Deck 13: Tax Accounting
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/78
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Tax Accounting
1
Repossessions of real property sold on the installment basis are generally nontaxable.
True
2
A taxable year may be as short as one day and may exceed 366 days.
True
3
Both cash and accrual basis taxpayers will be taxed on a dividend when it is actually received.
True
4
Taxpayers must generally obtain the permission of the IRS to change accounting methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A partnership may adopt any tax year without IRS permission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Computing "cost of goods sold"and being on the accrual basis are independent of each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
fte IRS can require a change in accounting methods if the method used by a taxpayer does not clearly reflect income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A short tax year with the subsequent annualizing of taxable income is required for which of the following?
A) In the year of death of an individual
B) In the year of termination of a partnership
C) In the first year of a new corporation
D) In the year of liquidation of a corporation
E) None of the above
A) In the year of death of an individual
B) In the year of termination of a partnership
C) In the first year of a new corporation
D) In the year of liquidation of a corporation
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
IRS permission is not required for a change from FIFO to LIFO.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not a method of accounting?
A) Cash receipts and disbursements method
B) Accrual method
C) LIFO inventory
D) Long-term contracts method
E) None of the above
A) Cash receipts and disbursements method
B) Accrual method
C) LIFO inventory
D) Long-term contracts method
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
fte installment method cannot be used unless the total selling price is known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A correction of an error in a tax return is usually considered a change in accounting method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What is the amount of tax to be paid for a short period assuming the tax from placing the short period on an annual basis is $2,300; the tax computation for the short period without annualizing is $2,100; and the tax computation using the full 12 months and prorating is $2,200.
A) $2,300
B) $2,200
C) $2,100
D) $100
E) None of the above
A) $2,300
B) $2,200
C) $2,100
D) $100
E) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In general, a CPA on the cash basis method will never have a bad debt deduction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A cash basis taxpayer may deduct prepaid business expenses currently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A grocery store may use the cash basis of reporting sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Under no circumstances may a corporation change its fiscal year without IRS permission.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A corporation filing its first return must "annualize" its income if the tax period is less than 12 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If, in the IRS's opinion, the taxpayer's books do not "clearly reflect income," the IRS may revise them so that they do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A taxpayer engaged in two or more separate and distinct businesses may use different accounting methods for both businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following entities may select any tax period (calendar or fiscal)?
A) sole partnership
B) partnership
C) S corporations
D) trusts
E) corporations other than S corporations.
A) sole partnership
B) partnership
C) S corporations
D) trusts
E) corporations other than S corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following tax years are acceptable tax years except:
A) 52-53-week tax year.
B) Short tax year which occurred because a business was not in existence for an entire year.
C) Short tax year which occurred because a business had a change in accounting period.
D) Fiscal tax year (other than a 52-53-week tax year) that ends on any day of the month other than the last day.
A) 52-53-week tax year.
B) Short tax year which occurred because a business was not in existence for an entire year.
C) Short tax year which occurred because a business had a change in accounting period.
D) Fiscal tax year (other than a 52-53-week tax year) that ends on any day of the month other than the last day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Paul Panda purchased property from Walter Wolf by assuming an existing mortgage of $12,000 and agreeing to pay an additional $6,000, plus interest, over the next three years. Walter Wolf had an adjusted basis of $8,800 in the building and paid selling expenses totaling $1,200. What were the sales price and the contract price in this transaction?
A) Sales price: $6,000; contract price: $12,000
B) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $10,000
C) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $8,000
D) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $6,000
A) Sales price: $6,000; contract price: $12,000
B) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $10,000
C) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $8,000
D) Sales price: $18,000; contract price: $6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Robert Graves sold his house to George Tombs for a total of $100,000. Earnest money of $5,000 was received at the end of the year prior to the closing. fte remaining $15,000 of the down payment was received at closing. George assumed a $50,000 mortgage on the property and signed a second mortgage for $30,000. If Robert's basis was $35,000 the tax results, in part, are as follows:
A) Contract price: $65,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $35,000
B) Contract price: $50,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $50,000
C) Contract price: $65,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $20,000
D) Contract price: $80,000; gross profit: 65/80%; payments in year of sale: $30,000
A) Contract price: $65,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $35,000
B) Contract price: $50,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $50,000
C) Contract price: $65,000; gross profit: 100%; payments in year of sale: $20,000
D) Contract price: $80,000; gross profit: 65/80%; payments in year of sale: $30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Simond is the owner of a hair salon. In addition to hair styling, he sells some hair products but the sales account for little revenue. Regarding accounting methods, Simond:
A) must use the accural basis to account for income and expenses
B) may use the cash basis to account for income and expenses
C) may use the cash basis to account for income and expenses except for inventory, for which he must use the accrual basis
D) none of the above
A) must use the accural basis to account for income and expenses
B) may use the cash basis to account for income and expenses
C) may use the cash basis to account for income and expenses except for inventory, for which he must use the accrual basis
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which entities must have tax years that conform with the tax years of their owners?
A) partnerships
B) S corporations
C) personal service corporations
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) partnerships
B) S corporations
C) personal service corporations
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following deferred payment sales qualify for installment reporting except:
A) Sale of depreciable property at a gain to seller's brother
B) Transfer of a building subject to a mortgage in excess of basis where no other consideration is paid
C) Sale of real property used in a trade or business
D) Sale of depreciable property to the seller's 82 percent owned corporation
A) Sale of depreciable property at a gain to seller's brother
B) Transfer of a building subject to a mortgage in excess of basis where no other consideration is paid
C) Sale of real property used in a trade or business
D) Sale of depreciable property to the seller's 82 percent owned corporation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
fte following statements about LIFO inventory are false except:
A) fte taxpayer needs IRS permission to adopt LIFO.
B) LIFO must be used for both "book" and tax purposes, but the numbers may still differ.
C) fte use of LIFO results in tax deferral and increased earnings per share per books.
D) LIFO was not acceptable for tax purposes until the 1954 Internal Revenue Code.
A) fte taxpayer needs IRS permission to adopt LIFO.
B) LIFO must be used for both "book" and tax purposes, but the numbers may still differ.
C) fte use of LIFO results in tax deferral and increased earnings per share per books.
D) LIFO was not acceptable for tax purposes until the 1954 Internal Revenue Code.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Sylvester Sueem, attorney-at-law, reports his income on the cash basis. Last year his books reflected the following: 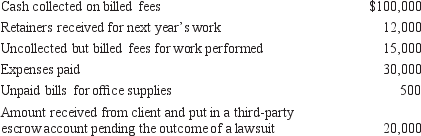 Sylvester's net self-employment income last year was:
Sylvester's net self-employment income last year was:
A) $70,000
B) $84,500
C) $82,000
D) $96,000
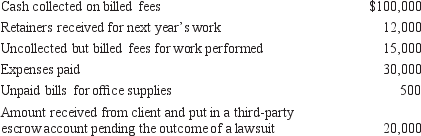 Sylvester's net self-employment income last year was:
Sylvester's net self-employment income last year was:A) $70,000
B) $84,500
C) $82,000
D) $96,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
fte uniform capitalization rules apply to which one of the following properties?
A) Property you produce under a long-term contract
B) Personal property you purchase for resale, if your average annual gross receipts are $10,000,000 or less
C) Costs paid or incurred by an individual (other than as an employee) or a qualified employee-owner of a personal service corporation in the business of being a writer, photographer, or artist
D) Real property or tangible personal property which you produce for sale to customers
A) Property you produce under a long-term contract
B) Personal property you purchase for resale, if your average annual gross receipts are $10,000,000 or less
C) Costs paid or incurred by an individual (other than as an employee) or a qualified employee-owner of a personal service corporation in the business of being a writer, photographer, or artist
D) Real property or tangible personal property which you produce for sale to customers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Jake Turner realized last December that he had almost reached the point where his medical expenses exceeded the 7.5 percent of AGI limitation. As a result, he insisted on paying his physician, Dr. Grope, $6,000 on account for future services for the Turner family. fte results of this prepayment are:
A) Turner's deduction: when paid; Dr. Grope's income: when received
B) Turner's deduction: when services are rendered; Dr. Grope's income: when received
C) Turner's deduction: when services are rendered; Dr. Grope's income: when services are rendered
D) Turner's deduction: when paid; Dr. Grope's income: when services are rendered
A) Turner's deduction: when paid; Dr. Grope's income: when received
B) Turner's deduction: when services are rendered; Dr. Grope's income: when received
C) Turner's deduction: when services are rendered; Dr. Grope's income: when services are rendered
D) Turner's deduction: when paid; Dr. Grope's income: when services are rendered

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Jones has two separate businesses. Jones:
A) must use the same accounting methods for each business
B) may use different accounting methods for each business with no restrictions
C) may use two different accounting methods but must reconcile the differences between businesses
D) may use two different accounting methods if separate books and records are kept for each business
E) none of the above
A) must use the same accounting methods for each business
B) may use different accounting methods for each business with no restrictions
C) may use two different accounting methods but must reconcile the differences between businesses
D) may use two different accounting methods if separate books and records are kept for each business
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
fte following statements about cash and accrual basis taxpayers are all false, except:
A) Both cash and accrual basis taxpayers include prepaid rent in gross income.
B) Both cash and accrual basis taxpayers are taxed on rent paid late when received.
C) fte timing of dividend income may depend on the record date.
D) Constructive receipt is a concept affecting both cash and accrual method taxpayers.
A) Both cash and accrual basis taxpayers include prepaid rent in gross income.
B) Both cash and accrual basis taxpayers are taxed on rent paid late when received.
C) fte timing of dividend income may depend on the record date.
D) Constructive receipt is a concept affecting both cash and accrual method taxpayers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Greg Owens owns a four-flat building. Last year, he recorded the following items:  His gross rental income, depending on whether he is on the cash or accrual basis, amounted to:
His gross rental income, depending on whether he is on the cash or accrual basis, amounted to:
A) Cash: $16,000; accrual: $17,000
B) Cash: $13,000; accrual: $17,000
C) Cash: $18,000; accrual: $16,000
D) Cash: $17,000; accrual: $17,000
 His gross rental income, depending on whether he is on the cash or accrual basis, amounted to:
His gross rental income, depending on whether he is on the cash or accrual basis, amounted to:A) Cash: $16,000; accrual: $17,000
B) Cash: $13,000; accrual: $17,000
C) Cash: $18,000; accrual: $16,000
D) Cash: $17,000; accrual: $17,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A corporation must "annualize" a short taxable year resulting from:
A) Going out of business
B) Starting in business
C) Changing from one fiscal year to another
D) Joining an affiliated group and filing consolidated returns
A) Going out of business
B) Starting in business
C) Changing from one fiscal year to another
D) Joining an affiliated group and filing consolidated returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
fte following statements about dispositions of installment obligations are all true, except:
A) If a father sells property at a gain to his daughter for an installment obligation, then forgives one of more installments, gain is recognized by the father, or his estate.
B) A sale of an installment obligation to the spouse for its fair market value does not accelerate the gain.
C) A gift of an installment obligation triggers gain, even if no consideration is received.
D) If the seller elected out of the installment method, a disposition of the obligation may result in a loss, but not in gain, since the gain was recognized up-front.
A) If a father sells property at a gain to his daughter for an installment obligation, then forgives one of more installments, gain is recognized by the father, or his estate.
B) A sale of an installment obligation to the spouse for its fair market value does not accelerate the gain.
C) A gift of an installment obligation triggers gain, even if no consideration is received.
D) If the seller elected out of the installment method, a disposition of the obligation may result in a loss, but not in gain, since the gain was recognized up-front.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
fte following statements about inventories for tax purposes are all true, except:
A) Inventories may not be valued on the basis of the "base stock" method, the prime cost method, nor the variable cost method.
B) If inventories are required to be kept, the taxpayer must be on the accrual basis for purchases and sales of inventory, but it may be on the cash method for the service portion of the business.
C) fte use of the LIFO method invariably results in an annual reduction in taxable income.
D) A strict adherence to GAAP is no guarantee that the IRS will allow a write-down of inventories.
A) Inventories may not be valued on the basis of the "base stock" method, the prime cost method, nor the variable cost method.
B) If inventories are required to be kept, the taxpayer must be on the accrual basis for purchases and sales of inventory, but it may be on the cash method for the service portion of the business.
C) fte use of the LIFO method invariably results in an annual reduction in taxable income.
D) A strict adherence to GAAP is no guarantee that the IRS will allow a write-down of inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
fte following statements about the cash basis method of accounting are false, except:
A) fte prepayment made for future services may be deducted currently.
B) Interest credited to a savings account is not taxed until withdrawn.
C) Stock received for services rendered are taxed only in the year sold.
D) fte exchange of services may lead to gross income to both parties.
A) fte prepayment made for future services may be deducted currently.
B) Interest credited to a savings account is not taxed until withdrawn.
C) Stock received for services rendered are taxed only in the year sold.
D) fte exchange of services may lead to gross income to both parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
All of the following statements regarding accounting methods are true except:
A) If inventory is a material, income-producing item for your business, you must use the accrual method for your sales and purchases.
B) If you use the cash method for reporting expenses, you can use the accrual method for figuring income.
C) If you use the accrual method for reporting expenses, you can use the cash method for figuring income.
D) If you operate more than one business, you may use a different accounting method for each separate and distinct business, provided that the method clearly reflects income.
A) If inventory is a material, income-producing item for your business, you must use the accrual method for your sales and purchases.
B) If you use the cash method for reporting expenses, you can use the accrual method for figuring income.
C) If you use the accrual method for reporting expenses, you can use the cash method for figuring income.
D) If you operate more than one business, you may use a different accounting method for each separate and distinct business, provided that the method clearly reflects income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
An accrual basis taxpayer must recognize income when a sale is made, even if on credit. ftis means that income is recognized:
A) When the order is received
B) When the delivery is made
C) When the invoice is mailed
D) At any of the above events, if consistently used
A) When the order is received
B) When the delivery is made
C) When the invoice is mailed
D) At any of the above events, if consistently used

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Sturdy Co. filed a short period return covering four months. It had an NOL of $75,000. With respect to the NOL, Sturdy Co.:
A) Carry it back two years and then forward 20 years
B) Carry it back two years but not carry it forward
C) Cannot carry it back but can carry it forward for 20 years
D) Cannot claim any benefit from the NOL (i.e., cannot carry it back nor forward)
A) Carry it back two years and then forward 20 years
B) Carry it back two years but not carry it forward
C) Cannot carry it back but can carry it forward for 20 years
D) Cannot claim any benefit from the NOL (i.e., cannot carry it back nor forward)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Schull Co. uses the LIFO method to account for its inventories. It can use the following method in combination with LIFO:
A) specific identification
B) lower cost or market
C) dollar value techniques
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) specific identification
B) lower cost or market
C) dollar value techniques
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following entities do not compute taxable income per se?
A) C corporations
B) Partnerships
C) Estates
D) Trusts
E) Individuals
A) C corporations
B) Partnerships
C) Estates
D) Trusts
E) Individuals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
CKC just received permission from the IRS to change its method of accounting. CKC is uncertain if it now wants to change methods. Since it already has received permission to change,
A) CKC must use the new method of accounting
B) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting only if it makes a timely election
C) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting only if it makes a timely election and subsequently receives IRS permission
D) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting even if it does not make a timely election
A) CKC must use the new method of accounting
B) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting only if it makes a timely election
C) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting only if it makes a timely election and subsequently receives IRS permission
D) CKC may continue to use its current method of accounting even if it does not make a timely election

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Hock Brothers uses the simplified dollar-value LIFO method to account for its inventory. Ending inventory at actual prices in 2012 and 2013 was $80,000 and $120,000, respectively. fte Consumer Price Index for 2012 and 2013 was 102% and 107%, respectively. fte value of Hock Brothers' ending inventory in 2013 is:
A) $114,393
B) $116,079
C) $120,000
D) $127,607
E) none of the above
A) $114,393
B) $116,079
C) $120,000
D) $127,607
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Gyan sold an oriental rug in 2012 for $25,000. He acquired the rug in 2002 for $17,000. He received $6,000 in 2012 and $10,000 in 2013. Gyan sold the installment obligation on January 3, 2014 for $8,500. Gyan's long- term capital gain on the sale of the installment obligation is:
A) $-0-
B) $2,380
C) $6,120
D) $8,500
E) none of the above
A) $-0-
B) $2,380
C) $6,120
D) $8,500
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In 2012, Rankin sold real estate he aquired in 1995 under an installment contract and used the installment method for tax purposes. In 2013, the buyer defaulted on the installment obligation and Rankin repossessed the property. Rankin sustained a $30,000 loss on the repossession. Rankin's recognized position in 2013 as a result of the repossession is:
A) $-0¬
B) $30,000 long-term capital gain
C) $30,000 ordinary income
D) none of the above
A) $-0¬
B) $30,000 long-term capital gain
C) $30,000 ordinary income
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Susan and Tom had the same aggregate taxable income over the last five years. Susan's income was relatively smooth over this period but Tom's income fluctuated greatly over this same time period. Assuming that tax rates have remained reasonably constant over this time period who would experience the greater total tax liability?
A) Susan
B) Tom
C) their tax liabilities would be equal
A) Susan
B) Tom
C) their tax liabilities would be equal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Rubin Inc. uses the FIFO and lower of cost market methods to account for its inventory. Information regarding inventories is as follows. 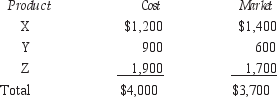 Rubin Inc's ending inventory will be valued at:
Rubin Inc's ending inventory will be valued at:
A) $3,500
B) $3,700
C) $4,000
D) $4,200
E) none of the above
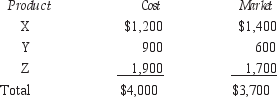 Rubin Inc's ending inventory will be valued at:
Rubin Inc's ending inventory will be valued at:A) $3,500
B) $3,700
C) $4,000
D) $4,200
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Peter sold a painting in 2012 for $100,000. Peter bought the painting in 2011 for $60,000. Peter received $30,000 in 2012 and is to receive $15,000 per year (plus interest) for 2013 through 2016. How much gain must Peter recognize in 2012?
A) $12,000
B) $28,000
C) $30,000
D) $40,000
E) none of the above
A) $12,000
B) $28,000
C) $30,000
D) $40,000
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Hal sold a rare automobile in 2012 for $110,000. Hal bought the automobile in 1988 for $25,000. Hal received $50,000 in 2012 and will receive $60,000 (plus interest) in 2013. Hal elects not to use the installment method for this sale. fte $60,000 note is worth $57,000 at the time of the sale. What gain (not including interest income) will Hal recognize in 2013 when he receives the $60,000?
A) $-0¬
B) $3,000 long-term capital gain
C) $3,000 ordinary income
D) $57,000 ordinary income
E) none of the above
A) $-0¬
B) $3,000 long-term capital gain
C) $3,000 ordinary income
D) $57,000 ordinary income
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Campbell Co. incurred a variety of costs associated with its long-term construction contract. Which of the following costs must be capitalized and deducted as profits are recognized?
A) construction period interest
B) general and administrative expenses relating to specific contracts
C) scrap and spoilage costs
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) construction period interest
B) general and administrative expenses relating to specific contracts
C) scrap and spoilage costs
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
It is late December 2012 and Jones Company, a calendar year taxpayer, wants to shift income from 2012 to 2013. Which of the following methods will not achieve its objective?
A) delay shipping of goods that are F.O.B. destination
B) use the installment method on current sales, if permitted
C) defer paying bonuses to officers
D) prepay nonrefundable commissions
E) none of the above
A) delay shipping of goods that are F.O.B. destination
B) use the installment method on current sales, if permitted
C) defer paying bonuses to officers
D) prepay nonrefundable commissions
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Newco is a 90% subsidiary of P Company. With respect to its accounting period:
A) Newco may select any accounting period
B) Newco should select the calendar year
C) Newco should select the same accounting period as P Company
D) Newco should select the same accounting period as its minority shareholders
A) Newco may select any accounting period
B) Newco should select the calendar year
C) Newco should select the same accounting period as P Company
D) Newco should select the same accounting period as its minority shareholders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In 2012, X Company received full payment of an account payable from Jones Company. X Company had written the account off as a bad debt in 2011. In deciding how to treat the payment from Jones Company, X Company would use:
A) the claim-of-right doctrine
B) the tax benefit rule
C) the constructive receipt doctrine
D) the Arrowsmith doctrine
E) none of the above
A) the claim-of-right doctrine
B) the tax benefit rule
C) the constructive receipt doctrine
D) the Arrowsmith doctrine
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In order to secure prior approval for a change in accounting period, the taxpayer:
A) need do nothing, just file the short period return by its due date
B) file Form 1040 requesting approval of the change
C) file Form 1128 requesting approval of the change
D) file Form 1120 requesting approval of the change
A) need do nothing, just file the short period return by its due date
B) file Form 1040 requesting approval of the change
C) file Form 1128 requesting approval of the change
D) file Form 1120 requesting approval of the change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which taxpayers cannot use the cash basis method of accounting?
A) Large C corporations
B) Tax shelters
C) Partnerships that have a C corporation as a partner
D) All of the above must not use the cash basis
E) All of the above may use the cash basis
A) Large C corporations
B) Tax shelters
C) Partnerships that have a C corporation as a partner
D) All of the above must not use the cash basis
E) All of the above may use the cash basis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Mars uses the cash basis of accounting and is a calendar year firm. On December 31, 2012, it mailed checks in payment of expenses. fte checks were not cashed until January 2013. Mars may take a deduction for these expenses in:
A) 2012
B) 2013
C) either 2012 or 2013, whichever it chooses
D) no deduction is permitted until the expenses are incurred
A) 2012
B) 2013
C) either 2012 or 2013, whichever it chooses
D) no deduction is permitted until the expenses are incurred

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
B&B Company uses the cash basis for accounting purposes. B&B primarily performs a service; however, it does sell a significant amount of inventory.
A) B&B must use the cash basis to account for its inventory
B) Since inventory is an income-producing factor, B&B must use the accrual basis to account for its inventory but may use the cash basis for its other transactions
C) Since inventory is an income-producing factor, B&B must use the accrual basis to account for all of its transactions
D) None of the above
A) B&B must use the cash basis to account for its inventory
B) Since inventory is an income-producing factor, B&B must use the accrual basis to account for its inventory but may use the cash basis for its other transactions
C) Since inventory is an income-producing factor, B&B must use the accrual basis to account for all of its transactions
D) None of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Mallie Co. uses the dollar-value LIFO inventory method. Inventory of January 1, 20112 was $100,000 at base year prices. Inventory on December 31, 2012 was $160,000 at base year prices and was $200,000 at actual prices. What is the value of Mallie Co.'s ending inventory?
A) $160,000
B) $175,000
C) $200,000
D) $275,000
E) none of the above
A) $160,000
B) $175,000
C) $200,000
D) $275,000
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Gregory McDonald sold a piece of land he purchased for $5,000 many years ago. He recently mortgaged the property for $30,000, but after six months he sold the land for $50,000 to his cousin, Gus.
A) If Gus purchased the land for cash and Gregory paid off the mortgage, what is the contract price, the gross profit, and the gross profit percentage?
B) If Gus took the land subject to the mortgage and paid $5,000 a year, plus 10 percent interest for four years, starting with the year of sale, what is the contract price and the gain in the year of the sale?
A) If Gus purchased the land for cash and Gregory paid off the mortgage, what is the contract price, the gross profit, and the gross profit percentage?
B) If Gus took the land subject to the mortgage and paid $5,000 a year, plus 10 percent interest for four years, starting with the year of sale, what is the contract price and the gain in the year of the sale?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
John sold a painting on November 8, 2011 for $100,000. He acquired the painting for $30,000 on May 16, 2001. He received $40,000 down and $30,000 on June 20, 2012 and June 10, 2013. He sold the installment obligation for $20,000 on January 15, 2013. What is John's recognized gain (loss) on the sale of the installment obligation?
A) $10,000 long-term loss
B) $$1,000 long-term capital loss
C) $11,000 long-term capital gain
D) $14,000 long-term capital gain
A) $10,000 long-term loss
B) $$1,000 long-term capital loss
C) $11,000 long-term capital gain
D) $14,000 long-term capital gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Failure to make a timely accounting election could result in:
A) permanent loss of expected benefits associated with the election
B) deferral of expected benefits associated with the election
C) increased tax liability
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) permanent loss of expected benefits associated with the election
B) deferral of expected benefits associated with the election
C) increased tax liability
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Sunel Corporation uses the FIFO method of accounting for its inventories and uses the full absorption cost method. Its beginning inventory on January 1, 2012 was $4,000,000. During the year it incurred $20,000,000 in "full absorption" costs and $2,000,000 in additional Code Sec. 263A costs. Its ending inventory on December 31, 2012 was $6,000,000 (prior to any Code Sec. 263A costs). Determine Sunel Corporation's ending inventory using the uniform capitalization rules of Code Sec. 263A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Barrack sold stock on November 6, 2012 for $20,000. He received $5,000 down and $15,000 was due on January 15, 2013. He acquired the stock on January 10, 2010 for $10,000. Barrack made numerous attempts to collect the $15,000 and on April 15, 2013 he repossessed the stock. He incurred $1,000 in repossession costs and the stock was worth $14,000 when repossessed. What is Barrack's recognized capital gain (loss) on the repossession?
A) $1,000 short-term capital loss
B) $2,000 long-term capital loss
C) $5,500 short-term capital gain
D) $5,500 long-term capital gain
A) $1,000 short-term capital loss
B) $2,000 long-term capital loss
C) $5,500 short-term capital gain
D) $5,500 long-term capital gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In 2012, Zog Company enters into a two-year contract to construct a building for $40,000,000. Zog Company estimates it will cost $30,000,000 to complete the building. It completed the building in 2013, and actual costs were $21,000,000 in 2012 and $7,000,000 in 2013. What gross profit does Zog Company report in 2012 and 2013? 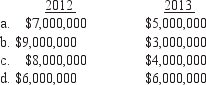
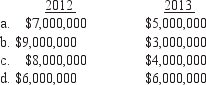

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Sarah sold land on November 8, 2012 for $400,000. She acquired the land on October 5, 2007 for $100,000. She received $80,000 down and $320,000 was due September 20, 2013. Sarah was unable to collect the remaining $320,000 and repossessed the land on November 15, 2013 when the land was worth $410,000, incurring $2,000 fees in the process. What is Sarah's recognized gain on the repossession?
A) $18,000 long-term capital gain
B) $20,000 long-term capital gain
C) $238,000 long-term capital gain
D) $248,000 long-term capital gain
A) $18,000 long-term capital gain
B) $20,000 long-term capital gain
C) $238,000 long-term capital gain
D) $248,000 long-term capital gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Christman Co. adopts the simplified dollar-value LIFO method in 2012. Ending inventory at actual prices in 2012 and 2013 was $100,000 and $160,000, respectively. Assume that the consumer price index was 1.20 and 1.25 in 2012 and 2013. What cost will Christman Co. use as ending inventory for 2013?
A) $160,000
B) $155,833
C) $153,600
D) $150,000
A) $160,000
B) $155,833
C) $153,600
D) $150,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Hillary Co. is a cash basis taxpayer. It sold machinery for $300,000 during the year. Hillary Co. acquired the machinery for $100,000 and took $60,000 in depreciation prior to the sale. fte machinery is subject to a $30,000 liability. fte buyer assumes the liability, gives Hillary Co. a $60,000 down payment and agrees to pay
$70,000 per year for the next three years. What is Hillary Co.'s gross profit percentage in the year of sale?
A) 100%
B) 96%
C) 74%
D) 63%
$70,000 per year for the next three years. What is Hillary Co.'s gross profit percentage in the year of sale?
A) 100%
B) 96%
C) 74%
D) 63%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Wonderworks Corporation sells and repairs equipment. Wonderworks is an accrual basis, calendar year taxpayer. In computing its taxable income for 2012, it is uncertain about the treatment of the following three items and seeks your advice:
a. It repaired a machine for Dandy Co. and submitted a bill for $7,000. Dandy Co. paid $3,000 at delivery but did not pay the remaining $4,000 because the repairs were faulty. By the end of 2012 Dandy Co. still had not paid the $4,000 and had filed a claim to recover the $3,000 already paid to Wonderworks.
b. Wonderworks provides free service in the year of sale for equipment that it sells. Included in the sales price (but unknown to its customers) is the cost of such service plus a profit. Total sales in 2012 were $300,000, of which $15,000 represented the cost of service and $5,000 represented the profit on said services. However, the equipment is high quality and no service calls were made in 2012. Wonderworks does not know how to treat the $20,000 with respect to income and deductions.
c. Wonderworks rents its premises from Acme Rental for $2,000 per month. In addition to making 12 monthly payments, Wonderworks paid $4,000 in January 2012 for November and December 2011 rents. Also, in December 2012, Wonderworks prepaid rent for January 2013 ($2,000).
a. It repaired a machine for Dandy Co. and submitted a bill for $7,000. Dandy Co. paid $3,000 at delivery but did not pay the remaining $4,000 because the repairs were faulty. By the end of 2012 Dandy Co. still had not paid the $4,000 and had filed a claim to recover the $3,000 already paid to Wonderworks.
b. Wonderworks provides free service in the year of sale for equipment that it sells. Included in the sales price (but unknown to its customers) is the cost of such service plus a profit. Total sales in 2012 were $300,000, of which $15,000 represented the cost of service and $5,000 represented the profit on said services. However, the equipment is high quality and no service calls were made in 2012. Wonderworks does not know how to treat the $20,000 with respect to income and deductions.
c. Wonderworks rents its premises from Acme Rental for $2,000 per month. In addition to making 12 monthly payments, Wonderworks paid $4,000 in January 2012 for November and December 2011 rents. Also, in December 2012, Wonderworks prepaid rent for January 2013 ($2,000).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Sandra Surrey sold her racehorse for $40,000 to Mickey Jockey and received $10,000 down and a note for $30,000 (value $25,000) due in three years together with accrued interest of 12 percent compounded semiannually. If the note is paid on time and the horse is Section 1231 property in which Sandra had a basis of $15,000, what are the tax consequences to Sandra if:
a. Sandra elects out of installment reporting?
b. Sandra reports her gain on the installment method?
a. Sandra elects out of installment reporting?
b. Sandra reports her gain on the installment method?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Cash Co. normally takes a physical count of inventory throughout the year. Due to some unexpected circumstances, it is unable to take a physical count at year end. Cash Co. wants to determine its ending inventory using estimates for shrinkage. It may do so if:
A) it normally uses this method to determine its inventory
B) it uses this method in conjunction with another method to verify actual amount
C) it normally takes a physical count on a routine basis
D) it may not use this estimating technique
A) it normally uses this method to determine its inventory
B) it uses this method in conjunction with another method to verify actual amount
C) it normally takes a physical count on a routine basis
D) it may not use this estimating technique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Xeno Corporation was formed in 2009 and adopted a calendar year. In 2012, it switched to a fiscal year beginning April 1. fte only available information is for January 1 through March 31. Taxable income for the three months was $23,000. Determine Xeno's tax liability for the short period. When is the short period's tax return due? Is there any relief available to Xeno Corporation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Sally sold a painting to Jenny for $2,500. Sally's adjusted basis in the painting was $1,000. Sally received $1,250 in the year of sale and $1,250 the next year. Since Sally knew Jenny she did not charge interest on the deferred payment, upon audit the IRS will:
A) impute interest at 6% on the deferred payment
B) impute interest at the applicable federal rate on the deferred payment
C) not impute any interest on the deferred payment
D) require Sally to recompute the contract with the current market interest rate
A) impute interest at 6% on the deferred payment
B) impute interest at the applicable federal rate on the deferred payment
C) not impute any interest on the deferred payment
D) require Sally to recompute the contract with the current market interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Builders Inc. entered into a contract to build a state-of-the art warehouse for Smith and Company for $18,000,000. Midway through the project, a dispute arose. fte dispute has not delayed the project; however, the dispute could affect the overall cost by $100,000. Builders Inc. uses the percentage-of¬completion method to account for its long-term contracts. Because of the dispute, Builders should:
A) revise its estimates, recompute previous years' income and file amended returns for each year
B) revise its estimates and base all subsequent income determinations on the new estimates
C) reduce income in the year the dispute arose
D) reduce income in the year the project is completed
A) revise its estimates, recompute previous years' income and file amended returns for each year
B) revise its estimates and base all subsequent income determinations on the new estimates
C) reduce income in the year the dispute arose
D) reduce income in the year the project is completed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
X Company has made sales throughout the year. If prices have been rising constantly throughout the year, then:
A) Taxable income will be lower under FIFO
B) Taxable income will be lower under LIFO
C) Taxable income will be lower under weighted average
D) Taxable income will be lower under specific identification
A) Taxable income will be lower under FIFO
B) Taxable income will be lower under LIFO
C) Taxable income will be lower under weighted average
D) Taxable income will be lower under specific identification

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In 2012, Bust Company requested and received permission from the IRS to switch its accounting method from the cash method to the accrual method. Taxable income in 2012 (computed under the accrual basis) was
$110,000. At the end of 2012, Bust had accounts receivable of $32,000, accounts payable of $27,000 and merchandise inventory of $10,000. Determine Bust Company's taxable income after all (if any) adjustments. Is any relief available to Bust Company?
$110,000. At the end of 2012, Bust had accounts receivable of $32,000, accounts payable of $27,000 and merchandise inventory of $10,000. Determine Bust Company's taxable income after all (if any) adjustments. Is any relief available to Bust Company?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Long Company entered into a contract to build an office building for $9,000,000. fte project is expected to be completed in two years at an estimated total cost of $6,000,000. Actual expenses incurred in each year were $2,000,000 and $3,000,000. fte income reported by Long Company for the first year would be:
A) $0 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed- contract method
B) $1,000,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method
C) $1,500,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method
D) $2,500,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method
A) $0 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed- contract method
B) $1,000,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method
C) $1,500,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method
D) $2,500,000 under the percentage-of-completion method and $0 under the completed-contract method

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 78 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



