Deck 1: Economic Questions and Data
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Economic Questions and Data
1
Studying inflation in the United States from 1970 to 2006 is an example of using
A)randomized controlled experiments.
B)time series data.
C)panel data.
D)cross-sectional data.
A)randomized controlled experiments.
B)time series data.
C)panel data.
D)cross-sectional data.
B
2
An example of a randomized controlled experiment is when
A)households receive a tax rebate in one year but not the other.
B)one U.S.state increases minimum wages and an adjacent state does not, and employment differences are observed.
C)random variables are controlled for by holding constant other factors.
D)some 5th graders in a specific elementary school are allowed to use computers at school while others are not, and their end-of-year performance is compared
Holding constant other factors.
A)households receive a tax rebate in one year but not the other.
B)one U.S.state increases minimum wages and an adjacent state does not, and employment differences are observed.
C)random variables are controlled for by holding constant other factors.
D)some 5th graders in a specific elementary school are allowed to use computers at school while others are not, and their end-of-year performance is compared
Holding constant other factors.
D
3
Panel data
A)is also called longitudinal data.
B)is the same as time series data.
C)studies a group of people at a point in time.
D)typically uses control and treatment groups.
A)is also called longitudinal data.
B)is the same as time series data.
C)studies a group of people at a point in time.
D)typically uses control and treatment groups.
A
4
Analyzing the effect of minimum wage changes on teenage employment across the 48 contiguous U.S.states from 1980 to 2004 is an example of using
A)time series data.
B)panel data.
C)having a treatment group vs.a control group, since only teenagers receive minimum wages.
D)cross-sectional data.
A)time series data.
B)panel data.
C)having a treatment group vs.a control group, since only teenagers receive minimum wages.
D)cross-sectional data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Econometrics can be defined as follows with the exception of
A)the science of testing economic theory.
B)fitting mathematical economic models to real-world data.
C)a set of tools used for forecasting future values of economic variables.
D)measuring the height of economists.
A)the science of testing economic theory.
B)fitting mathematical economic models to real-world data.
C)a set of tools used for forecasting future values of economic variables.
D)measuring the height of economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
To provide quantitative answers to policy questions
A)it is typically sufficient to use common sense.
B)you should interview the policy makers involved.
C)you should examine empirical evidence.
D)is typically impossible since policy questions are not quantifiable.
A)it is typically sufficient to use common sense.
B)you should interview the policy makers involved.
C)you should examine empirical evidence.
D)is typically impossible since policy questions are not quantifiable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ideal randomized controlled experiments in economics are
A)often performed in practice.
B)often used by the Federal Reserve to study the effects of monetary policy.
C)useful because they give a definition of a causal effect.
D)sometimes used by universities to determine who graduates in four years rather than five.
A)often performed in practice.
B)often used by the Federal Reserve to study the effects of monetary policy.
C)useful because they give a definition of a causal effect.
D)sometimes used by universities to determine who graduates in four years rather than five.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Most economic data are obtained
A)through randomized controlled experiments.
B)by calibration methods.
C)through textbook examples typically involving ten observation points.
D)by observing real-world behavior.
A)through randomized controlled experiments.
B)by calibration methods.
C)through textbook examples typically involving ten observation points.
D)by observing real-world behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Analyzing the behavior of unemployment rates across U.S.states in March of 2006 is an example of using
A)time series data.
B)panel data.
C)cross-sectional data.
D)experimental data.
A)time series data.
B)panel data.
C)cross-sectional data.
D)experimental data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The accompanying graph 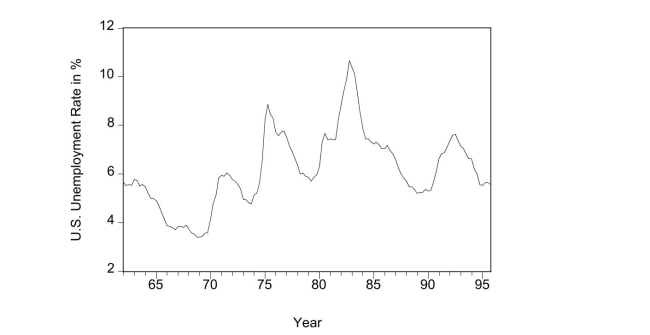 is an example of
is an example of
A)experimental data.
B)cross-sectional data.
C)a time series.
D)longitudinal data.
 is an example of
is an example ofA)experimental data.
B)cross-sectional data.
C)a time series.
D)longitudinal data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Give at least three examples from economics where each of the following type of data
can be used: cross-sectional data, time series data, and panel data.
can be used: cross-sectional data, time series data, and panel data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



