Deck 19: Introduction to Decision Analysis
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Introduction to Decision Analysis
1
A disadvantage of the maximax and maximin criteria is that they use only one value from the payoff table to make a decision.
True
2
Nonprobabilistic criteria are used when either the probabilities associated with the possible payoffs are unknown or the decision maker lacks confidence and/or information with which to assess probabilities for the various payoffs.
True
3
An optimistic decision criterion for dealing with uncertainty without using probability is the maximax criterion.
True
4
In business, you will encounter a wide variety of decision situations. The two primary decision environments are certainty and uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In reality, the typical business decision-making environment is one of certainty rather than uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The possible outcomes in a decision situation over which the decision maker has no control is referred to as the choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The established basis for making a decision gives us the criteria for analyzing a decision and making a "best" choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a certainty environment, the best decision is not necessarily associated with the best outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Some decision criteria take into account the probabilities associated with each outcome. One of the options, the expected-value criterion, refers to the long-run average outcome for a given alternative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Not all decisions require the use of decision analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
By "best decision," we mean the alternative course of action, using all available information that best satisfies the decision criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A loss of convenience is the difference between the actual payoff that occurs for a decision and the optimal payoff for the same state of nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
All three decision criteria (maximax, maximin, minimax regret) lead to the same decisions, describing a specific decision-making philosophy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The outcome that is associated with any combination of a particular state of nature and an alternative is called a payoff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A conservative decision criterion for dealing with uncertainty without using probability is referred to as the maximin criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Certainty represents a situation where the results of selecting each alternative are known before the decision is made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Probabilistic criteria incorporates the decision maker's probability of each state of nature occurring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Uncertainty is a decision environment in which the decision maker does not know what outcome will occur when an alternative is selected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A decision criterion that considers the results of selecting the "wrong" alternative is referred to as the maximax regret criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The payoffs associated with all possible combinations of alternatives and states of nature constitute a profit or loss table.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A decision tree is a diagram that illustrates the correct ordering of actions and events in a decision analysis problem. Each act or event is represented by a branch on the decision tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which one of the factors below would not affect the complexity of a decision?
A) The number of alternatives available to the decision maker.
B) The number of possible outcomes associated with each alternative.
C) The general level of uncertainty associated with the decision.
D) The probability of having a positive outcome.
A) The number of alternatives available to the decision maker.
B) The number of possible outcomes associated with each alternative.
C) The general level of uncertainty associated with the decision.
D) The probability of having a positive outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Sensitivity analysis measures how sensitive a decision is to the number of possible outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A cash flow is defined as usually any dollar change (positive or negative) in the decision maker's asset position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain the goal of decision analysis and identify three factors that affect the complexity of a decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Explain the difference between the two main categories of decision criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Select the best answer. A decision maker must identify the outcomes for each decision alternative and
A) keeps the choices organized by constructing a table.
B) determine the biggest money making alternative.
C) assess probabilities associated with each outcome.
D) all of the above.
A) keeps the choices organized by constructing a table.
B) determine the biggest money making alternative.
C) assess probabilities associated with each outcome.
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Jamie Anderson is analyzing the following payoff table. She is trying to choose how many salads to make in advance each day before she knows the actual demand. 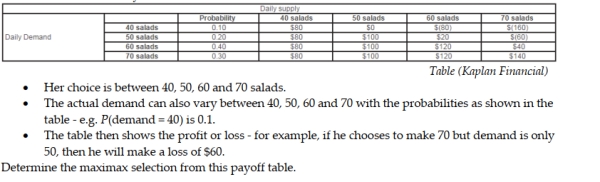


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Decision makers must continually remind themselves that
A) there is a difference between a good decision and a good outcome.
B) not all decisions require the use of decision analysis.
C) the complexity of the decision situation usually determines the usefulness of decision analysis.
D) All of the above.
A) there is a difference between a good decision and a good outcome.
B) not all decisions require the use of decision analysis.
C) the complexity of the decision situation usually determines the usefulness of decision analysis.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Jamie Anderson is analyzing the following payoff table. She is trying to choose how many salads to make in advance each day before she knows the actual demand. 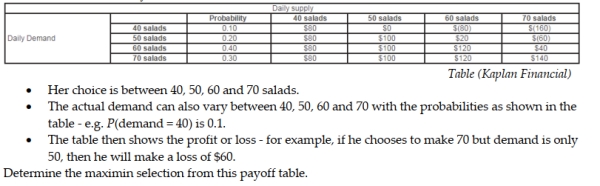


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In constructing a payoff table to compute the cost of uncertainty, which of the following defines the correct order of steps taken?
A) Add the probabilities, compute the expected value for each decision, and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
B) Compute the expected value for each decision alternative, calculate the probabilities, and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
C) Add the probabilities and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
D) Add the probabilities, compute the expected value for each decision, and determine the best decision using highest values.
A) Add the probabilities, compute the expected value for each decision, and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
B) Compute the expected value for each decision alternative, calculate the probabilities, and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
C) Add the probabilities and determine the best decision using expected-value decision criterion.
D) Add the probabilities, compute the expected value for each decision, and determine the best decision using highest values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A decision tree provides a "road map" for organizing events, starting with the most recent events and choices first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The disadvantage of the expected-value criterion is that it does not take into account the decision maker's attitude toward profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Explain as clearly as possible what the "best decision" is for a business problem and what the best decision will be associated with in a certainty environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When we apply the expected-value criterion, the best decision is to select the alternative with the highest average payoff or the lowest average loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Decision-tree analysis provides a way to take into account future decisions when making the most current decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following are not examples of non-probabilistic decision criteria?
A) Maximin decision criteria.
B) Minimum outcome criteria.
C) Maximax decision criteria.
D) Minimax regret decision criteria.
A) Maximin decision criteria.
B) Minimum outcome criteria.
C) Maximax decision criteria.
D) Minimax regret decision criteria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Explain the primary difference between the business decision-making environments of certainty versus uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In an uncertain environment, the best decision might not result in the best outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The expected-value criterion does not include which of the following steps:
A) Compute the expected value for each decision alternative.
B) Assign probabilities to the possible outcomes associated with each alternative.
C) Define only the positive outcomes.
D) Define the decision alternatives.
A) Compute the expected value for each decision alternative.
B) Assign probabilities to the possible outcomes associated with each alternative.
C) Define only the positive outcomes.
D) Define the decision alternatives.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Define sensitivity analysis and how it related to cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the disadvantage of the maximax and maximin criteria? What is another alternative approach?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify the 4 steps of the expected-value criterion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Define the process of "folding back the tree" in decision tree analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Identify the 8 steps of computing the cost of uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Identify the 4 steps to constructing a decision tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the process of growing a decision tree and why it is such a valuable method of making a business decision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Decision tree analysis could be missing branches on the tree. Define one important consideration that could be left out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



