Deck 8: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Carbohydrates
1
The compounds α-D-fructofuranose and β-D-fructofuranose are .
A) enantiomers
B) mutamers
C) anomers
D) conformational isomers
A) enantiomers
B) mutamers
C) anomers
D) conformational isomers
anomers
2
The structures of D-ribose and D-arabinose are shown below. These two molecules are .
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) tautomers
D) anomers
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) tautomers
D) anomers
epimers
3
In solution α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose .
A) rapidly polymerize to form a heteropolymer
B) can never exist together
C) form a racemic mixture
D) form an equilibrium mixture
A) rapidly polymerize to form a heteropolymer
B) can never exist together
C) form a racemic mixture
D) form an equilibrium mixture
form an equilibrium mixture
4
Below is the Fischer projection of D-galactose. Which is the proper Haworth projection of β-D-galactopyranose?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Below is the structure for a cyclic D-monosaccharide. Which is the anomeric carbon atom?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Pyranose rings are usually most stable when the ring adopts a conformation with the bulkiest ring substituents in positions.
A) chair; equatorial
B) chair; axial
C) boat; equatorial
D) boat; axial
A) chair; equatorial
B) chair; axial
C) boat; equatorial
D) boat; axial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Examine the cyclic D-monosaccharide shown below. The ring structure is the and the linear form of this monosaccharide must be a/an . 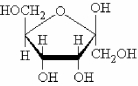
A) α anomer; ketose
B) β anomer; ketose
C) α anomer; aldose
D) β anomer; aldose

A) α anomer; ketose
B) β anomer; ketose
C) α anomer; aldose
D) β anomer; aldose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The functional group shown is a/an . 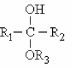
A) hemiacetal
B) hemiketal
C) acetal
D) ketal

A) hemiacetal
B) hemiketal
C) acetal
D) ketal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Anomers can be interconverted .
A) by rotation about carbon-carbon bonds
B) via a linear intermediate
C) by an isotopic exchange reaction
D) None of the above. Anomers cannot be interconverted.
A) by rotation about carbon-carbon bonds
B) via a linear intermediate
C) by an isotopic exchange reaction
D) None of the above. Anomers cannot be interconverted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which is not a glycoconjugate?
A) proteoglycan
B) glycolipid
C) glycoprotein
D) homoglycan
A) proteoglycan
B) glycolipid
C) glycoprotein
D) homoglycan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which is a product of the intramolecular cyclization of D-tagatose to form a furanose? 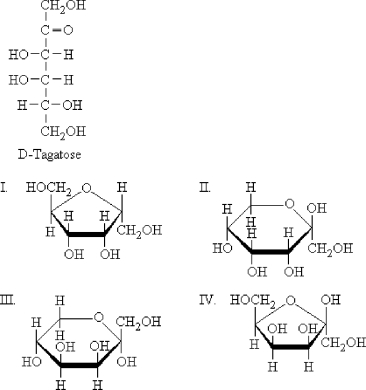
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ribitol is a sugar alcohol that is a component of
A) vitamin C.
B) RNA.
C) FMN and FAD.
D) NAD and NADH.
E) sialic acid.
A) vitamin C.
B) RNA.
C) FMN and FAD.
D) NAD and NADH.
E) sialic acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Fischer projections of linear D-glucose and D-galactose are shown below. These two molecules are . 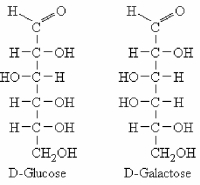
A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) anomers
D) structural constitutional) isomers

A) epimers
B) enantiomers
C) anomers
D) structural constitutional) isomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The structure of D-arabinose is shown below. How many stereoisomers are possible for this molecule including the one shown)? 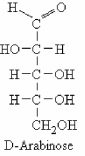
A) one
B) four
C) six
D) eight

A) one
B) four
C) six
D) eight

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Examine the Fischer projection below. How is this carbohydrate classified?
A) L enantiomer; aldopentose
B) L enantiomer; ketopentose
C) D enantiomer; aldohexose
D) D enantiomer; ketopentose
A) L enantiomer; aldopentose
B) L enantiomer; ketopentose
C) D enantiomer; aldohexose
D) D enantiomer; ketopentose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Monosaccharide derivatives in which an amino group replaces one of the hydroxyl groups may have important roles in
A) DNA structure.
B) intermediary metabolisms.
C) vitamin C.
D) sialic acids.
E) All of the above
A) DNA structure.
B) intermediary metabolisms.
C) vitamin C.
D) sialic acids.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which are possible conformations of a furanose molecule?
A) envelope and twist
B) chair and boat
C) cis and trans
D) A and B
A) envelope and twist
B) chair and boat
C) cis and trans
D) A and B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which does not apply to dihydroxyacetone?
A) ketose
B) triose
C) chiral
D) water-soluble
A) ketose
B) triose
C) chiral
D) water-soluble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is true about naturally occurring monosaccharides?
A) The L-isomers predominate.
B) The D-isomers predominate.
C) The L and D-isomers occur in equal ratios.
D) The ratio of L and D-isomers varies widely depending on the source.
A) The L-isomers predominate.
B) The D-isomers predominate.
C) The L and D-isomers occur in equal ratios.
D) The ratio of L and D-isomers varies widely depending on the source.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The intramolecular cyclization reaction of glucose in solution .
A) generates a chiral center
B) yields a hemiacetal
C) usually forms a pyranose
D) All of the above
A) generates a chiral center
B) yields a hemiacetal
C) usually forms a pyranose
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement is false about the sugar units in DNA?
A) They are cyclic in DNA.
B) It is a deoxy form of ribose
C) It is an epimer of glucose.
D) It has a D-configuration
A) They are cyclic in DNA.
B) It is a deoxy form of ribose
C) It is an epimer of glucose.
D) It has a D-configuration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A monosaccharide whose anomeric carbon atom has a glycosidic bond to an alcohol, amine or thiol is a .
A) glycoside
B) glycoprotein
C) heteroglycan
D) glucoconjugate
A) glycoside
B) glycoprotein
C) heteroglycan
D) glucoconjugate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What distinguishes an aldonic acid from an alduronic acid?
A) The oxidation of the aldehyde group in an aldonic acid and the oxidation of the highest numbered carbon in the alduronic acid.
B) Aldonic acids are derivatives of aldoses, alduronic acids are derivatives of ketoses.
C) Aldonic acids are oxidized forms of linear monosaccharides; alduronic acids are oxidized forms of cyclic monosaccharides.
D) The two terms are synonyms and are used interchangeably.
A) The oxidation of the aldehyde group in an aldonic acid and the oxidation of the highest numbered carbon in the alduronic acid.
B) Aldonic acids are derivatives of aldoses, alduronic acids are derivatives of ketoses.
C) Aldonic acids are oxidized forms of linear monosaccharides; alduronic acids are oxidized forms of cyclic monosaccharides.
D) The two terms are synonyms and are used interchangeably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Both amylose and amylopectin molecules isolated from plant cells can contain as many as glucose residues.
A) 25
B) 500
C) 1000
D) 2000
E) 6000
A) 25
B) 500
C) 1000
D) 2000
E) 6000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which is a difference between maltose and cellobiose?
A) One is in cellulose and the other in starch.
B) One is linear and the other is branched.
C) The glycosidic bond is different.
D) The subunit sugars are not glucose for both.
E) All of the above
A) One is in cellulose and the other in starch.
B) One is linear and the other is branched.
C) The glycosidic bond is different.
D) The subunit sugars are not glucose for both.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The structure of a disaccharide is shown below. Which statement applies? 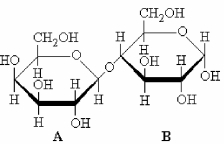
A) Both rings A and B are in equilibrium with an open chain form.
B) Only ring A is in equilibrium with an open chain form.
C) Only ring B is in equilibrium with an open chain form.
D) Neither ring is in equilibrium with an open chain form.

A) Both rings A and B are in equilibrium with an open chain form.
B) Only ring A is in equilibrium with an open chain form.
C) Only ring B is in equilibrium with an open chain form.
D) Neither ring is in equilibrium with an open chain form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Naturally occurring glycosides have roles in cells which include
A) subunits of DNA.
B) chemical signals to plants.
C) food flavoring.
D) units in cell membrane structure.
E) All of the above
A) subunits of DNA.
B) chemical signals to plants.
C) food flavoring.
D) units in cell membrane structure.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the name of the disaccharide shown below that is formed by joining two monomers of D-glucose? 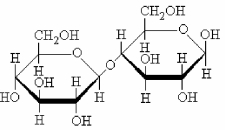
A) β-D-glucopyranosyl-1→4)-β-D-glucopyranose
B) α-D-glucopyranosyl-1→4)-α-D-glucopyranose
C) β-D-glucofuranosyl-1→4)-β-D-glucofuranose
D) α-D-glucopyranosyl-1→3)-β-D-glucopyranose

A) β-D-glucopyranosyl-1→4)-β-D-glucopyranose
B) α-D-glucopyranosyl-1→4)-α-D-glucopyranose
C) β-D-glucofuranosyl-1→4)-β-D-glucofuranose
D) α-D-glucopyranosyl-1→3)-β-D-glucopyranose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Enzymes in the human intestine which are needed to degrade plant starch into limit dextrin are
A) a-Amylase.
B) β-Amylase.
C) debranching enzymes.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C
A) a-Amylase.
B) β-Amylase.
C) debranching enzymes.
D) A and B
E) A, B, and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
You have two bottles, each of which contains a white, crystalline substance. Your lab director tells you that one contains lactose and the other sucrose. Your job is to determine which bottle contains which sugar. Which procedure would you use?
A) Test both for solubility in water. Sucrose is very soluble; lactose is only minimally soluble.
B) Test for the ability to reduce Ag+. Only lactose will react.
C) Dissolve each in water and record the pH. Lactose is far more acidic than sucrose.
D) React each with bromine Br2) water. Only sucrose will react.
A) Test both for solubility in water. Sucrose is very soluble; lactose is only minimally soluble.
B) Test for the ability to reduce Ag+. Only lactose will react.
C) Dissolve each in water and record the pH. Lactose is far more acidic than sucrose.
D) React each with bromine Br2) water. Only sucrose will react.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which is not a similarity between glycogen and amylopectin?
A) They each contain about 6000 glucose residues.
B) Each has one reducing end and many nonreducing ends.
C) Each is highly branched.
D) Each has branches of similar chain length.
A) They each contain about 6000 glucose residues.
B) Each has one reducing end and many nonreducing ends.
C) Each is highly branched.
D) Each has branches of similar chain length.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When a sugar polymer is analyzed and found to have equal portions of reducing and non-reducing ends, it is likely that
A) it shows directionality.
B) it is linear.
C) it is branched.
D) it is branched, but not very highly.
E) some of the internal glycosidic bonds are in equilibrium with open chain forms.
A) it shows directionality.
B) it is linear.
C) it is branched.
D) it is branched, but not very highly.
E) some of the internal glycosidic bonds are in equilibrium with open chain forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Hydrolysis of maltose will yield .
A) glucose and galactose
B) fructose and glucose
C) glucose and mannose
D) glucose only
A) glucose and galactose
B) fructose and glucose
C) glucose and mannose
D) glucose only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Amylase is a hydrolase that is an .
A) endonuclease
B) endoglycosidase
C) exonuclease
D) exoglycosidase that removes maltose
E) exoglycosidase that removes glucose monomers
A) endonuclease
B) endoglycosidase
C) exonuclease
D) exoglycosidase that removes maltose
E) exoglycosidase that removes glucose monomers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The chemical name for table sugar is and it is a .
A) lactose; monosaccharide
B) lactose; disaccharide
C) sucrose; monosaccharide
D) sucrose; disaccharide
A) lactose; monosaccharide
B) lactose; disaccharide
C) sucrose; monosaccharide
D) sucrose; disaccharide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Polysaccharide structure can be varied by differences in
A) chain length number of sugars in each polysaccharide).
B) the kinds) of sugars in each polysaccharides.
C) the presence of branching.
D) All of the above
A) chain length number of sugars in each polysaccharide).
B) the kinds) of sugars in each polysaccharides.
C) the presence of branching.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What type of bond links the monomers of a polysaccharide?
A) glucotide bond
B) phosphate ester bond
C) peptide bond
D) glycosidic bond
A) glucotide bond
B) phosphate ester bond
C) peptide bond
D) glycosidic bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A reducing sugar is one that
A) contains a b1→1) link.
B) has a hemiacetal group.
C) can reduce Cu2+ but not Ag+.
D) makes you lose weight.
A) contains a b1→1) link.
B) has a hemiacetal group.
C) can reduce Cu2+ but not Ag+.
D) makes you lose weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The abbreviation for glucose is .
A) glu
B) gcs
C) glc
D) gluc
A) glu
B) gcs
C) glc
D) gluc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Amylose differs from amylopectin in that amylose
A) has different monomers than amylopectin.
B) has more glucose residues than amylopectin.
C) is highly branched and amylopectin is not.
D) forms a helix and no branch points.
A) has different monomers than amylopectin.
B) has more glucose residues than amylopectin.
C) is highly branched and amylopectin is not.
D) forms a helix and no branch points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The main reasons that glycoproteins are so diverse when compared to other proteoglycans are
A) they may contain different sugars in different combinations and chain lengths.
B) β or a-glycosidic linkages may join various carbon atoms in the sugars.
C) they are found in both bacterial, plant and animal cells.
D) A and B
E) All of the above
A) they may contain different sugars in different combinations and chain lengths.
B) β or a-glycosidic linkages may join various carbon atoms in the sugars.
C) they are found in both bacterial, plant and animal cells.
D) A and B
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The chair conformation of furanoses is generally preferred to minimize steric repulsion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Steric strain is a major factor in determining the conformations of a monosaccharide that predominate in solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Furanoses have more three-dimensional conformations than pyranoses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The bacterial cell wall is sensitive to penicillin because it
A) blocks the linkage of the MurNAc and GlcNAc subunits.
B) blocks the pentaglycine bridge cross linkage.
C) binds to an enzyme which recognizes D-alanine-D-alanine dipeptide.
D) is not attacked by enzymes in animal cells.
E) All of the above
A) blocks the linkage of the MurNAc and GlcNAc subunits.
B) blocks the pentaglycine bridge cross linkage.
C) binds to an enzyme which recognizes D-alanine-D-alanine dipeptide.
D) is not attacked by enzymes in animal cells.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The reaction between one molecule of alcohol and one molecule of aldehyde yields an acetal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The ketohexoses have fewer chiral carbon atoms than the aldohexoses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Highly branched cores of amlyopectin that are resistant to hydrolysis are called .
A) core saccharides
B) non-reducing saccharides
C) dextran
D) limit dextrins
A) core saccharides
B) non-reducing saccharides
C) dextran
D) limit dextrins

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The major proteoglycan in cartilage is .
A) hyaluronic acid
B) cellobiose
C) link protein
D) aggrecan
A) hyaluronic acid
B) cellobiose
C) link protein
D) aggrecan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All carbohydrates have the empirical formula CH2O)n.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The elasticity and resistance to compression of connective tissue is due to
A) the branching of the glycosaminoglycans there.
B) the glycosidic linkage to the serine of proteins in the glycosaminoglycans.
C) the carboxyl and sulfated groups in the glycosaminoglycans.
D) the rigid structure of the glycosaminoglycans.
E) All of the above
A) the branching of the glycosaminoglycans there.
B) the glycosidic linkage to the serine of proteins in the glycosaminoglycans.
C) the carboxyl and sulfated groups in the glycosaminoglycans.
D) the rigid structure of the glycosaminoglycans.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Cellulose is not highly branched because it
A) does not have a polysaccharide backbone.
B) it does not have a-1→6) linkages.
C) it does not have β-1→4) linkages.
D) it is insoluble in water.
A) does not have a polysaccharide backbone.
B) it does not have a-1→6) linkages.
C) it does not have β-1→4) linkages.
D) it is insoluble in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Most of the carbohydrates on earth are produced by photosynthesis in plants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The simplest aldose is the chiral molecule glyceraldehyde.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In solution only one anomeric form of a monosaccharide will be present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Chitin is
A) found in insect and crustacean shells.
B) found in fungi cell walls.
C) composed of N-acetylglucosamine subunits.
D) composed of linear fibrils like cellulose.
E) All of the above
A) found in insect and crustacean shells.
B) found in fungi cell walls.
C) composed of N-acetylglucosamine subunits.
D) composed of linear fibrils like cellulose.
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
contain NeuNAc residues and sulfated sugars, and their negative charges contribute to the viscosity of mucins.
A) Proteoglycans
B) N-linked polysaccharides
C) O-linked polysaccharides
D) Hyaluronic acid
E) All of the above
A) Proteoglycans
B) N-linked polysaccharides
C) O-linked polysaccharides
D) Hyaluronic acid
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Nodulation factors are .
A) polysaccharides that help maintain the integrity of tree bark
B) lipo-oligosaccharides that stimulate the growth of nitrogen-fixing structures in plants
C) polysaccharides used to store energy in the roots of plants
D) lipo-saccharides that are often found in tumors
A) polysaccharides that help maintain the integrity of tree bark
B) lipo-oligosaccharides that stimulate the growth of nitrogen-fixing structures in plants
C) polysaccharides used to store energy in the roots of plants
D) lipo-saccharides that are often found in tumors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Vitamin C is an enediol of a lactone and is vital in the synthesis of collagen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
All D-enantiomers of carbohydrates are dextrorotatory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Unlike proteins, whose primary structures are encoded in DNA, polysaccharides have very little structural variations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
a-amylases hydrolyze (a-1→4) linkages and β-amylases hydrolyze (β-1→4) linkages, but neither attack (a-1→6) linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An oligosaccharide nodulation factor from one species can stimulate symbiosis in another species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The heteroglycan component of the cell wall is the same in all bacteria, but the cross-linking polypeptide is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The sugar derivative found in DNA is an oxidized form of ribose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Heteroglycan chains may or may not be covalently bound to proteins in proteoglycans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The large number of possible oligosaccharide structures in glycoproteins is limited in cells by the kinds of enzymes available for their synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cellulose cannot be degraded in cattle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Enzymatic lengthening and degradation of glycogen occurs only at the non-reducing ends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
For cattle, cellulose is a storage homoglycan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Homoglycans are used for storage, while heteroglycans are used for cell structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The main difference between structures of amylopectin and glycogen is the specific sugar subunit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Some glycoproteins may have identical protein components and variable polysaccharide components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
DNA could be referred to as a glycoside.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Sugar alcohols do not have a carbonyl group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Both nucleotides and nucleosides are glycosides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Enzymes that hydrolyze cellulose cannot hydrolyze amylopectin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



