Deck 1: Atoms and Molecules; Orbitals and Bonding
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Atoms and Molecules; Orbitals and Bonding
1
Indicate which of the species shown are expected to have a net dipole moment.
A)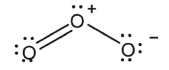
B)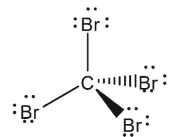
C)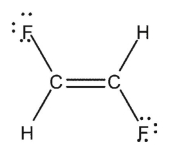
D)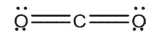
E)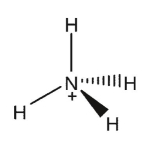
A)

B)

C)

D)
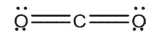
E)


2
Which of the following statements about atomic orbitals is false?
A) A 1 s orbital is spherically symmetrical.
B) An atomic orbital may contain zero, one, or two electrons.
C) A 2s orbital and a 2p orbital are equal in energy.
D) A 2px orbital and a 2py orbital are equal in energy.
E) A 2 p orbital is not spherically symmetrical.
A) A 1 s orbital is spherically symmetrical.
B) An atomic orbital may contain zero, one, or two electrons.
C) A 2s orbital and a 2p orbital are equal in energy.
D) A 2px orbital and a 2py orbital are equal in energy.
E) A 2 p orbital is not spherically symmetrical.
A 2s orbital and a 2p orbital are equal in energy.
3
Which of the following molecules has a net dipole moment?
A)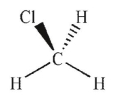
B)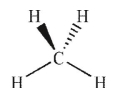
C)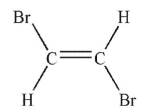
D)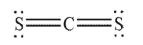
E)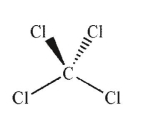
A)

B)

C)

D)
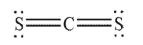
E)


4
What is the total number of occupied p orbitals in a neutral phosphorus atom?
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9
E)12
A)2
B)3
C)6
D)9
E)12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following statements accurately describes the node(s) in a 2 p orbital?
A) There are zero nodes in a 2 p orbital.
B) A 2 p orbital has one spherical node.
C) A 2 p orbital has one nodal plane.
D) A 2 p orbital has one spherical node and one nodal plane.
E) A 2 p orbital has two spherical nodes.
A) There are zero nodes in a 2 p orbital.
B) A 2 p orbital has one spherical node.
C) A 2 p orbital has one nodal plane.
D) A 2 p orbital has one spherical node and one nodal plane.
E) A 2 p orbital has two spherical nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In which of the following Lewis structures does the nitrogen atom have a formal charge of 1+?
A)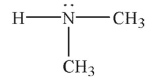
B)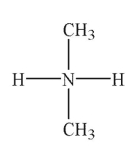
C)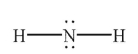
D)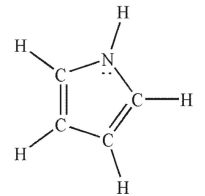
E)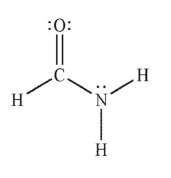
A)

B)

C)
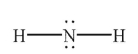
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following Lewis structures shows an incorrectly drawn bond dipole?
A)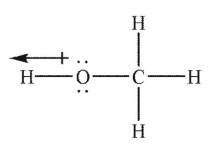
B)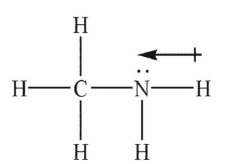
C)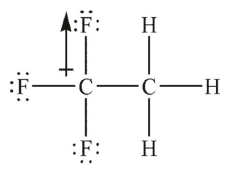
D)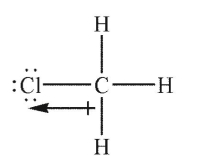
E)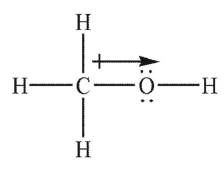
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following structures is the best Lewis structure for hypochlorous acid, HOCl?
A)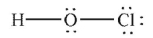
B)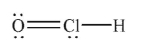
C)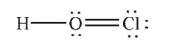
D)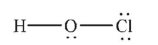
E)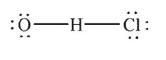
A)
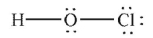
B)
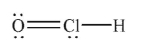
C)
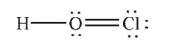
D)
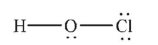
E)
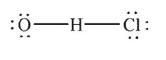

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following resonance forms would be expected to be the most important contributor for the anionic species?
A)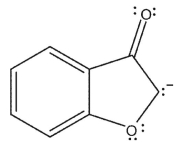
B)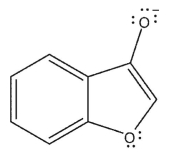
C)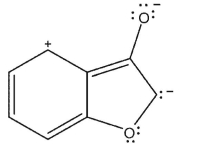
D)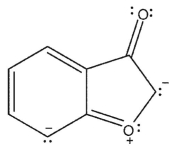
E)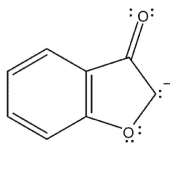
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the Lewis structures shown below is incorrect?
A)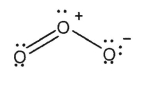
B)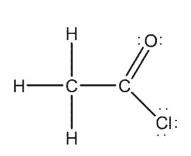
C)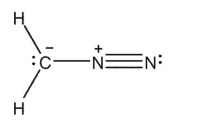
D)
E)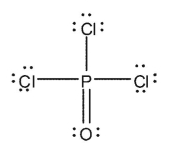
A)

B)

C)
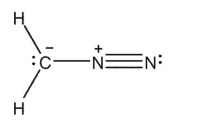
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which one of the following sets of quantum numbers is impossible?
A) n=1, l=0, ml=0, s=+1 / 2
B) n=1, l=1, ml=0, s=+1 / 2
C) n=2, l=1, ml=1, s=+1 / 2
D) n=2, l=1, ml=-1, s=-1 / 2
E) n=3, l=0, ml=0, s=-1 / 2
A) n=1, l=0, ml=0, s=+1 / 2
B) n=1, l=1, ml=0, s=+1 / 2
C) n=2, l=1, ml=1, s=+1 / 2
D) n=2, l=1, ml=-1, s=-1 / 2
E) n=3, l=0, ml=0, s=-1 / 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following Lewis structures contains an oxygen atom with a 1+ formal charge?
A)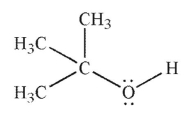
B)
C)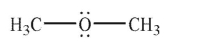
D)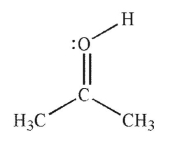
E)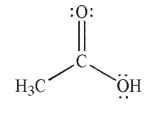
A)

B)

C)
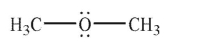
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following statements accurately describes the node(s) in a 2 s orbital?
A) There are zero nodes in a 2 s orbital.
B) A 2 s orbital has one spherical node.
C) A 2 s orbital has one nodal plane.
D) A 2 s orbital has one spherical node and one nodal plane.
E) A 2 s orbital has two spherical nodes.
A) There are zero nodes in a 2 s orbital.
B) A 2 s orbital has one spherical node.
C) A 2 s orbital has one nodal plane.
D) A 2 s orbital has one spherical node and one nodal plane.
E) A 2 s orbital has two spherical nodes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In which of the following structures does the carbon atom have a formal charge that is not zero?
A)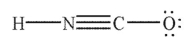
B)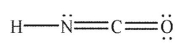
C)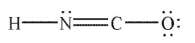
D)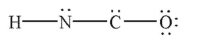
E) Both c and d
A)
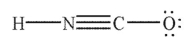
B)
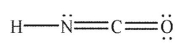
C)

D)
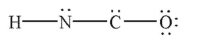
E) Both c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following arrow conventions is used to show the relationship of two chemical species as resonance structures?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)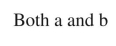
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Ionization potential decreases going across a row left to right.
B)Ionization potential increases going down a group.
C)Electron affinity increases going across a row left to right.
D)Electron affinity increases going down a group.
E)Atoms with high ionization potentials have correspondingly high electron affinities.
A)Ionization potential decreases going across a row left to right.
B)Ionization potential increases going down a group.
C)Electron affinity increases going across a row left to right.
D)Electron affinity increases going down a group.
E)Atoms with high ionization potentials have correspondingly high electron affinities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
d-orbitals have two nodal planes. How many spherical nodes will a 5 d orbital contain?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The rule or principle that states that the electronic state with the greatest number of unpaired spins will have the lowest energy is called
A)the Pauli principle
B)the aufbau principle
C)the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
D)Hund's rule
E)the octet rule
A)the Pauli principle
B)the aufbau principle
C)the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
D)Hund's rule
E)the octet rule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the formal charge on the oxygen atom in each of the following Lewis structures? 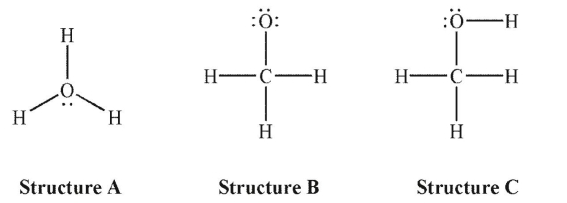
A) A: 0, B: 1-, C: 1+
B) A: 1+, B: 1-, C: 0
C) A: 1-, B: 1+, C: 0
D) A: 1-, B: 1-, C: 1-
E) A: 1+, B: 1+, C: 1-

A) A: 0, B: 1-, C: 1+
B) A: 1+, B: 1-, C: 0
C) A: 1-, B: 1+, C: 0
D) A: 1-, B: 1-, C: 1-
E) A: 1+, B: 1+, C: 1-

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these sets of quantum numbers would define an electron in the 5d subshell?
A) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-3, s=1 / 2
B) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-2, s=1 / 2
C) n=5 ; l=4, ml=-2, s=-1 / 2
D) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-2, s=1
E) n=5 ; l=1, ml=0, s=-1 / 2
A) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-3, s=1 / 2
B) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-2, s=1 / 2
C) n=5 ; l=4, ml=-2, s=-1 / 2
D) n=5 ; l=2, ml=-2, s=1
E) n=5 ; l=1, ml=0, s=-1 / 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements about the molecular orbital diagram for H2- is false?
A) There are two atomic orbitals that mix to produce molecular orbitals.
B) There is one bonding molecular orbital.
C) There is one antibonding molecular orbital.
D) All bonding orbitals are occupied.
E) All antibonding orbitals are unoccupied.
A) There are two atomic orbitals that mix to produce molecular orbitals.
B) There is one bonding molecular orbital.
C) There is one antibonding molecular orbital.
D) All bonding orbitals are occupied.
E) All antibonding orbitals are unoccupied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following pairs are related as resonance structures? All nonzero formal charges are shown.
A)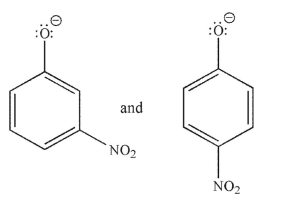
B)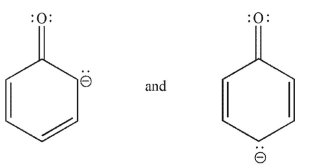
C)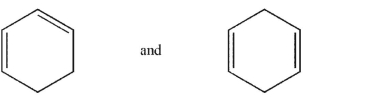
D)
E)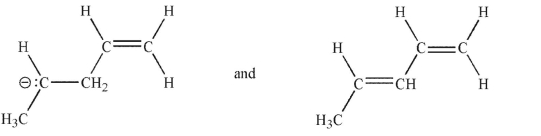
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)
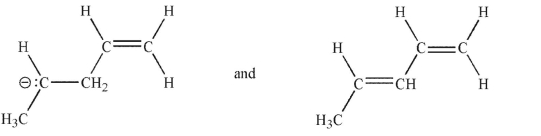

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
How many antibonding molecular orbitals are generated from combining one 2 p orbital on nitrogen and one 2 p orbital on carbon?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which two of the following structures are equivalent resonance contributors? 
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) B and C
D) A and D
E) All the structures are equivalent.

A) A and B
B) A and C
C) B and C
D) A and D
E) All the structures are equivalent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following molecular orbitals is the highest in energy? (All were generated by the mixing of four 2p orbitals.)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) All four orbitals shown are equal in energy.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E) All four orbitals shown are equal in energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A certain orbital interaction diagram has four bonding molecular orbitals and four antibonding molecular orbitals. How many atomic orbitals were mixed to create all these orbitals?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
E) It cannot be determined from the information given.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 16
E) It cannot be determined from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the orbital interaction diagram for ground state H2, how many electrons occupy the antibonding molecular orbital?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the structures shown is not related to Structure A as a resonance contributor? 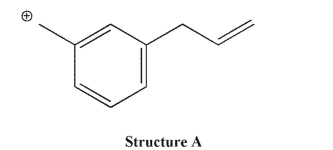
A)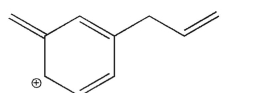
B)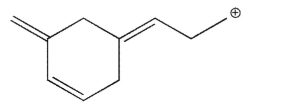
C)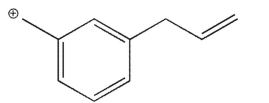
D)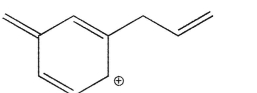
E)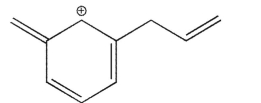

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Explain what is meant by the term quantized as it applies to the energy of an electron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Define the term node as it applies to an orbital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following pairs are not related as resonance structures?
A)
B)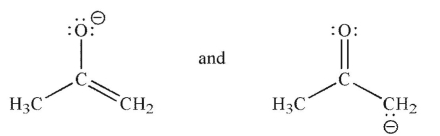
C)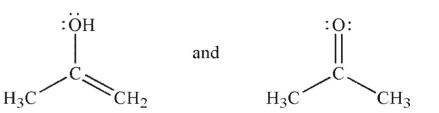
D)
E)
A)
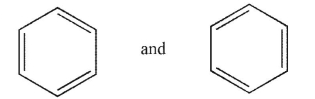
B)
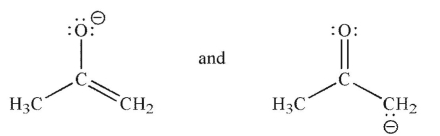
C)
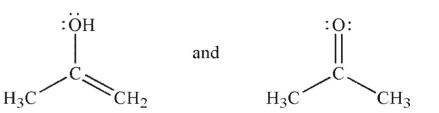
D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the relationship between the principal quantum number n and the number of nodes in an orbital?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements is true about Lewis acids and bases?
A)Lewis acids are also called nucleophiles.
B)A Lewis base always accepts a proton from a Lewis acid.
C)The interaction between a Lewis acid and a Lewis base leads to a covalent bond.
D)A Lewis base accepts an electron pair from a Lewis acid.
E)Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of a Lewis acid/base pair.
A)Lewis acids are also called nucleophiles.
B)A Lewis base always accepts a proton from a Lewis acid.
C)The interaction between a Lewis acid and a Lewis base leads to a covalent bond.
D)A Lewis base accepts an electron pair from a Lewis acid.
E)Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of a Lewis acid/base pair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A student wrote the following electron configuration for a ground state, neutral nitrogen atom: 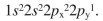 Explain why the configuration does not describe the lowest energy state of a ground-state nitrogen atom and provide the lowest-energy electron configuration for nitrogen.
Explain why the configuration does not describe the lowest energy state of a ground-state nitrogen atom and provide the lowest-energy electron configuration for nitrogen.
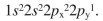 Explain why the configuration does not describe the lowest energy state of a ground-state nitrogen atom and provide the lowest-energy electron configuration for nitrogen.
Explain why the configuration does not describe the lowest energy state of a ground-state nitrogen atom and provide the lowest-energy electron configuration for nitrogen.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of these orbital interactions would be expected to form a covalent bond with the highest BDE?
A) H atom 1 s with H+cation 1 s
B) He atom 1 s with He atom 1 s
C) He atom 1 s with H atom 1 s
D)H+cation 1 s with He+ cation 1 s
E) H+cation 1 s with He atom 1 s
A) H atom 1 s with H+cation 1 s
B) He atom 1 s with He atom 1 s
C) He atom 1 s with H atom 1 s
D)H+cation 1 s with He+ cation 1 s
E) H+cation 1 s with He atom 1 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How many molecular orbitals are generated from combining one 2 p orbital on carbon and one 2 p orbital on oxygen?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
How many values can ml have for quantum number l=5 ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Write the lowest-energy electron configuration for a neutral, ground-state oxygen atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Each of the chemical events shown represents a mechanistic step in a reaction you will learn this semester.Which of the following pictures represents the heterolytic cleavage of a carbon-oxygen
Bond?
A)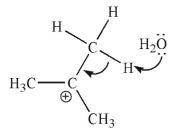
B)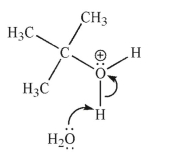
C)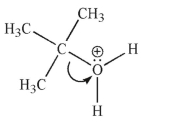
D)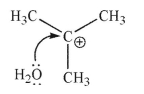
E)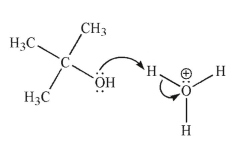
Bond?
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
State the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Draw a Lewis structure for methyl anion, -CH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Is forming a bond between an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom endothermic or exothermic? Briefly explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For each molecule shown, indicate whether the molecule is polar by drawing a dipole arrow  pointing towards the negative end of the molecule.
pointing towards the negative end of the molecule.
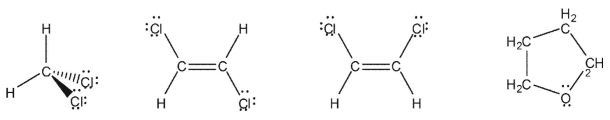
 pointing towards the negative end of the molecule.
pointing towards the negative end of the molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The carbon-nitrogen bond in formamide, HCONH2, has been shown to have a bond length that is in between a typical C-N single bond and a typical C-N double bond. Provide an explanation to account for this observation, using relevant structures as support.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The Lewis structure of the anion shown has an additional resonance structure that is a more important representation for this anion.Draw the better resonance contributor, using curved arrow formalism to show how the new structure is obtained from the original structure. 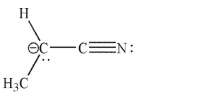


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Using curved arrow formalism, show the homolytic cleavage of the O-O bond in dimethyl peroxide. Draw the products of the reaction, including all lone pairs and unpaired electrons.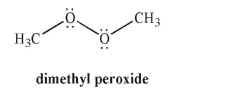


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use an orbital interaction diagram to provide an explanation for the fact that diatomic helium, He2, does not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Draw Lewis structures for the following compounds.Show all nonbonding electrons and indicate the formal charge on any atom that has a nonzero charge. 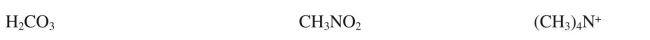
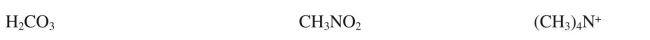

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Beryllium hydride (BeH2) is a linear molecule with two perpendicular p-orbitals on the beryllium atom:
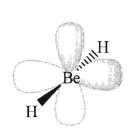
An s-orbital approaching BeH2 will only be able to interact with one of the two p-orbitals; explain why.

An s-orbital approaching BeH2 will only be able to interact with one of the two p-orbitals; explain why.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the orbital interaction diagram for H2 shown here, label the atomic orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital, and the antibonding molecular orbital.
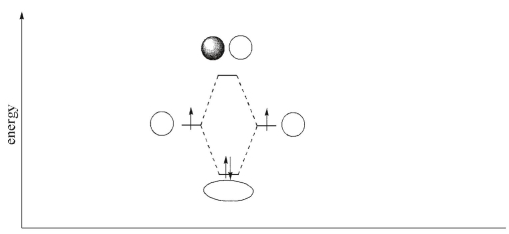


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following resonance structures is the least important contributor to the resonance hybrid, and why? 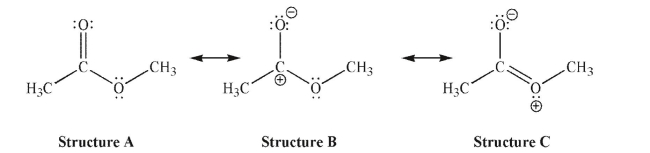


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Draw a Lewis structure for methyl cation, +CH3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Using the Lewis structure of acetaldehyde shown, draw an additional reasonable resonance contributor.Show the conversion of the original structure to your new structure using curved arrow formalism.Include all lone pairs of electrons and nonzero formal charges in the new
structure.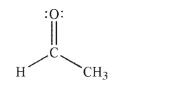
structure.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Draw a Lewis structure for acetamide, CH3CONH2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the bond dissociation energies given to estimate the enthalpy change, ΔH°, of the following reaction.
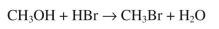
Bond dissociation energies (kcal/mol): C-O, 92; H-Br, 88; O-H, 119; C-Br, 72.
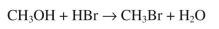
Bond dissociation energies (kcal/mol): C-O, 92; H-Br, 88; O-H, 119; C-Br, 72.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Lewis structure shown has an additional resonance contributor.Draw this contributor and determine which structure is a better contributor to the resonance hybrid.Provide a brief
explanation for your choice.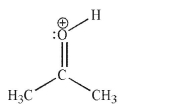
explanation for your choice.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Draw an orbital interaction diagram for a pair of 2 p orbitals interacting in a side-by-side manner. Draw the atomic orbitals and the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals and indicate the relative energy levels of all orbitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A molecule called boron trifluoride etherate has the formula BF3O(CH2CH3)2. Draw a Lewis structure for this molecule, including all nonzero formal charges and lone pairs of electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Draw a resonance form for each of the following species that would be expected to be a better contributor.Use curved arrows to show the "movement" of electrons and double-headed arrows between the resonance structures. 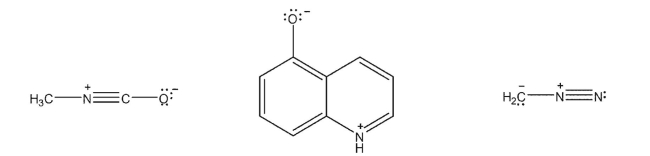


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Applying the aufbau principle and Hund's rule, construct the electronic configuration of the element nitrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The reaction shown here is an example of one you will learn later in the course.Identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in the reaction. 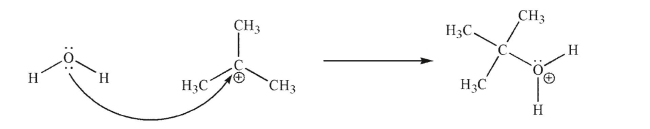
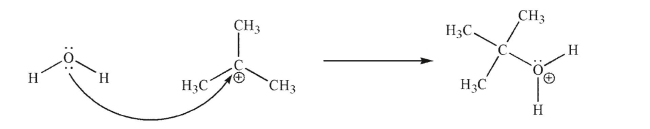

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Identify the nucleophile and the electrophile in the following reaction and draw the product of the reaction. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Define the term Lewis base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Draw a molecular orbital diagram showing the formation of a sigma-bond between the vacant 2p orbital on boron in BH3 and the filled 1s orbital of the hydride anion to form the borohydride anion:
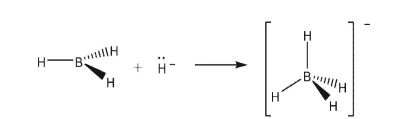


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 64 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



