Deck 19: Natural Resource and Energy Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/280
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Natural Resource and Energy Economics
1
If a country has a total fertility rate of 1.8, then, all else equal, we would expect
A)population in that country to rise over time.
B)population in that country to fall over time.
C)the replacement rate to also equal 1.8.
D)the population to remain stable over time.
A)population in that country to rise over time.
B)population in that country to fall over time.
C)the replacement rate to also equal 1.8.
D)the population to remain stable over time.
population in that country to fall over time.
2
The total fertility rate
A)measures the average number of children that a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
B)exceeds the replacement rate in countries with a falling population.
C)equals the rate of population change over time.
D)rises as income rises.
A)measures the average number of children that a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
B)exceeds the replacement rate in countries with a falling population.
C)equals the rate of population change over time.
D)rises as income rises.
measures the average number of children that a woman is expected to have during her lifetime.
3
The total fertility rate necessary to keep the population constant is approximately equal to
A)1.0.
B)1.5.
C)2.1.
D)3.0.
A)1.0.
B)1.5.
C)2.1.
D)3.0.
2.1.
4
Which of the following is not considered by demographers to be part of the three-step demographic transition?
A)simultaneous low birthrates and death rates
B)simultaneous high birthrates and death rates
C)low birthrates and high death rates
D)high birthrates and low death rates
A)simultaneous low birthrates and death rates
B)simultaneous high birthrates and death rates
C)low birthrates and high death rates
D)high birthrates and low death rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Relative to 1800, today in the world there are
A)more people but lower per-capita consumption.
B)more people but the same per-capita consumption.
C)more people and higher per-capita consumption.
D)the same number of people but higher per-capita consumption.
A)more people but lower per-capita consumption.
B)more people but the same per-capita consumption.
C)more people and higher per-capita consumption.
D)the same number of people but higher per-capita consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A rising standard of living will
A)necessarily reduce the population by reducing the birthrate.
B)increase the birthrate.
C)reduce the birthrate, but population may continue to grow if the death rate falls more quickly.
D)reduce the birthrate initially but will increase the birthrate significantly at higher levels of income as people can afford to have more children.
A)necessarily reduce the population by reducing the birthrate.
B)increase the birthrate.
C)reduce the birthrate, but population may continue to grow if the death rate falls more quickly.
D)reduce the birthrate initially but will increase the birthrate significantly at higher levels of income as people can afford to have more children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Since 1850, the
A)supply and demand for productive resources have grown at the same rate.
B)supply of productive resources has grown faster than the demand for those resources.
C)demand for productive resources has grown faster than the supply of those resources.
D)supply of productive resources has increased, while the demand has fallen.
A)supply and demand for productive resources have grown at the same rate.
B)supply of productive resources has grown faster than the demand for those resources.
C)demand for productive resources has grown faster than the supply of those resources.
D)supply of productive resources has increased, while the demand has fallen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which step of the demographic transition would we expect population to grow the fastest?
A)Step 1
B)Step 2
C)Step 3
D)There is no step that would be expected to consistently yield faster population growth.
A)Step 1
B)Step 2
C)Step 3
D)There is no step that would be expected to consistently yield faster population growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A total fertility rate of 1.0 will cause the
A)population to remain stable.
B)population to double in one generation.
C)population to collapse in one generation.
D)next generation to be half the size of the current generation.
A)population to remain stable.
B)population to double in one generation.
C)population to collapse in one generation.
D)next generation to be half the size of the current generation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is true about falling birthrates?
A)They tend to lag behind falling death rates, allowing population growth to continue for at least one or two more generations.
B)They tend to precede declines in death rates, causing a temporary dip in population before it stabilizes in a generation or two.
C)They tend to lag behind declining standards of living.
D)They always cause population to decline.
A)They tend to lag behind falling death rates, allowing population growth to continue for at least one or two more generations.
B)They tend to precede declines in death rates, causing a temporary dip in population before it stabilizes in a generation or two.
C)They tend to lag behind declining standards of living.
D)They always cause population to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the concept of demographic transition,
A)population growth rates should slow as nations move into the final stage.
B)population growth rates should rise as nations move into the final stage.
C)population growth becomes exponential when nations are in the final stage.
D)population plummets in the transition phase.
A)population growth rates should slow as nations move into the final stage.
B)population growth rates should rise as nations move into the final stage.
C)population growth becomes exponential when nations are in the final stage.
D)population plummets in the transition phase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following nations, as of 2015, has a total fertility rate that would suggest that its next generation will be just over half the size of the current generation?
A)Hong Kong
B)Australia
C)Sweden
D)all of these nations
A)Hong Kong
B)Australia
C)Sweden
D)all of these nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Many demographers expect world population to
A)increase exponentially into the foreseeable future.
B)decline from its current level in the next two decades.
C)peak at 9 billion or fewer and then decline.
D)plateau at around 7.5 billion and then start to increase rapidly.
A)increase exponentially into the foreseeable future.
B)decline from its current level in the next two decades.
C)peak at 9 billion or fewer and then decline.
D)plateau at around 7.5 billion and then start to increase rapidly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the relationship between living standards and birthrates?
A)The relationship is negative at low levels of income but becomes increasingly positive as incomes rise.
B)They are unrelated.
C)The relationship is positive (directly related).
D)The relationship is negative (inversely related).
A)The relationship is negative at low levels of income but becomes increasingly positive as incomes rise.
B)They are unrelated.
C)The relationship is positive (directly related).
D)The relationship is negative (inversely related).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following, in order, describes the three steps of the demographic transition?
A)low birthrates and death rates; high birthrates and low death rates; high birthrates and death rates
B)high birthrates and death rates; low birthrates and high death rates; low birthrates and death rates
C)high birthrates and low death rates; high birthrates and death rates; low birthrates and death rates
D)high birthrates and death rates; high birthrates and low death rates; low birthrates and death rates
A)low birthrates and death rates; high birthrates and low death rates; high birthrates and death rates
B)high birthrates and death rates; low birthrates and high death rates; low birthrates and death rates
C)high birthrates and low death rates; high birthrates and death rates; low birthrates and death rates
D)high birthrates and death rates; high birthrates and low death rates; low birthrates and death rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Population will necessarily fall if the
A)birthrate exceeds the replacement rate.
B)replacement rate exceeds the birthrate.
C)birthrate exceeds the total fertility rate.
D)total fertility rate exceeds the birthrate.
A)birthrate exceeds the replacement rate.
B)replacement rate exceeds the birthrate.
C)birthrate exceeds the total fertility rate.
D)total fertility rate exceeds the birthrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Rapid population growth since 1800 has occurred primarily because of
A)a significant increase in total fertility rates as living standards have risen.
B)a significant reduction in death rates as living standards have risen.
C)a significant increase in replacement rates as living standards have risen.
D)all of the reasons given in the other possible answers.
A)a significant increase in total fertility rates as living standards have risen.
B)a significant reduction in death rates as living standards have risen.
C)a significant increase in replacement rates as living standards have risen.
D)all of the reasons given in the other possible answers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
As of 2016, the world's population is approximately
A)7.4 billion.
B)5.3 billion.
C)10 billion.
D)1.2 trillion.
A)7.4 billion.
B)5.3 billion.
C)10 billion.
D)1.2 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Whose An Essay on the Principle of Population argued that human living standards could only temporarily rise above subsistence?
A)Adam Smith
B)Thomas Malthus
C)John Maynard Keynes
D)Alfred Marshall
A)Adam Smith
B)Thomas Malthus
C)John Maynard Keynes
D)Alfred Marshall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Relative to 1800, the living standard of the average person today in the United States is about times higher.
A)5
B)12
C)20
D)42
A)5
B)12
C)20
D)42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Power plants with the lowest operating costs tend to
A)have the lowest fixed costs in terms of construction.
B)have the highest fixed costs in terms of construction.
C)operate on the smallest scale of energy production.
D)generate the cleanest energy.
A)have the lowest fixed costs in terms of construction.
B)have the highest fixed costs in terms of construction.
C)operate on the smallest scale of energy production.
D)generate the cleanest energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
ACME Corporation used to produce $50 worth of goods (in 2000 dollars) per million BTUs used.Now it produces $60 worth of goods (in 2000 dollars) per million BTUs.Based on this, we can conclude
A)nothing about ACME's energy efficiency.
B)that ACME's energy efficiency has declined.
C)that ACME's energy efficiency has improved.
D)that ACME is using a single energy source and achieving economies of scale in production.
A)nothing about ACME's energy efficiency.
B)that ACME's energy efficiency has declined.
C)that ACME's energy efficiency has improved.
D)that ACME is using a single energy source and achieving economies of scale in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Since 1950, the energy efficiency of the U.S.economy in terms of producing goods and services has
A)not changed.
B)more than doubled.
C)risen about 50 percent.
D)risen more than threefold.
A)not changed.
B)more than doubled.
C)risen about 50 percent.
D)risen more than threefold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true about U.S.energy consumption and per capita real GDP since 1990?
A)Per capita energy consumption and per capita real GDP have both risen.
B)Per capita energy consumption has fallen, while per capita real GDP has risen.
C)Per capita energy consumption and per capita real GDP have both fallen.
D)Per capita consumption of energy has been unchanged, while per capita real GDP has risen.
A)Per capita energy consumption and per capita real GDP have both risen.
B)Per capita energy consumption has fallen, while per capita real GDP has risen.
C)Per capita energy consumption and per capita real GDP have both fallen.
D)Per capita consumption of energy has been unchanged, while per capita real GDP has risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Global resource demand has
A)remained relatively constant because increases in population have been offset by declining consumption per person.
B)declined because of technological progress.
C)remained constant because population growth and increased consumption per person have been offset by technological progress.
D)increased because population growth and increased consumption per person have more than offset reduced demand due to technological progress.
A)remained relatively constant because increases in population have been offset by declining consumption per person.
B)declined because of technological progress.
C)remained constant because population growth and increased consumption per person have been offset by technological progress.
D)increased because population growth and increased consumption per person have more than offset reduced demand due to technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If per capita trash generation is constant over time, this implies that
A)per capita consumption of solids has also been constant.
B)per capita consumption of goods and services has also been constant.
C)total consumption of solids has also been constant.
D)total consumption of goods and services has also been constant.
A)per capita consumption of solids has also been constant.
B)per capita consumption of goods and services has also been constant.
C)total consumption of solids has also been constant.
D)total consumption of goods and services has also been constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
World commodity prices over the past 150 years have
A)steadily decreased in both the short run and long run.
B)decreased in the long run despite occasional short-run increases.
C)remained constant in the long run despite occasional short-run fluctuations.
D)steadily increased in both the short run and long run.
A)steadily decreased in both the short run and long run.
B)decreased in the long run despite occasional short-run increases.
C)remained constant in the long run despite occasional short-run fluctuations.
D)steadily increased in both the short run and long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Just over half (55 percent) of U.S.electricity is generated from
A)hydroelectric.
B)petroleum.
C)nuclear energy.
D)coal and gas.
A)hydroelectric.
B)petroleum.
C)nuclear energy.
D)coal and gas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
To achieve economic efficiency in energy use, an economy
A)often uses a variety of energy sources.
B)must use the single energy source in which it can achieve economies of scale.
C)should use all energy sources in equal proportion.
D)should use only domestically produced energy.
A)often uses a variety of energy sources.
B)must use the single energy source in which it can achieve economies of scale.
C)should use all energy sources in equal proportion.
D)should use only domestically produced energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Average per capita water consumption in the United States was approximately how many gallons per day in 2010?
A)355
B)764
C)1,941
D)1,134
A)355
B)764
C)1,941
D)1,134

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In energy economics, "BTU" stands for
A)boiling temperature unit.
B)base tax utility.
C)British thermal unit.
D)base technology utility.
A)boiling temperature unit.
B)base tax utility.
C)British thermal unit.
D)base technology utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Over the past decade, U.S.per capita consumption of water
A)and energy have both increased.
B)has increased, while per capita consumption of energy has fallen.
C)and energy have leveled off or fallen.
D)has fallen, while per capita consumption of energy has increased.
A)and energy have both increased.
B)has increased, while per capita consumption of energy has fallen.
C)and energy have leveled off or fallen.
D)has fallen, while per capita consumption of energy has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Over the past two decades, total and per capita water use in the United States have
A)both increased.
B)leveled off and fallen, respectively.
C)fallen and leveled off, respectively.
D)increased and fallen, respectively.
A)both increased.
B)leveled off and fallen, respectively.
C)fallen and leveled off, respectively.
D)increased and fallen, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following explains why commodity prices have fallen since 1850?
A)The demand for productive resources has fallen faster than the supply of those resources.
B)The demand for productive resources has grown faster than the supply of those resources.
C)The supply of productive resources has increased, while the demand has fallen.
D)The supply of productive resources has grown faster than the demand for those resources.
A)The demand for productive resources has fallen faster than the supply of those resources.
B)The demand for productive resources has grown faster than the supply of those resources.
C)The supply of productive resources has increased, while the demand has fallen.
D)The supply of productive resources has grown faster than the demand for those resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Resource demand has grown over time
A)because of population growth only.
B)because of increased consumption per person only.
C)because of both increased population and greater consumption per person.
D)despite decreases in population and consumption per person.
A)because of population growth only.
B)because of increased consumption per person only.
C)because of both increased population and greater consumption per person.
D)despite decreases in population and consumption per person.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Since 1990, approximately how much trash per person per day has been generated in the United States?
A)2 pounds.
B)3.4 pounds.
C)4.5 pounds.
D)12.8 pounds.
A)2 pounds.
B)3.4 pounds.
C)4.5 pounds.
D)12.8 pounds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Over the past decade, total and per capita trash generated in the United States have
A)both increased at about the same rate.
B)increased slightly and leveled off, respectively.
C)both fallen.
D)leveled off and fallen, respectively.
A)both increased at about the same rate.
B)increased slightly and leveled off, respectively.
C)both fallen.
D)leveled off and fallen, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In the United States in 2014, one million BTUs of energy yielded worth of goods and services (in 2009 dollars).
A)$57.90
B)$63.09
C)$127.37
D)$162.07
A)$57.90
B)$63.09
C)$127.37
D)$162.07

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A BTU is the amount of energy needed to
A)raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
B)boil one gallon of water for one minute.
C)raise the air temperature one degree Celsius for one hour.
D)raise the temperature of one pint of water by one degree Celsius.
A)raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
B)boil one gallon of water for one minute.
C)raise the air temperature one degree Celsius for one hour.
D)raise the temperature of one pint of water by one degree Celsius.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Economist magazine's Commodities Price Index tracks the prices of the most
A)important finished goods that are traded internationally.
B)important minerals that are traded internationally.
C)important productive resources that are traded internationally.
D)heavily traded agricultural-based products.
A)important finished goods that are traded internationally.
B)important minerals that are traded internationally.
C)important productive resources that are traded internationally.
D)heavily traded agricultural-based products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Other things equal, extracting oil from shale becomes economically viable (same or lower cost than using conventionally extracted oil) when oil prices reach or more per barrel.
A)$80
B)$60
C)$50
D)$40
A)$80
B)$60
C)$50
D)$40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Productive inputs that are actually or virtually fixed in supply are known as
A)renewable natural resources.
B)natural capital.
C)nonrenewable natural resources.
D)alternative fuels.
A)renewable natural resources.
B)natural capital.
C)nonrenewable natural resources.
D)alternative fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
According to the concept of present value, a $50 barrel of oil today is worth
A)less than a $50 barrel in 2 years.
B)more than a $50 barrel in 2 years.
C)the same as a $50 barrel in 2 years.
D)the same as a $50 barrel in 2 years, but only if there is no inflation during those 2 years.
A)less than a $50 barrel in 2 years.
B)more than a $50 barrel in 2 years.
C)the same as a $50 barrel in 2 years.
D)the same as a $50 barrel in 2 years, but only if there is no inflation during those 2 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Other things equal, ethanol made from corn becomes economically viable (same or lower cost than using oil) when oil prices reach or more per barrel.
A)$60
B)$80
C)$100
D)$120
A)$60
B)$80
C)$100
D)$120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Productive inputs capable of replacing themselves if harvested at moderate rates are known as
A)renewable natural resources.
B)natural capital.
C)nonrenewable natural resources.
D)fossil fuels.
A)renewable natural resources.
B)natural capital.
C)nonrenewable natural resources.
D)fossil fuels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is considered a nonrenewable natural resource?
A)solar power
B)coal
C)oceans
D)aquifers
A)solar power
B)coal
C)oceans
D)aquifers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
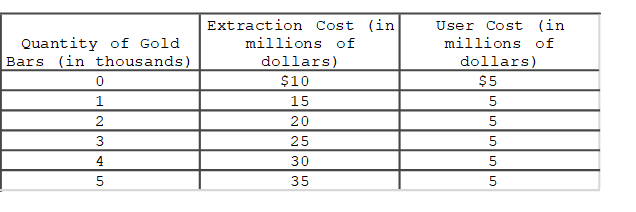
The table shows the quantity of gold bars (Qb) in thousands, the extraction cost for each thousand bars (in millions of dollars), and the user cost of each thousand bars (in millions of dollars) facing the OZ Mining Company this year.Suppose that a new government regulation is going to shut down OZ's mining operation one year from now.If the current price per bar of gold is $25,000, how many bars (in thousands) should OZ extract and sell this year?
A)3
B)4
C)5
D)As many as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
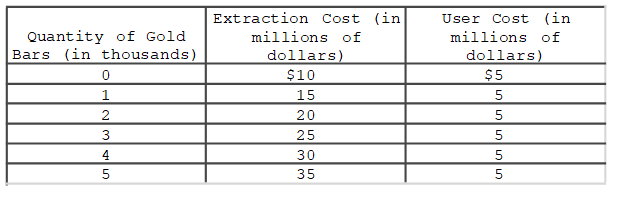
The table shows the quantity of gold bars (Qb) in thousands, the extraction cost for each thousand bars (in millions of dollars), and the user cost of each thousand bars (in millions of dollars) facing the OZ Mining Company this year.Suppose that a new government regulation is going to shut down OZ's mining operation one year from now.Assuming that all gold extracted is sold in the same year (cannot be stockpiled for later sale), how will the regulation affect
The user cost?
A)It will have no effect on the user cost.
B)The effect on the user cost cannot be determined.
C)The user cost will rise because the rate of extraction will rise.
D)The user cost will become zero because they will not be able to extract in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is considered a nonrenewable natural resource?
A)wind
B)timber
C)oceans
D)tin
A)wind
B)timber
C)oceans
D)tin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The user cost of extracting a nonrenewable resource is
A)the sum of the dollar expenditures incurred to extract the resource.
B)the cost of not being able to extract it in the future if it is extracted and sold in the present.
C)the selling price of the resource to the companies using it to produce goods and services.
D)directly proportional to how much of the nonrenewable resource remains.
A)the sum of the dollar expenditures incurred to extract the resource.
B)the cost of not being able to extract it in the future if it is extracted and sold in the present.
C)the selling price of the resource to the companies using it to produce goods and services.
D)directly proportional to how much of the nonrenewable resource remains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
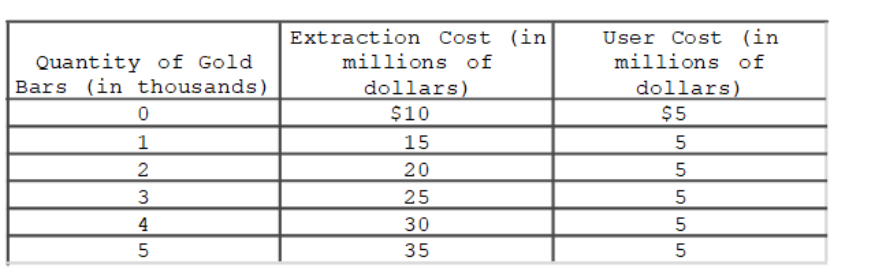
The table shows the quantity of gold bars (Qb) in thousands, the extraction cost for each thousand bars (in millions of dollars), and the user cost of each thousand bars (in millions of dollars) facing the OZ Mining Company this year.If the current price of a bar of gold is $25,000, how many bars (in thousands) should OZ extract and sell this year in order to maximize profits?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Unless people can benefit from conservation, there is a temptation to
A)delay resource extraction as long as possible.
B)extract and use resources at a constant rate.
C)extract and use resources as quickly as possible.
D)ban the extraction of nonrenewable resources.
A)delay resource extraction as long as possible.
B)extract and use resources at a constant rate.
C)extract and use resources as quickly as possible.
D)ban the extraction of nonrenewable resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The cost of not being able to extract and sell a nonrenewable resource in the future (because it is being extracted in the present) is known by natural resource economists as the
A)extraction cost.
B)future cost.
C)conservation cost.
D)user cost.
A)extraction cost.
B)future cost.
C)conservation cost.
D)user cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The user cost of extracting a nonrenewable resource is
A)inversely related to how much of the resource remains.
B)directly related to how much of the resource remains.
C)unrelated to how much of the resource remains.
D)inversely related to the expected future price of the resource.
A)inversely related to how much of the resource remains.
B)directly related to how much of the resource remains.
C)unrelated to how much of the resource remains.
D)inversely related to the expected future price of the resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the benefits of conservation and future use are excluded from a cost-benefit analysis, there is a tendency to
A)more efficiently allocate resources.
B)overvalue future resources by considering them "priceless."
C)stop resource extraction.
D)extract and use resources as quickly as possible.
A)more efficiently allocate resources.
B)overvalue future resources by considering them "priceless."
C)stop resource extraction.
D)extract and use resources as quickly as possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In 2014, the primary sources of U.S.electricity generation, in order from largest to smallest, were
A)natural gas, coal, petroleum, and nuclear.
B)natural gas, hydropower, nuclear, and renewables (wind and solar).
C)coal, natural gas, nuclear, and hydropower.
D)hydropower, nuclear, coal, and petroleum.
A)natural gas, coal, petroleum, and nuclear.
B)natural gas, hydropower, nuclear, and renewables (wind and solar).
C)coal, natural gas, nuclear, and hydropower.
D)hydropower, nuclear, coal, and petroleum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is considered a renewable natural resource?
A)natural gas
B)copper
C)solar power
D)coal
A)natural gas
B)copper
C)solar power
D)coal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Alternative fuels become more economically viable as
A)the demand for oil decreases.
B)subsidies for alternative fuels are removed.
C)oil exploration and drilling technology improve.
D)the price of oil rises.
A)the demand for oil decreases.
B)subsidies for alternative fuels are removed.
C)oil exploration and drilling technology improve.
D)the price of oil rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Other things equal, biodiesel becomes economically viable (as or less costly than using oil) when oil prices reach or more per barrel.
A)$60
B)$80
C)$100
D)$120
A)$60
B)$80
C)$100
D)$120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is considered a renewable natural resource?
A)aquifers
B)coal
C)petroleum
D)iron
A)aquifers
B)coal
C)petroleum
D)iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is the best example of a market failure that would lead a firm to extract resources at a rate that is faster than the rate that would maximize its long-term stream of profits?
A)The market price of the resource rises.
B)Weak property rights create fears that firms will not be allowed to extract in the future.
C)Market interest rates increase.
D)New information suggests that the demand for the resource will be greater in the future.
A)The market price of the resource rises.
B)Weak property rights create fears that firms will not be allowed to extract in the future.
C)Market interest rates increase.
D)New information suggests that the demand for the resource will be greater in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following would cause the present optimal extraction level of a nonrenewable resource to rise?
A)a decrease in the price of the resource
B)an increase in the extraction cost of the resource
C)a decrease in the user cost of the resource
D)a decrease in interest rates
A)a decrease in the price of the resource
B)an increase in the extraction cost of the resource
C)a decrease in the user cost of the resource
D)a decrease in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The optimal extraction level in the present for a nonrenewable resource is
A)zero.
B)where the market price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the last unit.
C)where the market price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the last unit plus the user cost of the last unit.
D)where the extraction cost of the last unit equals the user cost of the last unit.
A)zero.
B)where the market price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the last unit.
C)where the market price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the last unit plus the user cost of the last unit.
D)where the extraction cost of the last unit equals the user cost of the last unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Higher interest rates will, all else equal,
A)increase the extraction cost of a resource.
B)increase the user cost of extracting a resource.
C)reduce the user cost of extracting a resource.
D)have no impact on either the user cost or extraction cost of a resource.
A)increase the extraction cost of a resource.
B)increase the user cost of extracting a resource.
C)reduce the user cost of extracting a resource.
D)have no impact on either the user cost or extraction cost of a resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If property rights are weak or uncertain, resource extraction will tend to
A)occur faster than the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
B)occur slower than the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
C)occur at the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
D)stop.
A)occur faster than the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
B)occur slower than the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
C)occur at the rate that would maximize the long-run stream of profits.
D)stop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Mining of "conflict diamonds" tends to
A)be more profitable, as warring factions are willing to pay more for the diamonds.
B)occur at a slower pace than would maximize the long-term stream of profits because war increases extraction costs.
C)occur at a pace slower than would maximize the long-term stream of profits since the war disrupts production.
D)occur at a pace faster than would maximize the long-term stream of profits since warring factions extract diamonds as quickly as possible due to fears that they may soon lose control of the diamond mines.
A)be more profitable, as warring factions are willing to pay more for the diamonds.
B)occur at a slower pace than would maximize the long-term stream of profits because war increases extraction costs.
C)occur at a pace slower than would maximize the long-term stream of profits since the war disrupts production.
D)occur at a pace faster than would maximize the long-term stream of profits since warring factions extract diamonds as quickly as possible due to fears that they may soon lose control of the diamond mines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Profit-maximizing extraction companies will attempt to
A)extract resources as quickly as possible.
B)delay extraction as long as possible.
C)find rates of extraction that maximize the flow of profits over time.
D)extract resources at a constant rate every year to minimize price fluctuations.
A)extract resources as quickly as possible.
B)delay extraction as long as possible.
C)find rates of extraction that maximize the flow of profits over time.
D)extract resources at a constant rate every year to minimize price fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would cause the present optimal extraction level of a nonrenewable resource to fall?
A)an increase in the present value of expected future profits
B)a decrease in extraction costs
C)a decrease in user costs
D)an increase in the current price of the resource
A)an increase in the present value of expected future profits
B)a decrease in extraction costs
C)a decrease in user costs
D)an increase in the current price of the resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The amount of land covered by forests is
A)declining in all nations.
B)increasing in all nations.
C)increasing in places like the United States and Western Europe, while declining in countries in South America.
D)declining in places like the United States and Western Europe, while increasing in countries in South America.
A)declining in all nations.
B)increasing in all nations.
C)increasing in places like the United States and Western Europe, while declining in countries in South America.
D)declining in places like the United States and Western Europe, while increasing in countries in South America.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Extraction costs of a nonrenewable resource include the
A)cost of removal from the ground only.
B)cost of removal from the ground plus the cost of preparation for sale.
C)cost of removal from the ground, the cost of preparation for sale, and the cost of not being able to extract and sell the resource in the future.
D)cost of removal from the ground plus replanting costs.
A)cost of removal from the ground only.
B)cost of removal from the ground plus the cost of preparation for sale.
C)cost of removal from the ground, the cost of preparation for sale, and the cost of not being able to extract and sell the resource in the future.
D)cost of removal from the ground plus replanting costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following would cause the present optimal extraction level of a nonrenewable resource to fall?
A)a reduction in extraction costs
B)a reduction in user costs
C)a reduction in total costs
D)a reduction in the price of the resource
A)a reduction in extraction costs
B)a reduction in user costs
C)a reduction in total costs
D)a reduction in the price of the resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In countries like Botswana and Zimbabwe, local villages have been given property rights over local elephants with the result that elephant populations
A)have been decimated as villagers try to maximize short-run profit.
B)have grown as villagers have protected the elephants to support their tourist industry.
C)have grown exponentially, with adverse environmental impacts.
D)are in serious decline, as ivory prices have risen.
A)have been decimated as villagers try to maximize short-run profit.
B)have grown as villagers have protected the elephants to support their tourist industry.
C)have grown exponentially, with adverse environmental impacts.
D)are in serious decline, as ivory prices have risen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Alex and Ben are both loggers wanting to harvest timber from the same forest.Alex prefers to harvest and replant at a sustainable rate; Ben wants to harvest as many trees as possible to maximize short-run profit and then move on.They face the same production costs.If property rights are poorly enforced or nonexistent,
A)Ben will choose to harvest as quickly as possible, but Alex will choose to harvest more slowly and replant.
B)both will harvest trees as quickly as possible, before the other one does.
C)both now have an incentive to harvest and replant in a sustainable manner.
D)we would expect them to form an agreement on harvesting and replanting.
A)Ben will choose to harvest as quickly as possible, but Alex will choose to harvest more slowly and replant.
B)both will harvest trees as quickly as possible, before the other one does.
C)both now have an incentive to harvest and replant in a sustainable manner.
D)we would expect them to form an agreement on harvesting and replanting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in the present value of the profit that can be obtained by delaying resource extraction will lead profit-maximizing firms to
A)reduce extraction in the present.
B)increase the current rate of extraction.
C)invest in less extraction equipment.
D)hire more workers to support current production.
A)reduce extraction in the present.
B)increase the current rate of extraction.
C)invest in less extraction equipment.
D)hire more workers to support current production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Renewable resources
A)can never be exhausted permanently.
B)can be exhausted if harvest rates exceed replenishment rates for an extended period.
C)can be exhausted if replenishment rates exceed harvest rates for an extended period.
D)will tend to be overharvested when they are private property.
A)can never be exhausted permanently.
B)can be exhausted if harvest rates exceed replenishment rates for an extended period.
C)can be exhausted if replenishment rates exceed harvest rates for an extended period.
D)will tend to be overharvested when they are private property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A company's extraction cost curve slopes upward to reflect
A)that marginal extraction costs increase as the company extracts more of the resource.
B)that user costs rise as the company extracts more of the resource.
C)that the price of the nonrenewable resource increases as the amount extracted increases.
D)all of these.
A)that marginal extraction costs increase as the company extracts more of the resource.
B)that user costs rise as the company extracts more of the resource.
C)that the price of the nonrenewable resource increases as the amount extracted increases.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A user cost of zero implies that
A)a firm will extract all of a resource in the present.
B)a firm will extract resources at a faster rate than if the user cost was positive.
C)a firm will extract resources at a faster rate than if the user cost was negative.
D)the price of the resource will not change.
A)a firm will extract all of a resource in the present.
B)a firm will extract resources at a faster rate than if the user cost was positive.
C)a firm will extract resources at a faster rate than if the user cost was negative.
D)the price of the resource will not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Elephant populations have
A)expanded everywhere because of state control of elephant populations.
B)declined in countries where they are owned by local villages and expanded where they are owned by the state.
C)expanded in countries where they are owned by local villages and declined where they are owned by the state.
D)declined everywhere, regardless of whether property rights over elephants are recognized.
A)expanded everywhere because of state control of elephant populations.
B)declined in countries where they are owned by local villages and expanded where they are owned by the state.
C)expanded in countries where they are owned by local villages and declined where they are owned by the state.
D)declined everywhere, regardless of whether property rights over elephants are recognized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Some nations are increasing the amount of land covered by forests, while others are experiencing rapid deforestation.According to economists, this is largely because
A)different nations have different ethical views regarding treatment of the environment.
B)nations with increasing forest cover have poorly enforced or nonexistent property rights.
C)nations with declining forest cover treat forests as private property or strictly regulated government property.
D)nations with increasing forest cover treat forests as private property or strictly regulated government property.
A)different nations have different ethical views regarding treatment of the environment.
B)nations with increasing forest cover have poorly enforced or nonexistent property rights.
C)nations with declining forest cover treat forests as private property or strictly regulated government property.
D)nations with increasing forest cover treat forests as private property or strictly regulated government property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A profit-maximizing company should extract a nonrenewable resource in the present up to the quantity where the
A)selling price of the resource equals the extraction cost plus the user cost of the resource.
B)selling price of the resource equals the total cost plus the user cost of the resource.
C)selling price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the resource.
D)extraction cost of the resource equals the user cost of the resource.
A)selling price of the resource equals the extraction cost plus the user cost of the resource.
B)selling price of the resource equals the total cost plus the user cost of the resource.
C)selling price of the resource equals the extraction cost of the resource.
D)extraction cost of the resource equals the user cost of the resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 280 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



