not a part of folate?
A) porphyrin ring
B) p-aminobenzoic acid
C) pterin
D) glutamate residues
A) porphyrin ring
B) p-aminobenzoic acid
C) pterin
D) glutamate residues

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Raw egg white contains a protein called avidin. What happens if you ingest raw egg whites?
A) Avidin helps to build muscle tissue.
B) Avidin is the main protein involved in salmonella poisoning.
C) Avidin binds onto the coenzyme biotin and interferes with its absorption.
D) Avidin, also called intrinsic factor, helps transport cobalamin into the cells of the small intestine.
A) Avidin helps to build muscle tissue.
B) Avidin is the main protein involved in salmonella poisoning.
C) Avidin binds onto the coenzyme biotin and interferes with its absorption.
D) Avidin, also called intrinsic factor, helps transport cobalamin into the cells of the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which in not a lipid-soluble vitamin?
A) A
B) C
C) E
D) K
A) A
B) C
C) E
D) K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which type of atom is involved in the reactive center of lipoamide?
A) sulfur
B) nitrogen
C) phosphorous
D) oxygen
A) sulfur
B) nitrogen
C) phosphorous
D) oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What kind of reaction is most important for the reactive center of lipoamide?
A) oxidation of a carbonyl group
B) reduction of a disulfide bond
C) formation of a Schiff base
D) a cis-trans configurational change about a disulfide bond
A) oxidation of a carbonyl group
B) reduction of a disulfide bond
C) formation of a Schiff base
D) a cis-trans configurational change about a disulfide bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
TPP is a/an of yeast pyruvate decarboxylase.
A) cosubstrate
B) intrinsic factor
C) metalloenzyme
D) prosthetic group
A) cosubstrate
B) intrinsic factor
C) metalloenzyme
D) prosthetic group

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Enzymes with vitamin B6 as the prosthetic group catalyze a variety of reactions involving
A) lipids.
B) sugars.
C) amino acids.
D) other vitamins.
A) lipids.
B) sugars.
C) amino acids.
D) other vitamins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which characterizes cobalamin?
A) participates in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine
B) contains a corrin ring prosthetic group
C) requires a glycoprotein for its absorption
D) All of the above
A) participates in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine
B) contains a corrin ring prosthetic group
C) requires a glycoprotein for its absorption
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement is false about 5,6,7,8-tetrahydrobiopterin?
A) It is required by the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of nitric oxide from arginine.
B) It is synthesized by animals and other organisms.
C) It is used in the transfer of phosphate groups during DNA synthesis.
D) It is a reducing agent in the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine.
A) It is required by the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of nitric oxide from arginine.
B) It is synthesized by animals and other organisms.
C) It is used in the transfer of phosphate groups during DNA synthesis.
D) It is a reducing agent in the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which vitamin is shown below? 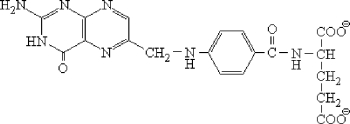
A) vitamin C
B) thiamin vitamin B1)
C) cobalamin vitamin B12)
D) folate

A) vitamin C
B) thiamin vitamin B1)
C) cobalamin vitamin B12)
D) folate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the prosthetic group of the retinal vision protein rhodopsin?
A) retinol
B) retinal
C) retinoic acid
D) β-carotene
A) retinol
B) retinal
C) retinoic acid
D) β-carotene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Lipid vitamins such as A, D, E, and K are stored by animal cells, so excessive daily intake may be toxic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In which type of reactions does Q participate?
A) One electron transfers only.
B) One or two electron transfers.
C) Hydride ion transfers.
D) Acetyl group transfers.
A) One electron transfers only.
B) One or two electron transfers.
C) Hydride ion transfers.
D) Acetyl group transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
A) ubiquinone
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) Vitamin K
A) ubiquinone
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) Vitamin K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which structure in shown? 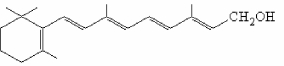
A) retinol
B) retinal
C) retinoic acid
D) β-carotene

A) retinol
B) retinal
C) retinoic acid
D) β-carotene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Vitamin D helps control the utilization of which ion?
A) Mg2+
B) Ca2+
C) Fe2+
D) Co2+
A) Mg2+
B) Ca2+
C) Fe2+
D) Co2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Vitamin C is a coenzyme during the hydroxylation of collagen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Metalloenzymes contain metal ions which are bound tightly to the protein and can attract electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Another name for α-tocopherol is vitamin .
A) A
B) B12
C) C
D) D
E) E
A) A
B) B12
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Mammalian cells can synthesize all needed coenzymes from simple precursors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults is caused by a lack of .
A) thiamin
B) hemoglobin
C) vitamin D
D) vitamin B12
A) thiamin
B) hemoglobin
C) vitamin D
D) vitamin B12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Minerals which are cofactors may be reversibly bound and are then usually directly involved in catalytic reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Organic compounds are coenzymes and cofactors while inorganic ions are cofactors only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which statement is false about plastoquinone?
A) It is water soluble.
B) It is important in photosynthetic electron transport.
C) It contains five-carbon isoprenoid units.
D) It can be converted to a semiquinone form.
A) It is water soluble.
B) It is important in photosynthetic electron transport.
C) It contains five-carbon isoprenoid units.
D) It can be converted to a semiquinone form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Vitamin K is important in the .
A) synthesis of collagen
B) absorption of Ca2+
C) coagulation of blood clotting)
D) scavenging of oxygen and free radicals
A) synthesis of collagen
B) absorption of Ca2+
C) coagulation of blood clotting)
D) scavenging of oxygen and free radicals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Metal-activated enzymes may require a metal ion or simply be stimulated in the presence of the ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which are common protein coenzymes?
A) cytochromes
B) phylloquinones
C) tetrahydrofolates
D) α-tocopherols
A) cytochromes
B) phylloquinones
C) tetrahydrofolates
D) α-tocopherols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
All enzymes require metallic cations to achieve full catalytic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Vitamin deficiency diseases are a result of the lack of formation of certain coenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Protein catalysts rely exclusively on the amino acid residues for reactivity at the sites of action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match each of the following vitamins with an associate nutritional deficiency disease. 
Ascorbate

Ascorbate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Structures of several dehydrogenases indicate that many possess one or more similar NAD or NADP-binding structures consisting of babab units in Rossman folds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Lack of thiamine vitamin B1) leads to the disease beriberi.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Lysine can join the prosthetic group biotin to an enzyme via an amide link at the ε-amino group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match each of the following vitamins with an associate nutritional deficiency disease. 
Folate

Folate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The oxidized forms of cytochromes c absorbs more strongly than the reduced form at the Soret band near 400 nm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The reactive center of CoA is the -NH3+ group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Pernicious anemia is caused by a deficiency in biotin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Tetrahydrofolate is a more oxidized form of the vitamin folate from which it is derived.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An internal aldimine forms when PLP is covalently bound to its enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Ubiquinone and plastoquinone transport electrons in membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match each of the following vitamins with an associate nutritional deficiency disease. 
Cobalamin B12)

Cobalamin B12)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Vitamin E is formed non-enzymatically in sun-exposed skin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match each of the following vitamins with an associate nutritional deficiency disease. 
Thiamine B1)

Thiamine B1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Vitamin A is produced from b-carotene by a condensation reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
There is little risk in taking megadoses of vitamin A since excess will tend to simply be excreted in the urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Cobalamin is synthesized by most organisms from simple precursors and does not need to be in the diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The corrin ring is very similar to a heme, but the corrin ring containing vitamin B12 has a cobalt ion rather than an iron ion as in heme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Another name for vitamin K is phylloquinone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match each of the following vitamins with an associate nutritional deficiency disease. 
Biotin

Biotin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



