Deck 10: Asking and Answering Questions About a Population Proportion
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Asking and Answering Questions About a Population Proportion
1
Suppose that the study in problem #2 was performed with a random sample ofn = 200 children, and 50 of the children remembered where to look for the object inthe setting that was away from home.
a) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the sampling distribution of if the nullhypothesis Hpo : = 0.35 were true.
b) Is there convincing evidence that the null hypothesis is not true, or is consistentwith what you would expect to see if the null hypothesis were true?
Carry out ahypothesis test to answer this question.
a) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the sampling distribution of if the nullhypothesis Hpo : = 0.35 were true.
b) Is there convincing evidence that the null hypothesis is not true, or is consistentwith what you would expect to see if the null hypothesis were true?
Carry out ahypothesis test to answer this question.
a) 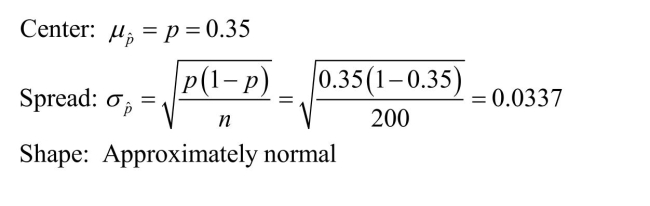
b)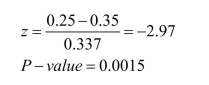
Since the P-value is very small, the null hypothesis is rejected.There is sufficient evidence at the .05 level of significance to conclude that the population proportion of 2-year-olds who remember to look when away from home is less than 0.35.
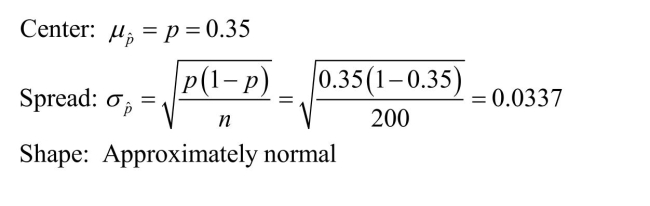
b)
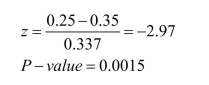
Since the P-value is very small, the null hypothesis is rejected.There is sufficient evidence at the .05 level of significance to conclude that the population proportion of 2-year-olds who remember to look when away from home is less than 0.35.
2
The two possible conclusions in a hypothesis test are to reject the nullhypothesis or to accept the null hypothesis.
False
3
The larger the difference between the hypothesized value and the actualvalue of p, the greater the power.
True
4
The larger the sample size, the greater the power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
There is disagreement among health care professionals about whether health careworkers should wear finger rings while performing patient-related work. Inparticular, plain rings are presumed to have little impact on bacterial transmission byhand. Previous studies have shown that bacteria are transmitted by patient contact inabout 25% of patient contacts where no ring is worn. Let p denote the proportion ofbacterial transmissions when a plain ring is worn. Investigators wish to determinewhether the proportion of bacterial transmissions when wearing plain rings is greaterthan 0.25.
a) What is the appropriate null hypothesis in this study?
b) What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis in this study?
c) In the context of this study, describe a Type I error and a Type II error.
a) What is the appropriate null hypothesis in this study?
b) What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis in this study?
c) In the context of this study, describe a Type I error and a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The probability of a Type I error is denoted by?.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If p = 0.90, a sample size of n =10 is large enough for the large-sampletest for a population proportion to be appropriate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The P-value is used to calculate the test statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Briefly address the following three questions about testing hypotheses.
a) Explain in your own words what a hypothesis test is.
b) Explain in your own words the distinction between a null hypothesis and analternative hypothesis
c) What are the two possible conclusions when testing a hypothesis?
a) Explain in your own words what a hypothesis test is.
b) Explain in your own words the distinction between a null hypothesis and analternative hypothesis
c) What are the two possible conclusions when testing a hypothesis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
? is also sometimes called the observed significance level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A hypothesis test uses population data to choose between two competinghypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A Type II error is the error of rejecting a true null hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
After assessing the consequences of Type I and Type II errors, you shouldidentify the largest acceptable ?.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Briefly address the following three questions about testing hypotheses
a)Explain in your own words what a hypothesis test is.
b) Explain in your own words the distinction between a null hypothesis andanalternative hypothesis
c) What are the two possible conclusions when testing a hypothesis?
a)Explain in your own words what a hypothesis test is.
b) Explain in your own words the distinction between a null hypothesis andanalternative hypothesis
c) What are the two possible conclusions when testing a hypothesis?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Children as young as 2 years of age, upon seeing an object placed under a pillow in afamiliar setting at home, will later remember where to look for about 35% of the time.Investigators believe this capability will be less pronounced in a laboratory situation,where the child is away from the familiar setting of home. Let p denote theproportion of 2-year-olds who remember in the laboratory situation. Investigatorswish to determine whether the proportion of 2-year-olds who remember where to lookis smaller than the know proportion for the home setting when children are in alaboratory situation.
a) What is the appropriate null hypothesis in this study?
b) What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis in this study?
c) In the context of this study, describe a Type I error and a Type II error.
a) What is the appropriate null hypothesis in this study?
b) What is the appropriate alternative hypothesis in this study?
c) In the context of this study, describe a Type I error and a Type II error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A hypothesis test is only capable of demonstrating strong support for thealternative hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A statistic is a characteristic of a population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
is a statistic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The smaller the significance level, ?, the greater the power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The choice of the alternative hypothesis depends on the objectives of thestudy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Let p denote the proportion of houses that are for rent in a neighborhood. For a large-sample z-test of Hp0 : = 0.15 versus Hpa : < 0.15 , find the P-value associated witheach of the following values of the z test statistic.
a) -1.75
b) -0.45
a) -1.75
b) -0.45

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Describe in a few sentences how each of the following affects the power of ahypothesis test.
a) The size of the difference between the actual value and the hypothesized value ofthe population proportion.
b) The significance level,?
c) The sample size
a) The size of the difference between the actual value and the hypothesized value ofthe population proportion.
b) The significance level,?
c) The sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Bats feed on insects at night and sleep during the day. Many species of bats use theundersides of bridges for sleeping places. The beams that support a bridge create twokinds of spaces in equal numbers: wide (approximately 55 cm) and narrow(approximately 17 cm.) Biologists believe the bats choose narrow spaces to providemore safety from predators. Investigators studying the sleeping position choices ofthe Big-eared Bat (Corynorhinus rafinesquii) observed that 67 out of 102 of themchose narrow beam spaces in which to sleep.Does this sample provide sufficient evidence to conclude that the bats prefer narrowover wide sleeping space?
Use a significance level of .05 to test the appropriatehypotheses.
Use a significance level of .05 to test the appropriatehypotheses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that the study in problem #2 was performed with a random sample ofn =121patient contacts where a plain ring was worn, and 40 of these patient contactsresulted in bacterial transmission.
a) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the sampling distribution of if the nullhypothesis Hpo : = 0.25 were true.
b) Is there convincing evidence that the null hypothesis is not true, or is consistentwith what you would expect to see if the null hypothesis were true?
Carry out ahypothesis test to answer this question.
a) Describe the shape, center, and spread of the sampling distribution of if the nullhypothesis Hpo : = 0.25 were true.
b) Is there convincing evidence that the null hypothesis is not true, or is consistentwith what you would expect to see if the null hypothesis were true?
Carry out ahypothesis test to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Let p denote the proportion of houses that are for rent in a neighborhood. For a large-sample z-test of Hp0 : = 0.35 versus Hpa : < 0.35 , find the P-value associated witheach of the following values of the z test statistic.
a) -0.55
b) -2.80
a) -0.55
b) -2.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Hermit crabs fight for ownership of shells. Fights are initiated when one crab raps onthe shell of another with its big claw. An exchange of shells occurs approximately50% of the time. Investigators wish to see if the rapping force helps decide the issue.They set up an experiment with a rubberized shell, which would dampen the force ofthe rapping. They reason that the reduced force should result in fewer exchanges ofshells. They then observed 59 fights to see how many shell exchanges occurred.
a) What null and alternative hypotheses should the investigators use?
In a fewsentences, justify your choice of the alternative hypothesis
b) Describe a Type I error and a Type II error in this context.
a) What null and alternative hypotheses should the investigators use?
In a fewsentences, justify your choice of the alternative hypothesis
b) Describe a Type I error and a Type II error in this context.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Assuming a random sample from a large population, for which of the following nullhypotheses and sample sizes is the large-sample z test appropriate?
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a)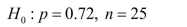
b)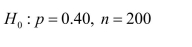
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a)
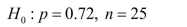
b)
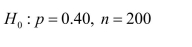

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Describe in a few sentences how each of the following affects the power of ahypothesis test.
a) The size of the difference between the actual value and the hypothesized value ofthe population proportion.
b) The significance level, ?
c) The sample size
a) The size of the difference between the actual value and the hypothesized value ofthe population proportion.
b) The significance level, ?
c) The sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assuming a random sample from a large population, for which of the following nullhypotheses and sample sizes is the large-sample z test appropriate?
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.36, n= 25
b) Hp0 : = 0.10, n= 200
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.36, n= 25
b) Hp0 : = 0.10, n= 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Let p denote the proportion of houses that are for rent in a neighborhood. For a large-sample z-test of Hp0 : = 0.45 versus Hpa : < 0.45 , find the P-value associated witheach of the following values of the z test statistic.
a) -0.65
b) -1.95
a) -0.65
b) -1.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Assuming a random sample from a large population, for which of the following nullhypotheses and sample sizes is the large-sample z test appropriate?
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.16, n= 50
b) Hp0 : = 0.20, n=180
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.16, n= 50
b) Hp0 : = 0.20, n=180

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In an analysis of hunting by African lions, biologists filmed prey captures from thesafety of their vehicles. Prey captures were then divided into a sequence of events.One of the events is the stalk, defined as the reduction of predator-prey distance forprey that has been specifically targeted. The investigators identified two types ofstalk: (a) "crouching," -- the lion is concealed and either the lion advances toward theprey or the prey advances (unaware) toward the lion, and (b)"running," -- the lion isless concealed and advances toward the prey in a rapid manner.
Data on lions' stalks of wildebeests and zebras from a simple random sample of 159kills are summarized in the table below. Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of wildebeests and zebras is different from 0.87?
Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of wildebeests and zebras is different from 0.87?
Data on lions' stalks of wildebeests and zebras from a simple random sample of 159kills are summarized in the table below.
 Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of wildebeests and zebras is different from 0.87?
Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of wildebeests and zebras is different from 0.87?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The field of pediatrics has consistently attracted a large number of women. Tobalance their personal and professional lives, many women choose part time pediatricpositions. In the year 2000, it was estimated that 45% of female pediatricians workedpart time. Researchers would like to collect data in order to see if there is evidencethat this percentage has changed in the intervening years.
a) What null and alternate hypotheses should the investigators use?
In a fewsentences, justify your choice of the alternative hypothesis
b) Describe a Type I error and a Type II error in this context.
a) What null and alternate hypotheses should the investigators use?
In a fewsentences, justify your choice of the alternative hypothesis
b) Describe a Type I error and a Type II error in this context.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
 a) 0.35
a) 0.35b) 1.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assuming a random sample from a large population, for which of the following nullhypotheses and sample sizes is the large-sample z test appropriate?
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.08, n= 50
b) Hp0 : = 0.20, n= 200
Show thecalculations leading to your responses.
a) Hp0 : = 0.08, n= 50
b) Hp0 : = 0.20, n= 200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In an analysis of hunting by African lions, biologists filmed prey captures from thesafety of their vehicles. The capture of prey was divided into a sequence of events forstudy, one of which is the stalk, defined as the reduction of predator-prey distance forprey that has been specifically located and the prey is unaware of or minimallyalarmed by the predator. The investigators identified two types of stalk: (a)"crouching," -- the lion is concealed and either the lion advances toward the prey orthe prey advances (unaware) toward the lion, and (b)"running," -- the lion is lessconcealed and advances toward the prey in a rapid manner.Data on lions' stalks of Thomson's and Grant's gazelles from a random sample of 151kills is summarized in the table below.  Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of Thomson's and Grant's gazelles is differentfrom 0.87?
Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of Thomson's and Grant's gazelles is differentfrom 0.87?
 Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of Thomson's and Grant's gazelles is differentfrom 0.87?
Researchers believe that the proportion of stalks that are the crouching type is about 0.87. Do the data above provide evidence that the researchers' belief is incorrect andthat the proportion of crouching stalks of Thomson's and Grant's gazelles is differentfrom 0.87?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



