Deck 15: Sample Size and Statistical Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Sample Size and Statistical Theory
1
If two random samples of equal size are drawn from the same population, we should expect the mean of both samples to be identical.
False
2
A researcher takes a modest sample and, if results are worthwhile, opts for a larger sample.This type of sampling is called sequential sampling.
True
3
The arithmetic average is the measurement of the sample mean.
True
4
A 95 percent confidence interval will be smaller than a 90 percent confidence interval.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If all members of the population have identical opinions on an issue, a sample of one is unsatisfactory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The size of a sample can be determined only by using statistical techniques.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Two samples are drawn from the same population with a known variance, 2.If the sample sizes are 100 and 400, then the standard error of the mean of the former sample will be half that of the latter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The equation for the sample variance is 1 n S2 = Xi - X )2 
 n - 1
n - 1

 n - 1
n - 1 
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Bo Derek calculates that she needs a sample size of 200, given the estimated mean, accuracy variance nd required Z-score.However, she learns that the variance is actually one-half of what she originally believed.Her required sample size will now be
A)100
B)800
C)400
D)50
E)none of the above
A)100
B)800
C)400
D)50
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the population variance is 10 and the sample size is 16, then the standard error of the mean is 2.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The two population characteristics of most interest to researchers are and .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the allowed error is increased, the required sample size would decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The sample variance, S2, can be used to estimate the population variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
It is sensible to use disproportionate sampling if one of the subgroups of the population is a relatively small percentage of the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What determines the statistical operations that can be performed on a scale type?
A)intransitivity property
B)invariance property
C)comparative property
D)isomorphic property
A)intransitivity property
B)invariance property
C)comparative property
D)isomorphic property

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The sample mean is not known, but it can be estimated from the population characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If we wanted to be 95 percent confident that we wouldn't make an error of more than 1 unit in our estimate of or = 2), we would need a sample size of approximately 16.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If the population variance is 4, the sample standard deviation must be 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The distribution which we say always assume to be "normal " or bell shaped is the
A)sampling distribution
B)population distribution
C)sample distribution
D)variance distribution
E)standard distribution
A)sampling distribution
B)population distribution
C)sample distribution
D)variance distribution
E)standard distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a complex multi-stage design is involved, a common approach is to replicate the entire sampling plan and get various independent estimates of the sample mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A market research firm has been engaged to do a study of dishwashing detergents preferred by homemakers in San Francisco 800,000 population) as compared to those preferred in New York 8,000,000 population).In order to obtain results of about equal reliability in each city, the number of homemakers polled in New York should be
A)ten times the number polled in San Francisco.
B)10 or 3.16 times the number polled in San Francisco.
C)about the same as in San Francisco.
D)half the number polled in San Francisco.
A)ten times the number polled in San Francisco.
B)10 or 3.16 times the number polled in San Francisco.
C)about the same as in San Francisco.
D)half the number polled in San Francisco.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
ABC Incorporated wants to find out the proportion of customers who would purchase their new product.They have decided to take a modest sample, look at the results, and then decide if more information, in the form of a larger sample, is needed.ABC is using
A)simple random sampling.
B)biased random sampling.
C)stratified sampling.
D)sequential sampling.
E)none of the above.
A)simple random sampling.
B)biased random sampling.
C)stratified sampling.
D)sequential sampling.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is true?
A)The sample size required to ensure 95 percent confidence limits will be smaller than that for 90 percent confidence limits.
B)The sample size required to ensure a smaller confidence interval will also be smaller.
C)The only way to reduce the width of a confidence interval is to reduce the confidence requirements.
D)The required sample size is dependent on å only.
E)The required sample size for given error and confidence levels is independent of the population size.
A)The sample size required to ensure 95 percent confidence limits will be smaller than that for 90 percent confidence limits.
B)The sample size required to ensure a smaller confidence interval will also be smaller.
C)The only way to reduce the width of a confidence interval is to reduce the confidence requirements.
D)The required sample size is dependent on å only.
E)The required sample size for given error and confidence levels is independent of the population size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The probability that a confidence level will include a population parameter is called
A)precision level
B)critical value
C)standard deviation
D)confidence level
A)precision level
B)critical value
C)standard deviation
D)confidence level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two samples are drawn from the same population: 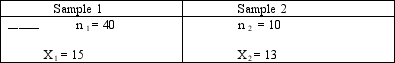 Which of the following statements is true? _ _ 1-The distribution of X1 will be taller than that of X2. 2-The standard deviations of the two means are equal. 3- 1 2 4-The two population variances are equal.
Which of the following statements is true? _ _ 1-The distribution of X1 will be taller than that of X2. 2-The standard deviations of the two means are equal. 3- 1 2 4-The two population variances are equal.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 4
 Which of the following statements is true? _ _ 1-The distribution of X1 will be taller than that of X2. 2-The standard deviations of the two means are equal. 3- 1 2 4-The two population variances are equal.
Which of the following statements is true? _ _ 1-The distribution of X1 will be taller than that of X2. 2-The standard deviations of the two means are equal. 3- 1 2 4-The two population variances are equal.A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the following four statements: 1.The distribution of the mean of a random sample approaches the normal distribution as the sample size increases, only if the parent population is normally distributed. 2-The distribution of the mean of a random sample taken from a normal population is normal, irrespective of the sample size. 3-The distribution of the mean of a random sample taken from practically any population approaches the normal distribution as the sample size increases. 4-The distribution of the mean of a random sample taken from practically any population is normal, irrespective of the sample size. Which of the above statements is/are true?
A)Only 1
B)2 and 3
C)2 and 4
D)Only 3
E)None of the above
A)Only 1
B)2 and 3
C)2 and 4
D)Only 3
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Use the following information for questions
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-What happens to the standard deviation of the sample mean, if we change the sample size from 25 to 100?
A)It is decreased by a factor of 4.
B)It is increased by a factor of 4.
C)It is decreased by a factor of 2.
D)It is decreased by a factor of 16.
E)None of the above.
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-What happens to the standard deviation of the sample mean, if we change the sample size from 25 to 100?
A)It is decreased by a factor of 4.
B)It is increased by a factor of 4.
C)It is decreased by a factor of 2.
D)It is decreased by a factor of 16.
E)None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following information for questions
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-The probability that the sample mean lies between 498 and 502 is closest to
A).3174
B).9772
C).9544
D).3108
E).6826
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-The probability that the sample mean lies between 498 and 502 is closest to
A).3174
B).9772
C).9544
D).3108
E).6826

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Means can only be meaningfully calculated on
A)nominal-or higher-scaled data
B)ratio-scaled data
C)interval-or ratio-scaled data
D)ordinal-or higher-scaled data
A)nominal-or higher-scaled data
B)ratio-scaled data
C)interval-or ratio-scaled data
D)ordinal-or higher-scaled data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is set in advance for the statistical determination of sample size?
A)sample size
B)standard deviation
C)sampling frame
D)precision level
A)sample size
B)standard deviation
C)sampling frame
D)precision level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Consider the following data: _ X = 10 2 = 4 n = 25 The lower and upper limits of 1-a 90 percent confidence interval will be 9.36 and 10.64, respectively. 2-a 95 percent confidence interval will be 9.216 and 10.784, respectively. 3-a 90 percent confidence interval cannot be determined for the given data. 4-a 95 percent confidence interval indicates the range within which must lie.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 2
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
As the sample size becomes larger, the mean of the sampling distribution becomes
A)greater than the population mean
B)smaller than the population mean
C)equal to the population mean
D)double that of the population mean
A)greater than the population mean
B)smaller than the population mean
C)equal to the population mean
D)double that of the population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Let the variance of a normally distributed random sample be 16.A point that is 8 units away from the mean is 1-a point such that the probability of getting any other point further from the mean is less than 0.025. 2-a point such that the probability of getting any other point further from the mean is less than or equal to .95. 3-a point such that the probability of getting any other point further from the mean is greater than 0.025. 4-two standard deviations away from the mean.
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 4
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)1 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The standard error of the mean is the same as the
A)standard deviation of the population
B)standard deviation of the normal distribution
C)standard deviation of the sampling distribution
D)none of the above
A)standard deviation of the population
B)standard deviation of the normal distribution
C)standard deviation of the sampling distribution
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
It is estimated that the proportion of Californians in favor of Proposition 5 is between 0.4 and 0.6.The sponsors of the proposition would like to sample Californians and get a 95 percent confidence interval for the true proportion of people in favor of Proposition 5.They want to restrict the error level to 5 percentage points.The required sample size is then
A)400.
B)40.
C)100.
D)1,000.
E)none of the above.
A)400.
B)40.
C)100.
D)1,000.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Use the following information for questions
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-The probability that X8 is between 495 and 505 pounds is closest to
A).0228
B).3174
C).9772
D).6826
E).3830
A soap factory produces 500-pound boxes of soap for industries.
However, the weight of the boxes varies somewhat due to the process.
Assume that the weight of each box is distributed normally with
mean = = 500 pounds variance = 2 = 25 pounds2
Quality control takes a random sample of 25 boxes per day.Let the
weight of these boxes be denoted as X1, X2, ..., X25.
-The probability that X8 is between 495 and 505 pounds is closest to
A).0228
B).3174
C).9772
D).6826
E).3830

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A distribution which tails off to the right and contains a few very large values is described as
A)negatively skewed
B)platykurtic
C)positively skewed
D)symmetric
A)negatively skewed
B)platykurtic
C)positively skewed
D)symmetric

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following isare.a statistics)?
A)sample mean
B)population median
C)population standard deviation
D)all the above
A)sample mean
B)population median
C)population standard deviation
D)all the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the following data from a random sample: 10 10  X I = 70 XI - X )2 = 18 i=1 _
X I = 70 XI - X )2 = 18 i=1 _
A)X = 7, S2 = 2
B) = 7, 2 = 2 _
C)X = 7, 2 = 2
D)The population mean is 7 and S2 = 2
E)It is not possible to estimate the population mean and standard deviation from the given information.
 X I = 70 XI - X )2 = 18 i=1 _
X I = 70 XI - X )2 = 18 i=1 _A)X = 7, S2 = 2
B) = 7, 2 = 2 _
C)X = 7, 2 = 2
D)The population mean is 7 and S2 = 2
E)It is not possible to estimate the population mean and standard deviation from the given information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following: 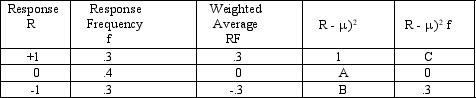 For the given data:
For the given data:
A) = .6, 2 = 0, A = 0, B = 1, C = .3.
B) = 0, 2 =.6, A = 0, B = -1, C = .3.
C) = 0, 2 = .6, A = 0,B = 1, C= .3.
D) = 0, 2 = .6, A = .4,B = -1, C = .3.
E) = .6, 2 = 0, A = .4,B = 1,C = .3.
 For the given data:
For the given data:A) = .6, 2 = 0, A = 0, B = 1, C = .3.
B) = 0, 2 =.6, A = 0, B = -1, C = .3.
C) = 0, 2 = .6, A = 0,B = 1, C= .3.
D) = 0, 2 = .6, A = .4,B = -1, C = .3.
E) = .6, 2 = 0, A = .4,B = 1,C = .3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Assume that is distributed normally with = 0, 2 = 1.What is Pz = 1)?
A).8413
B).1587
C).3413
D).0025
E)None of the above
A).8413
B).1587
C).3413
D).0025
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A college dean wants to determine the average time it takes a student to get from one class to the next.Preliminary studies have shown that it is reasonable to let t = 1.5 minutes the standard deviation of class travel times).What is the sample size which should be examined if the dean wants to assert with a probability of 95 percent that his estimate, the mean time of the random sample, will not be "off" by more than .25 minutes in either direction)? Choose the closest answer.
A)72 or more, but not less
B)81 or more, but not less
C)139 or more, but not less
D)200 or more, but not less
E)None of the above
A)72 or more, but not less
B)81 or more, but not less
C)139 or more, but not less
D)200 or more, but not less
E)None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following information for questions
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-Before the sample is drawn, the probability that the sample mean will exceed 9 ounces is closest to
A).3085
B).1587
C).1056
D).0256
E).0100
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-Before the sample is drawn, the probability that the sample mean will exceed 9 ounces is closest to
A).3085
B).1587
C).1056
D).0256
E).0100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Use the following information for questions
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-The probability that X1 will exceed 9 ounces is closest to
A).3085
B).1587
C).1056
D).0256
E).0100
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-The probability that X1 will exceed 9 ounces is closest to
A).3085
B).1587
C).1056
D).0256
E).0100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following information for questions
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-The standard error of the sample mean is
A).5
B).5 divided by 16
C).25 divided by 16
D).5 divided by 4
E).25
Consider a meat packing plant which produces packages of frozen
steak.Let X be the weight ounces) and assume that X is normally
distributed with x = 8.0 and x = .5, n sample size.= 16.
-The standard error of the sample mean is
A).5
B).5 divided by 16
C).25 divided by 16
D).5 divided by 4
E).25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



