Deck 5: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Chemical Reactions and Equations
1
Identify which image in the figure represents the reactants and which image therefore represents the products in the reaction between ozone gas (O3) and carbon monoxide gas to form oxygen gas and carbon dioxide gas. 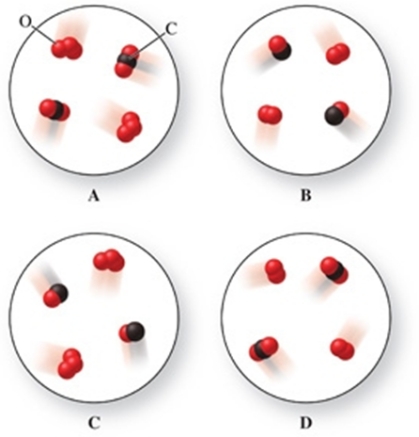
A)upper left image = reactants, upper right image = products
B)upper right image = reactants, upper left image = products
C)lower left image = reactants, lower right image = products
D)upper left image = reactants, lower right image = products
E)upper left image = reactants, lower left image = products

A)upper left image = reactants, upper right image = products
B)upper right image = reactants, upper left image = products
C)lower left image = reactants, lower right image = products
D)upper left image = reactants, lower right image = products
E)upper left image = reactants, lower left image = products
lower left image = reactants, lower right image = products
2
When solid ammonium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to form ammonia gas, carbon dioxide gas, and water vapor, so that the solid completely disappears.Write a complete, balanced equation for this reaction.
A)(NH4)2CO3(s) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
B)(NH4)2CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
C)NH4CO3(s) NH2(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
D)NH4CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
E)(NH4)2CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
A)(NH4)2CO3(s) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
B)(NH4)2CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
C)NH4CO3(s) NH2(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
D)NH4CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
E)(NH4)2CO3(s) NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
(NH4)2CO3(s) 2NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g)
3
The figure shows a reaction between methane gas (natural gas, CH4) and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.Is the diagram accurate, and if not, what is wrong with it, and how could it be fixed? 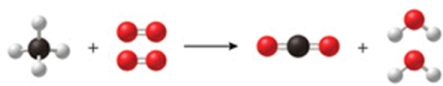
A)There are too many hydrogen atoms on the right-hand side of the reaction arrow.Remove one hydrogen atom from each water molecule.
B)There are too many oxygen atoms on the right-hand side of the reaction arrow.Remove one oxygen atom from the carbon dioxide.
C)The diagram is accurate as shown.
D)There are not enough carbon atoms on the left-hand side of the reaction arrow.Add another methane molecule on the left, and then another carbon dioxide molecule on the right of the arrow.
E)There are not enough oxygen molecules on the left-hand side of the reaction arrow.Add another oxygen molecule on the left of the arrow, and another water molecule on the right.

A)There are too many hydrogen atoms on the right-hand side of the reaction arrow.Remove one hydrogen atom from each water molecule.
B)There are too many oxygen atoms on the right-hand side of the reaction arrow.Remove one oxygen atom from the carbon dioxide.
C)The diagram is accurate as shown.
D)There are not enough carbon atoms on the left-hand side of the reaction arrow.Add another methane molecule on the left, and then another carbon dioxide molecule on the right of the arrow.
E)There are not enough oxygen molecules on the left-hand side of the reaction arrow.Add another oxygen molecule on the left of the arrow, and another water molecule on the right.
The diagram is accurate as shown.
4
Which of the following changes represents a physical change, rather than evidence of a chemical reaction?
A)When a piece of zinc metal is placed in a solution of HCl, bubbles begin to form, and the zinc begins to dissolve.
B)When solid ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3, is heated, the solid disappears, and gaseous ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) are formed.
C)When dry ice (solid CO2) is allowed to stand at room temperature, a white cloud and gaseous CO2 are formed.
D)When a solution of KI is mixed with a solution of Pb(NO3)2, a yellow solid is formed.
E)When a piece of copper wire is placed in a solution of AgNO3, a silvery solid begins to form on the surface of the wire, and the solution turns blue.
A)When a piece of zinc metal is placed in a solution of HCl, bubbles begin to form, and the zinc begins to dissolve.
B)When solid ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3, is heated, the solid disappears, and gaseous ammonia (NH3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) are formed.
C)When dry ice (solid CO2) is allowed to stand at room temperature, a white cloud and gaseous CO2 are formed.
D)When a solution of KI is mixed with a solution of Pb(NO3)2, a yellow solid is formed.
E)When a piece of copper wire is placed in a solution of AgNO3, a silvery solid begins to form on the surface of the wire, and the solution turns blue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In the figure shown, is a chemical reaction occurring? 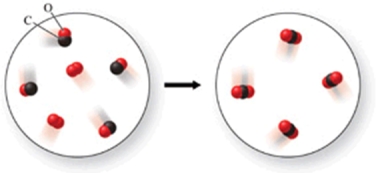
A)No, because there are the same number of atoms in both images.
B)Yes, because the atoms have rearranged, and therefore the formulas of the products and reactants are different.
C)No, because both the reactants and products are colorless gases.
D)No, because there are oxygen atoms and carbon atoms in both images.
E)Yes, because the reactants are gases, but the product is a solid.

A)No, because there are the same number of atoms in both images.
B)Yes, because the atoms have rearranged, and therefore the formulas of the products and reactants are different.
C)No, because both the reactants and products are colorless gases.
D)No, because there are oxygen atoms and carbon atoms in both images.
E)Yes, because the reactants are gases, but the product is a solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Zinc metal will react with aqueous hydrochloric acid to produce aqueous zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.Write a complete, balanced equation for this reaction.
A)Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)
B)Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
C)Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H(g)
D)2Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) 2ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)
E)Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)
A)Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)
B)Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
C)Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H(g)
D)2Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) 2ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)
E)Zn(s) + HCl(aq) ZnCl(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Gaseous nitrogen monoxide reacts with oxygen gas to form brown nitrogen dioxide gas.What would the products of the reaction be, if the reactants are those shown in the figure? 
A)6 molecules of nitrogen dioxide
B)5 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
C)6 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
D)4 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 2 molecules of nitrogen monoxide
E)3 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 3 molecules of nitrogen monoxide

A)6 molecules of nitrogen dioxide
B)5 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
C)6 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
D)4 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 2 molecules of nitrogen monoxide
E)3 molecules of nitrogen dioxide, and 3 molecules of nitrogen monoxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Identify which image in the figure represents the reactants and which image therefore represents the products in the reaction between xenon gas and fluorine gas to form xenon tetrafluoride gas. 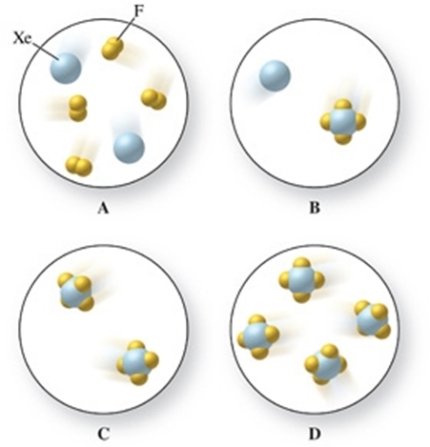
A)upper right image = reactants, upper left image = products
B)lower left image = reactants, upper left image = products
C)upper left image = reactants, upper right image = products
D)upper left image = reactants, lower left image = products
E)upper left image = reactants, lower right image = products

A)upper right image = reactants, upper left image = products
B)lower left image = reactants, upper left image = products
C)upper left image = reactants, upper right image = products
D)upper left image = reactants, lower left image = products
E)upper left image = reactants, lower right image = products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following chemical equations.Select the equations that represent chemical reactions, rather than physical changes.
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)I only
E)II and III only
A)I, II, and III
B)I and II only
C)I and III only
D)I only
E)II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The figure shows a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gases to produce water.Is the diagram accurate, and if not, what is wrong with it, and how could it be fixed? 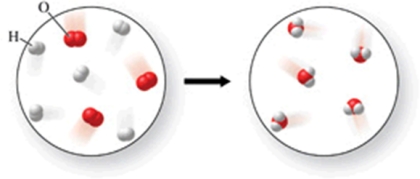
A)There are too many water molecules on the right.Remove one water molecule from the image on the right.
B)There are not enough oxygen atoms on the right.Add one more water molecule to the right image.
C)There are too many oxygen atoms in the image on the left.Remove one oxygen molecule.
D)There are not enough hydrogen atoms on the right.Add one more water molecule to the left image, and one more hydrogen molecule to the right image.
E)The diagram is accurate as shown.

A)There are too many water molecules on the right.Remove one water molecule from the image on the right.
B)There are not enough oxygen atoms on the right.Add one more water molecule to the right image.
C)There are too many oxygen atoms in the image on the left.Remove one oxygen molecule.
D)There are not enough hydrogen atoms on the right.Add one more water molecule to the left image, and one more hydrogen molecule to the right image.
E)The diagram is accurate as shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Sulfur dioxide gas reacts with oxygen gas to form sulfur trioxide gas.What would the products of the reaction be, if the reactants are those shown in the figure? 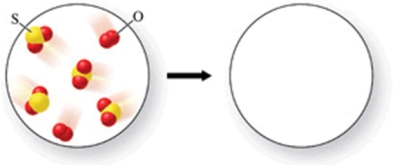
A)2 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 2 molecules of sulfur dioxide
B)4 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
C)3 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
D)3 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of sulfur dioxide
E)4 molecules of sulfur trioxide

A)2 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 2 molecules of sulfur dioxide
B)4 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
C)3 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of oxygen
D)3 molecules of sulfur trioxide, and 1 molecule of sulfur dioxide
E)4 molecules of sulfur trioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the figure shown, is a chemical reaction occurring? 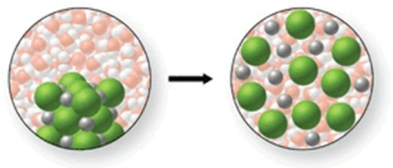
A)Yes, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are being removed from their ionic lattice as they are dissolved.
B)Yes, because the water molecules are reacting with the Na+ and Cl- ions to form a gas.
C)Yes, because a precipitate will be formed when the water and NaCl are mixed.
D)No, because there is no change occurring.
E)No, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are simply being surrounded by the water molecules as the salt dissolves.

A)Yes, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are being removed from their ionic lattice as they are dissolved.
B)Yes, because the water molecules are reacting with the Na+ and Cl- ions to form a gas.
C)Yes, because a precipitate will be formed when the water and NaCl are mixed.
D)No, because there is no change occurring.
E)No, because the Na+ and Cl- ions are simply being surrounded by the water molecules as the salt dissolves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Write a complete, balanced equation for the reaction that occurs when sodium metal reacts with water to form hydrogen gas and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
A)Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
B)Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
C)Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
D)Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H(g)
E)2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
A)Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
B)Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
C)Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
D)Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H(g)
E)2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The figure shows the chemical reaction between nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas to produce ammonia (NH3) gas.Which of the following changes would make the diagram correctly represent conservation of mass? 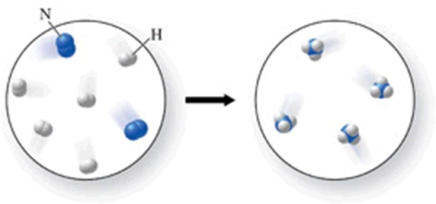
A)Add one H2 molecule from the image on the left.
B)Add three NH3 molecules to the image on the right.
C)Add three H2 molecules t the image on the right.
D)Remove one H2 molecules from the image on the left.
E)Remove one NH3 molecule from the image on the left.

A)Add one H2 molecule from the image on the left.
B)Add three NH3 molecules to the image on the right.
C)Add three H2 molecules t the image on the right.
D)Remove one H2 molecules from the image on the left.
E)Remove one NH3 molecule from the image on the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Fireworks which give off bright flashes of white light often contain magnesium metal.When the magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen, it forms solid magnesium oxide, and emits a bright white light.Write a complete, balanced equation for this reaction.
A)Mg(s) + O(g) MgO(s)
B)4Mg(s) + O2(g) 2Mg2O(s)
C)2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s)
D)Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO2(s)
E)Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO(s)
A)Mg(s) + O(g) MgO(s)
B)4Mg(s) + O2(g) 2Mg2O(s)
C)2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s)
D)Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO2(s)
E)Mg(s) + O2(g) MgO(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the following chemical equations.Select the equations that represent chemical reactions, rather than physical changes.
A)II only
B)I, II, and III
C)I and III only
D)I and II only
E)II and III only
A)II only
B)I, II, and III
C)I and III only
D)I and II only
E)II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The figure shows a reaction between xenon gas and fluorine gas.Is the diagram correct, and if not, how could it be modified to show that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed? 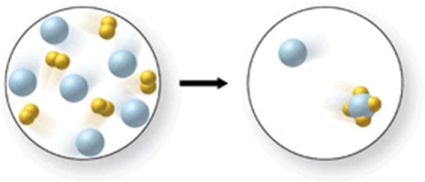
A)Add two more XeF4 molecules and two more Xe atoms to the right image.
B)Add four more XeF4 molecules to the right image.
C)Add three more XeF4 molecules and one more Xe atom to the right image.
D)Add one more XeF4 molecule and three more Xe atoms to the right image.
E)The diagram is accurate as shown.

A)Add two more XeF4 molecules and two more Xe atoms to the right image.
B)Add four more XeF4 molecules to the right image.
C)Add three more XeF4 molecules and one more Xe atom to the right image.
D)Add one more XeF4 molecule and three more Xe atoms to the right image.
E)The diagram is accurate as shown.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the following chemical equations.Select the equations that represent chemical reactions, rather than physical changes.
A)I and III only
B)II and III only
C)I, II, and III
D)I only
E)I and II only
A)I and III only
B)II and III only
C)I, II, and III
D)I only
E)I and II only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following changes represents a physical change, rather than evidence of a chemical reaction?
A)When water and a yellow solution of antifreeze are mixed, the resulting solution is a lighter shade of yellow than the original antifreeze solution.
B)When concentrated HNO3 is placed in contact with copper metal, a brown gas is formed, the copper dissolves, and a green solution is formed.
C)When an egg is fried, the clear part becomes white, and the egg becomes a solid.
D)When a piece of zinc metal is placed in a blue solution of copper sulfate, the solution turns from blue to colorless, the zinc dissolves, and copper metal is formed.
E)When solutions of AgNO3 and NaCl are mixed, a white solid forms.
A)When water and a yellow solution of antifreeze are mixed, the resulting solution is a lighter shade of yellow than the original antifreeze solution.
B)When concentrated HNO3 is placed in contact with copper metal, a brown gas is formed, the copper dissolves, and a green solution is formed.
C)When an egg is fried, the clear part becomes white, and the egg becomes a solid.
D)When a piece of zinc metal is placed in a blue solution of copper sulfate, the solution turns from blue to colorless, the zinc dissolves, and copper metal is formed.
E)When solutions of AgNO3 and NaCl are mixed, a white solid forms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the figure shown, is a chemical reaction occurring? 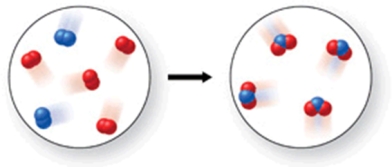
A)No, because there are the same number of atoms in both images.
B)Yes, because the atoms have rearranged, and therefore the formulas of the products and reactants are different.
C)No, because there are oxygen atoms and nitrogen atoms in both images.
D)No, because both the reactants and products are colorless gases.
E)Yes, because the reactants are gases, but the product is a solid.

A)No, because there are the same number of atoms in both images.
B)Yes, because the atoms have rearranged, and therefore the formulas of the products and reactants are different.
C)No, because there are oxygen atoms and nitrogen atoms in both images.
D)No, because both the reactants and products are colorless gases.
E)Yes, because the reactants are gases, but the product is a solid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the equation shown is balanced properly, what is the coefficient in front of O2(g)?
C6H14(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g)
A)6
B)19
C)9
D)12
E)7
C6H14(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g)
A)6
B)19
C)9
D)12
E)7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Balance the following skeletal equation: Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + KNO3(aq)
A)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
B)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + KNO3(aq)
C)Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
D)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + 3KNO3(aq)
E)Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + KNO3(aq)
A)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
B)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + KNO3(aq)
C)Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
D)2Ba(NO3)2(aq) + 2K2SO4(aq) 2BaSO4(s) + 3KNO3(aq)
E)Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + KNO3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
After the following equation is properly balanced, what is the coefficient in front of O2?
S8(s) + O2(g) SO3(g)
A)12
B)8
C)16
D)3
E)2
S8(s) + O2(g) SO3(g)
A)12
B)8
C)16
D)3
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A reaction which has two elements as reactants and one compound as a product is:
A)a single-displacement reaction.
B)a decomposition reaction.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a double-displacement reaction.
E)a combination reaction.
A)a single-displacement reaction.
B)a decomposition reaction.
C)a combustion reaction.
D)a double-displacement reaction.
E)a combination reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The gases carbon dioxide and hydrogen can react together to form carbon monoxide gas and water vapor.Which of the diagrams in the figure could be used to represent this reaction? 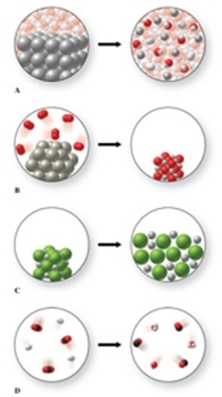
A)D
B)A
C)B
D)none of these
E)C

A)D
B)A
C)B
D)none of these
E)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Write a balanced equation to represent the reaction shown in the figure. 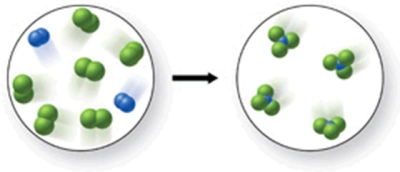
A)2N2 + 6Cl2 3NCl4
B)N2 + Cl2 2NCl3
C)2N2 + 6Cl2 4NCl3
D)N2 + 6Cl2 4NCl3
E)2N2 + 5Cl2 3NCl3

A)2N2 + 6Cl2 3NCl4
B)N2 + Cl2 2NCl3
C)2N2 + 6Cl2 4NCl3
D)N2 + 6Cl2 4NCl3
E)2N2 + 5Cl2 3NCl3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
After the following equation is properly balanced, what is the coefficient in front of O2(g)?
PbS(s) + O2(g) PbO(s) + SO2(g)
A)1
B)2
C)6
D)4
E)3
PbS(s) + O2(g) PbO(s) + SO2(g)
A)1
B)2
C)6
D)4
E)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Balance the following skeletal equation: CH4(g) C2H2(g) + H2(g).
A)4CH4(g) 2C2H2(g) + 5H2(g)
B)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + 3H2(g)
C)CH4(g) C2H2(g) + H2(g)
D)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + H2(g)
E)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + 2H2(g)
A)4CH4(g) 2C2H2(g) + 5H2(g)
B)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + 3H2(g)
C)CH4(g) C2H2(g) + H2(g)
D)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + H2(g)
E)2CH4(g) C2H2(g) + 2H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Write a balanced equation to represent the reaction shown in the figure. 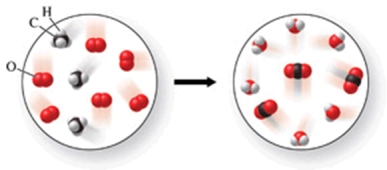
A)4CH3 + 6O2 4CO2 + 6H2O
B)3CH4 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
C)3CH3 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
D)3CH4 + 5O2 3CO2 + 5H2O
E)3CH4 + 6O2 3CO + 6H2O

A)4CH3 + 6O2 4CO2 + 6H2O
B)3CH4 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
C)3CH3 + 6O2 3CO2 + 6H2O
D)3CH4 + 5O2 3CO2 + 5H2O
E)3CH4 + 6O2 3CO + 6H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Balance the following skeletal equation: C3H8(g) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g).
A)C3H8(g) + O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
B)C3H8(g) + O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
C)C3H8(g) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
D)C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
E)C3H8(g) + 4O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
A)C3H8(g) + O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
B)C3H8(g) + O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
C)C3H8(g) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
D)C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)
E)C3H8(g) + 4O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A solution of silver nitrate is mixed with a solution of sodium chloride, resulting in a precipitate of silver chloride and a solution of sodium nitrate.The class of this reaction is:
A)combination reaction.
B)double-displacement reaction.
C)decomposition reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combustion reaction.
A)combination reaction.
B)double-displacement reaction.
C)decomposition reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combustion reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A reaction which has one element and one compound as reactants and one element and one compound as products is:
A)a double-displacement reaction.
B)a combination reaction.
C)a decomposition reaction.
D)a combustion reaction.
E)a single-displacement reaction.
A)a double-displacement reaction.
B)a combination reaction.
C)a decomposition reaction.
D)a combustion reaction.
E)a single-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Balance the following skeletal equation: NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + H2O(g).
A)NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
B)NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + H2O(g)
C)2NH3(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
D)4NH3(g) + 7O2(g) 4NO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
E)2NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
A)NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
B)NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + H2O(g)
C)2NH3(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
D)4NH3(g) + 7O2(g) 4NO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
E)2NH3(g) + O2(g) NO2(g) + 2H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When aqueous solutions of hydrochloric acid and sodium carbonate are mixed,
A)CO2 gas is produced.
B)a precipitate is formed.
C)no reaction occurs.
D)H2 gas is formed.
E)sodium metal is formed.
A)CO2 gas is produced.
B)a precipitate is formed.
C)no reaction occurs.
D)H2 gas is formed.
E)sodium metal is formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A reaction which has one compound as a reactant and two elements as products is:
A)a decomposition reaction.
B)a combustion reaction.
C)a single-displacement reaction.
D)a combination reaction.
E)a double-displacement reaction.
A)a decomposition reaction.
B)a combustion reaction.
C)a single-displacement reaction.
D)a combination reaction.
E)a double-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Balance the following skeletal equation: Li(s) + H2O(l) LiOH(aq) + H2(g).
A)Li(s) + H2O(l) LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
B)2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
C)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
D)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
E)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
A)Li(s) + H2O(l) LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
B)2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
C)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) LiOH(aq) + H2(g)
D)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
E)Li(s) + 2H2O(l) 2LiOH(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Balance the following skeletal equation: C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g).
A)C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
B)C2H5OH(l) + 2O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
C)C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
D)C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
E)2C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
A)C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
B)C2H5OH(l) + 2O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
C)C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
D)C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
E)2C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) 4CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Balance the following skeletal equation: Pb(NO3)2(aq) + KI(aq) PbI2(s) + KNO3(aq)
A)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + KI(aq) PbI2(s) + KNO3(aq)
B)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
C)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + KNO3(aq)
D)2Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + 4KNO3(aq)
E)2Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) 2PbI2(s) + 4KNO3(aq)
A)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + KI(aq) PbI2(s) + KNO3(aq)
B)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
C)Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + KNO3(aq)
D)2Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) PbI2(s) + 4KNO3(aq)
E)2Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) 2PbI2(s) + 4KNO3(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Balance the following skeletal equation: HCl(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
A)2HCl(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
B)HCl(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
C)2HCl(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
D)4HCl(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) + 2Cl2(g)
A)2HCl(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
B)HCl(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
C)2HCl(g) + O2(g) H2O(l) + Cl2(g)
D)4HCl(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) + 2Cl2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A reaction which has two compounds as reactants and two compounds as products is:
A)a combustion reaction.
B)a single-displacement reaction.
C)a decomposition reaction.
D)a combination reaction.
E)a double-displacement reaction.
A)a combustion reaction.
B)a single-displacement reaction.
C)a decomposition reaction.
D)a combination reaction.
E)a double-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The class of the reaction shown in the figure is: 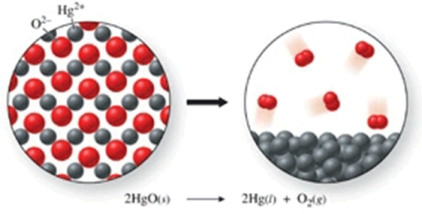
A)double-displacement reaction.
B)combination reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)decomposition reaction.
E)single-displacement reaction.

A)double-displacement reaction.
B)combination reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)decomposition reaction.
E)single-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The class of the reaction shown in the figure is: 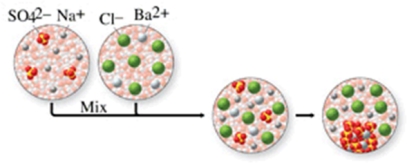
A)combination reaction.
B)combustion reaction.
C)single-displacement reaction.
D)double-displacement reaction.
E)decomposition reaction.

A)combination reaction.
B)combustion reaction.
C)single-displacement reaction.
D)double-displacement reaction.
E)decomposition reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sodium metal reacts with water in a single-displacement reaction.Which of the following best describes the identity of the products of this reaction?
A)NaH(aq) and O2(g)
B)NaOH(aq) and H2(g)
C)NaOH2(aq)
D)NaH2(aq) and O(g)
E)NaOH(aq) and H(g)
A)NaH(aq) and O2(g)
B)NaOH(aq) and H2(g)
C)NaOH2(aq)
D)NaH2(aq) and O(g)
E)NaOH(aq) and H(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and NaOH are mixed, _______ will occur.
A)no reaction
B)a double-displacement reaction
C)a single-displacement reaction
D)a decomposition reaction
E)a combination reaction
A)no reaction
B)a double-displacement reaction
C)a single-displacement reaction
D)a decomposition reaction
E)a combination reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Write and balance the equation for the combination reaction that occurs when solid potassium metal reacts with chlorine gas.
A)2K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)
B)K(s) + Cl(g) KCl(s)
C)2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2ClK(s)
D)2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2KCl(s)
E)K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)
A)2K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)
B)K(s) + Cl(g) KCl(s)
C)2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2ClK(s)
D)2K(s) + Cl2(g) 2KCl(s)
E)K(s) + Cl2(g) KCl(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Crystals of red mercury(II) oxide, when heated, form liquid mercury and oxygen gas.The class of this reaction is:
A)double-displacement reaction.
B)combination reaction.
C)single-displacement reaction.
D)decomposition reaction.
E)combustion reaction.
A)double-displacement reaction.
B)combination reaction.
C)single-displacement reaction.
D)decomposition reaction.
E)combustion reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The class of the reaction shown in the figure is: 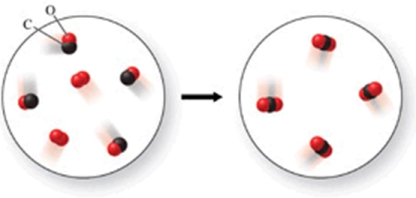
A)combustion reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)double-displacement reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combination reaction.

A)combustion reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)double-displacement reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combination reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following equations best describes the reaction that occurs when potassium metal reacts with oxygen gas in a combination reaction?
A)K(s) + O2(g) KO2(s)
B)4K(s) + O2(g) 2K2O(s)
C)K(s) + O2(g) KO(s) + O(g)
D)2K(s) + O(g) K2O(s)
E)K(s) + O(g) KO(s)
A)K(s) + O2(g) KO2(s)
B)4K(s) + O2(g) 2K2O(s)
C)K(s) + O2(g) KO(s) + O(g)
D)2K(s) + O(g) K2O(s)
E)K(s) + O(g) KO(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
When heated, calcium carbonate (limestone) undergoes a decomposition reaction.Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
A)CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
B)CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO2(g)
C)2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + 3CO2(g)
D)CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO3(g)
E)2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + CO2(g)
A)CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g)
B)CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO2(g)
C)2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + 3CO2(g)
D)CaCO3(s) Ca(s) + CO3(g)
E)2CaCO3(s) 2CaO(s) + CO2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A piece of magnesium metal is placed in a solution of hydrochloric acid, resulting in the formation of hydrogen gas and a solution of magnesium chloride.The class of this reaction is:
A)single-displacement reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)combination reaction.
E)double-displacement reaction.
A)single-displacement reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)combination reaction.
E)double-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The class of the reaction shown in the figure is: 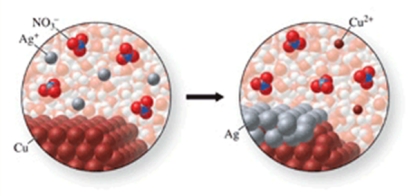
A)combination reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)double-displacement reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combustion reaction.

A)combination reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)double-displacement reaction.
D)single-displacement reaction.
E)combustion reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the product of the combination reaction that occurs when magnesium metal reactions with oxygen gas?
A)MgO2(s)
B)Mg2O3(s)
C)Mg2O(s)
D)MgO(s)
E)Mg2O2(s)
A)MgO2(s)
B)Mg2O3(s)
C)Mg2O(s)
D)MgO(s)
E)Mg2O2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What are the products of the combustion reaction of methane, CH4, with oxygen?
A)CO2(g) and H2O(g)
B)H2CO3(aq)
C)CO2(g) only
D)C(s), and H2O(g)
E)CO(g) and H2(g)
A)CO2(g) and H2O(g)
B)H2CO3(aq)
C)CO2(g) only
D)C(s), and H2O(g)
E)CO(g) and H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Write and balance the equation for the decomposition reaction that occurs when Mercury(II) oxide decomposes to its elements.
A)HgO(s) Hg(l) + O2(g)
B)2HgO(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
C)Hg2O(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
D)HgO2(s) Hg(l) + 2O(g)
E)2Hg(l) +O2(g) HgO2(s)
A)HgO(s) Hg(l) + O2(g)
B)2HgO(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
C)Hg2O(s) 2Hg(l) + O2(g)
D)HgO2(s) Hg(l) + 2O(g)
E)2Hg(l) +O2(g) HgO2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The class of the reaction shown in the figure is: 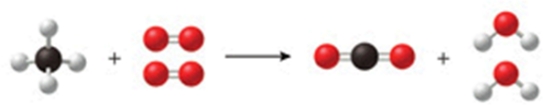
A)double-displacement reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)combination reaction.
E)single-displacement reaction.

A)double-displacement reaction.
B)decomposition reaction.
C)combustion reaction.
D)combination reaction.
E)single-displacement reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A piece of magnesium metal is burned in air (containing oxygen gas), and a white powder of magnesium oxide is formed.The class of this reaction is:
A)combustion reaction.
B)single-displacement reaction.
C)decomposition reaction.
D)double-displacement reaction.
E)combination reaction.
A)combustion reaction.
B)single-displacement reaction.
C)decomposition reaction.
D)double-displacement reaction.
E)combination reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the correct formula for the product of the combination reaction between calcium metal and oxygen gas?
A)Ca2O(s)
B)Ca2O3(s)
C)Ca2O2(s)
D)CaO(s)
E)CaO2(s)
A)Ca2O(s)
B)Ca2O3(s)
C)Ca2O2(s)
D)CaO(s)
E)CaO2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Write and balance the equation for the decomposition reaction that occurs when solid copper(II) hydroxide, Cu(OH)2, is heated.
A)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + (OH)2(g)
B)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + 2OH(g)
C)2Cu(OH)2(s) 2CuO(s) + H2O(g)
D)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + H2O(g)
E)Cu(OH)2(s) CuO(s) + H2O(g)
A)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + (OH)2(g)
B)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + 2OH(g)
C)2Cu(OH)2(s) 2CuO(s) + H2O(g)
D)Cu(OH)2(s) Cu(s) + H2O(g)
E)Cu(OH)2(s) CuO(s) + H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Write and balance the equation for the decomposition reaction that occurs when solid magnesium sulfate trihydrate, MgSO4·3H2O, is heated.
A)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + 3H2O(g)
B)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgS(s) + 6H2O(g)
C)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4·3H2O(s)
D)MgSO4·3H2O(s) Mg(s) + SO4·3H2O(s)
E)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + H2O(g)
A)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + 3H2O(g)
B)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgS(s) + 6H2O(g)
C)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4·3H2O(s)
D)MgSO4·3H2O(s) Mg(s) + SO4·3H2O(s)
E)MgSO4·3H2O(s) MgSO4(s) + H2O(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Classify the following reaction: 2C8H18(l) + 25O2(g) 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g)
A)combination
B)combustion
C)single-displacement
D)decomposition
E)double-displacement
A)combination
B)combustion
C)single-displacement
D)decomposition
E)double-displacement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When calcium metal is placed in water, a single-displacement reaction occurs.Write a balanced equation to describe this reaction.
A)Ca(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
B)Ca(s) + H2O(l) CaO(s) + H2(g)
C)Ca(s) + H2O(l) CaO(aq) + H2(g)
D)2Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) 2Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
E)Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
A)Ca(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
B)Ca(s) + H2O(l) CaO(s) + H2(g)
C)Ca(s) + H2O(l) CaO(aq) + H2(g)
D)2Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) 2Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
E)Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When copper metal is placed in a solution of platinum(II) chloride, will a reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Cu(s) + Pt2Cl(aq) CuCl(aq) + 2Pt(aq)
B)Yes.Cu(s) + PtCl2(aq) CuCl(aq) + PtCl(aq)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.Cu(s) + Pt2Cl(aq) CuCl(aq) + Pt(aq)
E)Yes.Cu(s) + PtCl2(aq) CuCl2(aq) + Pt(s)
A)Cu(s) + Pt2Cl(aq) CuCl(aq) + 2Pt(aq)
B)Yes.Cu(s) + PtCl2(aq) CuCl(aq) + PtCl(aq)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.Cu(s) + Pt2Cl(aq) CuCl(aq) + Pt(aq)
E)Yes.Cu(s) + PtCl2(aq) CuCl2(aq) + Pt(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Write and balance the equation for the combination reaction that occurs when aluminum metal reacts with oxygen gas.
A)4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3(s)
B)2Al(s) + 2O2(g) 2AlO2(s)
C)2Al(s) + 2O2(g) Al2O3(s)
D)Al(s) + O2(g) AlO(s)
E)Al(s) + O2(g) AlO2(s)
A)4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3(s)
B)2Al(s) + 2O2(g) 2AlO2(s)
C)2Al(s) + 2O2(g) Al2O3(s)
D)Al(s) + O2(g) AlO(s)
E)Al(s) + O2(g) AlO2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When aqueous solutions of sodium chloride and silver nitrate are mixed, a double-displacement reaction occurs.What is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + ClAg(s)
B)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(aq)
C)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s)
D)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + 3AgCl(s)
E)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) Na(s) + AgNO3Cl(aq)
A)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + ClAg(s)
B)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(aq)
C)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s)
D)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + 3AgCl(s)
E)NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) Na(s) + AgNO3Cl(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When iron metal is placed into a solution of hydrochloric acid, will a reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Yes.Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
B)Yes.Fe(s) + 3HCl(aq) FeCl3(aq) + H2(g)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.2Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) 2FeCl(aq) + H2(g)
A)Yes.Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
B)Yes.Fe(s) + 3HCl(aq) FeCl3(aq) + H2(g)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.2Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) 2FeCl(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the metals (Fe, Zn, Mg) will react in an aqueous solution of Al(NO3)3 to produce aluminum metal?
A)Zn
B)Mg
C)Fe
D)None of these
E)All of these
A)Zn
B)Mg
C)Fe
D)None of these
E)All of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If solutions of potassium chromate and calcium nitrate are mixed, will a double-displacement reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
B)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaK(s)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
E)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) K2(NO3)2(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
A)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
B)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaK(s)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + CaCrO4(s)
E)Yes.K2CrO4(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) K2(NO3)2(aq) + CaCrO4(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following ionic compounds would be expected to be insoluble in water?
A)NaOH
B)KI
C)CaS
D)Ca(NO3)2
E)Na2SO4
A)NaOH
B)KI
C)CaS
D)Ca(NO3)2
E)Na2SO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following ionic compounds would be expected to be insoluble in water?
A)Li2SO4
B)AgI
C)Ca(CH3CO2)2
D)NaCl
E)KOH
A)Li2SO4
B)AgI
C)Ca(CH3CO2)2
D)NaCl
E)KOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the reaction CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l).The driving force that causes the reaction to go to completion is:
A)formation of a soluble salt.
B)formation of an element.
C)formation of an insoluble gas.
D)formation of a precipitate.
E)none of these.
A)formation of a soluble salt.
B)formation of an element.
C)formation of an insoluble gas.
D)formation of a precipitate.
E)none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If solutions of potassium carbonate and calcium nitrate are mixed, will a double-displacement reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaK(s)
B)No reaction will occur.
C)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaCO3(s)
D)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) K2(NO3)2(aq) + CaCO3(s)
E)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + CaCO3(s)
A)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaK(s)
B)No reaction will occur.
C)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + CaCO3(s)
D)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) K2(NO3)2(aq) + CaCO3(s)
E)Yes.K2CO3(aq) + Ca(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + CaCO3(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When copper metal is placed into a silver nitrate solution, a single-displacement reaction occurs, forming a copper(II) compound.Write a balanced equation to describe this reaction.
A)Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
B)Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) CuNO3(aq) + AgNO3(aq)
C)Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Ag(s)
D)2Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) 2Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Ag(s)
E)Cu(s) + AgNO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + Ag(aq)
A)Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
B)Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) CuNO3(aq) + AgNO3(aq)
C)Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Ag(s)
D)2Cu(s) + Ag(NO3)2(aq) 2Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Ag(s)
E)Cu(s) + AgNO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + Ag(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When copper metal is placed in a solution of zinc nitrate, will a reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Zn(s)
B)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) CuNO3(aq) + ZnNO3(aq)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn2NO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + Zn(aq)
E)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn2NO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + 2Zn(aq)
A)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) Cu(NO3)2(aq) + Zn(s)
B)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn(NO3)2(aq) CuNO3(aq) + ZnNO3(aq)
C)No reaction will occur.
D)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn2NO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + Zn(aq)
E)Yes.Cu(s) + Zn2NO3(aq) CuNO3(aq) + 2Zn(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When potassium metal is placed in water, will a reaction occur? If so, what is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
B)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KH2O(aq)
C)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
D)No reaction will occur.
E)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2K(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
A)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KOH(aq) + H2(g)
B)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KH2O(aq)
C)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2KOH(aq) + 2H2(g)
D)No reaction will occur.
E)Yes.2K(s) + 2H2O(l) 2K(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following ionic compounds would be expected to be insoluble in water?
A)NH4NO3
B)PbI2
C)NaCH3CO2
D)KCl
E)CuSO4
A)NH4NO3
B)PbI2
C)NaCH3CO2
D)KCl
E)CuSO4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Write and balance the equation for the combination reaction that occurs when sulfur dioxide gas, SO2, reacts with oxygen gas.
A)3SO2(g) + 2O2(g) 3SO3(g)
B)SO2(g) + O2(g) SO3(g)
C)SO2(g) + O2(g) SO4(g)
D)2SO2(g) + 2O2(g) 2SO3(g)
E)2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g)
A)3SO2(g) + 2O2(g) 3SO3(g)
B)SO2(g) + O2(g) SO3(g)
C)SO2(g) + O2(g) SO4(g)
D)2SO2(g) + 2O2(g) 2SO3(g)
E)2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When aqueous solutions of potassium chloride and lead(II) nitrate are mixed, a double-displacement reaction occurs.What is the balanced equation for the reaction?
A)KCl(aq) + Pb2NO3(aq) KNO3(aq) + PbCl(aq)
B)KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) K(s) + PbNO3Cl(aq)
C)KCl(aq) + Pb2NO3(aq) KNO3(aq) + 2PbCl(s)
D)2KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + ClPb(s)
E)2KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + PbCl2(s)
A)KCl(aq) + Pb2NO3(aq) KNO3(aq) + PbCl(aq)
B)KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) K(s) + PbNO3Cl(aq)
C)KCl(aq) + Pb2NO3(aq) KNO3(aq) + 2PbCl(s)
D)2KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) KNO3(aq) + ClPb(s)
E)2KCl(aq) + Pb(NO3)2(aq) 2KNO3(aq) + PbCl2(s)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider the reaction Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l).The driving force that causes the reaction to go to completion is:
A)formation of water.
B)formation of a soluble salt.
C)formation of a precipitate.
D)formation of an insoluble gas.
E)formation of an element.
A)formation of water.
B)formation of a soluble salt.
C)formation of a precipitate.
D)formation of an insoluble gas.
E)formation of an element.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When zinc metal is placed into a copper(II) nitrate solution, a single-displacement reaction occurs.Write a balanced equation to describe this reaction.
A)2Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) 2Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
B)Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + CuNO3(aq)
C)Zn(s) + Cu2NO3(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + Cu(aq)
D)Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
E)Zn(s) + Cu2NO3(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + 2Cu(aq)
A)2Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) 2Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
B)Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + CuNO3(aq)
C)Zn(s) + Cu2NO3(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + Cu(aq)
D)Zn(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq) Zn(NO3)2(aq) + Cu(s)
E)Zn(s) + Cu2NO3(aq) ZnNO3(aq) + 2Cu(aq)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Predict which of the following reactions will occur?
A)All three will occur.
B)i only
C)iii only
D)ii only
E)ii and iii
A)All three will occur.
B)i only
C)iii only
D)ii only
E)ii and iii

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



