Deck 13: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
1
Name the following symbol and identify the proper drafting dimensions A and B. 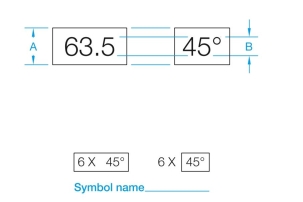

. 

2
Completely define the term basic dimension.
. A basic dimension is considered a theoretically perfect dimension. Basic dimensions are used to describe the theoretically exact size, profile, orientation, or location of a feature or datum target. These dimensions provide the basis from where permissible variations are established by tolerances on other dimensions, in notes, or in feature control frames.
3
Given the following symbols, provide the meaning of each symbol in the spaces to the right. 


4
Name the five types of geometric characteristic symbols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
List the five basic types of dimensioning and geometric tolerancing symbols.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Name each of the elements in the following feature control frame. 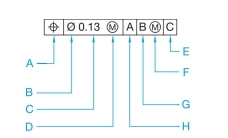


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What information is placed in the top half of the datum target symbol?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Label the symbol in the following application using the blank provided. 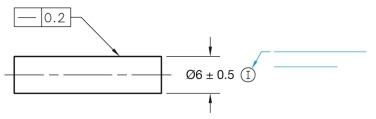


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Name each of the following geometric characteristic symbols. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Define datum plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Name the following symbols. 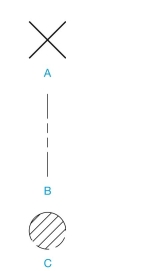


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Identify at least five locations where a feature control frame can be placed on a drawing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What information is placed in the lower half of the datum target symbol?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Any letter of the alphabet can be used to identify a datum ex- cept for , , and .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Define datum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Describe datum feature simulators. Include the term simu- lated datums in your description and give at least three ex- amples of datum feature simulators used in manufacturing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Name the following symbols and identify the proper draft- ing dimensions and features C through G and put symbol name at A and B. 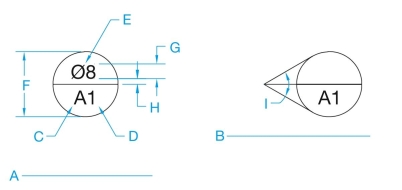


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Name the following symbol and identify the proper drafting dimensions B through F and put symbol name at A. 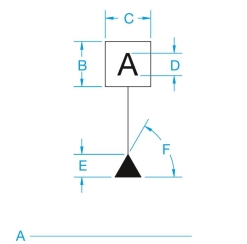


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Define datum feature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
How are basic dimensions shown on a drawing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Depending on the functional requirements of a part, more than one datum reference frame can be established. This is referred to as a(n) datum reference frame.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What does a movable datum target symbol indicate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The secondary datum plane must be established by at least point(s) on the secondary datum surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The tertiary datum plane must be established by at least point(s) on the tertiary datum surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When referring to the datum reference frame in the feature control frame, the datum is given first fol- lowed by the and datums. This is known as the datum .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Define actual mating envelope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
List at least five items that can be considered as datum fea- tures on an object or part.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Define tangent plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
How are datum target areas treated on a drawing when the target area is too small to draw?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Name the three datums of a complete datum reference frame.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How are datum target lines represented on a drawing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Describe how to properly display the symbols for a circular datum target area, a square datum target area, a rectangular datum target area, and a spherical datum target area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Define degrees of freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two or more surfaces that are on the same plane are re- ferred to as surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When a portion of a surface is used to establish a single da- tum, this is referred to as a(n) datum surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Define datum targets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The primary datum plane must be established by at least point(s) on the primary datum surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify the datum feature, the part, the simulated datum plane, the physical datum feature simulator, and the datum plane labeled A through F on the following illustration. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How is a datum target area represented on a drawing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify at least three required conditions for datum feature simulators.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Given the following drawing and a list of possible produced sizes, specify the geometric tolerance at each possible produced size. 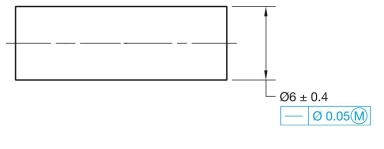


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements are true in regard to da- tum precedence and datum reference? (More than one can be true.) A) Datum precedence is established by the order of place- ment in the feature control frame. B) Datum precedence is established by alphabetical order of datum reference letters. 59728_ch13_EOC_ptg01.indd 4 2/3/16 2:21 PM C) The first datum listed in the feature control frame is the primary datum reference. D) "A" is always the primary datum. E) The third datum listed in the feature control frame is the tertiary datum reference. F) RMB is assumed unless otherwise specified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the difference between the circularity geometric tolerance and the cylindricity geometric tolerance?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the basic function of the continuous feature symbol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Given the following drawing and a list of possible produced sizes, specify the geometric tolerance at each possible produced size. 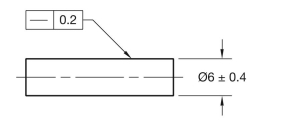


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Define form tolerances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Explain the difference between the methods used to repre- sent surface and axis straightness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Axis straightness can be specified on an MMC basis by plac- ing the MMC symbol after the geometric tolerance in the feature control frame. The specified geometric tolerance is held at the MMC produced size. Explain what happens to the geometric tolerance as the produced size departs from MMC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Given the following drawing and a list of possible produced sizes, specify the geometric tolerance at each possible pro- duced size. 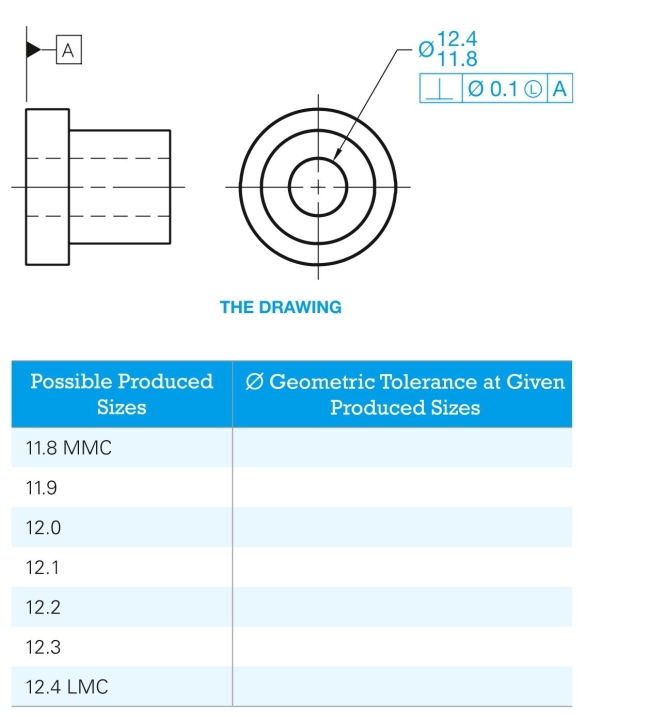


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define free state variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Define regardless of feature size (RFS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which geometric tolerance is characterized by any given cross section taken perpendicular to the axis of a cylinder or cone or through the common center of a sphere?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Give the proper abbreviation and definition for regardless of material boundary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Define restrained condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How is a feature control frame connected to a related fea- ture when surface control is intended?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Given the following drawing and a list of possible produced sizes, specify the geometric tolerance at each possible pro- duced size. 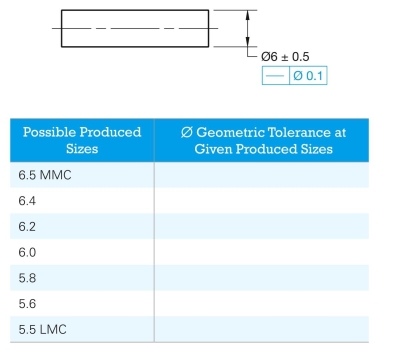


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What geometric tolerance establishes the distance between two parallel planes within which the surface must lie?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Define perfect form boundary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How is an axis geometric control specified?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Name the geometric tolerance that specifies a zone within which the required surface element or axis must lie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Define true position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Give the formulas for internal and external features that can be used when calculating the positional tolerance at any produced size when LMC is applied to the positional tolerance. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A(n) geometric tolerance zone is established by two parallel planes at any specified basic angle, other than 908, to a datum plane or axis. The specified angle must be , and it must be dimensioned from the plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How is the feature control frame placed in relation to a hole and counterbore when the positional tolerance is the same for the hole and counterbore?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A tolerance is established by a geometric tolerance zone made up of two parallel planes that are a basic 908 to a given datum plane or axis where the actual surface must lie.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What does it mean when a feature control frame with a par- allelism geometric characteristic symbol is placed below a diameter dimension?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Give the formulas for calculating the slot boundary when applying positional tolerancing to slotted features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Define perpendicularity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Given the following drawing, a reference chart showing a range of possible produced sizes, and four optional feature control frames that can be applied to the diameter dimen- sion, provide the positional tolerance at each possible pro- duced size for each feature control frame application. 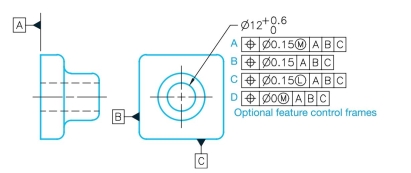


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When the axis of a hole is at an extreme angle inside the positional tolerance zone, it is referred to as .

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe when composite positional tolerancing is used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Define tangent plane and describe the relationship among the actual surface, the tangent plane, and the geometric tolerance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Define radial element and describe how a radial element specification is applied to a drawing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Given the following drawing, a reference chart showing a range of possible produced sizes, and three optional feature control frames that can be applied to the diameter dimension, provide the geometric tolerance at each possible produced size for each feature control frame application. 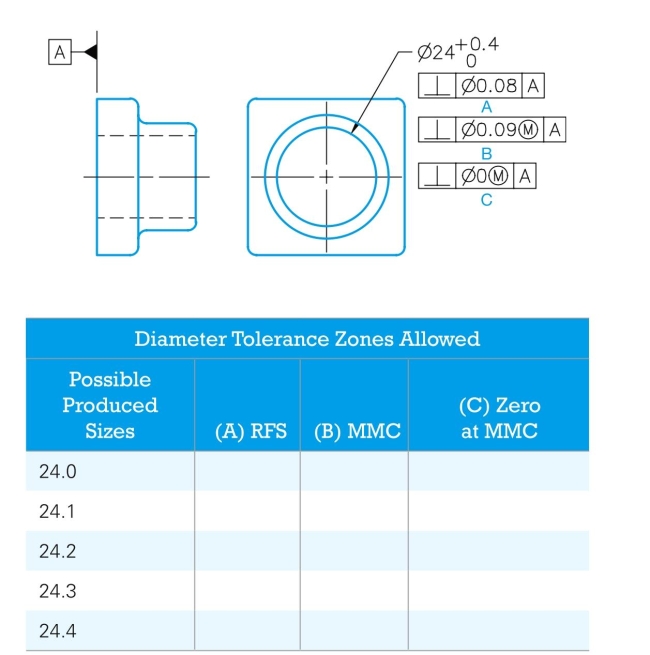


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Give the formulas for internal and external features that can be used when calculating the positional tolerance at any produced size when MMC is applied to the positional tolerance. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Name the two types of dimensioning systems that are nor- mally used when locating multiple features.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Calculate the minimum edge distance or minimum wall thickness between the edge of a hole and the outside surface of the part for an LMC positional tolerance application given the following information (dimensions are in millimeters). 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Define parallelism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Describe the purpose of location tolerances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When using composite positional tolerancing, the upper part of the feature control frame is referred to as the and specifies the larger tolerance for the pat- tern of features as a group, while the lower half of the frame is called the and specifies a smaller positional tolerance for individual features within the pattern.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



