Deck 16: Lipid Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Lipid Metabolism
1
Eicosanoids are not like hormones in that they
A) can alter blood flow.
B) act in the area where they are formed.
C) can mediate inflammation and swelling.
D) are chemically diverse.
A) can alter blood flow.
B) act in the area where they are formed.
C) can mediate inflammation and swelling.
D) are chemically diverse.
act in the area where they are formed.
2
Fatty acid synthesis is different in bacteria than in eukaryotic cells because .
A) bacteria do not form malonyl CoA
B) eukaryotes use acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA
C) bacteria do not form acetyl ACP
D) bacteria do not form acetoacetyl CoA
A) bacteria do not form malonyl CoA
B) eukaryotes use acetyl CoA to form malonyl CoA
C) bacteria do not form acetyl ACP
D) bacteria do not form acetoacetyl CoA
bacteria do not form acetyl ACP
3
Drugs called statins lower cholesterol levels because they .
A) degrade HMG-CoA reductase
B) bind serum cholesterol
C) inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
D) bind bile salts
A) degrade HMG-CoA reductase
B) bind serum cholesterol
C) inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
D) bind bile salts
inhibit HMG-CoA reductase
4
The cyclooxygenase-hydroperoxidase pathway is a precursor for each of the following except
A) thromboxane A2.
B) prostacyclin.
C) prostaglandins.
D) epinephrine.
A) thromboxane A2.
B) prostacyclin.
C) prostaglandins.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Why are triacylglycerols able to provide more energy than carbohydrates gram for gram)?
A) The triacylglycerols have an extremely high group transfer potential.
B) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglycerols.
C) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds.
D) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates.
A) The triacylglycerols have an extremely high group transfer potential.
B) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglycerols.
C) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds.
D) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Phosphatidate is an intermediate in the synthesis of .
A) triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids
B) glycerophospholipids only
C) sphingolipids
D) cholesterol
A) triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids
B) glycerophospholipids only
C) sphingolipids
D) cholesterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Linoleate is an essential fatty acid in mammalian diets because mammalian cells .
A) synthesize it from arachidonate
B) do not use this acid for biosynthesis
C) can use it to synthesize eicosanoids
D) do not have a desaturase that acts beyond the carbon-9 position
A) synthesize it from arachidonate
B) do not use this acid for biosynthesis
C) can use it to synthesize eicosanoids
D) do not have a desaturase that acts beyond the carbon-9 position

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a true statement, concerning HMG-CoA reductase?
A) It is regulated by covalent modification of a serine in its active site.
B) It catalyzes the first committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis.
C) It causes the production of NADPH.
D) The product of the reaction it catalyzes is acetoacetyl CoA.
A) It is regulated by covalent modification of a serine in its active site.
B) It catalyzes the first committed step in cholesterol biosynthesis.
C) It causes the production of NADPH.
D) The product of the reaction it catalyzes is acetoacetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The first step in fatty acid synthesis is the formation of from acetyl CoA and carbon dioxide.
A) acetyl ACP
B) acetoacetyl ACP
C) malonyl CoA
D) acetoacetyl CoA
A) acetyl ACP
B) acetoacetyl ACP
C) malonyl CoA
D) acetoacetyl CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Cholesterol is a precursor for each of the following, except
A) bile salts.
B) vitamin D.
C) testosterone.
D) vitamin C.
A) bile salts.
B) vitamin D.
C) testosterone.
D) vitamin C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is a true statement for fatty acid synthesis?
A) It occurs in the mitochondria.
B) The reducing power for synthesis is supplied by NAD+ and ubiquinone.
C) Both A and B
D) None of the above
A) It occurs in the mitochondria.
B) The reducing power for synthesis is supplied by NAD+ and ubiquinone.
C) Both A and B
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true for carboxylation of acetyl CoA?
A) In animals and yeast, it requires three separate protein subunits.
B) It is a metabolically reversible reaction.
C) In bacteria, it is catalyzed by a bifunctional enzyme.
D) The regulatory enzyme is acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
A) In animals and yeast, it requires three separate protein subunits.
B) It is a metabolically reversible reaction.
C) In bacteria, it is catalyzed by a bifunctional enzyme.
D) The regulatory enzyme is acetyl-CoA carboxylase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Lysosomal storage diseases occur when mutations cause defects in .
A) sphingolipid biosynthesis enzymes
B) sphingolipid degradation enzymes
C) lysosome formation
D) formation of N-acetylgalactosamine derivatives
A) sphingolipid biosynthesis enzymes
B) sphingolipid degradation enzymes
C) lysosome formation
D) formation of N-acetylgalactosamine derivatives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The elongation of fatty acids is a repetition of three reactions adding carbons from after each cycle until completion.
A) malonyl CoA
B) malonyl ACP
C) acetyl CoA
D) acetyl ACP
A) malonyl CoA
B) malonyl ACP
C) acetyl CoA
D) acetyl ACP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not a stage of fatty acid synthesis?
A) condensation of precursors
B) rearrangement
C) reduction
D) dehydration
A) condensation of precursors
B) rearrangement
C) reduction
D) dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Properties of aspirin may include
A) inhibition of COX activity.
B) increased production of prostaglandins.
C) Both A and B
D) None of the above
A) inhibition of COX activity.
B) increased production of prostaglandins.
C) Both A and B
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
All of the following occur during synthesis of ether lipids except
A) esterification of an acyl group from fatty acyl CoA to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
B) displacement of the fatty acid of 1-acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate by a fatty alcohol.
C) oxidation of the keto group of 1-acyldihydroxyacetone by NADPH.
D) esterification of 1-alkylglycero-3-phosphate to produce 1-alkyl-2-acylglycero-3-phosphate.
A) esterification of an acyl group from fatty acyl CoA to dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
B) displacement of the fatty acid of 1-acyldihydroxyacetone phosphate by a fatty alcohol.
C) oxidation of the keto group of 1-acyldihydroxyacetone by NADPH.
D) esterification of 1-alkylglycero-3-phosphate to produce 1-alkyl-2-acylglycero-3-phosphate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The reaction, Palmitoyl-ACP→Palmitate + HS-ACP proceeds via which of the following enzymes?
A) thioesterase
B) ketoacyl-ACP synthase
C) transacylase
D) None of the above
A) thioesterase
B) ketoacyl-ACP synthase
C) transacylase
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which sphingolipid is a precursor for all other types of sphingolipids?
A) sphingomyelin
B) cerebroside
C) ganglioside
D) ceramide
A) sphingomyelin
B) cerebroside
C) ganglioside
D) ceramide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is the regulated step of fatty acid synthesis in eukaryotes?
A) carboxylation of acetyl CoA
B) transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol
C) assembly of the fatty acid chain
D) All of the above
A) carboxylation of acetyl CoA
B) transportation of mitochondrial acetyl CoA into the cytosol
C) assembly of the fatty acid chain
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which statement is false about polyunsaturated fatty acids?
A) They have both odd-numbered and even-numbered double bonds.
B) Their synthesis is more energy-efficient than the synthesis of saturated fatty acids.
C) Some double bonds are rearranged during their degradation.
D) They require D3, D2-enoyl-CoA isomerase for their oxidation.
A) They have both odd-numbered and even-numbered double bonds.
B) Their synthesis is more energy-efficient than the synthesis of saturated fatty acids.
C) Some double bonds are rearranged during their degradation.
D) They require D3, D2-enoyl-CoA isomerase for their oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
To oxidize the fatty acid molecule shown below, what enzymes) are needed in addition to the enzymes needed for β-oxidation? 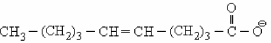
A) enoyl-CoA isomerase only
B) 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only
C) both enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase
D) No additional enzymes are needed besides the normal ones for β-oxidation.
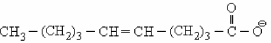
A) enoyl-CoA isomerase only
B) 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only
C) both enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase
D) No additional enzymes are needed besides the normal ones for β-oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Fatty acids are oxidized in the .
A) mitochondrial matrix
B) cytosol
C) endoplasmic reticulum
D) mitochondrial inner membrane space
A) mitochondrial matrix
B) cytosol
C) endoplasmic reticulum
D) mitochondrial inner membrane space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Why is poor plasmalogen synthesis potentially fatal?
A) The nervous system is affected because plasmalogens are important constituents of the myelin sheath.
B) The mitochondria will not function properly due to lack of plasmalogen produced cardiolipin.
C) Poor nutrient absorption will occur in the small intestine where plasmalogens aid with the absorption of lipid-soluble vitamins and other hydrophobic substances.
D) Protein synthesis is affected due to the inability of plasmalogens binding ribosomes to the endoplasmic reticulum.
A) The nervous system is affected because plasmalogens are important constituents of the myelin sheath.
B) The mitochondria will not function properly due to lack of plasmalogen produced cardiolipin.
C) Poor nutrient absorption will occur in the small intestine where plasmalogens aid with the absorption of lipid-soluble vitamins and other hydrophobic substances.
D) Protein synthesis is affected due to the inability of plasmalogens binding ribosomes to the endoplasmic reticulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is the precursor for which of the following?
A) terpenes
B) vitamin K
C) quinones
D) All of the above
E) None of the above
A) terpenes
B) vitamin K
C) quinones
D) All of the above
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which enzyme requires adenosylcobalamin as a cofactor?
A) carnitine acyl transferase I
B) methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
C) enoyl-CoA hydratase
D) propionyl-CoA carboxylase
A) carnitine acyl transferase I
B) methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
C) enoyl-CoA hydratase
D) propionyl-CoA carboxylase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the carbonyl carbon of a fatty acyl CoA molecule with a C10 chain is labeled with 14C, how many rounds of β-oxidation are required to produce a radioactively labeled acetyl CoA?
A) one
B) two
C) four
D) five
A) one
B) two
C) four
D) five

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What structure is shown below and what is its main function? 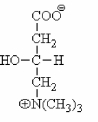
A) coenzyme A; activation of fatty acids before β-oxidation
B) carnitine; transport of fatty acyl CoA into the mitochondrial matrix
C) taurocholate; one of the bile salts
D) acetoacetate; synthesis of fatty acids

A) coenzyme A; activation of fatty acids before β-oxidation
B) carnitine; transport of fatty acyl CoA into the mitochondrial matrix
C) taurocholate; one of the bile salts
D) acetoacetate; synthesis of fatty acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Elevated levels of the hormone stimulate the conversion of triacylglycerols stored in adipose cells to free fatty acids and monoacylglycerols to provide energy when carbohydrate stores are depleted.
A) insulin
B) glucagon
C) epinephrine
D) ergosterol
A) insulin
B) glucagon
C) epinephrine
D) ergosterol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Phosphatidylcholine synthesis occurs in the .
A) endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells
B) Golgi apparatus
C) mitochondrion
D) plasma membrane
A) endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells
B) Golgi apparatus
C) mitochondrion
D) plasma membrane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The conversion of the fatty acid palmitate C16) to carbon dioxide via β-oxidation, the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation yield approximately ATP equivalents.
A) 3
B) 32
C) 106
D) 800
A) 3
B) 32
C) 106
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the main function of the carnitine shuttle system?
A) To transport fatty acids into the mitochondrion.
B) To transport newly synthesized sphingolipids to the blood.
C) To carry cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane.
D) To aid in the assembly of chylomicrons.
A) To transport fatty acids into the mitochondrion.
B) To transport newly synthesized sphingolipids to the blood.
C) To carry cholesterol from its site of synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane.
D) To aid in the assembly of chylomicrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
How many QH2 and NADH are produced by one round of the β-oxidation pathway?
A) 1 each
B) 1 QH2 and 2 NADH
C) 2 each
D) 2 QH2 and 1 NADH
A) 1 each
B) 1 QH2 and 2 NADH
C) 2 each
D) 2 QH2 and 1 NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How many cycles of β-oxidation are required to completely process a saturated C18 fatty acid?
A) 6
B) 8
C) 9
D) 18
A) 6
B) 8
C) 9
D) 18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
To oxidize the fatty acid molecule shown below, what enzymes) isare) needed in addition to the enzymes needed for β-oxidation? 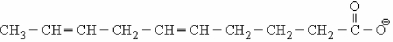
A) enoyl-CoA isomerase only
B) 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only
C) both enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase
D) No additional enzymes are needed besides the normal ones for β-oxidation.
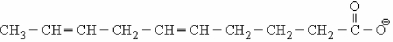
A) enoyl-CoA isomerase only
B) 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only
C) both enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase
D) No additional enzymes are needed besides the normal ones for β-oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which enzyme is needed for the oxidation of odd-chain saturated fatty acids that is not needed for even-chain fatty acids?
A) methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
B) propionyl-CoA carboxylase
C) methylmalonyl-CoA racemase
D) All of the above
A) methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
B) propionyl-CoA carboxylase
C) methylmalonyl-CoA racemase
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
There are four steps in the β-oxidation pathway. Some reaction types are listed below. Give the proper reaction types in the order that they occur in the β-oxidation pathway. 1. condensation
2. oxidation
3. reduction
4. thiolysis
5. hydration
6. phosphorylation
7. rearrangement
A) 1,7,2,2
B) 6,3,4,2
C) 1,2,3,5
D) 2,5,2,4
2. oxidation
3. reduction
4. thiolysis
5. hydration
6. phosphorylation
7. rearrangement
A) 1,7,2,2
B) 6,3,4,2
C) 1,2,3,5
D) 2,5,2,4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which lipid form is transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane before β-oxidation?
A) acylcarnitine
B) fatty acyl CoA
C) acetoacetyl CoA
D) lysophospholipid CoA
A) acylcarnitine
B) fatty acyl CoA
C) acetoacetyl CoA
D) lysophospholipid CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a true statement for fatty acid oxidation?
A) It occurs in the cytosol.
B) Oxidation requires a three carbon substrate, which transfers a two-carbon unit to the chain.
C) Both NADH and QH2 are produced.
D) None of the above
A) It occurs in the cytosol.
B) Oxidation requires a three carbon substrate, which transfers a two-carbon unit to the chain.
C) Both NADH and QH2 are produced.
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is mis-matched?
A) bile salts - intestinal absorption of lipids
B) b-estradiol - sex characteristics
C) cholesterol - membrane fluidity
D) squalene - lipid vitamin
A) bile salts - intestinal absorption of lipids
B) b-estradiol - sex characteristics
C) cholesterol - membrane fluidity
D) squalene - lipid vitamin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following does do) not occur during the fasting state?
A) increased insulin levels
B) inhibition of lipolysis
C) an increase in the concentration of albumin-bound fatty acids in the blood
D) A and B only
E) All of the above
A) increased insulin levels
B) inhibition of lipolysis
C) an increase in the concentration of albumin-bound fatty acids in the blood
D) A and B only
E) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In adult mammals fatty acid synthesis largely occurs in the cytosol of liver cells and adipocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which do you expect to have the highest protein content by percent?
A) VLDLs
B) ILDs
C) HDLs
D) All of the lipids above have about the same protein content.
A) VLDLs
B) ILDs
C) HDLs
D) All of the lipids above have about the same protein content.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The structure shown below is . 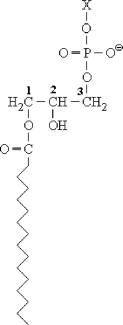
A) taurocholate
B) glycerophospholipid
C) carnitine
D) lysophosphoglyceride

A) taurocholate
B) glycerophospholipid
C) carnitine
D) lysophosphoglyceride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The main function of the bile salts is to .
A) transport lipids to the intestinal wall
B) act as counterions for the ionized forms of lipids
C) cleave the ester bonds in triacylglycerols to release free fatty acids
D) form the surface layer of chylomicrons
A) transport lipids to the intestinal wall
B) act as counterions for the ionized forms of lipids
C) cleave the ester bonds in triacylglycerols to release free fatty acids
D) form the surface layer of chylomicrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Each of the following is a principle hormonal regulator of fatty acid metabolism, except
A) glucagon.
B) adrenaline.
C) insulin.
D) epinephrine.
A) glucagon.
B) adrenaline.
C) insulin.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Animals use a type I fatty acid synthesis system FAS (I) while bacteria use a type II fatty acid synthesis system FAS (II).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A biotin-dependent enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the carboxylation of acetyl CoA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Regulation of acetyl CoA-carboxylase is accomplished by
A) inhibition by fatty acyl CoA.
B) activation by citrate in vitro).
C) inactivation by high levels of glycagon.
D) All of the above
A) inhibition by fatty acyl CoA.
B) activation by citrate in vitro).
C) inactivation by high levels of glycagon.
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which bonds of the triacylglycerol shown are hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipase? 
A) The carbon-carbon bonds between atoms 1,2 and 3.
B) The ester bond at carbon 2 only.
C) The bonds between the carbonyl carbons 4 and 6 and the first carbon of the hydrocarbon chains.
D) The ester bonds at carbons 1 and 3 only.

A) The carbon-carbon bonds between atoms 1,2 and 3.
B) The ester bond at carbon 2 only.
C) The bonds between the carbonyl carbons 4 and 6 and the first carbon of the hydrocarbon chains.
D) The ester bonds at carbons 1 and 3 only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which is not a ketone body?
A) dihydroxyacetone
B) acetoacetate
C) acetone
D) β-hydroxybutyrate
A) dihydroxyacetone
B) acetoacetate
C) acetone
D) β-hydroxybutyrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus NIDDM) is characterized by .
A) insulin secretion that is always at levels well below normal
B) insufficient insulin levels initiated during gestational diabetes
C) a shortage of insulin receptors that leads to accumulation of blood glucose
D) an inherited genetic abnormality in the insulin gene that yields a much less active insulin
A) insulin secretion that is always at levels well below normal
B) insufficient insulin levels initiated during gestational diabetes
C) a shortage of insulin receptors that leads to accumulation of blood glucose
D) an inherited genetic abnormality in the insulin gene that yields a much less active insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The largest lipoproteins are the .
A) chylomicrons
B) VLDLs
C) LDLs
D) HDLs
A) chylomicrons
B) VLDLs
C) LDLs
D) HDLs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
During the fed state, which of the following occurs)?
A) insulin inhibition of the hydrolysis of stored triacylglycerols
B) insulin stimulation of malonyl CoA formation
C) allosteric inhibition of carnitine acyltransferase I
D) All of the above
A) insulin inhibition of the hydrolysis of stored triacylglycerols
B) insulin stimulation of malonyl CoA formation
C) allosteric inhibition of carnitine acyltransferase I
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Triacylglycerols are more efficient to store than carbohydrates because their hydrophobicity allows them to be stored in adipose cells without large amounts of bound water molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which dietary lipid usually contains no ester bonds?
A) cholesterol
B) triacylglycerides
C) glycerophospholipids
D) None of the above, all dietary lipids are esterified
A) cholesterol
B) triacylglycerides
C) glycerophospholipids
D) None of the above, all dietary lipids are esterified

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the fate of most glycerol that is released during the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols from adipocytes?
A) It is transported to the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
B) It is used in the synthesis of sphingolipids.
C) It is converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis in the liver.
D) It is absorbed by the chylomicrons.
A) It is transported to the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
B) It is used in the synthesis of sphingolipids.
C) It is converted to glucose via gluconeogenesis in the liver.
D) It is absorbed by the chylomicrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Why is it undesirable to have high concentrations of free fatty acids in cells?
A) They are unstable, free radicals that can react to form toxic substances.
B) They polymerize easily and can cause the cytosol to become too gel-like.
C) They are amphipathic and act as detergents that can degrade membranes.
D) They inhibit the uptake of pyruvate by mitochondria.
A) They are unstable, free radicals that can react to form toxic substances.
B) They polymerize easily and can cause the cytosol to become too gel-like.
C) They are amphipathic and act as detergents that can degrade membranes.
D) They inhibit the uptake of pyruvate by mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is the major role of phospholipase A2?
A) To cleave the phosphate group from phospholipids.
B) To phosphorylate the enzyme enoyl-CoA.
C) To hydrolyze an ester bond in glycerophospholipids to form lysophosphoglyceride.
D) To transport glycerophospholipids in the blood.
A) To cleave the phosphate group from phospholipids.
B) To phosphorylate the enzyme enoyl-CoA.
C) To hydrolyze an ester bond in glycerophospholipids to form lysophosphoglyceride.
D) To transport glycerophospholipids in the blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A patient is found to have a high concentration of cholesterol in the blood and deposits of cholesterol under the skin. The patient is diagnosed with familial hypercholesterolemia. What is the likely cause of this condition?
A) A deficiency in insulin production by the pancreas.
B) Insufficient chylomicron concentration in the blood.
C) Overproduction of lysosomal lipases.
D) Lack of LDL receptors on the surfaces of nonhepatic cells.
A) A deficiency in insulin production by the pancreas.
B) Insufficient chylomicron concentration in the blood.
C) Overproduction of lysosomal lipases.
D) Lack of LDL receptors on the surfaces of nonhepatic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
High levels of VLDLs have been found to have a protective effect against atherosclerosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Ketone bodies are normally broken down in the liver in preparation for excretion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Most of the lipids in the diets of mammals are free fatty acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An increase in glucagon levels activates the enzyme which catalyzes malonyl CoA synthesis in the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In mammals the oxidation of fatty acids produces a two-carbon product and the synthesis of fatty acids begins with a two-carbon substrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Chylomicrons are found in high concentrations in the blood only during fasting when lipids from adipose tissue are mobilized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
CoA derivatives are the active thioesters in fatty acid oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Cytosolic HMG-CoA is used for ketone body synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In eukaryotes the enzyme complex called fatty acid synthase is responsible for the assembly of the fatty acid chain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The enzyme for b-oxidation is trifunctional with a2b2 tertiary structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Snake venom can cause the lysis of red blood cells due to the presence of phospholipase A2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During starvation ketone bodies can take the place of glucose as a fuel for brain cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
S-adenosylmethionine methylates phosphatidylethanolamine to form phosphatidylcholine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The bile salts taurocholate and glycocholate are amphipathic derivatives of cholesterol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Double bonds positioned farther than nine carbons from the carboxyl end of fatty acids occur only in vertebrates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



