Deck 14: Taxation and Income Distribution
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Taxation and Income Distribution
1
The tax-induced difference between the price paid by consumers and the price received by producers is
A)the supply side effect.
B)the tax incidence.
C)the tax difference.
D)the tax wedge.
A)the supply side effect.
B)the tax incidence.
C)the tax difference.
D)the tax wedge.
the tax wedge.
2
Ad valorem taxes vary along with the price of the taxed commodity.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
True
3
Useful general equilibrium results can be obtained from models with ________ commodities, factors of production and no savings.
A)1, 1
B)2, 2
C)0, 2
D)2, 0
A)1, 1
B)2, 2
C)0, 2
D)2, 0
2, 2
4
A tax wedge causes
A)all prices to fall.
B)the price paid by consumers to separate from the price received by producers.
C)the price paid by consumers to equal the price received by producers.
D)the price received by producers to rise above the price paid by consumers.
A)all prices to fall.
B)the price paid by consumers to separate from the price received by producers.
C)the price paid by consumers to equal the price received by producers.
D)the price received by producers to rise above the price paid by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a general equilibrium model, a tax on a single factor in its use only in a particular sector can affect returns to all factors in all sectors.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A subsidy on consumers will cause
A)a movement up the demand curve.
B)the demand curve to shift left.
C)the demand curve to shift right.
D)a movement down the demand curve.
A)a movement up the demand curve.
B)the demand curve to shift left.
C)the demand curve to shift right.
D)a movement down the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A lump sum tax is one for which the individual's tax liability does not depend upon behaviour.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Ad valorem taxes create tax wedges just like unit taxes.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A demand curve that is perfectly inelastic is
A)horizontal.
B)parallel to the X-axis.
C)vertical.
D)at a 45 degree angle.
A)horizontal.
B)parallel to the X-axis.
C)vertical.
D)at a 45 degree angle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A tax on suppliers will cause
A)a movement up the supply curve.
B)the supply curve to shift left.
C)the supply curve to shift right.
D)a movement down the supply curve.
A)a movement up the supply curve.
B)the supply curve to shift left.
C)the supply curve to shift right.
D)a movement down the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A monopoly has seller(s)in the market.
A)0
B)1
C)few
D)many
A)0
B)1
C)few
D)many

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Unit taxes cause pivots, while ad valorem taxes cause shifts.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Partial equilibrium is
A)the study of individual markets.
B)the study of only the demand side of the market.
C)the study of only the supply side of the market.
D)identical to general equilibrium.
A)the study of individual markets.
B)the study of only the demand side of the market.
C)the study of only the supply side of the market.
D)identical to general equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In 2005, the top 1% based on family income faced a total tax rate of
A)30.5%
B)50.0%
C)22.5%
D)10.0%
A)30.5%
B)50.0%
C)22.5%
D)10.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Tax wedge is the difference between tax-induced price paid by consumers and the tax amount.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An industry where the capital-labour ratio is relatively high is characterized as
A)labour intensive.
B)capital intensive.
C)income intensive.
D)market intensive.
A)labour intensive.
B)capital intensive.
C)income intensive.
D)market intensive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Marginal tax rates supply reliable measures of tax progressiveness.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Taxes
A)are the only way of financing government expenditures.
B)do not directly relate to the benefit of government goods and services received.
C)are mandatory payments.
D)all of these answer options are correct.
A)are the only way of financing government expenditures.
B)do not directly relate to the benefit of government goods and services received.
C)are mandatory payments.
D)all of these answer options are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How the tax system changes the distribution of income among capitalists, labourers, and landlords in referred to as
A)size distribution of income.
B)functional distribution of income.
C)balanced-budget incidence.
D)proportional distribution of income.
A)size distribution of income.
B)functional distribution of income.
C)balanced-budget incidence.
D)proportional distribution of income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An ad valorem tax is a fixed amount per unit of a commodity sold.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Even with a tax, the price that consumers pay will always be higher than the price producers receive.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Why is it the case that a commodity tax on goods like food and shelter is sometimes seen as being regressive?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A supply curve that is perfectly elastic is
A)vertical.
B)horizontal.
C)at a 45 degree angle.
D)parallel to the Y-axis.
A)vertical.
B)horizontal.
C)at a 45 degree angle.
D)parallel to the Y-axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
As long as firms are profit maximizing, a tax on economic profits cannot be shifted and is borne only by the owners of the firm.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The economic incidence of a tax is
A)generally borne by sellers.
B)generally borne by buyers.
C)the change in the distribution of public funds.
D)the change in the distribution of private real income.
A)generally borne by sellers.
B)generally borne by buyers.
C)the change in the distribution of public funds.
D)the change in the distribution of private real income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In an open economy where capital is perfectly mobile across countries, the supply of capital is
A)zero.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)unknown.
A)zero.
B)perfectly inelastic.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)unknown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose that demand is perfectly inelastic. Supply is normal and upward sloping. What is the economic incidence of a unit tax placed on suppliers? Illustrate this with an appropriate diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
General equilibrium analysis
A)finds equilibrium from general information.
B)examines markets without specific information.
C)takes into account how various markets are interrelated.
D)studies individual markets.
A)finds equilibrium from general information.
B)examines markets without specific information.
C)takes into account how various markets are interrelated.
D)studies individual markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Refer to the figure below. Suppose the original before-tax demand curve for champagne is P = 100 - 2Qd. Suppose further that supply is P = 5 + 3Qs. Now suppose a $5 unit tax is imposed on consumers.
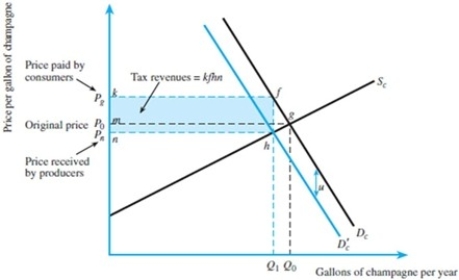 (A)What is the before-tax equilibrium price and quantity?
(A)What is the before-tax equilibrium price and quantity?
(B)What is the after-tax equilibrium price and quantity?
(C)How much tax revenue is raised?
 (A)What is the before-tax equilibrium price and quantity?
(A)What is the before-tax equilibrium price and quantity?(B)What is the after-tax equilibrium price and quantity?
(C)How much tax revenue is raised?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The ease with which capital can be substituted for labour, or vice versa, is the
A)factor elasticity.
B)elasticity of substitution.
C)elasticity of production.
D)income elasticity.
A)factor elasticity.
B)elasticity of substitution.
C)elasticity of production.
D)income elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Examining how incidence differs when one tax is replaced with another, holding the government budget constant, is referred to as absolute tax incidence.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Statutory incidence of a tax deals with
A)the amount of tax revenue generated after a tax is imposed.
B)the amount of revenue left over after taxes.
C)the amount of taxes paid after accounting for inflation.
D)the person(s)legally responsible for paying the tax.
A)the amount of tax revenue generated after a tax is imposed.
B)the amount of revenue left over after taxes.
C)the amount of taxes paid after accounting for inflation.
D)the person(s)legally responsible for paying the tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When the ratio of taxes paid to income is constant regardless of income level, it is called a
A)marginal tax.
B)progressive tax.
C)proportional tax.
D)lump sum tax.
A)marginal tax.
B)progressive tax.
C)proportional tax.
D)lump sum tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the press, there has been a considerable amount of attention given to the notion of corporations being taxed. Explain how it is that a tax on a business could be borne entirely by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose there is a market that has market demand characterized as X = 30 - P/3.
Suppose further that market supply can be written as X = P/2 - 2.
(A)Find the equilibrium price and quantity in this market.
(B)If a unit tax of $16 is imposed on good X, what are the equilibrium price, quantity, and tax revenue in the market?
(C)Suppose an ad valorem tax of 30 percent is imposed on good X. The after-tax demand equation would be X = 30 - P/2. Now find the equilibrium price, quantity, and tax revenue in the market.
(D)What can be said about the amount of tax revenue generated under each taxing scheme, and why
Suppose further that market supply can be written as X = P/2 - 2.
(A)Find the equilibrium price and quantity in this market.
(B)If a unit tax of $16 is imposed on good X, what are the equilibrium price, quantity, and tax revenue in the market?
(C)Suppose an ad valorem tax of 30 percent is imposed on good X. The after-tax demand equation would be X = 30 - P/2. Now find the equilibrium price, quantity, and tax revenue in the market.
(D)What can be said about the amount of tax revenue generated under each taxing scheme, and why

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Partial factor taxes are levied on an input in only some of its uses.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider a monopolist who has a total cost curve of: TC = 7X + (1/2)X2. The market demand equation is Xd = 386 - (1/2)P.
A)What are the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price, and profits in this market?
B)Suppose that a unit tax of $1 is placed on the monopolist. What happens to the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price paid by consumers, and profits? How much tax revenue does the government generate?
C)Suppose that the same unit tax of $1 is placed on consumers. What happens to the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price paid by consumers, and profits? How much tax revenue does the government generate?
D)What can be said about the tax revenues generated?
A)What are the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price, and profits in this market?
B)Suppose that a unit tax of $1 is placed on the monopolist. What happens to the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price paid by consumers, and profits? How much tax revenue does the government generate?
C)Suppose that the same unit tax of $1 is placed on consumers. What happens to the equilibrium quantity, equilibrium price paid by consumers, and profits? How much tax revenue does the government generate?
D)What can be said about the tax revenues generated?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An ad valorem tax is
A)always legally paid by consumers.
B)given as a proportion of the price.
C)identical in form to a unit tax.
D)Latin for "buyer beware."
A)always legally paid by consumers.
B)given as a proportion of the price.
C)identical in form to a unit tax.
D)Latin for "buyer beware."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In 2005, the top 1% based on family income faced the highest effective tax rates in Canada.
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain
A)True
B)False
C)Uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When marginal tax rates are constant,
A)the change in taxes paid is always greater than the change in income.
B)the change in taxes paid is always the same as the change in income.
C)the change in taxes paid is always less than the change in income.
D)none of these answer options is correct.
A)the change in taxes paid is always greater than the change in income.
B)the change in taxes paid is always the same as the change in income.
C)the change in taxes paid is always less than the change in income.
D)none of these answer options is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Why is it the case that taxes in one market can have impacts on supply and demand in others and should policy makers take this into account when setting taxes?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 41 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



