Deck 3: Cells: the Living Units
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Cells: the Living Units
1
Which of the following is NOT a function of lysosomes?
A) degrading worn- out or nonfunctional organelles
B) breaking down bone to release calcium ions into the blood
C) forming acid hydrolases which are necessary to help form cell membranes
D) digesting particles taken in by endocytosis
A) degrading worn- out or nonfunctional organelles
B) breaking down bone to release calcium ions into the blood
C) forming acid hydrolases which are necessary to help form cell membranes
D) digesting particles taken in by endocytosis
C
2
Caveolae are closely associated with all of the following except .
A) enzymes involved in cell regulation
B) lipid rafts
C) enzymes involved in cell metabolism
D) receptors for hormones
A) enzymes involved in cell regulation
B) lipid rafts
C) enzymes involved in cell metabolism
D) receptors for hormones
C
3
Which of the following is a function of a plasma membrane protein?
A) forms a lipid bilayer
B) circulating antibody
C) molecular transport through the membrane
D) oxygen transport
A) forms a lipid bilayer
B) circulating antibody
C) molecular transport through the membrane
D) oxygen transport
C
4
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the membrane potential?
A) The resting membrane potential occurs due to active transport of ions across the membrane due to the sodium- potassium pump.
B) In their resting state, all body cells exhibit a resting membrane potential.
C) The resting membrane potential is maintained by solely by passive transport processes.
D) The resting membrane potential is determined mainly by the concentration gradients and differential permeability of the plasma membrane to K+ and Na+ions.
A) The resting membrane potential occurs due to active transport of ions across the membrane due to the sodium- potassium pump.
B) In their resting state, all body cells exhibit a resting membrane potential.
C) The resting membrane potential is maintained by solely by passive transport processes.
D) The resting membrane potential is determined mainly by the concentration gradients and differential permeability of the plasma membrane to K+ and Na+ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Mitosis .
A) creates diversity in genetic potential
B) is division of the nucleus
C) is the formation of sex cells
D) is always a part of the cell cycle
A) creates diversity in genetic potential
B) is division of the nucleus
C) is the formation of sex cells
D) is always a part of the cell cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following describes the plasma membrane?
A) a single- layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell
B) a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell
C) a membrane composed of tiny shelves or cristae
D) a double layer of protein enclosing the plasma
A) a single- layered membrane that surrounds the nucleus of the cell
B) a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell
C) a membrane composed of tiny shelves or cristae
D) a double layer of protein enclosing the plasma

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of these is an inclusion, not an organelle?
A) microtubule
B) melanin
C) lysosome
D) cilia
A) microtubule
B) melanin
C) lysosome
D) cilia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is correct regarding net diffusion?
A) The lower the temperature, the faster the rate.
B) Molecular weight of a substance does not affect the rate.
C) The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate.
D) The rate is independent of temperature.
A) The lower the temperature, the faster the rate.
B) Molecular weight of a substance does not affect the rate.
C) The greater the concentration gradient, the faster the rate.
D) The rate is independent of temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is correct regarding RNA?
A) Messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA play a role in protein synthesis.
B) There is exactly one specific type of mRNA for each amino acid.
C) rRNA is always attached to the rough ER.
D) If the base sequence of DNA is ATTGCA, the messenger RNA template will be UCCAGU.
A) Messenger RNA, transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA play a role in protein synthesis.
B) There is exactly one specific type of mRNA for each amino acid.
C) rRNA is always attached to the rough ER.
D) If the base sequence of DNA is ATTGCA, the messenger RNA template will be UCCAGU.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What moves cell organelles from one location to another inside a cell?
A) Motor proteins
B) Microfilaments
C) Microtubules
D) Intermediate filaments
A) Motor proteins
B) Microfilaments
C) Microtubules
D) Intermediate filaments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which structures are fingerlike projections that greatly increase the absorbing surface of cells?
A) stereocilia
B) flagella
C) primary cilia
D) microvilli
A) stereocilia
B) flagella
C) primary cilia
D) microvilli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Passive membrane transport processes include _ .
A) consumption of ATP
B) movement of a substance down its concentration gradient
C) movement of water from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low concentration
D) the use of transport proteins when moving substances from areas of low to high concentration
A) consumption of ATP
B) movement of a substance down its concentration gradient
C) movement of water from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low concentration
D) the use of transport proteins when moving substances from areas of low to high concentration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is not a factor that binds cells together?
A) special membrane junctions
B) glycoproteins in the glycocalyx
C) wavy contours of the membranes of adjacent cells
D) glycolipids in the glycocalyx
A) special membrane junctions
B) glycoproteins in the glycocalyx
C) wavy contours of the membranes of adjacent cells
D) glycolipids in the glycocalyx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The electron microscope has revealed that one of the components within the cell consists of pinwheel array of 9 triplets of microtubules arranged to form a hollow tube. This structure is a
)
A) centrosome
B) centriole
C) ribosome
D) chromosome
)
A) centrosome
B) centriole
C) ribosome
D) chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which type of cell junction acts as anchors and distributes tension through a cellular sheet and reduces the chance of tearing when it is subjected to great mechanical stress?
A) tight junctions
B) connexons
C) gap junctions
D) desmosomes
A) tight junctions
B) connexons
C) gap junctions
D) desmosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Once solid material is phagocytized and taken into a vacuole, which of the following statements best describes what happens?
A) A lysosome combines with the vacuole and digests the enclosed solid material.
B) The vacuole remains separated from the cytoplasm and the solid material persists unchanged.
C) The phagocytized material is stored until further breakdown can occur..
D) A ribosome enters the vacuole and uses the amino acids in the "invader" to form new protein.
A) A lysosome combines with the vacuole and digests the enclosed solid material.
B) The vacuole remains separated from the cytoplasm and the solid material persists unchanged.
C) The phagocytized material is stored until further breakdown can occur..
D) A ribosome enters the vacuole and uses the amino acids in the "invader" to form new protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following would not be a constituent of a plasma membrane?
A) messenger RNA
B) glycolipids
C) glycoproteins
D) phospholipids
A) messenger RNA
B) glycolipids
C) glycoproteins
D) phospholipids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Crenation (shrinking) is likely to occur in blood cells immersed in .
A) blood plasma
B) a hypertonic solution
C) an isotonic solution
D) a hypotonic solution
A) blood plasma
B) a hypertonic solution
C) an isotonic solution
D) a hypotonic solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Some hormones enter cells via _ _.
A) exocytosis
B) primary active transport
C) receptor- mediated endocytosis
D) pinocytosis
A) exocytosis
B) primary active transport
C) receptor- mediated endocytosis
D) pinocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a tRNA had an AGC anticodon, it could attach to a(n) mRNA codon.
A) AUG
B) UGA
C) TCG
D) UCG
A) AUG
B) UGA
C) TCG
D) UCG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which transport process is the main mechanism for the movement of most macromolecules by body cells?
A) pinocytosis
B) receptor- mediated endocytosis
C) phagocytosis
D) secondary active transport
A) pinocytosis
B) receptor- mediated endocytosis
C) phagocytosis
D) secondary active transport

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is NOT a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
A) protein synthesis in conjunction with ribosomes
B) breakdown of stored glycogen to form free glucose
C) steroid- based hormone synthesis
D) lipid metabolism and cholesterol synthesis
A) protein synthesis in conjunction with ribosomes
B) breakdown of stored glycogen to form free glucose
C) steroid- based hormone synthesis
D) lipid metabolism and cholesterol synthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In certain kinds of muscle cells, calcium ions are stored in .
A) both smooth and rough ER
B) the cytoplasm
C) the smooth ER
D) the rough ER
A) both smooth and rough ER
B) the cytoplasm
C) the smooth ER
D) the rough ER

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which vesicular transport process occurs primarily in some white blood cells and macrophages?
A) pinocytosis
B) exocytosis
C) intracellular vesicular trafficking
D) phagocytosis
A) pinocytosis
B) exocytosis
C) intracellular vesicular trafficking
D) phagocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A gene can best be defined as .
A) noncoding segments of DNA up to 100,000 nucleotides long
B) a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for one polypeptide chain
C) an RNA messenger that codes for a particular polypeptide
D) a three- base triplet that specifies a particular amino acid
A) noncoding segments of DNA up to 100,000 nucleotides long
B) a segment of DNA that carries the instructions for one polypeptide chain
C) an RNA messenger that codes for a particular polypeptide
D) a three- base triplet that specifies a particular amino acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In which stage of mitosis do the identical sets of chromosomes uncoil and resume their chromatin form?
A) telophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) prophase
A) telophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) prophase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the nucleotide or base sequence of the DNA strand used as a template for messenger RNA synthesis is ACGTT, then what would be the sequence of bases in the corresponding mRNA?
A) ACGTT
B) UGCAA
C) GUACC
D) TGCAA
A) ACGTT
B) UGCAA
C) GUACC
D) TGCAA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Peroxisomes _.
A) are also called microbodies, and contain acid hydrolases
B) sometimes function as secretory vesicles
C) are able to detoxify substances by enzymatic action
D) function to digest particles ingested by endocytosis
A) are also called microbodies, and contain acid hydrolases
B) sometimes function as secretory vesicles
C) are able to detoxify substances by enzymatic action
D) function to digest particles ingested by endocytosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The main component of the cytosol is _.
A) sugars
B) proteins
C) salts
D) water
A) sugars
B) proteins
C) salts
D) water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of these is not a function of the plasma membrane?
A) It encloses the cell contents in such a way that water I the body is divided into separate compartments.
B) It acts as a site of cell- to- cell interaction and recognition.
C) It prevents potassium ions from leaking out and sodium ions from crossing into the cell.
D) It is selectively permeable but permits water and gases to cross.
A) It encloses the cell contents in such a way that water I the body is divided into separate compartments.
B) It acts as a site of cell- to- cell interaction and recognition.
C) It prevents potassium ions from leaking out and sodium ions from crossing into the cell.
D) It is selectively permeable but permits water and gases to cross.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is most correct regarding the intracellular chemical signals known as "second messengers"?
A) Second messengers usually act to remove nitric oxide (NO) from the cell.
B) Second messengers usually inactivate protein kinase enzymes.
C) Second messengers act through receptors called K- proteins.
D) Cyclic AMP and calcium may be second messengers.
A) Second messengers usually act to remove nitric oxide (NO) from the cell.
B) Second messengers usually inactivate protein kinase enzymes.
C) Second messengers act through receptors called K- proteins.
D) Cyclic AMP and calcium may be second messengers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus functionally act in sequence to synthesize and modify proteins for secretory use (export) only, never for use by the cell. This statement is _ .
A) true
B) false; proteins thus manufactured are for use inside the cell only
C) false; integral cell membrane proteins are also synthesized this way
D) false; lipids, not proteins, are synthesized this way
A) true
B) false; proteins thus manufactured are for use inside the cell only
C) false; integral cell membrane proteins are also synthesized this way
D) false; lipids, not proteins, are synthesized this way

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is a principle of the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure?
A) All proteins associated with the cell membrane are contained in a fluid layer on the outside of the cell.
B) Phospholipids consist of a polar head and a nonpolar tail made of three fatty acid chains.
C) The lipid bilayer is a solid at body temperature, thus protecting the cell.
D) Phospholipids form a bilayer that is largely impermeable to water- soluble molecules.
A) All proteins associated with the cell membrane are contained in a fluid layer on the outside of the cell.
B) Phospholipids consist of a polar head and a nonpolar tail made of three fatty acid chains.
C) The lipid bilayer is a solid at body temperature, thus protecting the cell.
D) Phospholipids form a bilayer that is largely impermeable to water- soluble molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Mitochondria .
A) synthesize proteins for use outside the cell
B) are single- membrane structures involved in the breakdown of ATP
C) contain some of the DNA and RNA code necessary for their own function
D) are always the same shape
A) synthesize proteins for use outside the cell
B) are single- membrane structures involved in the breakdown of ATP
C) contain some of the DNA and RNA code necessary for their own function
D) are always the same shape

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT a role of cell adhesion molecules:
A) anchor cells to molecules in the extracellular space and to each other
B) mechanical sensors
C) transmitters of intracellular signals that direct cell migration, proliferation, and specialization
D) initiators of cell- to- cell signaling for muscle contraction
A) anchor cells to molecules in the extracellular space and to each other
B) mechanical sensors
C) transmitters of intracellular signals that direct cell migration, proliferation, and specialization
D) initiators of cell- to- cell signaling for muscle contraction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following does not serve as a signal for cell division?
A) loss of contact inhibition
B) shrinking surface- to- volume ratio
C) joining of cyclins and Cdks
D) repressor genes
A) loss of contact inhibition
B) shrinking surface- to- volume ratio
C) joining of cyclins and Cdks
D) repressor genes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If cells are placed in a hypertonic solution containing a solute to which the membrane is impermeable, what could happen?
A) The cells will lose water and shrink.
B) The cells will swell and ultimately burst.
C) The cells will shrink at first, but will later reach equilibrium with the surrounding solution and return to their original condition.
D) The cells will show no change due to diffusion of both solute and solvent.
A) The cells will lose water and shrink.
B) The cells will swell and ultimately burst.
C) The cells will shrink at first, but will later reach equilibrium with the surrounding solution and return to their original condition.
D) The cells will show no change due to diffusion of both solute and solvent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which statement is the most correct regarding transcription/translation?
A) The nucleotide sequence in a mRNA codon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine.
B) The nucleotide sequence in a mRNA codon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it.
C) The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it.
D) The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine.
A) The nucleotide sequence in a mRNA codon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine.
B) The nucleotide sequence in a mRNA codon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it.
C) The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it.
D) The nucleotide sequence in a tRNA anticodon is an exact copy of the DNA triplet that coded for it except that uracil is substituted for thymine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The functions of centrioles include .
A) producing ATP
B) organizing the mitotic spindle in cell division
C) serving as the site for ribosomal RNA synthesis
D) providing a whiplike beating motion to move substances along cell surfaces
A) producing ATP
B) organizing the mitotic spindle in cell division
C) serving as the site for ribosomal RNA synthesis
D) providing a whiplike beating motion to move substances along cell surfaces

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Riboswitches are folded RNAs that act as switches to turn protein synthesis on or off in response to
)
A) specific codes from the DNA
B) the presence or absence of ubiquitins
C) specific tRNAs
D) changes in the environment
)
A) specific codes from the DNA
B) the presence or absence of ubiquitins
C) specific tRNAs
D) changes in the environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The RNA responsible for bringing the amino acids to the ribosome for protein formation is
)
A) ssRNA
B) mRNA
C) rRNA
D) tRNA
)
A) ssRNA
B) mRNA
C) rRNA
D) tRNA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The process of discharging particles from inside a cell to the outside is called _ .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
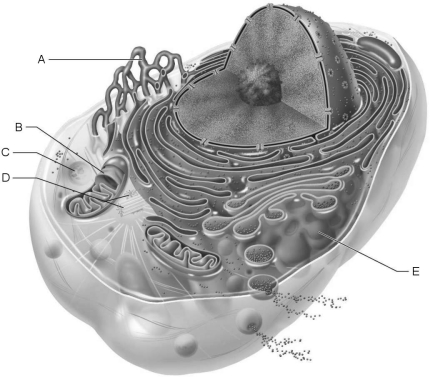 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Water may move through membrane pores constructed by transmembrane proteins called
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Site of enzymatic breakdown of phagocytized material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
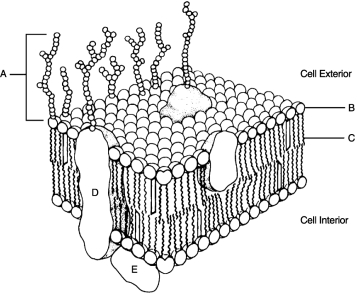 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:List possible causes of aging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Polar region of phospholipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
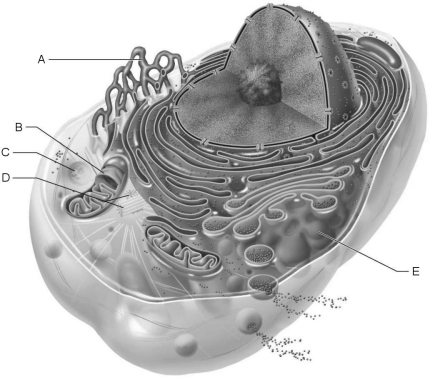 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Source of cell autolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What major chemical is responsible for apoptosis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A red blood cell would swell if its surrounding solution were .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe two important functions of the Golgi apparatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
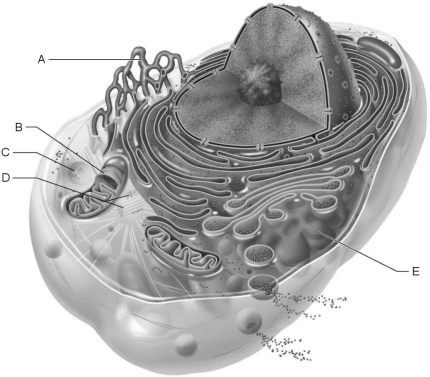 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Replicate for cell division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
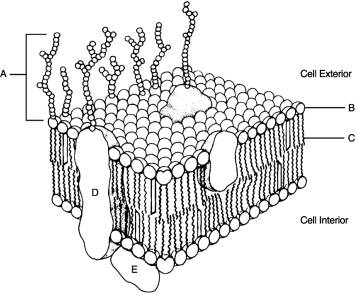 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Peripheral protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Nonpolar region of phospholipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why can we say that a cell without a nucleus will ultimately die?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
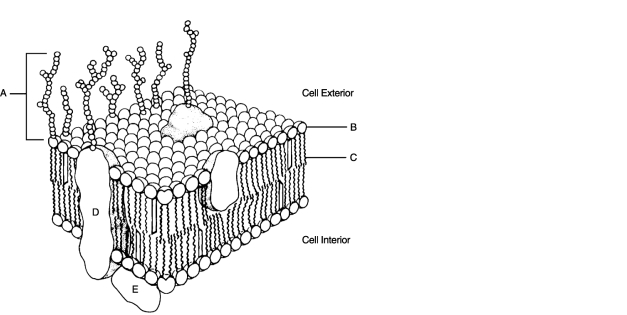 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:What processes maintain a steady state "resting" membrane potential?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain the term genetic code. What does it code for? What are the letters of the code?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A red blood cell placed in pure water would .
A) swell and burst
B) shrink
C) neither shrink nor swell
D) swell initially, then shrink as equilibrium is reached
A) swell and burst
B) shrink
C) neither shrink nor swell
D) swell initially, then shrink as equilibrium is reached

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Identification "tags" for the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
is the division of the cytoplasmic mass into two parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:In all living cells hydrostatic and osmotic pressures exist. Define these pressures and explain how they are used in the concept of tonicity of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
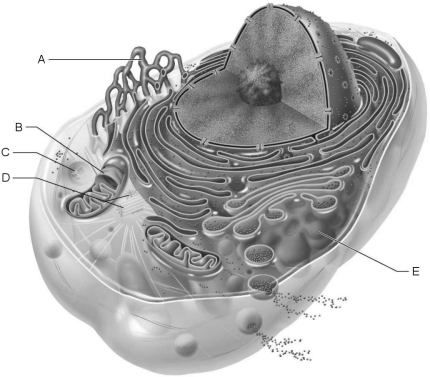 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Forms the mitotic spindle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
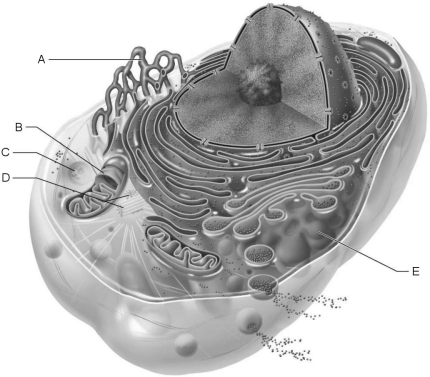 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Packages proteins for insertion in the cell membrane or for exocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:What is the common route of entry for flu viruses into a cell?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Briefly name the subphases of interphase and tell what they do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
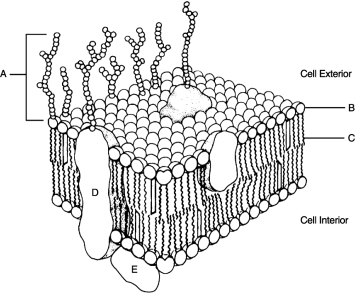 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:are hollow tubes made of spherical protein subunits called tubulins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What are cell exons and introns?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Are Brownian motion, diffusion, and osmosis seen only in living tissue?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
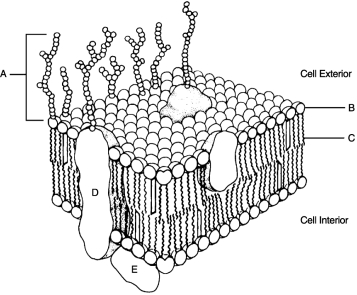 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:In order for the DNA molecule to get "short and fat" to become a chromosome, it must first wrap around small molecules called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Why are free radicals so dangerous to cells, and how are they dealt with by the body?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:The metabolic or growth phase of a cell life cycle is called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Hydrophilic portion of phospholipid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
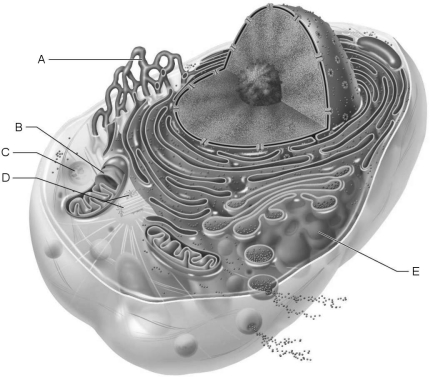 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:Produces ATP aerobically.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
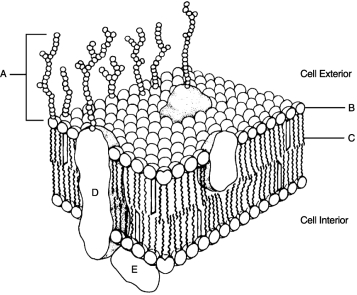 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Integral protein.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Hollow cylinders that connect plasma membranes composed of transmembrane protein are called .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
How is the resting potential formed? How is it maintained?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Glycocalyx.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
 Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:
Figure 3.1Using Figure 3.1, match the following:What are lipid rafts? What are their functions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What are nucleolar organizer regions?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
 Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:
Figure 3.2Using Figure 3.2, match the following:Other than the nucleus, which organelle has its own DNA?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



