Deck 12: Environmental Protection and Negative Externalities
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Environmental Protection and Negative Externalities
1
Which of the following have historically been more willing to sacrifice their environmental quality for some additional economic output?
A) high-income, market-oriented economies
B) low incomes and command economies
C) the United States
D) European Union
A) high-income, market-oriented economies
B) low incomes and command economies
C) the United States
D) European Union
low incomes and command economies
2
The term _______ refers to a market exchange that affects a third party who is outside or external to the exchange.
A) social costs
B) spillover
C) market failure
D) private costs
A) social costs
B) spillover
C) market failure
D) private costs
spillover
3
Command-and-control regulation is a body of law that
A) fails to consider private costs of firms.
B) specifies allowable quantities of pollution.
C) details which pollution-control technologies must be used.
D) can include both b and c.
A) fails to consider private costs of firms.
B) specifies allowable quantities of pollution.
C) details which pollution-control technologies must be used.
D) can include both b and c.
can include both b and c.
4
Which of the following has become the least willing to sacrifice their environmental quality for some additional economic output?
A) the European Union
B) China
C) Ohio
D) command economies
A) the European Union
B) China
C) Ohio
D) command economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Since 1969, when the Cuyahoga River in Ohio was so polluted that it spontaneously burst into flame, the overall quality of water in the U.S. has
A) steadily declined.
B) remained unchanged.
C) steadily improved.
D) remained a non-issue.
A) steadily declined.
B) remained unchanged.
C) steadily improved.
D) remained a non-issue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The problem of pollution arises in primarily _______economies around the world.
A) command-oriented
B) market-oriented
C) middle income
D) both a and b
A) command-oriented
B) market-oriented
C) middle income
D) both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is an example of economic output that can injure the environment?
A) gold mine discharging arsenic into a natural lake it's using for a tailings pond
B) paper mill discharging raw chemical waste into a river
C) excessive clear cutting of wood resources by logging companies
D) radio-active waste leaking into a river, and all of the above
A) gold mine discharging arsenic into a natural lake it's using for a tailings pond
B) paper mill discharging raw chemical waste into a river
C) excessive clear cutting of wood resources by logging companies
D) radio-active waste leaking into a river, and all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A positive externality arises in a situation where a third party, outside the transaction,
A) fails to allocate resources efficiently.
B) suffers from a market transaction by others.
C) benefits from a market transaction by others.
D) pays a pollution tax to balance social costs.
A) fails to allocate resources efficiently.
B) suffers from a market transaction by others.
C) benefits from a market transaction by others.
D) pays a pollution tax to balance social costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Market failure describes a situation in which the market itself _______ in a way that balances social costs and benefits.
A) remains outside the transaction
B) incurs the costs outside the production process
C) fails to allocate resources efficiently
D) avoids externalities
A) remains outside the transaction
B) incurs the costs outside the production process
C) fails to allocate resources efficiently
D) avoids externalities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The problem of pollution typically arises in _______economies around the world.
A) high-income
B) low-income
C) high or low-income
D) middle income
A) high-income
B) low-income
C) high or low-income
D) middle income

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The number of people served by advanced wastewater treatment plants doubled between 1968 and the mid-1990s, but because the treatment plants _______, the quantity of waste emitted into the water after treatment _______.
A) became so much more effective; decreased by about one-third
B) became so much less effective; increased by about one-third
C) remained ineffective; remained the same
D) moderately improved; increased by 10%
A) became so much more effective; decreased by about one-third
B) became so much less effective; increased by about one-third
C) remained ineffective; remained the same
D) moderately improved; increased by 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In addition to the current levels of air and water pollution, a list of important environmental issues would most likely include:
A) emissions of greenhouse gases
B) safe disposal of hazardous waste materials
C) destruction of wetlands and other habitats
D) extinction of species and all of the above
A) emissions of greenhouse gases
B) safe disposal of hazardous waste materials
C) destruction of wetlands and other habitats
D) extinction of species and all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following will need to strike some balance between economic output and environmental quality as a prominent climate change priority?
A) countries with high-incomes
B) every country
C) market-oriented countries
D) command-oriented countries
A) countries with high-incomes
B) every country
C) market-oriented countries
D) command-oriented countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
While the traditional approach of U.S. government policies for environmental protection has had some level of success, some economists are proposing a change to
A) a range of more flexible, market-oriented pollution control policies.
B) a range of polices stipulating set limits governing pollutant emissions.
C) stringent polices balance industry profit goals and environmental quality.
D) stringent polices that will return the environment to its former pristine quality.
A) a range of more flexible, market-oriented pollution control policies.
B) a range of polices stipulating set limits governing pollutant emissions.
C) stringent polices balance industry profit goals and environmental quality.
D) stringent polices that will return the environment to its former pristine quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is used to describe the full spectrum of animal and plant genetic material?
A) ecodiversity
B) biodiversity
C) envirodiversity
D) duodiversity
A) ecodiversity
B) biodiversity
C) envirodiversity
D) duodiversity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Traditionally, policies for environmental protection in the U.S. have focused on _______
Pollutant could be emitted.
A) eliminating the risk that any
B) setting limits for how much of each
C) avoiding the risk that any air
D) eliminating the risk that a toxic
Pollutant could be emitted.
A) eliminating the risk that any
B) setting limits for how much of each
C) avoiding the risk that any air
D) eliminating the risk that a toxic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Property rights are the legal rights of ownership on which others are
A) allowed to infringe by paying the property owner's pollution tax.
B) able to enforce use of pollution-control technologies.
C) able to specify allowable quantities of pollution.
D) not allowed to infringe without paying compensation.
A) allowed to infringe by paying the property owner's pollution tax.
B) able to enforce use of pollution-control technologies.
C) able to specify allowable quantities of pollution.
D) not allowed to infringe without paying compensation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A pollution charge is a form of tax imposed on
A) the quantity of pollution that a firm emits.
B) pollution control technologies.
C) every economy in the world.
D) low-income market-orientated industries.
A) the quantity of pollution that a firm emits.
B) pollution control technologies.
C) every economy in the world.
D) low-income market-orientated industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why would a typical U.S. business fail to take the social costs of pollution into consideration during the development of their operating strategies?
A) the range of flexible, market-oriented pollution control policies are flawed
B) government regulated the limits for how much pollutant can be emitted
C) it isn't required to pay any of the cost of cleaning up its pollution
D) it is following the principle of voluntary exchange of benefits
A) the range of flexible, market-oriented pollution control policies are flawed
B) government regulated the limits for how much pollutant can be emitted
C) it isn't required to pay any of the cost of cleaning up its pollution
D) it is following the principle of voluntary exchange of benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Around the world, the cities with the dirtiest air and water are typically found in _______.
A) high-income countries like France and the U.S.
B) in low-income African nations
C) low-income countries in Africa and Asia
D) in low-income East Asian nations
A) high-income countries like France and the U.S.
B) in low-income African nations
C) low-income countries in Africa and Asia
D) in low-income East Asian nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would an economist identify as a difficulty relating to environmental command-control regulations?
A) high degree of inflexibility
B) clear distinctions drawn between firms
C) lack of incentive to reduce pollution
D) obvious lack of loopholes
A) high degree of inflexibility
B) clear distinctions drawn between firms
C) lack of incentive to reduce pollution
D) obvious lack of loopholes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is viewed as a fundamental building block of the U.S. economic way of thinking?
A) the principle of setting high toxic emission limits to preserve a healthy environment
B) the belief that industry must be allowed to prevail over the environment
C) the needs of both parties to a voluntary exchange must be completely satisfied
D) the principle that a system of voluntary exchange benefits both parties
A) the principle of setting high toxic emission limits to preserve a healthy environment
B) the belief that industry must be allowed to prevail over the environment
C) the needs of both parties to a voluntary exchange must be completely satisfied
D) the principle that a system of voluntary exchange benefits both parties

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If you are highly asthmatic, then having high levels of industrial air pollutants waft over your house every day
A) is a voluntary exchange.
B) is positively a voluntary exchange.
C) would be a negative externality.
D) would be an external voluntary exchange.
A) is a voluntary exchange.
B) is positively a voluntary exchange.
C) would be a negative externality.
D) would be an external voluntary exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Some economists argue that if privately owned firms were required to pay the social costs of their pollution, the result would be:
A) each would create less pollution
B) each would lower production to decrease pollution levels
C) their supply curves will represent all of those social costs
D) the price of goods will rise and a and b above
A) each would create less pollution
B) each would lower production to decrease pollution levels
C) their supply curves will represent all of those social costs
D) the price of goods will rise and a and b above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If no externalities of pollution exist in a particular industry, the interaction of demand and supply _______.
A) is based on benefits individuals perceive while maximizing utility
B) is based on choices about production relative to total average costs
C) will coordinate social costs and benefits
D) shifts so supply has no relation to social costs
A) is based on benefits individuals perceive while maximizing utility
B) is based on choices about production relative to total average costs
C) will coordinate social costs and benefits
D) shifts so supply has no relation to social costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Because of the nature of the comprehensive environmental laws adopted during the late 1960s and early 1970s by the United States government, these laws are typically referred to as _______.
A) positive regulations
B) command and control regulations
C) control and command regulations
D) negative regulations
A) positive regulations
B) command and control regulations
C) control and command regulations
D) negative regulations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the U.S., the command-and-control environmental laws of the early 1970s, together with the ensuing amendments and updates that have been made to them over time,
A) were necessary as US industries had zero incentive to control pollution.
B) were an inexpensive incentive for industrial polluters to improve performance.
C) are given considerable credit for cleaner air and water in recent decades.
D) draws distinctions between the needs of firms and costly equipment upgrades.
A) were necessary as US industries had zero incentive to control pollution.
B) were an inexpensive incentive for industrial polluters to improve performance.
C) are given considerable credit for cleaner air and water in recent decades.
D) draws distinctions between the needs of firms and costly equipment upgrades.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a steel manufacturer considers the costs of labor and materials, as well as the broader costs of environmental injuries resulting from its manufacturing processes,
A) its supply curve will be based on perceived benefits of maximizing utility.
B) it is factoring in the social costs of the pollution it generates.
C) its demand curve will be based on production choices relating to marginal costs.
D) its costs will be the same as society's costs and all of the above.
A) its supply curve will be based on perceived benefits of maximizing utility.
B) it is factoring in the social costs of the pollution it generates.
C) its demand curve will be based on production choices relating to marginal costs.
D) its costs will be the same as society's costs and all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A _______ would lead a large greenhouse gas emitter to reduce emissions by less.
A) flat charge
B) higher pollution tax
C) lower pollution tax
D) pollution tax
A) flat charge
B) higher pollution tax
C) lower pollution tax
D) pollution tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following would be classified as a situation where a third party benefits from a market transaction by others?
A) City buying 10,000 trees for green space renewal projects.
B) Increased levels of air pollution in neighborhoods near a football stadium.
C) Allowing a mining company to use a natural lake to discharge waste.
D) Two firms trading pollution credits to avoid cutting their toxic emissions.
A) City buying 10,000 trees for green space renewal projects.
B) Increased levels of air pollution in neighborhoods near a football stadium.
C) Allowing a mining company to use a natural lake to discharge waste.
D) Two firms trading pollution credits to avoid cutting their toxic emissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If pollutants are emitted into the air and water, what costs might be incurred as a result?
A) compromised recreation possibilities
B) decreased property values
C) loss from destruction of wildlife habitat
D) health injuries and all of the above
A) compromised recreation possibilities
B) decreased property values
C) loss from destruction of wildlife habitat
D) health injuries and all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If an externality of pollution exists for all manufacturers in a given industry, then all related social costs
A) are no longer represented in their supply curves.
B) continue to be represented in their supply curves.
C) are no longer represented in their demand curves.
D) continue to be represented in their demand curves.
A) are no longer represented in their supply curves.
B) continue to be represented in their supply curves.
C) are no longer represented in their demand curves.
D) continue to be represented in their demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The objective of imposing a higher pollution tax is to
A) ensure firms have pollution charge credits for all reduced emissions.
B) provide incentive for firms to maintain regulation emission levels.
C) provide adequate incentive for firms to reduce their emissions by more.
D) ensure firms must pay the pollution charge for all reduced emissions.
A) ensure firms have pollution charge credits for all reduced emissions.
B) provide incentive for firms to maintain regulation emission levels.
C) provide adequate incentive for firms to reduce their emissions by more.
D) ensure firms must pay the pollution charge for all reduced emissions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Market-oriented environmental tools _______ for firms to take the social costs of pollution into account and _______ in reacting to these incentives.
A) draw distinctions; lower the social costs incurred
B) lack incentives; prohibit firms from having flexibility
C) create incentives; allow firms some flexibility
D) specify particular technology; lower the social costs incurred
A) draw distinctions; lower the social costs incurred
B) lack incentives; prohibit firms from having flexibility
C) create incentives; allow firms some flexibility
D) specify particular technology; lower the social costs incurred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Why do U.S. economists commonly refer to externalities as an example of market failure?
A) firms that are required to pay social costs of externalities produce more
B) externalities present a case where markets consider all social costs
C) externalities present a case where markets only consider some social costs
D) firms avoid having to pay social costs of externalities by lowering prices
A) firms that are required to pay social costs of externalities produce more
B) externalities present a case where markets consider all social costs
C) externalities present a case where markets only consider some social costs
D) firms avoid having to pay social costs of externalities by lowering prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The main categories of market-oriented approaches to pollution control are
A) redefined property rights; pollution permits; marketable charges.
B) marketable permits; better-defined property rights; pollution charges.
C) pollution charges; extended property rights; marketable permits.
D) pollution permits; defined property rights; marketable charges.
A) redefined property rights; pollution permits; marketable charges.
B) marketable permits; better-defined property rights; pollution charges.
C) pollution charges; extended property rights; marketable permits.
D) pollution permits; defined property rights; marketable charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
To be effective, U.S. command-and-control environmental regulation required
A) social costs of industrial pollution to become unavoidable business costs.
B) firms to take the social costs of pollution into account.
C) firms to increase their costs by installing specified anti-pollution equipment.
D) the EPA to oversee all environmental laws and all of the above.
A) social costs of industrial pollution to become unavoidable business costs.
B) firms to take the social costs of pollution into account.
C) firms to increase their costs by installing specified anti-pollution equipment.
D) the EPA to oversee all environmental laws and all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The comprehensive environmental laws adopted during the late 1960s and early 1970s by the United States government
A) stipulated mandatory use of particular pollution-control technologies.
B) allowed pollution credits to be traded between polluters to avoid bearing social costs.
C) stipulated exemptions for industries that lobbied politicians hard to avoid regulation.
D) allowed industries to determine pollution levels based on profit margins.
A) stipulated mandatory use of particular pollution-control technologies.
B) allowed pollution credits to be traded between polluters to avoid bearing social costs.
C) stipulated exemptions for industries that lobbied politicians hard to avoid regulation.
D) allowed industries to determine pollution levels based on profit margins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A pollution charge gives the trucking industry an incentive to reduce its emissions, as long as the of reducing the emissions is _______.
A) total cost; less than the tax
B) total cost; equal to the social cost
C) marginal cost; less than the tax
D) marginal cost; equal to the social cost
A) total cost; less than the tax
B) total cost; equal to the social cost
C) marginal cost; less than the tax
D) marginal cost; equal to the social cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The arguments presented by economists regarding U.S. environmental command-and-control regulations generally
A) accept the goal of reducing pollution.
B) question the regulations as being the best policy tools for meeting reduction goals.
C) assert that these laws are clear of the usual fine print, loopholes and exceptions.
D) lack flexibility and a and b above.
A) accept the goal of reducing pollution.
B) question the regulations as being the best policy tools for meeting reduction goals.
C) assert that these laws are clear of the usual fine print, loopholes and exceptions.
D) lack flexibility and a and b above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Environmentalist groups act to directly reduce of emissions by
A) allowing a limited amount of pollution to occur.
B) allowing a declining amount of pollution to occur.
C) buying marketable emission permits and not re-selling them.
D) buying, trading, and re-selling marketable emission permits.
A) allowing a limited amount of pollution to occur.
B) allowing a declining amount of pollution to occur.
C) buying marketable emission permits and not re-selling them.
D) buying, trading, and re-selling marketable emission permits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Market-oriented environmental policies are_______ , and _______ will work better in some situations than in others.
A) a tool-kit; specific tools
B) productive policies; some policies
C) inflexible; incentives to protect endangered species
D) flexible; the command-and-control approach
A) a tool-kit; specific tools
B) productive policies; some policies
C) inflexible; incentives to protect endangered species
D) flexible; the command-and-control approach

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In circumstances involving millions of emitters of small amounts of pollution who have no strong interest in trading, _______ will typically offer a better choice for achieving desired reductions of environmental pollution levels.
A) marketable permits
B) pollution charges
C) enhanced property rights
D) ecotourism
A) marketable permits
B) pollution charges
C) enhanced property rights
D) ecotourism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An economist is more likely to identify _______ as a more efficient and flexible way for society to _______.
A) marketable permits; allow a limited, declining amount of pollution to occur
B) better defined property rights; to address issues of allowable levels of pollution
C) market-oriented environmental tools; enforce strict limits on emissions
D) better defined property rights; to shrink pollution levels over time
A) marketable permits; allow a limited, declining amount of pollution to occur
B) better defined property rights; to address issues of allowable levels of pollution
C) market-oriented environmental tools; enforce strict limits on emissions
D) better defined property rights; to shrink pollution levels over time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The International Ecotourism Society estimates that international tourists interested in seeing nature or wildlife spend over
A) $450 billion per year.
B) $550 billion per year.
C) $250 billion annually.
D) $200 billion annually.
A) $450 billion per year.
B) $550 billion per year.
C) $250 billion annually.
D) $200 billion annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
One concern that environmentalists have is that market-oriented environmental tools are
A) an inflexible took that won't reduce pollution levels.
B) an excuse to implement strict limits on emissions.
C) an excuse to allow pollution to be maintained or to grow.
D) able to achieve desired reductions in pollution at a lower cost.
A) an inflexible took that won't reduce pollution levels.
B) an excuse to implement strict limits on emissions.
C) an excuse to allow pollution to be maintained or to grow.
D) able to achieve desired reductions in pollution at a lower cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Marketable permits can be viewed as a form of improved _______.
A) command-and-control regulations
B) property rights
C) refundable tax credits
D) flat fee pollution tax
A) command-and-control regulations
B) property rights
C) refundable tax credits
D) flat fee pollution tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The refundable charge of 5 or 10 cents for returning recyclable cans and bottles works like
A) an incentive to throw bottles and cans in the trash.
B) command-and-control regulation.
C) a market permit program.
D) a pollution tax incentive to avoid littering.
A) an incentive to throw bottles and cans in the trash.
B) command-and-control regulation.
C) a market permit program.
D) a pollution tax incentive to avoid littering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The flexibility of marketable permits program developed for the oil refining industry is credited
With achieving the reduction in lead pollution for _______ control regulation would have required.
A) at least 50%
B) 50%
C) 20%
D) at least 20%
With achieving the reduction in lead pollution for _______ control regulation would have required.
A) at least 50%
B) 50%
C) 20%
D) at least 20%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The property rights approach to environmental issues often becomes highly relevant in cases involving _______.
A) greenhouse gas emissions
B) harmful affects of acid rain
C) endangered species
D) fresh water resources
A) greenhouse gas emissions
B) harmful affects of acid rain
C) endangered species
D) fresh water resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When a government establishes a marketable permit program to address environmental pollution, it is actually issuing a form of
A) command-and-control regulation.
B) pollution tax.
C) permit to pollute.
D) inflexible, costly regulation.
A) command-and-control regulation.
B) pollution tax.
C) permit to pollute.
D) inflexible, costly regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Certain schools of economic thought suggest that a _______ would reduce pollution in a _______, when compared to command-and-control regulation.
A) marketable permit; less cost-effective way
B) pollution tax; flexible, more cost-effective way
C) marketable permit; less flexible manner
D) pollution tax; less cost effective, but flexible way
A) marketable permit; less cost-effective way
B) pollution tax; flexible, more cost-effective way
C) marketable permit; less flexible manner
D) pollution tax; less cost effective, but flexible way

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a glass manufacturer has only a few _______ of reducing pollutants, it will _______.
A) costly ways; end up paying the pollution tax.
B) inexpensive ways; incur the pollution tax instead.
C) costly ways; do so to minimize its pollution taxes.
D) inexpensive ways; buy the most expensive technology.
A) costly ways; end up paying the pollution tax.
B) inexpensive ways; incur the pollution tax instead.
C) costly ways; do so to minimize its pollution taxes.
D) inexpensive ways; buy the most expensive technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why was the Clean Air Act amended in 1990?
A) to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from electric power plants to half of 1980 levels
B) so flat fees for excessive pollution could be determined by the federal government
C) to reduce sulfur dioxide emission through command-and-control regulations
D) to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from electric power plants to half of 1970 levels
A) to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from electric power plants to half of 1980 levels
B) so flat fees for excessive pollution could be determined by the federal government
C) to reduce sulfur dioxide emission through command-and-control regulations
D) to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from electric power plants to half of 1970 levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Marketable permits work best when there are _______ permit holders who are highly interested in trading.
A) several dozen or a several hundred
B) less than a hundred
C) more than a thousand
D) a few dozen or a few hundred
A) several dozen or a several hundred
B) less than a hundred
C) more than a thousand
D) a few dozen or a few hundred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Some of the leading ecotourism destinations include:
A) Costa Rica and Panama in Central America
B) Malaysia and the Galapagos Islands
C) the Serengeti in Tanzania; the Amazon rain forests
D) the Caribbean, New Zealand and all of the above
A) Costa Rica and Panama in Central America
B) Malaysia and the Galapagos Islands
C) the Serengeti in Tanzania; the Amazon rain forests
D) the Caribbean, New Zealand and all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Environmentalist groups tend to prefer _______ to _______.
A) command-and-control regulations; marketable permits
B) marketable permits; pollution charges
C) pollution taxes; marketable permits
D) marketable permits; monetary refunds
A) command-and-control regulations; marketable permits
B) marketable permits; pollution charges
C) pollution taxes; marketable permits
D) marketable permits; monetary refunds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If a government chooses a system of marketable permits as its environmental managing tool, the reduction in pollution will
A) take place in the firms where it is least expensive to do so.
B) take place in every firm within the time set by the permit.
C) be initiated at the household level.
D) be rewarded with refundable charges.
A) take place in the firms where it is least expensive to do so.
B) take place in every firm within the time set by the permit.
C) be initiated at the household level.
D) be rewarded with refundable charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What type of environmental tool was adopted by the U.S. government in 1990, in order to reduce emissions of coal burning electricity-generating plants?
A) shrinkable marketable permits
B) free marketable permits
C) command-and-control permits
D) both a and b above
A) shrinkable marketable permits
B) free marketable permits
C) command-and-control permits
D) both a and b above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Those firms in the oil refining industry that can reduce pollution _______ will do so _______.
A) for a flat charge; at the industrial level
B) cheaply and easily; to minimize their pollution taxes
C) for a flat charge; with the most expensive technologies
D) cheaply and easily; with the most expensive technologies
A) for a flat charge; at the industrial level
B) cheaply and easily; to minimize their pollution taxes
C) for a flat charge; with the most expensive technologies
D) cheaply and easily; with the most expensive technologies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When making decisions about what safety systems should be required in cars or airplanes, the will only approve rules where the estimated cost per life saved is _______
Or less.
A) U.S. Senate; $5 million
B) U.S. Congress; $2 million
C) Environmental Protection Agency; $3 million
D) Environmental Regulation Agency; $7 million
Or less.
A) U.S. Senate; $5 million
B) U.S. Congress; $2 million
C) Environmental Protection Agency; $3 million
D) Environmental Regulation Agency; $7 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Low and middle-income societies correctly point out that high-income countries have historically
A) been the primary contributors to greenhouse warming.
B) been the primary contributors to reduced biodiversity.
C) failed to put environmental protection ahead of corporate profits.
D) legitimately lacked moral standing in addition to all the above.
A) been the primary contributors to greenhouse warming.
B) been the primary contributors to reduced biodiversity.
C) failed to put environmental protection ahead of corporate profits.
D) legitimately lacked moral standing in addition to all the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Four companies, Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta, are burning coal to produce electricity. As a result, they also produce emissions. The first row of the table below shows the total pounds of emissions currently produced by each firm. The other rows of the table show the cost for each firm of reducing emissions by the first 50 tons, the second 50 tons, and so on. The government wants to reduce emissions by one third, and does so by issuing marketable permits based on the current level of emissions where the permits will shrink the allowable amount of pollution by one third.

Alpha will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Beta will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Gamma will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Delta will reduce emissions by _______ tons, for a total cost of _______.
A) 50, 150, 50, 250, $130
B) 50, 200, 0, 250, $150
C) 0, 200, 50, 250, $120
D) 50, 200, 50, 200, $100

Alpha will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Beta will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Gamma will reduce emissions by _______ tons, Delta will reduce emissions by _______ tons, for a total cost of _______.
A) 50, 150, 50, 250, $130
B) 50, 200, 0, 250, $150
C) 0, 200, 50, 250, $120
D) 50, 200, 50, 200, $100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The challenge of preserving biodiversity,
A) any nation itself can reduce emissions to solve global warming.
B) any nation acting alone can protect biodiversity around the world.
C) includes the full spectrum of animal and plant genetic material.
D) a nation can protect biodiversity within its own borders and c.
A) any nation itself can reduce emissions to solve global warming.
B) any nation acting alone can protect biodiversity around the world.
C) includes the full spectrum of animal and plant genetic material.
D) a nation can protect biodiversity within its own borders and c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
With respect to the benefits of clean air and water, which of the following would most likely be classified as being relatively easy to value in economic terms?
A) gains in farming, fishing and tourism
B) gains from lower levels of corrosion
C) gains in environmental enjoyment
D) all of the above are correct answers
A) gains in farming, fishing and tourism
B) gains from lower levels of corrosion
C) gains in environmental enjoyment
D) all of the above are correct answers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A beekeeper decides to locate her business on a plot of land that is between an apple orchard and an elementary school. A negative externality that can result is
A) the cost of the bee hives to the beekeeper.
B) the possibility of the bees stinging the students at the school.
C) the bees helping to pollinate the orchard, leading to more fruit.
D) the honey the bees produce.
A) the cost of the bee hives to the beekeeper.
B) the possibility of the bees stinging the students at the school.
C) the bees helping to pollinate the orchard, leading to more fruit.
D) the honey the bees produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Four companies, Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta, are burning coal to produce electricity. As a result, they also produce emissions. In the table below, the first row of shows the total pounds of emissions currently produced by each firm. The other rows of the table show the cost for each firm of reducing emissions by the first 50 tons, the second 50 tons, and so on.

The total cost of requiring each firm to reduce its garbage by one third is
A) $167
B) $137
C) $187
D) $127

The total cost of requiring each firm to reduce its garbage by one third is
A) $167
B) $137
C) $187
D) $127

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Michigan MI) and Wisconsin WI) both border Lake Michigan. Both states pollute Lake Michigan and both states suffer the consequences of the pollution. However, the two states face a prisoner's dilemma of the sort studied in Chapter 12. Each country must decide whether to protect or not to protect Lake Michigan from pollution. The payoffs from the choices are shown in the table below.

From the table, we know that if Wisconsin chooses to protect the lake, Michigan will choose to _______
The lake. If Wisconsin chooses to not protect the lake, Michigan will choose to _______ the lake
A) protect, protect
B) not protect, protect
C) protect, not protect
D) not protect, not protect

From the table, we know that if Wisconsin chooses to protect the lake, Michigan will choose to _______
The lake. If Wisconsin chooses to not protect the lake, Michigan will choose to _______ the lake
A) protect, protect
B) not protect, protect
C) protect, not protect
D) not protect, not protect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When the quantity of environmental protection is low so that pollution is extensive, then there are usually _______ to reduce pollution and the _______.
A) a few inexpensive and easy ways; average benefit are slightly higher
B) a lot of expensive and innovative methods; marginal benefits are quite high
C) only a few expensive and innovative methods; average benefits are higher
D) a lot of cheap and easy ways; marginal benefits of doing so are quite high
A) a few inexpensive and easy ways; average benefit are slightly higher
B) a lot of expensive and innovative methods; marginal benefits are quite high
C) only a few expensive and innovative methods; average benefits are higher
D) a lot of cheap and easy ways; marginal benefits of doing so are quite high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Rather than arguing over whether the ultimate goal is zero pollution or a reasonable level of pollution, the immediate focus should be to tackle the environmental issues where the _______
And the _______.
A) marginal benefits are least; marginal costs are greatest
B) marginal benefits are greatest; marginal costs are least
C) environmental benefits are greatest; social costs are least
D) social costs are greatest; environmental benefits are least
And the _______.
A) marginal benefits are least; marginal costs are greatest
B) marginal benefits are greatest; marginal costs are least
C) environmental benefits are greatest; social costs are least
D) social costs are greatest; environmental benefits are least

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Kip and Yale run separate mining companies in the same forest. Both pollute the river flowing through the forest with debris from their work. In the table below, the first row shows the current level of debris that makes its way into the river from their work. The following table set out information that shows how much it would cost each company to reduce its pollution by additional increments of 10 pounds.

If each mining company is forced to cut its debris in half, the respective cost to Kip and Yale will be
A) $5, $2
B) $10, $4
C) $30, $20
D) $30, $12

If each mining company is forced to cut its debris in half, the respective cost to Kip and Yale will be
A) $5, $2
B) $10, $4
C) $30, $20
D) $30, $12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The supply and demand conditions facing a firm that makes widgets and generates a negative externality by dumping a highly toxic sludge in a nearby river is given in the table below.
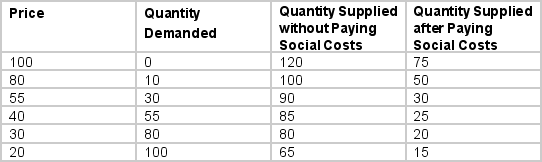
The equilibrium price and quantity when social costs are taken into account are
A) Price = $55, Quantity = 30
B) Price = $40, Quantity = 55
C) Price = $30, Quantity = 20
D) Price = $30, Quantity = 80

The equilibrium price and quantity when social costs are taken into account are
A) Price = $55, Quantity = 30
B) Price = $40, Quantity = 55
C) Price = $30, Quantity = 20
D) Price = $30, Quantity = 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
As environmental protection increases,
A) the biggest marginal benefits are achieved first, smaller marginal benefits follow.
B) inexpensive and easy methods of reducing pollution begin to dwindle.
C) the more costly and innovative methods can be readily avoided.
D) in addition to a and b above, the quality of environmental protection increases.
A) the biggest marginal benefits are achieved first, smaller marginal benefits follow.
B) inexpensive and easy methods of reducing pollution begin to dwindle.
C) the more costly and innovative methods can be readily avoided.
D) in addition to a and b above, the quality of environmental protection increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The supply and demand conditions facing a firm that makes widgets and generates a negative externality by dumping a highly toxic sludge in a nearby river is given in the table below.
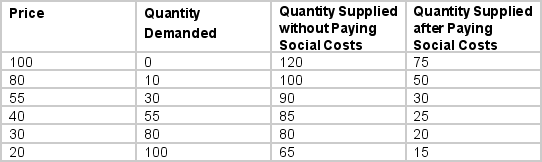
The equilibrium price and quantity when only private costs are taken into account are
A) Price = $55, Quantity = 30
B) Price = $40, Quantity = 55
C) Price = $30, Quantity = 20
D) Price = $30, Quantity = 80

The equilibrium price and quantity when only private costs are taken into account are
A) Price = $55, Quantity = 30
B) Price = $40, Quantity = 55
C) Price = $30, Quantity = 20
D) Price = $30, Quantity = 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A study by the Environmental Protection Agency looked at the costs and benefits of the Clean Air Act from 1970 to 1990. This study found that a middle-range estimate of the health and other benefits from cleaner air was $22 trillion. This amount was about _______ than the costs of reducing the pollution.
A) 10 time lower
B) 44 times higher
C) 10 times higher
D) 44 times lower
A) 10 time lower
B) 44 times higher
C) 10 times higher
D) 44 times lower

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If market-oriented environmental tools offer a mechanism or providing either the same environmental protection at lower cost, or providing a greater degree of environmental protection for the same cost, then this _______ will arise for _______.
A) spillover; market-oriented countries
B) trade-off; command-oriented countries
C) trade-off; all countries around the globe
D) spillover; only the high-income countries
A) spillover; market-oriented countries
B) trade-off; command-oriented countries
C) trade-off; all countries around the globe
D) spillover; only the high-income countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Kip and Yale run separate mining companies in the same forest. Both pollute the river flowing through the forest with debris from their work. In the table below, the first row shows the current level of debris that makes its way into the river from their work. The following table set out information that show how much it would cost each company to reduce its pollution by additional
Increments of 10 pounds.

If a system of tradable permits is introduced, the total cost of cutting current debris in half is
A) $40
B) $45
C) $50
D) $55
Increments of 10 pounds.

If a system of tradable permits is introduced, the total cost of cutting current debris in half is
A) $40
B) $45
C) $50
D) $55

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Bringing the nations of the world to act together in addressing environmental issues that spill over national borders requires _______ between countries with _______.
A) a different approach to negotiations; similar income levels and sets of priorities
B) a difficult set of negotiations; different income levels and sets of priorities
C) a different approach to negotiations; low and middle-income levels.
D) deliberate negotiations; high-income levels and similar sets of priorities.
A) a different approach to negotiations; similar income levels and sets of priorities
B) a difficult set of negotiations; different income levels and sets of priorities
C) a different approach to negotiations; low and middle-income levels.
D) deliberate negotiations; high-income levels and similar sets of priorities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A beekeeper decides to locate her business on a plot of land that is between an apple orchard and an elementary school. A positive externality that can result is
A) the cost of the bee hives to the beekeeper.
B) the possibility of the bees stinging the students at the school.
C) the bees helping to pollinate the orchard, leading to more fruit.
D) the honey the bees produce.
A) the cost of the bee hives to the beekeeper.
B) the possibility of the bees stinging the students at the school.
C) the bees helping to pollinate the orchard, leading to more fruit.
D) the honey the bees produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Carl and Don run separate chemical fertilizer manufacturing companies in the same industrial park. Both pollute the river flowing through the industrial park with waste from their manufacturing processes. In the table below, the first row shows the current level of waste that makes its way into the river from their respective operations. The table also sets out information that indicates how much it would cost each manufacturer to reduce its pollution by additional increments of 10 pounds.

If each company is required to reduce debris by exactly 20 pounds, the total cost will be
A) $7
B) $14
C) $21
D) $30

If each company is required to reduce debris by exactly 20 pounds, the total cost will be
A) $7
B) $14
C) $21
D) $30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



