Deck 19: Decision Making
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/126
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Decision Making
1
The difference between expected payoff under certainty and expected value of the best act without certainty is the:
A) expected monetary value.
B) expected net present value.
C) expected value of perfect information.
D) expected rate of return.
A) expected monetary value.
B) expected net present value.
C) expected value of perfect information.
D) expected rate of return.
C
2
A tabular presentation that shows the outcome for each decision alternative under the various states of nature is called:
A) a payback period matrix.
B) a decision matrix.
C) a decision tree.
D) a payoff table.
A) a payback period matrix.
B) a decision matrix.
C) a decision tree.
D) a payoff table.
D
3
A company that manufactures designer jeans is contemplating whether to increase its advertising budget by $1 million for next year. If the expanded advertising campaign is successful, the company
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the actions in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the actions in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.
A
4
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, the opportunity loss for A3 when S2 occurs is
A) 0
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, the opportunity loss for A3 when S2 occurs is
A) 0
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected monetary value (EMV ) for A2 is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6.5
D) 8
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected monetary value (EMV ) for A2 is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6.5
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A1 is
A) 3
B) 4.5
C) 7
D) 8
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A1 is
A) 3
B) 4.5
C) 7
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A company that manufactures designer jeans is contemplating whether to increase its advertising budget by $1 million for next year. If the expanded advertising campaign is successful, the company
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the events in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the events in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2 and S2 is 0.8, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A1 is
A) 0
B) 1.2
C) 4.8
D) 5.6
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2 and S2 is 0.8, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A1 is
A) 0
B) 1.2
C) 4.8
D) 5.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A company that manufactures designer jeans is contemplating whether to increase its advertising budget by $1 million for next year. If the expanded advertising campaign is successful, the company
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the payoffs in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the payoffs in this decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.4, then the probability of S2 is
A) 0.4
B) 0.5
C) 0.6
D) 1.0
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.4, then the probability of S2 is
A) 0.4
B) 0.5
C) 0.6
D) 1.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, the opportunity loss for A2 when S1 occurs is
A) - 2
B) 0
C) 5
D) 14
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, the opportunity loss for A2 when S1 occurs is
A) - 2
B) 0
C) 5
D) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2, what is the optimal alternative using EOL?
A) A1.
B) A2.
C) A3.
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2, what is the optimal alternative using EOL?
A) A1.
B) A2.
C) A3.
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A company that manufactures designer jeans is contemplating whether to increase its advertising budget by $1 million for next year. If the expanded advertising campaign is successful, the company
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the outcomes in this decision-making
Problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.
Expects sales to increase by $1.6 million next year. If the advertising campaign fails, the company
Expects sales to increase by only $400,000 next year. If the advertising budget is not increased, the
Company expects sales to increase by $200,000. Identify the outcomes in this decision-making
Problem.
A) Two choices: (1) increase the budget and (2) do not increase the budget.
B) Two possibilities: (1) campaign is successful and (2) campaign is not successful.
C) Four consequences resulting from the Increase/Do Not Increase and Successful/Not Successful combinations.
D) The increase in sales dollars next year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected monetary value (EMV ) for A1 is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6.5
D) 8
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected monetary value (EMV ) for A1 is
A) 3
B) 4
C) 6.5
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A medical doctor is involved in a $1 million malpractice suit. He can either settle out of court for $250,000 or go to court. If he goes to court and loses, he must pay $825,000 plus $175,000 in court
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the actions of this decision-making
Problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the actions of this decision-making
Problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2 and S2 is 0.8, then the expected monetary value of A1 is
A) 2.4
B) 5.6
C) 8
D) 16
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.2 and S2 is 0.8, then the expected monetary value of A1 is
A) 2.4
B) 5.6
C) 8
D) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A medical doctor is involved in a $1 million malpractice suit. He can either settle out of court for $250,000 or go to court. If he goes to court and loses, he must pay $825,000 plus $175,000 in court
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the outcomes of this decision-
Making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the outcomes of this decision-
Making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, what is the optimal alternative using EMV?
A) A1
B) A2
C) A3
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, what is the optimal alternative using EMV?
A) A1
B) A2
C) A3
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A medical doctor is involved in a $1 million malpractice suit. He can either settle out of court for $250,000 or go to court. If he goes to court and loses, he must pay $825,000 plus $175,000 in court
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the states of nature of this
Decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.
Costs. If he wins in court the plaintiffs pay the court costs. Identify the states of nature of this
Decision-making problem.
A) Two choices: (1) go to court and (2) settle out of court.
B) Two possibilities: (1) win the case in court and (2) lose the case in court.
C) Four consequences resulting from Go/Settle and Win/Lose combinations.
D) The amount of money paid by the doctor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A3 is
A) 3
B) 4.5
C) 7
D) 8
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected opportunity loss (EOL) for A3 is
A) 3
B) 4.5
C) 7
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the coefficient of variation for A2 is
A) 0.231
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 2
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the coefficient of variation for A2 is
A) 0.231
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal EMV for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,700
D) $1,900
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal EMV for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,700
D) $1,900

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The opportunity loss for buying 400 dozen roses and selling 200 dozen roses at the full price is
A) - $2,000
B) $1,000
C) $500
D) $0
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The opportunity loss for buying 400 dozen roses and selling 200 dozen roses at the full price is
A) - $2,000
B) $1,000
C) $500
D) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the return to risk ratio for A3 is
A) 0.667
B) 1.5
C) 2
D) 4.333
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the return to risk ratio for A3 is
A) 0.667
B) 1.5
C) 2
D) 4.333

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, what is the best action using the maximin criterion?
A) Action A1
B) Action A2
C) Action A3
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, what is the best action using the maximin criterion?
A) Action A1
B) Action A2
C) Action A3
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the EVPI for the payoff table is
A) - 3
B) 3
C) 8
D) 11
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the EVPI for the payoff table is
A) - 3
B) 3
C) 8
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EMV for buying 200 dozen roses is
A) $4,500
B) $2,500
C) $1,700
D) $1,000
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EMV for buying 200 dozen roses is
A) $4,500
B) $2,500
C) $1,700
D) $1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The number of states of nature for the payoff table is
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) It cannot be determined.
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The number of states of nature for the payoff table is
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal EOL for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,500
D) $1,600
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal EOL for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,500
D) $1,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The payoff for buying and selling 400 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $12,000
B) $6,000
C) $4,000
D) It cannot be determined.
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The payoff for buying and selling 400 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $12,000
B) $6,000
C) $4,000
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The payoff for buying 200 dozen roses and selling 100 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $2,000
B) $1,000
C) $500
D) - $500
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The payoff for buying 200 dozen roses and selling 100 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $2,000
B) $1,000
C) $500
D) - $500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The number of alternatives for the payoff table is
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) It cannot be determined.
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The number of alternatives for the payoff table is
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the coefficient of variation for A1 is
A) 0.231
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 2
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the coefficient of variation for A1 is
A) 0.231
B) 0.5
C) 1.5
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. If the probability of selling 100 dozen roses is 0.2 and 200 dozen roses is 0.5, then the
Probability of selling 400 dozen roses is
A) 0.7
B) 0.5
C) 0.3
D) 0.2
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. If the probability of selling 100 dozen roses is 0.2 and 200 dozen roses is 0.5, then the
Probability of selling 400 dozen roses is
A) 0.7
B) 0.5
C) 0.3
D) 0.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, what is the best action using the maximax criterion?
A) Action A1
B) Action A2
C) Action A3
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, what is the best action using the maximax criterion?
A) Action A1
B) Action A2
C) Action A3
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EOL for buying 200 dozen roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,500
D) $1,600
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EOL for buying 200 dozen roses is
A) $700
B) $900
C) $1,500
D) $1,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal alternative using EMV for selling roses is to buy dozen
Roses.
A) 100
B) 200
C) 400
D) 600
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the optimal alternative using EMV for selling roses is to buy dozen
Roses.
A) 100
B) 200
C) 400
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected profit under certainty (EPUC ) is
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 11
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the expected profit under certainty (EPUC ) is
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
SCENARIO 19-1
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the return to risk ratio for A1 is
A) 0.667
B) 1.5
C) 2
D) 4.333
The following payoff table shows profits associated with a set of 3 alternatives under 2 possible states
of nature.
where: is state of nature 1 is action alternative 1
is state of nature 2 is action alternative 2
is action alternative 3
-Referring to Scenario 19-1, if the probability of S1 is 0.5, then the return to risk ratio for A1 is
A) 0.667
B) 1.5
C) 2
D) 4.333

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The opportunity loss for buying 200 dozen roses and selling 100 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $1,000
B) $500
C) - $500
D) - $2,000
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. The opportunity loss for buying 200 dozen roses and selling 100 dozen roses at the full price is
A) $1,000
B) $500
C) - $500
D) - $2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Blossom's Flowers purchases roses for sale for Valentine's Day. The roses are purchased for $10 a dozen and are sold for $20 a dozen. Any roses not sold on Valentine's Day can be sold for $5 per
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EVPI for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $1,500
C) $1,900
D) $2,600
Dozen. The owner will purchase 1 of 3 amounts of roses for Valentine's Day: 100, 200, or 400 dozen
Roses. Given 0.2, 0.4, and 0.4 are the probabilities for the sale of 100, 200, or 400 dozen roses,
Respectively, then the EVPI for buying roses is
A) $700
B) $1,500
C) $1,900
D) $2,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the return to risk ratio for Action B is
A) 0.167
B) 3.0
C) 6.0
D) 9.0
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the return to risk ratio for Action B is
A) 0.167
B) 3.0
C) 6.0
D) 9.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the action with the preferable return to risk ratio?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the action with the preferable return to risk ratio?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EMV for Action A is
A) $300
B) $550
C) $600
D) $700
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EMV for Action A is
A) $300
B) $550
C) $600
D) $700

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
SCENARIO 19-3
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, which investment has the optimal coefficient of variation?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) The investments are equal.
D) It cannot be determined.
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, which investment has the optimal coefficient of variation?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) The investments are equal.
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the best action using the maximax criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the best action using the maximax criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the optimal action using the EOL criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the optimal action using the EOL criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the coefficient of variation for Action A is
A) 12.8%
B) 33.3%
C) 133.33%
D) 333.3%
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the coefficient of variation for Action A is
A) 12.8%
B) 33.3%
C) 133.33%
D) 333.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The minimum expected opportunity loss is also equal to
A) expected profit under certainty.
B) expected value of perfect information.
C) coefficient of variation.
D) expected value under certainty minus the expected monetary value of the worst
Alternative.
A) expected profit under certainty.
B) expected value of perfect information.
C) coefficient of variation.
D) expected value under certainty minus the expected monetary value of the worst
Alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the expected profit under certainty (EPUC ) is
A) 0
B) 300
C) 500
D) 600
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the expected profit under certainty (EPUC ) is
A) 0
B) 300
C) 500
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EVPI is
A) 0
B) 300
C) 400
D) 600
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EVPI is
A) 0
B) 300
C) 400
D) 600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
SCENARIO 19-3
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, which investment has the optimal return to risk ratio?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) The investments are equal.
D) It cannot be determined.
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, which investment has the optimal return to risk ratio?
A) Investment A
B) Investment B
C) The investments are equal.
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For a potential investment of $5,000, a portfolio has an EMV of $1,000 and a standard deviation of $100. The return to risk ratio is
A) 50
B) 20
C) 10
D) 5
A) 50
B) 20
C) 10
D) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For a potential investment of $5,000, a portfolio has an EMV of $1,000 and a standard deviation of $100. What is the coefficient of variation?
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 50%
D) 100%
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 50%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the action with the preferable coefficient of variation?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the action with the preferable coefficient of variation?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EOL for Action A is
A) 0
B) 100
C) 200
D) 300
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, the EOL for Action A is
A) 0
B) 100
C) 200
D) 300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the optimal action using the EMV criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the optimal action using the EMV criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
SCENARIO 19-3
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, what is the coefficient of variation for investment A?
A) 90.0%
B) 11.1%
C) 8.3%
D) 5.0%
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, what is the coefficient of variation for investment A?
A) 90.0%
B) 11.1%
C) 8.3%
D) 5.0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For a potential investment of $5,000, a portfolio has an EMV of $1,000 and a standard deviation of $100. What is the rate of return?
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 20%
D) 50%
A) 5%
B) 10%
C) 20%
D) 50%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
SCENARIO 19-2
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the best action using the maximin criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.
The following payoff matrix is given in dollars.
Suppose the probability of Event 1 is 0.5 and Event 2 is 0.5.
-Referring to Scenario 19-2, what is the best action using the maximin criterion?
A) Action A
B) Action B
C) Either Action A or Action B
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Opportunity loss is the difference between the lowest profit for an event and the actual
profit obtained for an action taken.
profit obtained for an action taken.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Look at the utility function graphed below and select the type of decision maker that corresponds to the graph.
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player
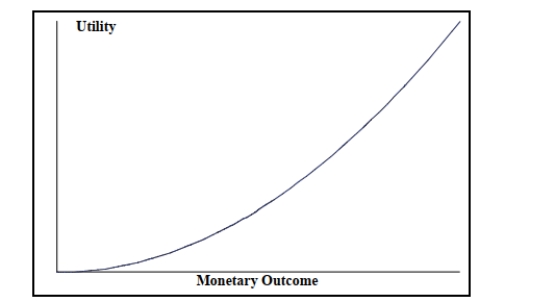
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In a local cellular phone area, company A accounts for 60% of the cellular phone market, while company B accounts for the remaining 40% of the market. Of the cellular calls made with company
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random and has interference, what is the
Probability that it was with company A?
A) 0.071
B) 0.429
C) 0.571
D) It cannot be determined.
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random and has interference, what is the
Probability that it was with company A?
A) 0.071
B) 0.429
C) 0.571
D) It cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
At Eastern University, 60% of the students are from suburban areas, 30% are from rural areas, and 10% are from urban areas. Of the students from the suburban areas, 60% are nonbusiness majors. Of
The students from the rural areas, 70% are nonbusiness majors. Of the students from the urban areas,
90% are nonbusiness majors. The probability that a randomly selected student is a business major is
A) 0.66
B) 0.54
C) 0.44
D) 0.34
The students from the rural areas, 70% are nonbusiness majors. Of the students from the urban areas,
90% are nonbusiness majors. The probability that a randomly selected student is a business major is
A) 0.66
B) 0.54
C) 0.44
D) 0.34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
SCENARIO 19-3
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, what is the return to risk ratio for Investment B?
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 24
The following information is from 2 investment opportunities.
-Referring to Scenario 19-3, what is the return to risk ratio for Investment B?
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 24

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In a local cellular phone area, company A accounts for 60% of the cellular phone market, while company B accounts for the remaining 40% of the market. Of the cellular calls made with company
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random, the probability that it will have
Interference is
A) 0.014
B) 0.028
C) 0.14
D) 0.986
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random, the probability that it will have
Interference is
A) 0.014
B) 0.028
C) 0.14
D) 0.986

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
_________ is a procedure for revising probabilities based upon additional information.
A) Utility theory
B) Bernoulli's theorem
C) Beckman's theorem
D) Bayes' theorem
A) Utility theory
B) Bernoulli's theorem
C) Beckman's theorem
D) Bayes' theorem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Look at the utility function graphed below and select the type of decision maker that corresponds to the graph.
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player
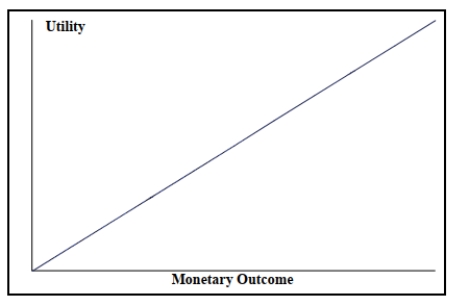
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
To calculate expected profit under certainty, you need to have perfect information
about which event will occur.
about which event will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Look at the utility function graphed below and select the type of decision-maker that corresponds to the graph.
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player
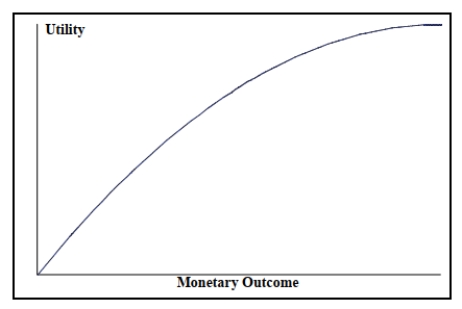
A) Risk averter
B) Risk neutral
C) Risk taker
D) Risk player


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
SCENARIO 19-4
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the EMV?
A) $180
B) $130
C) $90
D) $80
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the EMV?
A) $180
B) $130
C) $90
D) $80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
SCENARIO 19-4
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the coefficient of variation?
A) 88.8%
B) 90.3%
C) 100%
D) 156.1%
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the coefficient of variation?
A) 88.8%
B) 90.3%
C) 100%
D) 156.1%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The risk seeker's curve represents the utility of one who enjoys taking risks. Therefore, the slope of the utility curve becomes for large dollar amounts.
A) smaller
B) stable
C) larger
D) uncertain
A) smaller
B) stable
C) larger
D) uncertain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
SCENARIO 19-4
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the standard deviation?
A) 4,890
B) 4,840
C) 124.9
D) 69.6
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the standard deviation?
A) 4,890
B) 4,840
C) 124.9
D) 69.6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The curve represents the expected monetary value approach.
A) risk averter's
B) risk taker's
C) risk neutral
D) Bernoulli
A) risk averter's
B) risk taker's
C) risk neutral
D) Bernoulli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In a local cellular phone area, company A accounts for 60% of the cellular phone market, while company B accounts for the remaining 40% of the market. Of the cellular calls made with company
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random, the probability that it will not have
Interference is
A) 0.014
B) 0.028
C) 0.14
D) 0.986
A, 1% of the calls will have some sort of interference, while 2% of the cellular calls with company B
Will have interference. If a cellular call is selected at random, the probability that it will not have
Interference is
A) 0.014
B) 0.028
C) 0.14
D) 0.986

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
SCENARIO 19-4
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the return to risk ratio?
A) 0.64
B) 1.08
C) 1.18
D) 2.00
A stock portfolio has the following returns under the market conditions listed below.
-Referring to Scenario 19-4, what is the return to risk ratio?
A) 0.64
B) 1.08
C) 1.18
D) 2.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Removal of uncertainty from a decision-making problem leads to a case referred to as
perfect information.
perfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
At Eastern University, 60% of the students are from suburban areas, 30% are from rural areas, and 10% are from urban areas. Of the students from the suburban areas, 60% are nonbusiness majors. Of
The students from the rural areas, 70% are nonbusiness majors. Of the students from the urban areas,
90% are nonbusiness majors. If a randomly selected student is not a business major, the probability
That the student is from the urban area is
A) 0.136
B) 0.214
C) 0.666
D) 0.706
The students from the rural areas, 70% are nonbusiness majors. Of the students from the urban areas,
90% are nonbusiness majors. If a randomly selected student is not a business major, the probability
That the student is from the urban area is
A) 0.136
B) 0.214
C) 0.666
D) 0.706

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The curve for the will show a rapid increase in utility for initial amounts of money followed by a gradual leveling off for increasing dollar amounts.
A) risk taker
B) risk averter
C) risk neutral
D) profit seeker
A) risk taker
B) risk averter
C) risk neutral
D) profit seeker

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 126 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



