Deck 14: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/117
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
1
Which of the following reactions is not an oxidation-reduction reaction?
A)C(s) + CO2(g) CO2(g)
B)CO(g) + Cl2(g) COCl2(g)
C)2H2O2(l) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
D)CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
E)2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g)
A)C(s) + CO2(g) CO2(g)
B)CO(g) + Cl2(g) COCl2(g)
C)2H2O2(l) 2H2O(l) + O2(g)
D)CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
E)2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g)
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
2
In which of the following choices is the oxidation number incorrect?
A)Fe2+(aq); oxidation number = 2+
B)Cl-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)H2(s); oxidation number = 1+
D)Cu2+(aq); oxidation number = 2+
E)C(s); oxidation number = 0
A)Fe2+(aq); oxidation number = 2+
B)Cl-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)H2(s); oxidation number = 1+
D)Cu2+(aq); oxidation number = 2+
E)C(s); oxidation number = 0
H2(s); oxidation number = 1+
3
In which compound does bromine have an oxidation number of 3+?
A)Br2O
B)BrO3
C)Br2O3
D)BrO2
E)Br2O5
A)Br2O
B)BrO3
C)Br2O3
D)BrO2
E)Br2O5
Br2O3
4
Consider the following reaction: Mg(s) + ZnSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Zn(s) Which of the following statements regarding this reaction is correct?
A)Magnesium is neither oxidized nor reduced.
B)The sulfate ion is reduced.
C)Zinc is the reducing agent.
D)Magnesium is the oxidizing agent.
E)Zinc gains two electrons.
A)Magnesium is neither oxidized nor reduced.
B)The sulfate ion is reduced.
C)Zinc is the reducing agent.
D)Magnesium is the oxidizing agent.
E)Zinc gains two electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
All of these statements concerning oxidation are correct except that
A)oxygen is necessary for oxidation to take place.
B)the oxidizing agent receives electrons from another species.
C)oxidation must accompany reduction.
D)the oxidizing agent increases the oxidation number of another element.
E)the oxidation of a metal produces positive ions.
A)oxygen is necessary for oxidation to take place.
B)the oxidizing agent receives electrons from another species.
C)oxidation must accompany reduction.
D)the oxidizing agent increases the oxidation number of another element.
E)the oxidation of a metal produces positive ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which of the following choices is the oxidation number incorrect?
A)Al3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)F-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)Br2(s); oxidation number = 0
D)Na+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Cu(s); oxidation number = 2+
A)Al3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)F-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)Br2(s); oxidation number = 0
D)Na+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Cu(s); oxidation number = 2+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In which compound does phosphorus have an oxidation number of 3-?
A)AlPO4
B)PF5
C)H3PO4
D)H3PO3
E)PH3
A)AlPO4
B)PF5
C)H3PO4
D)H3PO3
E)PH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In which substance does chlorine have an oxidation number of 4+?
A)KClO4
B)Cl2
C)ClO2
D)Cl2O7
E)NaCl
A)KClO4
B)Cl2
C)ClO2
D)Cl2O7
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In which compound does phosphorus have an oxidation number of 3+?
A)AlPO4
B)PF5
C)H3PO4
D)H3PO3
E)PH3
A)AlPO4
B)PF5
C)H3PO4
D)H3PO3
E)PH3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In which of the following choices is the oxidation number incorrect?
A)Fe3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)I-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)Cl2(s); oxidation number = 1-
D)Cu+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Ni(s); oxidation number = 0
A)Fe3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)I-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)Cl2(s); oxidation number = 1-
D)Cu+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Ni(s); oxidation number = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When a piece of copper wire is placed in a colorless solution of silver nitrate, the surface of the wire becomes coated with a shiny silvery material, and the copper begins to form aqueous copper(II) nitrate, which is blue.Which of the following statements regarding this reaction is correct?
A)The copper(II) is being oxidized.
B)The silver ion is being oxidized.
C)The nitrate ion is being reduced.
D)The solution will become more blue as the reaction progresses.
E)The reaction described is nonspontaneous.
A)The copper(II) is being oxidized.
B)The silver ion is being oxidized.
C)The nitrate ion is being reduced.
D)The solution will become more blue as the reaction progresses.
E)The reaction described is nonspontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a strip of zinc metal is placed in a blue aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate, the surface of the zinc becomes coated with a reddish solid, and the zinc begins to dissolve to form aqueous zinc sulfate.Which of the following statements regarding this reaction is correct?
A)The copper(II) is being oxidized.
B)The zinc is being reduced.
C)The sulfate ion is being reduced.
D)The solution will lose its blue color as the reaction progresses.
E)The reaction described is nonspontaneous.
A)The copper(II) is being oxidized.
B)The zinc is being reduced.
C)The sulfate ion is being reduced.
D)The solution will lose its blue color as the reaction progresses.
E)The reaction described is nonspontaneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Consider the following reaction: Mn(s) + CuSO4(aq) MnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Which of the following statements regarding this reaction is correct?
A)Manganese is neither oxidized nor reduced.
B)The sulfate ion is oxidized.
C)Copper is the reducing agent.
D)Manganese is the oxidizing agent.
E)Each copper gains two electrons.
A)Manganese is neither oxidized nor reduced.
B)The sulfate ion is oxidized.
C)Copper is the reducing agent.
D)Manganese is the oxidizing agent.
E)Each copper gains two electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which one of the following reactions is an example of an oxidation-reduction reaction?
A)BaO(s) + CO2(g) BaCO3(s)
B)H2(g) + F2(g) 2HF(g)
C)CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
D)HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
E)Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) BaSO4(s)
A)BaO(s) + CO2(g) BaCO3(s)
B)H2(g) + F2(g) 2HF(g)
C)CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
D)HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
E)Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) BaSO4(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the following reaction: Mg(s) + NiSO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + Ni(s) Which of the following statements regarding this reaction is correct?
A)Each magnesium atom gains two electrons.
B)The sulfate ion is reduced.
C)Nickel ion is the oxidizing agent.
D)Magnesium is reduced.
E)Each nickel ion loses two electrons.
A)Each magnesium atom gains two electrons.
B)The sulfate ion is reduced.
C)Nickel ion is the oxidizing agent.
D)Magnesium is reduced.
E)Each nickel ion loses two electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements regarding oxidation-reduction reactions is correct?
A)Oxidation-reduction reactions involve sharing electrons.
B)Oxidation can occur without reduction.
C)You can tell that a substance is oxidized if it loses electrons.
D)You can tell that a substance is reduced if its oxidation number increases.
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)Oxidation-reduction reactions involve sharing electrons.
B)Oxidation can occur without reduction.
C)You can tell that a substance is oxidized if it loses electrons.
D)You can tell that a substance is reduced if its oxidation number increases.
E)None of these statements is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In which substance does chlorine have an oxidation number of 7+?
A)KClO4
B)Cl2
C)ClO2
D)NaClO
E)NaCl
A)KClO4
B)Cl2
C)ClO2
D)NaClO
E)NaCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In which of the following choices is the oxidation number incorrect?
A)Cr3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)Cl-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)F2(g); oxidation number = 0
D)K+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Ag(s); oxidation number = 1+
A)Cr3+(aq); oxidation number = 3+
B)Cl-(aq); oxidation number = 1-
C)F2(g); oxidation number = 0
D)K+(aq); oxidation number = 1+
E)Ag(s); oxidation number = 1+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What are the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the MnO4- ion?
A)Mn = 0, O = 1-
B)Mn = 3+, O = 1-
C)Mn = 7+, O = 2-
D)Mn = 8+, O = 2-
E)Mn = 1-, O = 0
A)Mn = 0, O = 1-
B)Mn = 3+, O = 1-
C)Mn = 7+, O = 2-
D)Mn = 8+, O = 2-
E)Mn = 1-, O = 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ion shown has a charge of 2-.What are the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the ion? 
A)S = 0, O = 2-
B)S = 2-, O = 0
C)S = 8+, O = 2-
D)S = 6+, O = 2-
E)S = 4+, O = 1-

A)S = 0, O = 2-
B)S = 2-, O = 0
C)S = 8+, O = 2-
D)S = 6+, O = 2-
E)S = 4+, O = 1-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Examine the following reaction: 5FeCl2(aq) + KMnO4(aq) + 8HCl(aq) 5FeCl3(aq) + MnCl2(aq) + KCl(aq) + 4H2O(l) Which element has undergone oxidation?
A)Fe
B)H
C)Cl
D)O
E)Mn
A)Fe
B)H
C)Cl
D)O
E)Mn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Consider the reaction: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Nitrogen is oxidized.
B)Hydrogen is reduced.
C)Nitrogen is the reducing agent.
D)The reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
E)Hydrogen is the reducing agent.
A)Nitrogen is oxidized.
B)Hydrogen is reduced.
C)Nitrogen is the reducing agent.
D)The reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
E)Hydrogen is the reducing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Consider the reaction: H2O(l) + 3SO32-(aq) + 2MnO4-(aq) 3SO42-(aq) + 2MnO2(s) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is oxidized?
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following sulfur species cannot be further reduced?
A)H2SO3
B)SO42-
C)S2O32-
D)SO32-
E)S2-
A)H2SO3
B)SO42-
C)S2O32-
D)SO32-
E)S2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is the oxidation number of boron in sodium tetraborate, Na2B4O7?
A)+12
B)-3
C)+14
D)+3
E)+4
A)+12
B)-3
C)+14
D)+3
E)+4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider the reaction: Ba(NO3)2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2NaNO3(aq) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Barium is oxidized.
B)Sodium is reduced.
C)Nitrate ion is the reducing agent.
D)Sulfate ion is the oxidizing agent.
E)This reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A)Barium is oxidized.
B)Sodium is reduced.
C)Nitrate ion is the reducing agent.
D)Sulfate ion is the oxidizing agent.
E)This reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the following oxidation-reduction reaction: 2Fe3+(aq) + 2Hg(l) + 2Cl-(aq) 2Fe2+(aq) + Hg2Cl2(s) Which one of the following pairs correctly indicates the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in this reaction? Oxidizing agent Reducing agent
A)Hg(l) Fe3+(aq)
B)Hg(l) Cl-(aq)
C)Fe3+(aq) Cl-(aq)
D)Fe3+(aq) Hg(l)
E)Cl-(aq) Fe3+(aq)
A)Hg(l) Fe3+(aq)
B)Hg(l) Cl-(aq)
C)Fe3+(aq) Cl-(aq)
D)Fe3+(aq) Hg(l)
E)Cl-(aq) Fe3+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Consider the following reaction: 2Fe3+(aq) + 2Hg(l) + 2Cl-(aq) 2Fe2+(aq) + Hg2Cl2(s) In this reaction,
A)Fe3+(aq) is the reducing agent.
B)Fe3+(aq) loses electrons.
C)Hg(l) loses electrons.
D)Hg(l) is reduced.
E)Hg(l) is the oxidizing agent.
A)Fe3+(aq) is the reducing agent.
B)Fe3+(aq) loses electrons.
C)Hg(l) loses electrons.
D)Hg(l) is reduced.
E)Hg(l) is the oxidizing agent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider the reaction: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Carbon is oxidized.
B)Oxygen is the reducing agent.
C)Oxygen is oxidized.
D)Carbon is the oxidizing agent.
E)The reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A)Carbon is oxidized.
B)Oxygen is the reducing agent.
C)Oxygen is oxidized.
D)Carbon is the oxidizing agent.
E)The reaction is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the AsO43- ion?
A)As = 0, O = 1-
B)As = 1+, O = 1-
C)As = 3-, O = 0
D)As = 3+, O = 2-
E)As = 5+, O = 2-
A)As = 0, O = 1-
B)As = 1+, O = 1-
C)As = 3-, O = 0
D)As = 3+, O = 2-
E)As = 5+, O = 2-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In which of the following does chlorine have an oxidation number of +3?
A)HCl
B)HOCl
C)HClO2
D)HClO3
E)HClO4
A)HCl
B)HOCl
C)HClO2
D)HClO3
E)HClO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The change, Br2 + H2O HOBr + HBr, is
A)oxidation only.
B)reduction only.
C)both oxidation and reduction.
D)neither oxidation nor reduction.
E)an acid-base reaction.
A)oxidation only.
B)reduction only.
C)both oxidation and reduction.
D)neither oxidation nor reduction.
E)an acid-base reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in S2O32-?
A)+6
B)-2
C)+4
D)+2
E)+3
A)+6
B)-2
C)+4
D)+2
E)+3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Consider the reaction: 2HgO(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Mercury is reduced.
B)Oxygen is oxidized.
C)Mercury(II) ion is the oxidizing agent.
D)Oxide ion is the reducing agent.
E)All of these statements are correct.
A)Mercury is reduced.
B)Oxygen is oxidized.
C)Mercury(II) ion is the oxidizing agent.
D)Oxide ion is the reducing agent.
E)All of these statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What are the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the Cr2O72- ion?
A)Cr = 1-, O = 0
B)Cr = 0, O = 2-
C)Cr = 6+, O = 2-
D)Cr = 7+, O = 2-
E)Cr = 3+, O = 1-
A)Cr = 1-, O = 0
B)Cr = 0, O = 2-
C)Cr = 6+, O = 2-
D)Cr = 7+, O = 2-
E)Cr = 3+, O = 1-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is the oxidation number of chlorine in sodium perchlorate, NaClO4?
A)+8
B)-7
C)+16
D)+7
E)-8
A)+8
B)-7
C)+16
D)+7
E)-8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Consider the reaction: H2O(l) + 3SO32-(aq) + 2MnO4-(aq) 3SO42-(aq) + 2MnO2(s) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is the reducing agent?
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Consider the reaction: Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Calcium is reduced.
B)Hydrogen is oxidized.
C)Oxygen is oxidized.
D)Oxygen is the reducing agent.
E)Calcium is oxidized.
A)Calcium is reduced.
B)Hydrogen is oxidized.
C)Oxygen is oxidized.
D)Oxygen is the reducing agent.
E)Calcium is oxidized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Consider the reaction: H2O(l) + 3SO32-(aq) + 2MnO4-(aq) 3SO42-(aq) + 2MnO2(s) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is reduced?
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2
A)H2O
B)SO32-
C)MnO4-
D)SO42-
E)MnO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Examine the following reaction: 5FeCl2(aq) + KMnO4(aq) + 8HCl(aq) - 5FeCl3(aq) + MnCl2(aq) + KCl(aq) + 4H2O(l)
Which element has undergone reduction?
A)Fe
B)H
C)Cl
D)O
E)Mn
Which element has undergone reduction?
A)Fe
B)H
C)Cl
D)O
E)Mn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Copper is the reducing agent.
B)The Cu2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the silver electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The copper electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred in this reaction per atom of copper that reacts.
A)Copper is the reducing agent.
B)The Cu2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the silver electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The copper electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred in this reaction per atom of copper that reacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Mg(s) + Sn2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + Sn(s) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Magnesium is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Sn2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the magnesium electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The tin electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred per atom of magnesium that reacts.
A)Magnesium is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Sn2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the magnesium electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The tin electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred per atom of magnesium that reacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For the following reaction, what is the oxidizing agent? 2Cl2(g) + C(s) + 2H2O(l) CO2(g) + 4HCl(aq)
A)Cl2
B)C
C)H2O
D)CO2
E)HCl
A)Cl2
B)C
C)H2O
D)CO2
E)HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the reaction: Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) Which species is the reducing agent, and how many electrons are transferred per atom of zinc that reacts?
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Consider the reaction: Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) Which species is reduced, and how many electrons are transferred per SN2+ ion that reacts?
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Given the following reaction in a voltaic cell: Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) 2Ag(s) + Cu2+(aq) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Cu(s) is the anode.
B)Oxidation occurs at the silver electrode.
C)There is no cathode for this cell.
D)Ag(s) is the anode.
E)One mole of electrons is transferred in the reaction as written.
A)Cu(s) is the anode.
B)Oxidation occurs at the silver electrode.
C)There is no cathode for this cell.
D)Ag(s) is the anode.
E)One mole of electrons is transferred in the reaction as written.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Consider the reaction: Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is oxidized?
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In a voltaic cell, the electron flow is always from
A)the salt bridge to the cathode.
B)the salt bridge to the anode.
C)the oxidizing agent through the salt bridge to the reducing agent.
D)the reducing agent through the salt bridge to the oxidizing agent.
E)the anode to the cathode.
A)the salt bridge to the cathode.
B)the salt bridge to the anode.
C)the oxidizing agent through the salt bridge to the reducing agent.
D)the reducing agent through the salt bridge to the oxidizing agent.
E)the anode to the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) If this reaction takes place in the electrochemical cell shown in the figure, which of the following statements is incorrect? 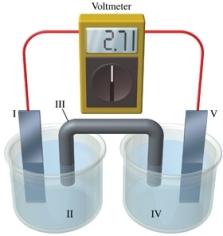
A)I is the zinc electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Cu2+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)IV contains the substance that is being reduced.
E)V is the copper electrode, which is the cathode.

A)I is the zinc electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Cu2+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)IV contains the substance that is being reduced.
E)V is the copper electrode, which is the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Zinc is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Cu2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the zinc electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The zinc electrode is the cathode.
E)Two electrons will be transferred in this reaction per atom of zinc that reacts.
A)Zinc is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Cu2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the zinc electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The zinc electrode is the cathode.
E)Two electrons will be transferred in this reaction per atom of zinc that reacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s) If this reaction takes place in the electrochemical cell shown in the figure, which of the following statements is incorrect? 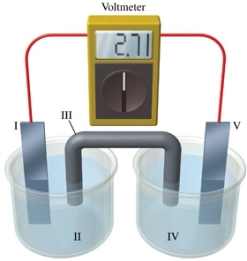
A)I is the copper electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Ag+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)V contains the substance that is being reduced.
E)V is the silver electrode, which is the cathode.

A)I is the copper electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Ag+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)V contains the substance that is being reduced.
E)V is the silver electrode, which is the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the reaction: Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is the reducing agent?
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Consider the reaction: Cu(s) + 4HNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + 2OH-(aq) Which species is the oxidizing agent?
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu
A)OH-
B)NO2
C)Cu(NO3)2
D)HNO3
E)Cu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the reaction: Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) Which species is the oxidizing agent, and how many electrons are transferred per Sn2+ ion that reacts?
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Consider the reaction: Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) Which species is oxidized, and how many electrons are transferred per atom of zinc that reacts?
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In a fuel cell that uses gaseous hydrogen and oxygen as reactants, which one of the following reactions is occurring at the anode?
A)2H2O F 2H2 + O2
B)H2 2H+ + 2e-
C)2H+ + 2e- H2
D)O2 + 4e- 2O2-
E)2O2- O2 + 4e-
A)2H2O F 2H2 + O2
B)H2 2H+ + 2e-
C)2H+ + 2e- H2
D)O2 + 4e- 2O2-
E)2O2- O2 + 4e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the reaction: Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g) Which species is reduced, and how many electrons are transferred per atom of zinc that reacts?
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons
A)Zn, 2 electrons
B)H+, 2 electrons
C)SO42-, 4 electrons
D)Zn2+, 4 electrons
E)H2, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Fe(s) + Ni2+(aq) Fe2+(aq) + Ni(s) Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Iron is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Ni2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the iron electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The nickel electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred per atom of iron that reacts.
A)Iron is the oxidizing agent.
B)The Ni2+ solution must be in the half-cell with the iron electrode.
C)No salt bridge is necessary, since the charge is 2+ on both sides of the equation.
D)The nickel electrode is the cathode.
E)Four electrons will be transferred per atom of iron that reacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Consider a voltaic cell that corresponds to the following reaction: Mg(s) + Sn2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + Sn(s) If this reaction takes place in the electrochemical cell shown in the figure, which of the following statements is incorrect? 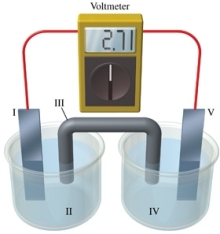
A)I is the magnesium electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Mg2+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)IV contains the substance that is being oxidized.
E)V is the tin electrode, which is the cathode.

A)I is the magnesium electrode, which is the anode.
B)II is the Mg2+ solution.
C)III is the salt bridge.
D)IV contains the substance that is being oxidized.
E)V is the tin electrode, which is the cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the reaction: Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq) Which species is oxidized, and how many electrons are transferred per SN2+ ion that reacts?
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons
A)Sn2+, 2 electrons
B)Fe3+, 2 electrons
C)Sn4+, 4 electrons
D)Fe2+, 4 electrons
E)Fe2+, 2 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A voltaic cell is prepared in which copper metal is oxidized to Cu(II), and silver ion is reduced to silver metal.Which of the following represents the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode?
A)Cu(s) - 2e- Cu2+(aq)
B)Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
C)2Cu(s) 2Cu2+(aq) + e-
D)Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s)
E)Ag(s) Ag+(aq) + e-
A)Cu(s) - 2e- Cu2+(aq)
B)Cu(s) Cu2+(aq) + 2e-
C)2Cu(s) 2Cu2+(aq) + e-
D)Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s)
E)Ag(s) Ag+(aq) + e-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A mercury button battery that is used in watches and calculators is powered by the following reaction: Zn(s) + HgO(s) ZnO(s) + Hg(s) The substance that is oxidized in this battery is:
A)HgO
B)Hg
C)ZnO
D)Zn
A)HgO
B)Hg
C)ZnO
D)Zn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The reaction that occurs in an alkaline battery is as follows: Zn(s) + MnO2(s) + H2O(l) ZnO(s) + Mn(OH)2(s) The substance that is oxidized in this battery is:
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The reaction that occurs in an alkaline battery is as follows: Zn(s) + MnO2(s) + H2O(l) ZnO(s) + Mn(OH)2(s) The substance that is reduced in this battery is:
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following reaction occurs in acid solution.When the equation is properly balanced with the smallest whole-number coefficients, what is the coefficient of Bi3+? Mn2+(aq) + BiO3-(aq) MnO4-(aq) + Bi3+(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A voltaic cell is prepared in which copper metal is oxidized to Cu(II), and silver ion is reduced to silver metal.Which of the following represents the correctly balanced equation for this reaction?
A)Cu(s) + Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s)
B)2Cu(s) + Ag+(aq) 2Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s)
C)Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
D)3Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) 3Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
E)2Cu(s) + 3Ag+(aq) 2Cu2+(aq) + 3Ag(s)
A)Cu(s) + Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s)
B)2Cu(s) + Ag+(aq) 2Cu2+(aq) + Ag(s)
C)Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
D)3Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) 3Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
E)2Cu(s) + 3Ag+(aq) 2Cu2+(aq) + 3Ag(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A voltaic cell is prepared in which aluminum metal is oxidized to Al3+, and nickel(II) is reduced to nickel metal.Which of the following represents the equation for the reaction that occurs at the anode?
A)Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e-
B)Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s)
C)Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
D)Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s)
E)2Al3+(aq) + 3e- 2Al(s)
A)Al(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e-
B)Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s)
C)Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e-
D)Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s)
E)2Al3+(aq) + 3e- 2Al(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The following reaction occurs in a lead storage battery: PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + H2SO4(aq) ⇌ 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) Which statement is true?
A)The concentration of H2SO4 increases as the battery discharges.
B)Pb is formed at the anode during charging.
C)PbO2 is formed at the anode during charging.
D)The mass of Pb decreases during charging.
E)The mass of PbSO4 remains constant during charging and discharging.
A)The concentration of H2SO4 increases as the battery discharges.
B)Pb is formed at the anode during charging.
C)PbO2 is formed at the anode during charging.
D)The mass of Pb decreases during charging.
E)The mass of PbSO4 remains constant during charging and discharging.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The following reaction occurs in acid solution.When the equation is properly balanced with the smallest whole-number coefficients, what is the coefficient of MnO4- MnO4-(aq) + I-(aq) Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Given the following reaction in a voltaic cell: Zn(s) + Ni2+(aq) Ni(s) + Zn2+(aq) In this cell, Zn(s) is called the
A)anode.
B)oxidizing agent.
C)salt bridge.
D)electrolyte.
E)cathode.
A)anode.
B)oxidizing agent.
C)salt bridge.
D)electrolyte.
E)cathode.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Consider the skeletal equation: Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) When balanced, the equation will be:
A)Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
B)2Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
C)2Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) 2Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
D)Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq)
E)4Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) 2Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
A)Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
B)2Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
C)2Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) 2Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)
D)Sn2+(aq) + 2Fe3+(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2Fe2+(aq)
E)4Sn2+(aq) + Fe3+(aq) 2Sn4+(aq) + Fe2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The figure shows a molecular-level representation of the following voltaic cell: Mg(s) + Sn2+(aq) Mg2+(aq) + Sn(s) When drawing the "after" representation one would note that: 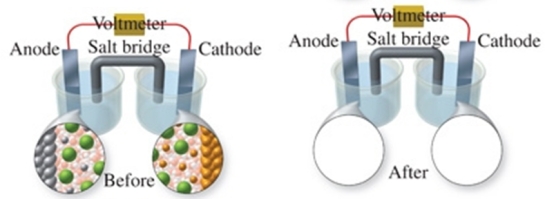
A)the tin electrode will be smaller.
B)the magnesium electrode will be larger.
C)the number of Mg2+ ions in solution will remain constant.
D)deposits will form in the salt bridge.
E)the number of Sn2+ ions in solution will decrease.

A)the tin electrode will be smaller.
B)the magnesium electrode will be larger.
C)the number of Mg2+ ions in solution will remain constant.
D)deposits will form in the salt bridge.
E)the number of Sn2+ ions in solution will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A lead-acid battery that is used in cars and trucks is powered by the reaction: PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(s) + H2O(l) The substance that is the oxidizing agent in this battery is:
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The figure shows a molecular-level representation of the following voltaic cell: Fe(s) + Ni2+(aq) Fe2+(aq) + Ni(s) When drawing the "after" representation one would note that: 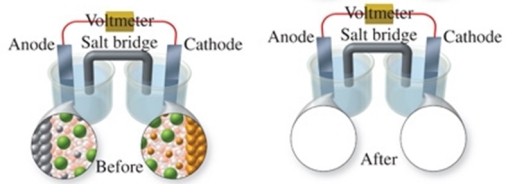
A)the nickel electrode will be smaller.
B)the iron electrode will be larger.
C)the number of Ni2+ ions in solution will decrease.
D)deposits will form in the salt bridge.
E)the number of Fe2+ ions in solution will remain constant.

A)the nickel electrode will be smaller.
B)the iron electrode will be larger.
C)the number of Ni2+ ions in solution will decrease.
D)deposits will form in the salt bridge.
E)the number of Fe2+ ions in solution will remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Consider the half-reaction Cr3+(aq) Cr2O72-(aq).When the equation is balanced in acid solution, the coefficient for water will be__________, and the number of electrons transferred will be __________.
A)3, 3
B)6, 6
C)7, 6
D)5, 4
E)3, 6
A)3, 3
B)6, 6
C)7, 6
D)5, 4
E)3, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The following reaction occurs in a lead storage battery: PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + H2SO4(aq) ⇌ 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) What happens to the sulfuric acid in a lead storage battery when the battery is being discharged?
A)Sulfate ions are consumed and their concentration decreases.
B)Protons are released so the pH drops.
C)The solution gets increasingly more viscous due to an increase in sulfuric acid concentration.
D)Its concentration increases.
E)All of these are correct.
A)Sulfate ions are consumed and their concentration decreases.
B)Protons are released so the pH drops.
C)The solution gets increasingly more viscous due to an increase in sulfuric acid concentration.
D)Its concentration increases.
E)All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A voltaic cell is prepared in which aluminum metal is oxidized to Al3+, and nickel(II) is reduced to nickel metal.Which of the following represents the correctly balanced equation for this reaction?
A)Al(s) + Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s)
B)Al(s) + 2Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + 2Ni(s)
C)2Al(s) + 3Ni2+(aq) 2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s)
D)Al3+(aq) + 2Ni(s) Al(s) + 2Ni2+(aq)
E)2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s) 2Al(s) + 3Ni2+(aq)
A)Al(s) + Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + Ni(s)
B)Al(s) + 2Ni2+(aq) Al3+(aq) + 2Ni(s)
C)2Al(s) + 3Ni2+(aq) 2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s)
D)Al3+(aq) + 2Ni(s) Al(s) + 2Ni2+(aq)
E)2Al3+(aq) + 3Ni(s) 2Al(s) + 3Ni2+(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A lead-acid battery that is used in cars and trucks is powered by the reaction: PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(s) + H2O(l) The substance that is the reducing agent in this battery is:
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A lead-acid battery that is used in cars and trucks is powered by the reaction: PbO2(s) + Pb(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(s) + H2O(l) The substance that is reduced in this battery is:
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4
A)PbSO4
B)H2O
C)PbO2
D)Pb
E)H2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The reaction that occurs in an alkaline battery is as follows: Zn(s) + MnO2(s) + H2O(l) ZnO(s) + Mn(OH)2(s) The substance that is the reducing agent in this battery is:
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2
A)Zn
B)ZnO
C)MnO2
D)H2O
E)Mn(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 117 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



