Deck 17: International Banking: Reserves, debt, and Risk
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: International Banking: Reserves, debt, and Risk
1
Which of the following is not considered an "owned" reserve?
A) National currencies
B) Gold
C) Special drawing rights
D) Oil facility
A) National currencies
B) Gold
C) Special drawing rights
D) Oil facility
D
2
The U.S.gold outflow that began in the late 1940s and continued through the 1960s was due in part to:
A) Crawling pegged exchange rates
B) Freely floating exchange rates
C) An undervalued dollar
D) An overvalued dollar
A) Crawling pegged exchange rates
B) Freely floating exchange rates
C) An undervalued dollar
D) An overvalued dollar
D
3
Which of the following is not a condition of the international gold standard? That a nation must:
A) Convert gold into paper currency, and vice versa, at a stipulated rate
B) Permit gold to be freely imported and exported
C) Tolerate wide fluctuations in its exchange rate
D) Define its monetary unit in terms of a stipulated amount of gold
A) Convert gold into paper currency, and vice versa, at a stipulated rate
B) Permit gold to be freely imported and exported
C) Tolerate wide fluctuations in its exchange rate
D) Define its monetary unit in terms of a stipulated amount of gold
C
4
All of the following exchange-rate systems require international reserves to finance balance-of-payments disequilibriums except:
A) Pegged or fixed exchange rates
B) Managed floating exchange rates
C) Adjustable pegged exchange rates
D) Freely floating exchange rates
A) Pegged or fixed exchange rates
B) Managed floating exchange rates
C) Adjustable pegged exchange rates
D) Freely floating exchange rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following constitute(s)the largest component of the world's international reserves?
A) Gold
B) Special drawing rights
C) IMF drawings
D) Foreign currencies
A) Gold
B) Special drawing rights
C) IMF drawings
D) Foreign currencies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the Eurodollar market? It:
A) Is mainly located in the United Kingdom and continental Europe
B) Operates as a financial intermediary, bringing together lenders and borrowers
C) Deals in interest-bearing time deposits and loans to governments
D) Grew in response to the deregulation of interest rate ceilings on U.S. savings accounts
A) Is mainly located in the United Kingdom and continental Europe
B) Operates as a financial intermediary, bringing together lenders and borrowers
C) Deals in interest-bearing time deposits and loans to governments
D) Grew in response to the deregulation of interest rate ceilings on U.S. savings accounts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following assets makes use of the basket valuation technique?
A) Swap agreements
B) Oil facility
C) Buffer stock facility
D) Special drawing rights
A) Swap agreements
B) Oil facility
C) Buffer stock facility
D) Special drawing rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following does not represent a form of international liquidity?
A) IMF reserve positions
B) General arrangements to borrow
C) U.S. government securities
D) Reciprocal currency arrangements
A) IMF reserve positions
B) General arrangements to borrow
C) U.S. government securities
D) Reciprocal currency arrangements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Eurodollars are:
A) Dollar-denominated deposits in overseas banks
B) European currencies used to finance transactions in the United States
C) Dollars that U.S. residents spend in Europe
D) European currencies used to finance imports from the United States
A) Dollar-denominated deposits in overseas banks
B) European currencies used to finance transactions in the United States
C) Dollars that U.S. residents spend in Europe
D) European currencies used to finance imports from the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The currencies generally referred to as "reserve currencies" are the:
A) Japanese yen and U.S. dollar
B) Swiss franc and Japanese yen
C) British pound and U.S. dollar
D) Swiss franc and British pound
A) Japanese yen and U.S. dollar
B) Swiss franc and Japanese yen
C) British pound and U.S. dollar
D) Swiss franc and British pound

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is not considered a "borrowed" reserve?
A) Special drawing rights
B) Oil facility
C) IMF drawings
D) Reciprocal currency arrangement
A) Special drawing rights
B) Oil facility
C) IMF drawings
D) Reciprocal currency arrangement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
With an international gold standard,if a country ended up with a deficit from the balances on its current and capital accounts,it would:
A) Import gold to settle the balance
B) Export gold to settle the balance
C) Officially decrease the price of gold
D) Officially increase the price of gold
A) Import gold to settle the balance
B) Export gold to settle the balance
C) Officially decrease the price of gold
D) Officially increase the price of gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Swap agreements are generally conducted by the:
A) Federal Reserve with foreign central banks
B) Federal Reserve with foreign commercial banks
C) U.S. Treasury with foreign central banks
D) U.S. Treasury with foreign commercial banks
A) Federal Reserve with foreign central banks
B) Federal Reserve with foreign commercial banks
C) U.S. Treasury with foreign central banks
D) U.S. Treasury with foreign commercial banks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The U.S.dollar glut of the 1960s was due in part to:
A) An undervalued dollar
B) An overvalued dollar
C) Freely floating exchange rates
D) Crawling pegged exchange rates
A) An undervalued dollar
B) An overvalued dollar
C) Freely floating exchange rates
D) Crawling pegged exchange rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The purpose of international reserves is to finance:
A) Short-term surpluses in the balance of payments
B) Long-term surpluses in the balance of payments
C) Short-term deficits in the balance of payments
D) Long-term deficits in the balance of payments
A) Short-term surpluses in the balance of payments
B) Long-term surpluses in the balance of payments
C) Short-term deficits in the balance of payments
D) Long-term deficits in the balance of payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is a main central bank function of the International Monetary Fund?
A) The conduct of open market operations
B) The issuance of gold certificates
C) The provision of monetary policy for member nations
D) The granting of loans to member nations
A) The conduct of open market operations
B) The issuance of gold certificates
C) The provision of monetary policy for member nations
D) The granting of loans to member nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A dollar shortage would indicate that the dollar is:
A) Undervalued in international markets
B) Overvalued in international markets
C) Overvalued in terms of gold
D) Overvalued in terms of special drawing rights
A) Undervalued in international markets
B) Overvalued in international markets
C) Overvalued in terms of gold
D) Overvalued in terms of special drawing rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
International trade and investment are most frequently financed by the U.S.dollar and the:
A) Japanese yen
B) British pound
C) Australian dollar
D) Swiss franc
A) Japanese yen
B) British pound
C) Australian dollar
D) Swiss franc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Federal Reserve's swap network represents:
A) Efforts to stabilize only the value of the dollar
B) Efforts to stabilize only the value of foreign currencies
C) Long-term borrowing among countries
D) Short-term borrowing among countries
A) Efforts to stabilize only the value of the dollar
B) Efforts to stabilize only the value of foreign currencies
C) Long-term borrowing among countries
D) Short-term borrowing among countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following assets was (were)created in 1970 to provide additional international liquidity,in the belief that increasing world trade requires more liquidity for larger expected payments imbalances?
A) Eurodollar market
B) Special drawing rights
C) Reciprocal currency arrangements
D) General arrangements to borrow
A) Eurodollar market
B) Special drawing rights
C) Reciprocal currency arrangements
D) General arrangements to borrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Bilateral agreements between central banks,which provide for an exchange of currencies to help finance temporary balance-of-payments disequilibriums,are referred to as:
A) IMF drawings
B) Special drawing rights
C) Buffer stock facility
D) Swap agreements
A) IMF drawings
B) Special drawing rights
C) Buffer stock facility
D) Swap agreements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
"Country risk" analysis is concerned with all of the following except:
A) Depreciation of the borrowing country's currency
B) Political instability in the borrowing country
C) Economic growth in the borrowing country
D) External debt of the borrowing country
A) Depreciation of the borrowing country's currency
B) Political instability in the borrowing country
C) Economic growth in the borrowing country
D) External debt of the borrowing country

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Concerning international lending risk of commercial banks,____ is closely related to political developments in a borrowing country,especially the government's views concerning international investments and loans.
A) Economic risk
B) Credit risk
C) Country risk
D) Currency risk
A) Economic risk
B) Credit risk
C) Country risk
D) Currency risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The exchange of borrowing country debt for an ownership position in the borrowing country is known as:
A) Debt forgiveness
B) Debt-for-debt swap
C) Debt reduction
D) Debt/equity swap
A) Debt forgiveness
B) Debt-for-debt swap
C) Debt reduction
D) Debt/equity swap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To reduce their exposure to developing country debt,lending commercial banks have practiced all of the following except:
A) Making outright loan sales to other commercial banks
B) Reducing their capital base as a cushion against losses
C) Dealing in debt-for-debt swaps with foreign governments
D) Dealing in debt/equity swaps with foreign governments
A) Making outright loan sales to other commercial banks
B) Reducing their capital base as a cushion against losses
C) Dealing in debt-for-debt swaps with foreign governments
D) Dealing in debt/equity swaps with foreign governments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Concerning international lending risk of commercial banks,____ refers to the probability that part/all of the interest/principal of a loan will not be repaid.
A) Country risk
B) Credit risk
C) Currency risk
D) Presidential risk
A) Country risk
B) Credit risk
C) Currency risk
D) Presidential risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following are major goals of the International Monetary Fund except:
A) Promoting international cooperation among member countries
B) Fostering a multilateral system of international payments
C) Making long-term development and reconstruction loans
D) Promoting exchange-rate stability and the elimination of exchange restrictions
A) Promoting international cooperation among member countries
B) Fostering a multilateral system of international payments
C) Making long-term development and reconstruction loans
D) Promoting exchange-rate stability and the elimination of exchange restrictions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Most analysts feel that the financial difficulties in East Asia were triggered by
A) Misallocation of investment
B) Unavailability of cheap foreign labor
C) Lack of alignment of the exchange rate with the dollar
D) Surpluses in the trade accounts of the Asian countries
A) Misallocation of investment
B) Unavailability of cheap foreign labor
C) Lack of alignment of the exchange rate with the dollar
D) Surpluses in the trade accounts of the Asian countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which indicator of international debt burden schedules interest and principal payments on long-term debt as a percent of export earnings?
A) Debt service ratio
B) Debt-to-export ratio
C) Ratio of external debt to gross domestic product
D) Ratio of external debt to gross national product
A) Debt service ratio
B) Debt-to-export ratio
C) Ratio of external debt to gross domestic product
D) Ratio of external debt to gross national product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which international reserve asset was officially phased out of the international monetary system by the United States in the early 1970s?
A) Special drawing rights
B) Swap agreements
C) General arrangements to borrow
D) Gold
A) Special drawing rights
B) Swap agreements
C) General arrangements to borrow
D) Gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In response to the international debt problem,the United States set up a special fund in 1986 to help make up for lost oil revenues.Under the plan,the United States would make more money available as world oil prices fell.This plan was designed to help:
A) Argentina
B) Saudi Arabia
C) Mexico
D) Brazil
A) Argentina
B) Saudi Arabia
C) Mexico
D) Brazil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
To reduce losses on developing country loans,commercial banks sometimes sell their loans,at a discount,to a developing country government for local currency which is then used to finance purchases of ownership shares in developing country industries.This practice is known as:
A) Debt forgiveness
B) Debt buyback
C) Debt-for-debt swap
D) Debt/equity swap
A) Debt forgiveness
B) Debt buyback
C) Debt-for-debt swap
D) Debt/equity swap

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
"Owned" international reserves consist of:
A) Special drawing rights
B) Oil facility
C) IMF drawings
D) Reciprocal currency arrangements
A) Special drawing rights
B) Oil facility
C) IMF drawings
D) Reciprocal currency arrangements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Debt reduction
A) Refers to any voluntary scheme that lessens the burden on the debtor nation
B) May be accomplished through debt rescheduling
C) May be achieved through debt/equity swaps
D) All of the above
A) Refers to any voluntary scheme that lessens the burden on the debtor nation
B) May be accomplished through debt rescheduling
C) May be achieved through debt/equity swaps
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
For developing countries such as Mexico and Brazil,severe economic problems in the 1980s were caused by:
A) A fall in the world demand for products produced by developing countries
B) High prices of basic raw materials and other commodities
C) Low real interest rates in the United States
D) High levels of income and imports for the United States
A) A fall in the world demand for products produced by developing countries
B) High prices of basic raw materials and other commodities
C) Low real interest rates in the United States
D) High levels of income and imports for the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Concerning international lending risk of commercial banks,____ is associated with possible changes in the exchange value of a nation's currency.
A) Political risk
B) Country risk
C) Credit risk
D) Currency risk
A) Political risk
B) Country risk
C) Credit risk
D) Currency risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which term best describes the process in which the International Monetary Fund provides loans to countries facing balance-of-payments difficulties provided that they initiate programs holding promise of correcting these difficulties?
A) Conditionality
B) Debt service
C) Reciprocal currency arrangement
D) Swap agreement
A) Conditionality
B) Debt service
C) Reciprocal currency arrangement
D) Swap agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Concerning international debt,____ refers to a negotiated reduction in the contractual obligations of the debtor country and includes schemes such as markdowns and write-offs of debt.
A) Debt/equity swap
B) Debt-for-debt swap
C) Debt forgiveness
D) Debt sales
A) Debt/equity swap
B) Debt-for-debt swap
C) Debt forgiveness
D) Debt sales

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
"Borrowed" international reserves consist of:
A) IMF drawings
B) Foreign currencies
C) Gold
D) Special drawing rights
A) IMF drawings
B) Foreign currencies
C) Gold
D) Special drawing rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which organization is largely intended to make long-term reconstruction loans to developing nations?
A) Export-Import Bank
B) World Bank
C) International Monetary Fund
D) United Nations
A) Export-Import Bank
B) World Bank
C) International Monetary Fund
D) United Nations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When exchange rates are fixed by central bankers,the need for international reserves disappears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 17.1 Foreign Exchange Market
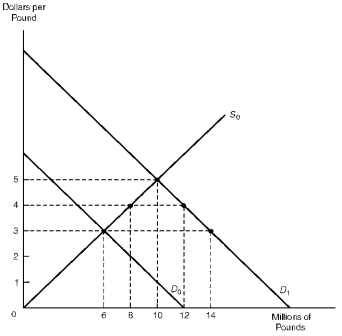
Refer to Figure 17.1.Under a floating exchange rate system,the exchange rate would rise to $4 and U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 4 million pounds to the foreign exchange market in exchange for dollars to maintain this rate.

Refer to Figure 17.1.Under a floating exchange rate system,the exchange rate would rise to $4 and U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 4 million pounds to the foreign exchange market in exchange for dollars to maintain this rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When exchange rates are fixed by central bankers,international reserves are necessary for financing payments imbalances and the stabilization of exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
There exists a direct relationship between the degree of exchange rate flexibility and the need for international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 17.1 Foreign Exchange Market

Refer to Figure 17.1.Under a fixed exchange rate system,U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 8 million pounds in exchange for dollars to keep the exchange rate at $3 per pound.

Refer to Figure 17.1.Under a fixed exchange rate system,U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 8 million pounds in exchange for dollars to keep the exchange rate at $3 per pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
With floating exchange rates,countries require sizable amounts of international reserves for the stabilization of exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The supply of international reserves consists of owned reserves and borrowed reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Foreign currencies constitute the smallest component of the world's international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 17.1 Foreign Exchange Market

Refer to Figure 17.1.If the exchange rate was allowed to rise to $4 per pound,U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 6 million pounds to the foreign exchange market in exchange for dollars to maintain this rate.

Refer to Figure 17.1.If the exchange rate was allowed to rise to $4 per pound,U.S.monetary authorities would have to supply 6 million pounds to the foreign exchange market in exchange for dollars to maintain this rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Swap arrangements
A) Are agreements between governments
B) Require repayment within a stipulated period
C) Are usually multilateral agreements
D) Are never initiated by telephone
A) Are agreements between governments
B) Require repayment within a stipulated period
C) Are usually multilateral agreements
D) Are never initiated by telephone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
An advantage of international reserves is that they allow countries to sustain temporary balance-of-payments deficits until acceptable adjustment measures can operate to correct the disequilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The demand for international reserves tend to increase with the level of world income and trade activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
With floating exchange rates,payments imbalances tend to be corrected by market-induced fluctuations in the exchange rate,and the need for exchange-rate stabilization and international reserves disappears.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under a system of fixed exchange rates,international reserves are needed to bridge the gap between monetary receipts and monetary payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If a nation with a balance-of-payments deficit is willing and able to initiate quick actions to increase export receipts and decrease import payments,the amount of international reserves needed will be relatively large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A nation may experience debt-servicing problems because of
A) Pursuit of improper macroeconomic policies
B) Inadequate borrowing
C) Adverse economic events
D) Both a and c
A) Pursuit of improper macroeconomic policies
B) Inadequate borrowing
C) Adverse economic events
D) Both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
To the extent that adjustments in prices,interest rates,and income levels promote balance-of-payments equilibrium,the demand for international reserves decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
International reserves allow a country to finance disequilibria in its balance-of-payments position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The greater a nation's propensity to apply tariffs and quotas to key sectors,the greater will be the need for international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The demand for international reserves is negatively related to the level of world prices and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When a deficit nation borrows from the International Monetary Fund,it purchases with its currency the foreign currency required to help finance the payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Created by the International Monetary Fund,special drawing rights (SDRs)are unconditional rights to draw currencies of other nations,thus enabling countries to finance their current-account deficits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Gold constitutes the largest component of the world's international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The SDR has replaced the dollar,yen,and mark as the key asset of the international financial system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Because the value of the SDR is tied directly to the value of the U.S.dollar,a 10 percent dollar depreciation would result in a 10 percent decrease in the SDR's value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the 1970s,the major industrial countries abandoned the managed-floating exchange rate system and adopted a system of fixed exchange rates tied to the price of gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A goal of the International Monetary Fund is to make short-term loans to member nations so as to allow them to correct balance of payments disequilibriums without resorting to measures that would destroy national prosperity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A main purpose of the International Monetary Fund is to make loans of foreign currencies to member countries which are experiencing current-account surpluses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In 1975 the official price of gold was abolished as the unit of account for the international monetary system.As a result,gold was demonetized as an international reserve asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The U.S.dollar,Japanese yen,British pound,and Mexican peso are the major reserve currencies of the international monetary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The so-called General Arrangements to Borrow provide a permanent increase in the supply of international reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The U.S.dollar has been considered a reserve (key)currency because trading nations have been willing to hold it as an international reserve asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Gold is currently the most widely used asset in the international monetary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When granting loans to financially troubled nations,the International Monetary Fund requires some degree of conditionality,meaning that the borrowing nation must agree to implement economic policies as mandated by the IMF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The International Monetary Fund has sometimes demanded that financially-troubled nations,that borrow from the IMF,undergo austerity programs including slashing of public spending and private consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The value of the SDR is tied to a currency basket consisting of the U.S.dollar,German mark,Japanese yen,French franc,and British pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The main purpose of the International Monetary Fund is to grant long-term loans to developing nations to help them finance the development of infrastructure such as roads,dams,and bridges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In 1974 the United States revoked a 41-year ban on U.S.citizen's ownership of gold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
By the 1990s,the British pound had replaced the U.S.dollar as the world's key currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Swap arrangements are bilateral agreements between central banks to allow countries to temporarily borrow funds to ease current-account deficits and discourage speculative capital flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



