Deck 20: Special Topic: Carbohydrates
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Special Topic: Carbohydrates
1
Which of the structures shown here are 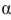 -anomers of D-sugars?
-anomers of D-sugars?
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) I, III, and IV
E) all
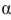 -anomers of D-sugars?
-anomers of D-sugars?
A) I
B) II
C) III and IV
D) I, III, and IV
E) all
II
2
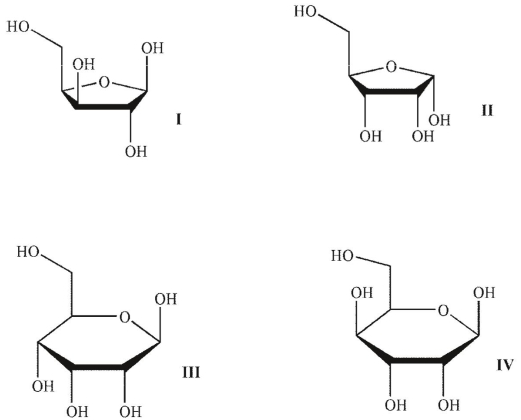
Consider the structures shown and complete the sentence. 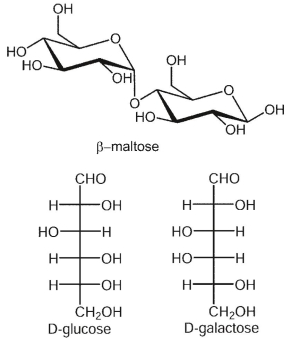
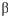 - Maltose is a disaccharide, which is formed by
- Maltose is a disaccharide, which is formed by
A) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by an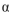 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage.
B) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by a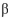 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage.
C) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by a 1-6 linkage.
D) an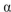 -1-4 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of D-glucose and C-4 atom of galactose.
-1-4 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of D-glucose and C-4 atom of galactose.
E) a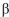 -1-6 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of L-glucose and C-6 atom of D-glucose .
-1-6 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of L-glucose and C-6 atom of D-glucose .

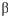 - Maltose is a disaccharide, which is formed by
- Maltose is a disaccharide, which is formed byA) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by an
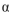 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage.B) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by a
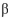 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage.C) two molecules of D-glucose, joined by a 1-6 linkage.
D) an
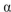 -1-4 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of D-glucose and C-4 atom of galactose.
-1-4 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of D-glucose and C-4 atom of galactose.E) a
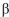 -1-6 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of L-glucose and C-6 atom of D-glucose .
-1-6 linkage between C-1 atom of molecule of L-glucose and C-6 atom of D-glucose . two molecules of D-glucose, joined by an 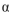 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage.
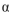 -1-4 linkage.
-1-4 linkage. 3
What is the product of the following reaction?
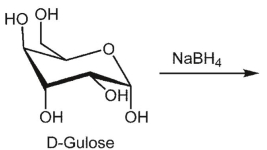
A)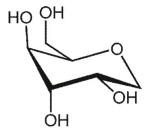
B)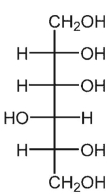
C)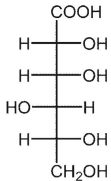
D)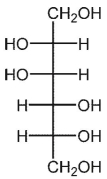
E)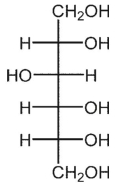

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


4
Which of the following structures corresponds to the Fischer projection shown?
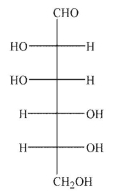
A)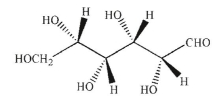
B)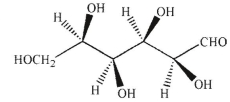
C)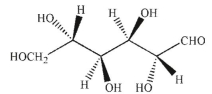
D)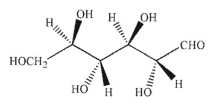
E)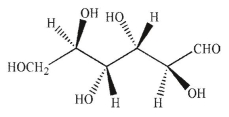

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
D-Glucose was treated with calcium hydroxide in aqueous solution.What is the product of this reaction?
A)calcium gluconate
B)L-glucose
C)no reaction occurs
D)D-fructose
E)a mixture consisting mainly of D-glucose and D-fructose
A)calcium gluconate
B)L-glucose
C)no reaction occurs
D)D-fructose
E)a mixture consisting mainly of D-glucose and D-fructose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements about mutarotation of sugars is false?
A) Mutarotation of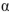 -glucopyranose in water results in a mixture of
-glucopyranose in water results in a mixture of 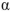 -glucopyranose and
-glucopyranose and 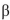 - glucopyranose.
- glucopyranose.
B)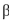 -Glucopyranose is the predominant form in water.
-Glucopyranose is the predominant form in water.
C) Mutarotation can only happen in basic media.
D) Mutarotation proceeds via an open-chain form of a carbohydrate.
E) I-O -Methyl-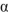 -glucopyranose does not ungergo mutarotation.
-glucopyranose does not ungergo mutarotation.
A) Mutarotation of
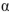 -glucopyranose in water results in a mixture of
-glucopyranose in water results in a mixture of 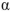 -glucopyranose and
-glucopyranose and 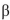 - glucopyranose.
- glucopyranose.B)
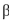 -Glucopyranose is the predominant form in water.
-Glucopyranose is the predominant form in water.C) Mutarotation can only happen in basic media.
D) Mutarotation proceeds via an open-chain form of a carbohydrate.
E) I-O -Methyl-
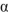 -glucopyranose does not ungergo mutarotation.
-glucopyranose does not ungergo mutarotation.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
D-glucaric acid can also be named L-gularic acid.Complete the sentence. D-glucitol and L-gulitol are ____________
A)identical compounds.
B)enantiomers.
C)epimers.
D)diastereomers, but not epimers.
E)compounds whose relationship cannot be deduced from the facts provided above.
A)identical compounds.
B)enantiomers.
C)epimers.
D)diastereomers, but not epimers.
E)compounds whose relationship cannot be deduced from the facts provided above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following sugars would produce the same osazone?
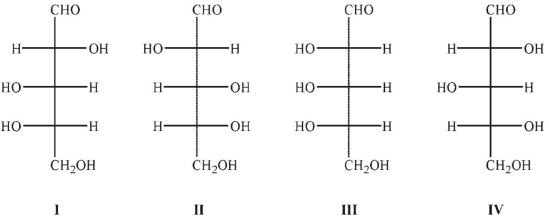
A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV

A) I and II
B) I and III
C) II and III
D) II and IV
E) III and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Predict the product of the following reaction conditions.

A)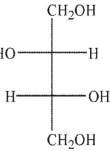
B)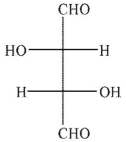
C)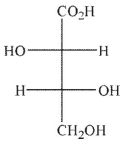
D)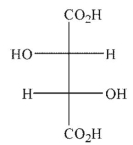
E)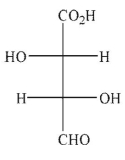

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the product of the following oxidation of D-altrose?
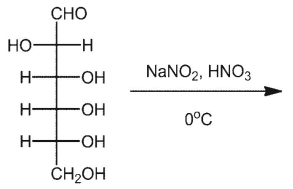
A)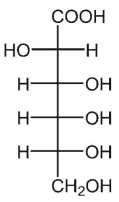
B)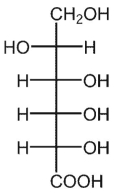
C)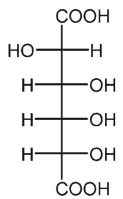
D)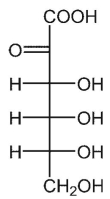
E)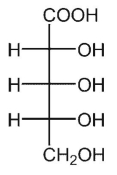

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of these structures is  -L-arabinose? The Fischer projection of L -arabinose is shown.
-L-arabinose? The Fischer projection of L -arabinose is shown.
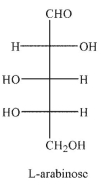
A)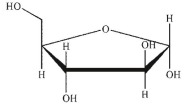
B)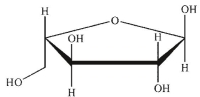
C)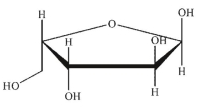
D)
E)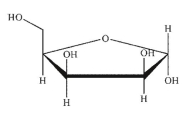
 -L-arabinose? The Fischer projection of L -arabinose is shown.
-L-arabinose? The Fischer projection of L -arabinose is shown.
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following sugars is a ketopentose?
A)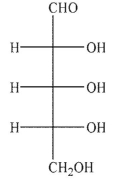
B)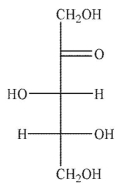
C)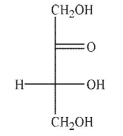
D)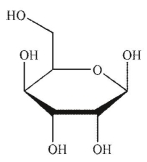
E)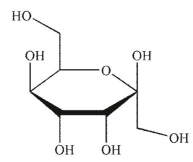
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which pair of structures represents the same stereoisomer?
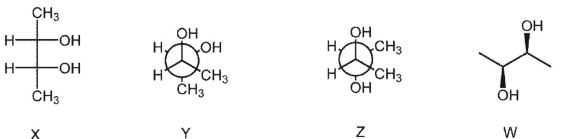
A) X and Y
B) Y and Z
C) Z and W
D) X and Z
E) Y and W

A) X and Y
B) Y and Z
C) Z and W
D) X and Z
E) Y and W

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following structures would be a product of the conditions shown?
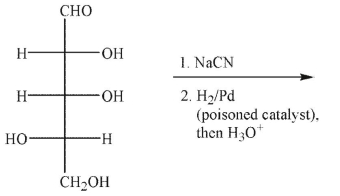
A)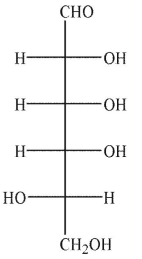
B)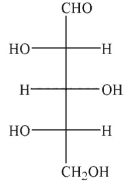
C)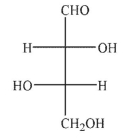
D)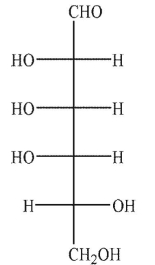
E)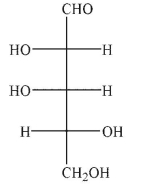

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the product of the following reaction?
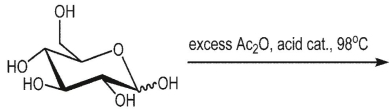
A)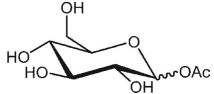
B)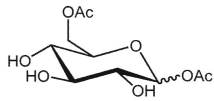
C)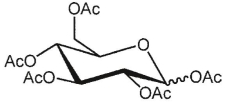
D)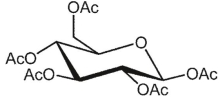
E)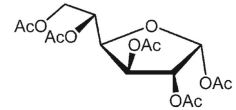

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following sugars is an aldotetrose?
A)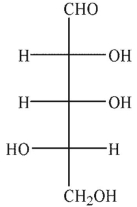
B)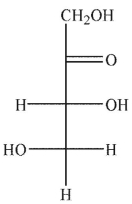
C)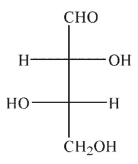
D)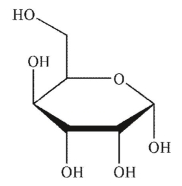
E)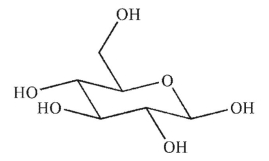
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An aldopentose is oxidized with sodium nitrite and nitric acid to produce an optically active aldaric acid.The same aldopentose is treated with Ruff degradation conditions and the product is Reduced with sodium borohydride to give an optically inactive alditol.Which of the following Structures is the aldopentose?
A)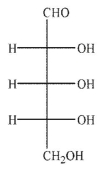
B)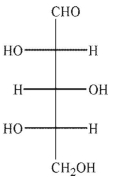
C)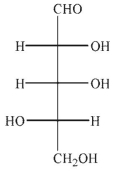
D)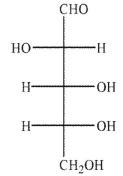
E)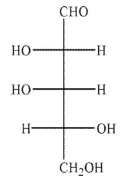
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is the correct name for this structure? (The Fischer projections of D-gulose and L-gulose are shown.)
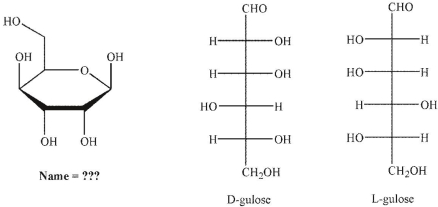
A)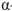 -D-gulofuranose
-D-gulofuranose
B)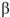 -D-gulopyranose
-D-gulopyranose
C)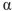 -D-gulofuranose
-D-gulofuranose
D)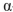 -L-gulofuranose
-L-gulofuranose
E)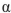 -D-gulopyranose
-D-gulopyranose

A)
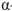 -D-gulofuranose
-D-gulofuranoseB)
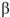 -D-gulopyranose
-D-gulopyranoseC)
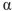 -D-gulofuranose
-D-gulofuranoseD)
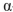 -L-gulofuranose
-L-gulofuranoseE)
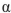 -D-gulopyranose
-D-gulopyranose
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following structures are furanose forms?
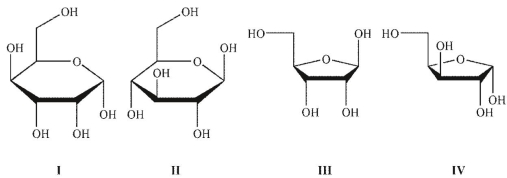
A) I and IV
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) III and IV
E) none of these structures

A) I and IV
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) III and IV
E) none of these structures

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the Fischer projections corresponds to the following structure?
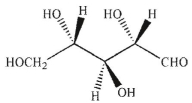
A)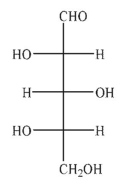
B)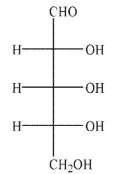
C)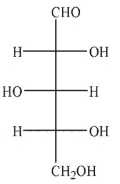
D)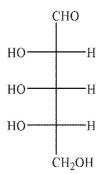
E)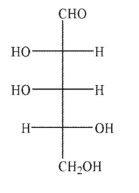

A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Predict the product of the following reaction 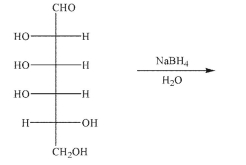


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ketosaccharides, such as fructose, are generally considered nonreducing sugars, since they lack a
free aldehyde group in an open-chain form.However, in strongly basic media fructose reacts with
copper-based oxidants, thus exhibiting the reducing sugar properties.Explain this phenomenon.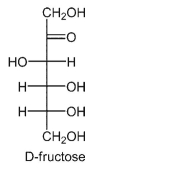
free aldehyde group in an open-chain form.However, in strongly basic media fructose reacts with
copper-based oxidants, thus exhibiting the reducing sugar properties.Explain this phenomenon.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A certain aldotetrose, A , produces an optically active aldaric acid on oxidation with sodium nitrite and nitric acid. When A is subjected to modified Kiliani-Fischer conditions, two compounds are produced, B and C . On sodium borohydride reduction, B yields an optically inactive alditol, while C gives an optically active alditol. The configurational carbon in A,B , and C matches that of R -glyceraldehyde. What are the structures of A, B , and C ?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Even though glucose is an aldose, its 1H NMR spectrum shows virtually no signal for the aldehyde proton. Explain this fact.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Draw a Fischer projection of the compound below, placing the most oxidized carbon on top.
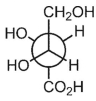


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Draw a Fischer projection for the sugar shown.
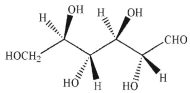


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Draw the structure of the product that would result when D-allose is subjected to the conditions shown.
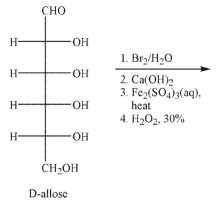


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Two L-aldohexoses, A and B, are subjected to oxidation with sodium nitrite and nitric acid.A
gives an optically active aldaric acid, while B gives an optically inactive aldaric acid.When A and
B are reduced with sodium borohydride, A produces an optically active alditol, and B produces an
optically inactive alditol.Ruff degradation of either A or B gives the same compound.What are
the structures of A and B?
gives an optically active aldaric acid, while B gives an optically inactive aldaric acid.When A and
B are reduced with sodium borohydride, A produces an optically active alditol, and B produces an
optically inactive alditol.Ruff degradation of either A or B gives the same compound.What are
the structures of A and B?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is a complete IUPAC name for this form of galactose?
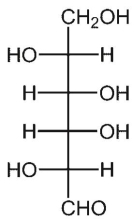


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is a complete IUPAC name for this form of talose?
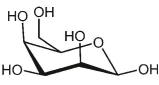


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
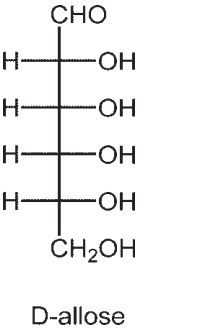
The structure of D-allose is shown below. Draw the most thermodynamically stable anomer of D-allopyranose. Is it 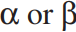 ?
?
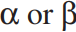 ?
?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the product of the following reaction? 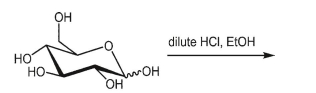


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Predict the product of the following transformation. 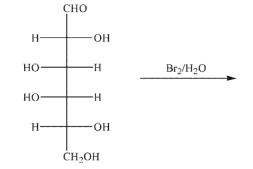


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is a complete IUPAC name for this form of galactose?
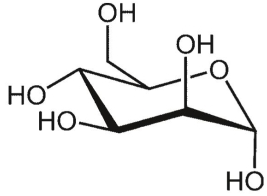


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Xylobiose is a disaccharide consisting of two D-xylopyranose units in a 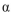 linkage between C-1 of one unit and C-4 of the other. Draw xylobiose using Haworth projections. The structure of D-xylose is provided.
linkage between C-1 of one unit and C-4 of the other. Draw xylobiose using Haworth projections. The structure of D-xylose is provided.
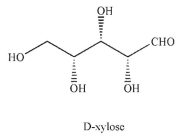
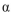 linkage between C-1 of one unit and C-4 of the other. Draw xylobiose using Haworth projections. The structure of D-xylose is provided.
linkage between C-1 of one unit and C-4 of the other. Draw xylobiose using Haworth projections. The structure of D-xylose is provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A sugar was subjected to the reaction conditions shown. Draw the structure of the products of these conditions.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
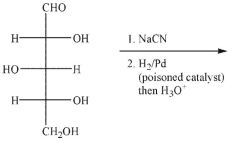
Either of two sugars could have been the starting material for a Ruff degradation to produce the
monosaccharide shown here.Draw Fischer projections of these two sugars.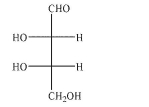
monosaccharide shown here.Draw Fischer projections of these two sugars.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Predict the product of the following reaction conditions. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw the structure of the sugar that underwent the indicated conditions to produce these two
products.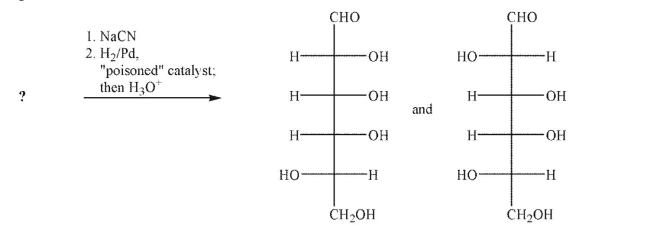
products.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Draw the structure of alpha-D-ribofuranose.The Fischer projection for D-ribose is shown. 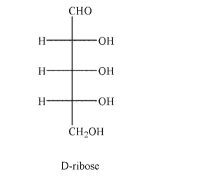


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



