Deck 14: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/29
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
1
How many peaks would be observed for each of the circled protons in the compounds below?
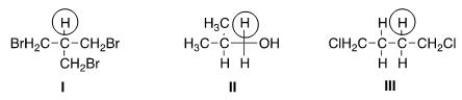
A)I = 6; II = 2; III = 3.
B)I = 7; II = 3; III = 3.
C)I = 7; II = 1; III = 3.
D)I = 7; II = 2; III = 3.

A)I = 6; II = 2; III = 3.
B)I = 7; II = 3; III = 3.
C)I = 7; II = 1; III = 3.
D)I = 7; II = 2; III = 3.
I = 7; II = 2; III = 3.
2
How many unique protons are present in each of the following compounds?
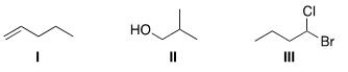
A)I = 6; II = 3; III = 6.
B)I = 5; II = 4; III = 6.
C)I = 6; II = 4; III = 4.
D)I = 6; II = 4; III = 6.

A)I = 6; II = 3; III = 6.
B)I = 5; II = 4; III = 6.
C)I = 6; II = 4; III = 4.
D)I = 6; II = 4; III = 6.
I = 6; II = 4; III = 6.
3
For each of the following compounds, indicate how many 13C NMR signals will be observed. 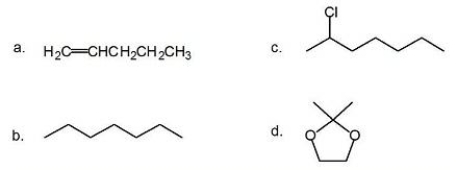
A)a: 4; b: 4; c: 7; d: 4
B)a: 5; b: 4; c: 7; d: 3
C)a: 4; b: 7; c: 7; d: 3
D)a: 5; b: 4; c: 6; d: 5

A)a: 4; b: 4; c: 7; d: 4
B)a: 5; b: 4; c: 7; d: 3
C)a: 4; b: 7; c: 7; d: 3
D)a: 5; b: 4; c: 6; d: 5
a: 5; b: 4; c: 7; d: 3
4
What is the relationship between Ha and Hb in the following compound?
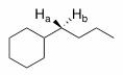
A)Homotopic
B)Enantiotopic
C)Diastereotopic
D)Mesotopic

A)Homotopic
B)Enantiotopic
C)Diastereotopic
D)Mesotopic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the indicated protons would absorb furthest downfield in a 1H NMR spectrum?
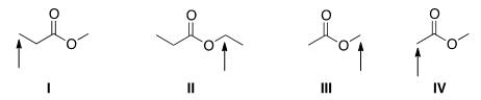
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How many different kinds of protons are present in each of the following compounds?
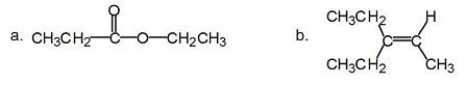
A)a: 5; b: 6
B)a: 5; b: 5
C)a: 4; b: 6
D)a: 4; b: 5

A)a: 5; b: 6
B)a: 5; b: 5
C)a: 4; b: 6
D)a: 4; b: 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the labeled protons absorbs furthest upfield in the 1H NMR spectrum?
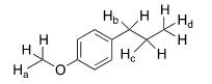
A)Ha
B)Hb
C)Hc
D)Hd

A)Ha
B)Hb
C)Hc
D)Hd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many different kinds of protons are present in each of the following compounds?
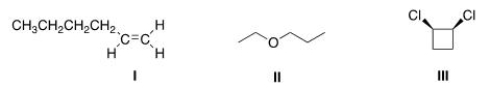
A)I = 6; II = 5; III = 3.
B)I = 7; II = 5; III = 3.
C)I = 7; II = 6; III = 3.
D)I = 6; II = 6; III = 3.

A)I = 6; II = 5; III = 3.
B)I = 7; II = 5; III = 3.
C)I = 7; II = 6; III = 3.
D)I = 6; II = 6; III = 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Into how many peaks will the circled proton be split?
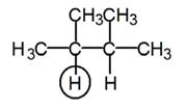
A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8

A)5
B)6
C)7
D)8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many different kinds of protons are present in each of the following molecules?
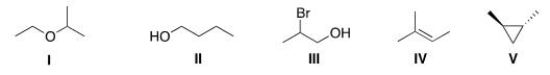
A)I = 3; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 4; V = 3.
B)I = 4; II = 5; III = 4; IV = 4; V = 3.
C)I = 4; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 4; V = 3.
D)I = 4; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 3; V = 4.

A)I = 3; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 4; V = 3.
B)I = 4; II = 5; III = 4; IV = 4; V = 3.
C)I = 4; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 4; V = 3.
D)I = 4; II = 5; III = 5; IV = 3; V = 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the indicated protons in the molecules below would absorb furthest downfield in a 1H NMR spectrum?
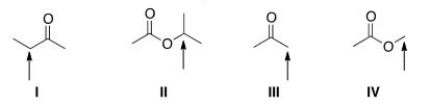
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the indicated protons absorbs furthest downfield?
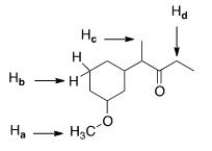
A)Ha
B)Hb
C)Hc
D)Hd

A)Ha
B)Hb
C)Hc
D)Hd

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the relationship between Ha and Hb in the following compound?
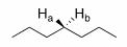
A)Homotopic
B)Enantiotopic
C)Diastereotopic
D)Mesotopic

A)Homotopic
B)Enantiotopic
C)Diastereotopic
D)Mesotopic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Compound X has a molecular formula C8H10 and gives the 1H NMR spectrum below.What is the structure of X?
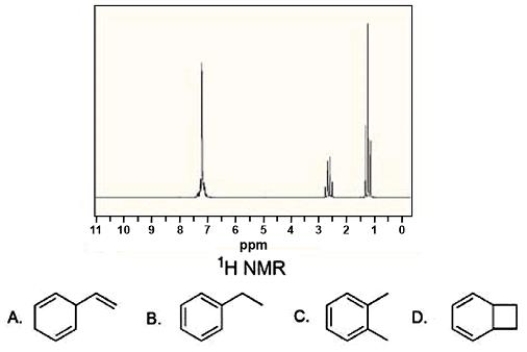
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following compounds would give rise to a 13C spectrum with 6 peaks?
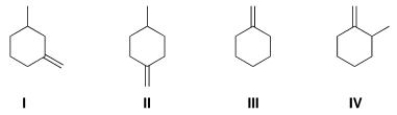
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How many different kinds of protons are present in each of the following compounds?

A)I = 4; II = 3; III = 1.
B)I = 4; II = 4; III = 1.
C)I = 4; II = 4; III = 2.
D)I = 3; II = 3; III = 1.

A)I = 4; II = 3; III = 1.
B)I = 4; II = 4; III = 1.
C)I = 4; II = 4; III = 2.
D)I = 3; II = 3; III = 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
How many different kinds of protons are present in each of the following compounds?
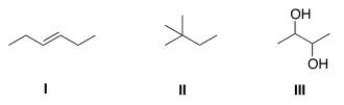
A)I = 2; II = 3; III = 4.
B)I = 2; II = 3; III = 3.
C)I = 3; II = 3; III = 3.
D)I = 3; II = 3; III = 4.

A)I = 2; II = 3; III = 4.
B)I = 2; II = 3; III = 3.
C)I = 3; II = 3; III = 3.
D)I = 3; II = 3; III = 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How could spectroscopy be used to distinguish between the following compounds?
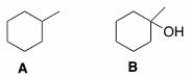
A)Compound A has a triplet in its 1H NMR spectrum at 1.0 ppm.
B)Compound B has a peak at 3200-3500 cm-1 in its IR spectrum.
C)Compound A has a peak in its IR spectrum at 2900 cm-1.
D)Compound A has a triplet in its 1H NMR spectrum at 1.0 ppm and compound B has a peak at 3200-3500 cm-1 in its IR spectrum.

A)Compound A has a triplet in its 1H NMR spectrum at 1.0 ppm.
B)Compound B has a peak at 3200-3500 cm-1 in its IR spectrum.
C)Compound A has a peak in its IR spectrum at 2900 cm-1.
D)Compound A has a triplet in its 1H NMR spectrum at 1.0 ppm and compound B has a peak at 3200-3500 cm-1 in its IR spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following compounds does not show only one signal in its 1H NMR spectrum?
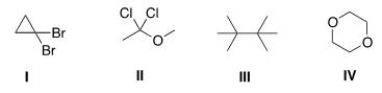
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Into how many peaks will each of the circled protons be split?
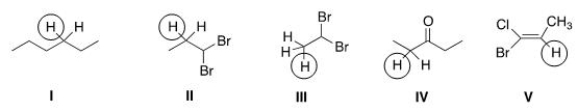
A)I = 3; II = 8; III = 1; IV = 4; V = 3.
B)I = 9; II = 8; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 4.
C)I = 4; II = 8; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 5.
D)I = 4; Ii = 7; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 3.

A)I = 3; II = 8; III = 1; IV = 4; V = 3.
B)I = 9; II = 8; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 4.
C)I = 4; II = 8; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 5.
D)I = 4; Ii = 7; III = 2; IV = 4; V = 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements about 13C NMR is not true?
A)In 13C proton-decoupled NMR spectra, all peaks are singlets.
B)(13C) NMR spectra display peaks for only carbons that bear hydrogen atoms.
C)(13C) NMR chemical shifts occur over a greater range than 1H NMR chemical shifts.
D)(13C) NMR easily differentiates between the different hybridized carbons (sp3, sp2, and sp hybridized carbons).
A)In 13C proton-decoupled NMR spectra, all peaks are singlets.
B)(13C) NMR spectra display peaks for only carbons that bear hydrogen atoms.
C)(13C) NMR chemical shifts occur over a greater range than 1H NMR chemical shifts.
D)(13C) NMR easily differentiates between the different hybridized carbons (sp3, sp2, and sp hybridized carbons).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An unknown compound A has the molecular formula C7H14O2.Compound A absorbs strongly in the IR at 1700 cm-1.The 1H NMR spectral data for compound A are given below.What is the structure of compound A?
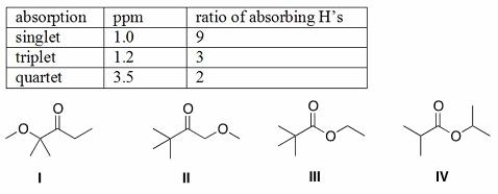
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the indicated protons absorbs further downfield?
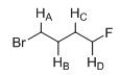
A)HA
B)HB
C)HC
D)HD

A)HA
B)HB
C)HC
D)HD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What effect does increasing the operating frequency of a 1H NMR spectrum have on the frequency of an absorption in Hz?
A)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will also increase.
B)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will decrease.
C)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will remain the same.
D)It is not possible to predict the change in frequency of an absorption in Hz.
A)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will also increase.
B)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will decrease.
C)Frequency of an absorption in Hz will remain the same.
D)It is not possible to predict the change in frequency of an absorption in Hz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following spectroscopy methods does not involve the interaction of organic molecules with electromagnetic radiation?
A)Nuclear magnetic resonance
B)Infrared spectroscopy
C)Mass spectroscopy
D)Ultraviolet spectroscopy
A)Nuclear magnetic resonance
B)Infrared spectroscopy
C)Mass spectroscopy
D)Ultraviolet spectroscopy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following statements is true about electromagnetic radiation?
A)All molecules absorb electromagnetic radiation at some frequency.
B)Frequency is directly proportional to wavelength.
C)NMR uses the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
D)The radio frequency region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the largest energy per photon.
E)Energy is inversely proportional to frequency.
A)All molecules absorb electromagnetic radiation at some frequency.
B)Frequency is directly proportional to wavelength.
C)NMR uses the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
D)The radio frequency region of the electromagnetic spectrum has the largest energy per photon.
E)Energy is inversely proportional to frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
An unknown compound A has the molecular formula C12H16O.Compound A absorbs strongly in the IR at 1700 cm-1.The NMR spectral data for compound A are given below.What is the structure of compound A?
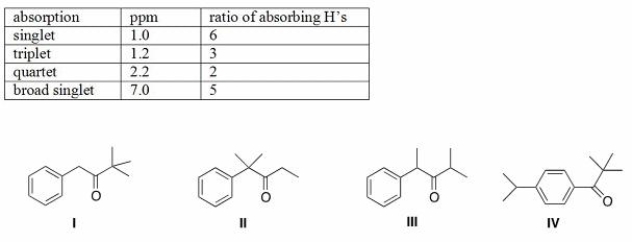
A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

A)I
B)II
C)III
D)IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What region of the electromagnetic spectrum does nuclear magnet resonance spectroscopy use?
A)Radio frequency
B)Microwave frequency
C)Infrared frequency
D)Visible frequency
E)Ultraviolet frequency
A)Radio frequency
B)Microwave frequency
C)Infrared frequency
D)Visible frequency
E)Ultraviolet frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What effect does increasing the operating frequency of a 1H NMR spectrum have on the magnitude of a coupling constant J in Hz?
A)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will also increase.
B)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will decrease.
C)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will remain the same.
D)It is not possible to predict the change in the magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz.
A)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will also increase.
B)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will decrease.
C)Magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz will remain the same.
D)It is not possible to predict the change in the magnitude of coupling constant J in Hz.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 29 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



