Deck 22: Special Topic: Amino Acids and Polyamino Acids Peptides and Proteins
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Special Topic: Amino Acids and Polyamino Acids Peptides and Proteins
1
Which of the following residues does not appear in RNA?
A)C
B)A
C)G
D)T
E)U
A)C
B)A
C)G
D)T
E)U
T
2
Which of these structurs is alanine?
A)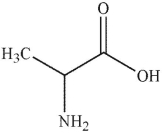
B)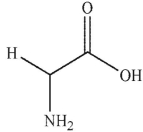
C)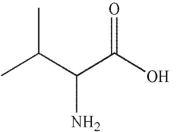
D)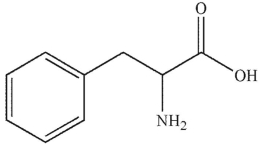
E)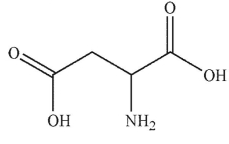
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


3
A sample of a mixture containing lysine, glutamic acid, cysteine, and histidine is placed on a piece of paper moistened with a solution at pH 5.0 . An electrical field is then applied across the paper to separate the amino acids (electrophoresis). Starting from a position closest to the anode and proceeding toward the cathode, what amino acids would be encountered?
A) Glu, Cys, His, Lys
B) Lys, His, Cys, Glu
C) Cys, His, Glu, Lys
D) His, Glu, Cys, Lys
E) Cys, Glu, His, Lys
A) Glu, Cys, His, Lys
B) Lys, His, Cys, Glu
C) Cys, His, Glu, Lys
D) His, Glu, Cys, Lys
E) Cys, Glu, His, Lys
Glu, Cys, His, Lys
4
What is the name for this peptide? 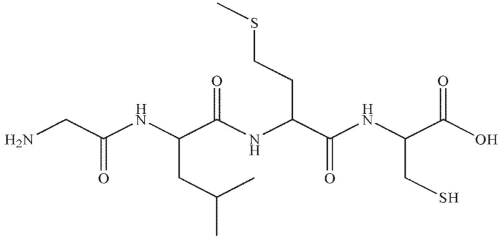
A) Gly-Leu-Met-Cys
B) Ala-Leu-Met-Cys
C) Ala-Ile-Cys-Met
D) Gly-Ile-Cys-Met
E) Ile-Met-Cys

A) Gly-Leu-Met-Cys
B) Ala-Leu-Met-Cys
C) Ala-Ile-Cys-Met
D) Gly-Ile-Cys-Met
E) Ile-Met-Cys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement is true?
A)Kinetic resolution is used to separate diastereomeric amino acids.
B)Optically inactive alkaloids are used to convert two enantiomeric amino acids into two diastereomeric ammonium salts.
C)A racemic mixture of amino acids can be separated by enzymatically modifying either the D- or L-amino acid in such a way that it can be separated from the other.
D)D-amino acids are more prevalent in nature than L-amino acids.
E)A racemic mixture of amino acids can be separated by fractional crystallization.
A)Kinetic resolution is used to separate diastereomeric amino acids.
B)Optically inactive alkaloids are used to convert two enantiomeric amino acids into two diastereomeric ammonium salts.
C)A racemic mixture of amino acids can be separated by enzymatically modifying either the D- or L-amino acid in such a way that it can be separated from the other.
D)D-amino acids are more prevalent in nature than L-amino acids.
E)A racemic mixture of amino acids can be separated by fractional crystallization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The isoelectric point 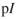 for an artificial amino acid is 6.2 and the
for an artificial amino acid is 6.2 and the 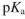 of its carboxyl group is 2.4 . What is the
of its carboxyl group is 2.4 . What is the 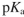 of its ammonium group?
of its ammonium group?
A) 10.0
B) 8.6
C) 3.8
D) 9.4
E) 4.3
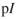 for an artificial amino acid is 6.2 and the
for an artificial amino acid is 6.2 and the 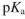 of its carboxyl group is 2.4 . What is the
of its carboxyl group is 2.4 . What is the 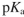 of its ammonium group?
of its ammonium group?A) 10.0
B) 8.6
C) 3.8
D) 9.4
E) 4.3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The first Merrifield machine produced a 125 amino acid peptide with an overall yield of 17%. What was the average yield of each step in this synthesis?
A)83.0%
B)96.8%
C)99.8%
D)98.6%
E)The average yield cannot be determined.
A)83.0%
B)96.8%
C)99.8%
D)98.6%
E)The average yield cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of these structures correctly shows proline at pH=7 ? The pKa values for the carboxylic acid and amine group in proline are 2.0 and 10.6 , respectively.
A)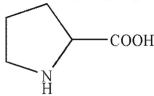
B)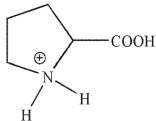
C)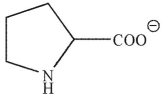
D)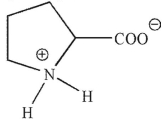
E)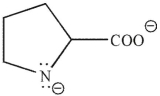
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of these is the correct Fischer projection for L-serine?
A)
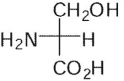
B)
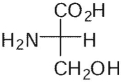
C)
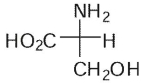
D)
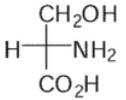
E)
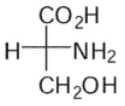
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Given the following information about a polypeptide
Hydrolysis of the polypeptide gives the following amino acids: Arg; Gly; Lys; Met(3) ; Phe(2);
Ser(2) ; Tyr.
Treatment of the polypeptide with chymotrypsin gives the following fragments: Met-Lys-Ser-Phe; Ser-Gly-Tyr; Met-Arg-Phe; Met.
Treatment of the polypeptide with cyanogen bromide gives the following fragments:
Ser-Gly-Tyr-[lactone]; Arg-Phe-[lactone]; Lys-Ser-Phe-[lactone].
Sanger degradation gives 2,4-DNP-Ser.
What is the primary structure of the original polypeptide?
A) Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met
B) Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Arg-Phe-Met
C) Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr
D) Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Met-Phe
E) Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Lys
Hydrolysis of the polypeptide gives the following amino acids: Arg; Gly; Lys; Met(3) ; Phe(2);
Ser(2) ; Tyr.
Treatment of the polypeptide with chymotrypsin gives the following fragments: Met-Lys-Ser-Phe; Ser-Gly-Tyr; Met-Arg-Phe; Met.
Treatment of the polypeptide with cyanogen bromide gives the following fragments:
Ser-Gly-Tyr-[lactone]; Arg-Phe-[lactone]; Lys-Ser-Phe-[lactone].
Sanger degradation gives 2,4-DNP-Ser.
What is the primary structure of the original polypeptide?
A) Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met
B) Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Arg-Phe-Met
C) Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr
D) Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Lys-Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Met-Phe
E) Ser-Phe-Met-Arg-Phe-Met-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Met-Lys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why does proline not give a positive test with ninhydrin?
A) The secondary amine of proline is too weak a nucleophile to add to ninhydrin.
B) The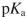 of the ammonium in proline (10.6) is too high to react with ninhydrin.
of the ammonium in proline (10.6) is too high to react with ninhydrin.
C) Hydrolysis of the second imine in the reaction mechanism cannot occur with proline.
D) The first imine cannot form in the reaction between proline and ninhydrin.
E) The second imine formed by decarboxylation in the mechanism is too unstable to form.
A) The secondary amine of proline is too weak a nucleophile to add to ninhydrin.
B) The
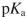 of the ammonium in proline (10.6) is too high to react with ninhydrin.
of the ammonium in proline (10.6) is too high to react with ninhydrin.C) Hydrolysis of the second imine in the reaction mechanism cannot occur with proline.
D) The first imine cannot form in the reaction between proline and ninhydrin.
E) The second imine formed by decarboxylation in the mechanism is too unstable to form.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A certain amino acid has 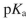 values of 2.35 and 9.6 for its carboxylic acid and amino group, respectively. What is the isoelectric point for this amino acid?
values of 2.35 and 9.6 for its carboxylic acid and amino group, respectively. What is the isoelectric point for this amino acid?
A) 2.35
B) 9.6
C) 6.0
D) 7.25
E) 11.95
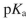 values of 2.35 and 9.6 for its carboxylic acid and amino group, respectively. What is the isoelectric point for this amino acid?
values of 2.35 and 9.6 for its carboxylic acid and amino group, respectively. What is the isoelectric point for this amino acid?A) 2.35
B) 9.6
C) 6.0
D) 7.25
E) 11.95

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which statement is true about aspartic acid at pH 3.0 ? The 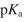 values are shown in the following figure.
values are shown in the following figure.
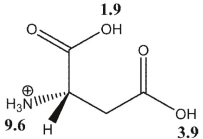
A) There is an overall 1+ charge.
B) There is an overall 1 - charge.
C) The molecule is neutral, and as shown in the figure, there are no nonzero formal charges on any of the atoms in the major resonance contributor.
D) The molecule is a zwitterion.
E) There is an overall 2+ charge.
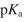 values are shown in the following figure.
values are shown in the following figure.
A) There is an overall 1+ charge.
B) There is an overall 1 - charge.
C) The molecule is neutral, and as shown in the figure, there are no nonzero formal charges on any of the atoms in the major resonance contributor.
D) The molecule is a zwitterion.
E) There is an overall 2+ charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of these structures are L-amino acids?
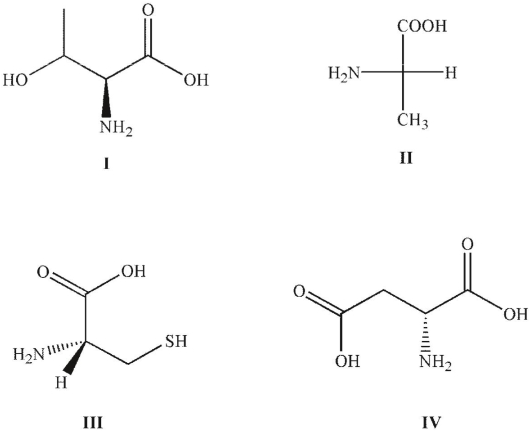
A) I
B) I and II
C) I, II, and III
D) III and IV
E) I and IV

A) I
B) I and II
C) I, II, and III
D) III and IV
E) I and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following would you use to protect the amino terminus in a polypeptide synthesis?
A)phenylisothiocyanate
B)2.4-dinitrofluorobenzene
C)DCC
D)BrCN
E)benzylchloroformate
A)phenylisothiocyanate
B)2.4-dinitrofluorobenzene
C)DCC
D)BrCN
E)benzylchloroformate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following properties dictate the overall structure of a polypeptide?
A)the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
B)the presence of disulfide bonds between sulfur containing residues on the chain
C)hydrogen bonding between side chains on peptide residues
D)orientation of hydrophilic groups out and hydrophobic groups in in the structure
E)all these properties impact the overall structure of the polypeptide
A)the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
B)the presence of disulfide bonds between sulfur containing residues on the chain
C)hydrogen bonding between side chains on peptide residues
D)orientation of hydrophilic groups out and hydrophobic groups in in the structure
E)all these properties impact the overall structure of the polypeptide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Denaturation is
A)disruption of the primary structure of a protein.
B)disruption of the secondary structure of a protein.
C)disruption of the tertiary structure of a protein.
D)disruption of the quaternary structure of a protein.
E)all of these.
A)disruption of the primary structure of a protein.
B)disruption of the secondary structure of a protein.
C)disruption of the tertiary structure of a protein.
D)disruption of the quaternary structure of a protein.
E)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which steps will be necessary to synthesize the peptide shown here? 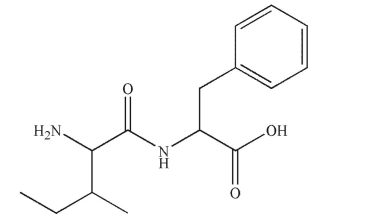 I.The N-terminus of Ile will require protection. II.The N-terminus of Phe will require protection.
I.The N-terminus of Ile will require protection. II.The N-terminus of Phe will require protection.
III)The carboxy terminus of Ile will require protection.
IV)The carboxy terminus of Phe will require protection.
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)I and IV
D)II and III
E)I, II, III, and IV
 I.The N-terminus of Ile will require protection. II.The N-terminus of Phe will require protection.
I.The N-terminus of Ile will require protection. II.The N-terminus of Phe will require protection.III)The carboxy terminus of Ile will require protection.
IV)The carboxy terminus of Phe will require protection.
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)I and IV
D)II and III
E)I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
α-helix and β-pleated sheets are examples of what type of protein structure?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
E)all of these
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
E)all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements about ninhydrin is false?
A)Reaction of an amino acid with ninhydrin results in a decarboxylation.
B)Reaction of ninhydrin with any amino acid eventually produces an imine that appears purple.
C)When an amino acid reacts with ninhydrin, eventually the "R" group is lost from the amino acid.
D)Ninhydrin reacts with amino acids through its carbonyl form, not its hydrated form.
E)The purple molecule that results from reaction of ninhydrin with an amino acid is an imine.
A)Reaction of an amino acid with ninhydrin results in a decarboxylation.
B)Reaction of ninhydrin with any amino acid eventually produces an imine that appears purple.
C)When an amino acid reacts with ninhydrin, eventually the "R" group is lost from the amino acid.
D)Ninhydrin reacts with amino acids through its carbonyl form, not its hydrated form.
E)The purple molecule that results from reaction of ninhydrin with an amino acid is an imine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Show the mechanism of the first step in the Strecker synthesis to prepare racemic leucine from
3-methylbutanal.
3-methylbutanal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Draw the structure of Asp-Gln-Tyr.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Explain how kinetic resolution can be used to separate a racemic mixture of D- and L-
phenylalanine.
phenylalanine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Draw the structure of methionine at pH=5 . Show all nonzero formal charges. The 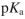 values for methionine are 2.3 for the carboxylic acid and 9.2 for the amino group.
values for methionine are 2.3 for the carboxylic acid and 9.2 for the amino group.
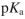 values for methionine are 2.3 for the carboxylic acid and 9.2 for the amino group.
values for methionine are 2.3 for the carboxylic acid and 9.2 for the amino group.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Draw the lettered intermediates and product in the following synthesis. 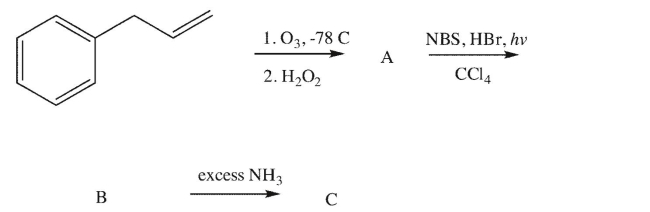


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Draw a structure for (R)-tyrosine.Show stereochemistry using wedge-and-dash notation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Give the IUPAC name for L-valine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Draw the intermediates and product in the Gabriel synthesis of an amino acid. 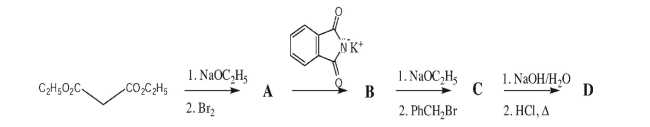


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Draw a Haworth projection of β-2-deoxyribofuranose.The Fischer projection of ribose is shown
for your reference.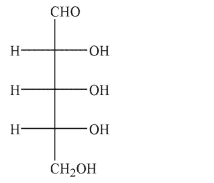
for your reference.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An 11-amino-acid polypeptide is subjected to the following processes:
Complete hydrolysis of the polypeptide, followed by separation of the component amino acids, shows Gln, Gly, Arg (2), Ala, Cys, Ser, Phe (2), Ile, Val.
Treament with chymotrypsin gives the following peptide chains:
Gln-Arg-Cys-Ala-Ser-Phe; Arg; Gly-Ile-Val-Phe.
Treatment with 2,4-DNP followed by hydrolysis (Sanger degradation) gives 2,4-DNP-Gly.
Treatment with a carbopeptidase removes an arginine (Arg) amino acid from the peptide.
What is the sequence of the amino acids in the original polypeptide?
Complete hydrolysis of the polypeptide, followed by separation of the component amino acids, shows Gln, Gly, Arg (2), Ala, Cys, Ser, Phe (2), Ile, Val.
Treament with chymotrypsin gives the following peptide chains:
Gln-Arg-Cys-Ala-Ser-Phe; Arg; Gly-Ile-Val-Phe.
Treatment with 2,4-DNP followed by hydrolysis (Sanger degradation) gives 2,4-DNP-Gly.
Treatment with a carbopeptidase removes an arginine (Arg) amino acid from the peptide.
What is the sequence of the amino acids in the original polypeptide?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At a pH of 6.0 , indicate whether each amino acid shown would be in cationic, anionic, or zwitterionic form.
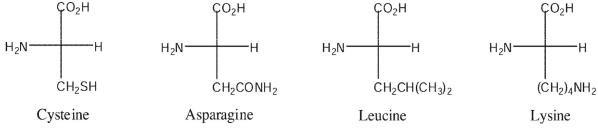


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Outline a synthesis of this peptide using any amino acids and protecting groups necessary.
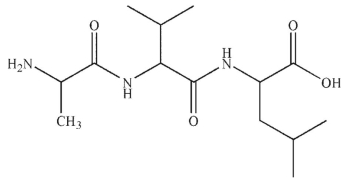


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Draw a Fischer projection for L-glutamic acid at pH=6 . The 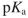 values are: carboxylic acid, 2.2 ; ammonium group, 9.7 ; side chain, 4.3 .
values are: carboxylic acid, 2.2 ; ammonium group, 9.7 ; side chain, 4.3 .
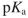 values are: carboxylic acid, 2.2 ; ammonium group, 9.7 ; side chain, 4.3 .
values are: carboxylic acid, 2.2 ; ammonium group, 9.7 ; side chain, 4.3 .
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Explain how the Merrifield method of synthesizing polypeptides results in very high yields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the mRNA fragment that will be generated by this strand of DNA? 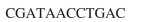
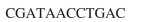

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Provide a name for this peptide using the three-letter code for amino acids. 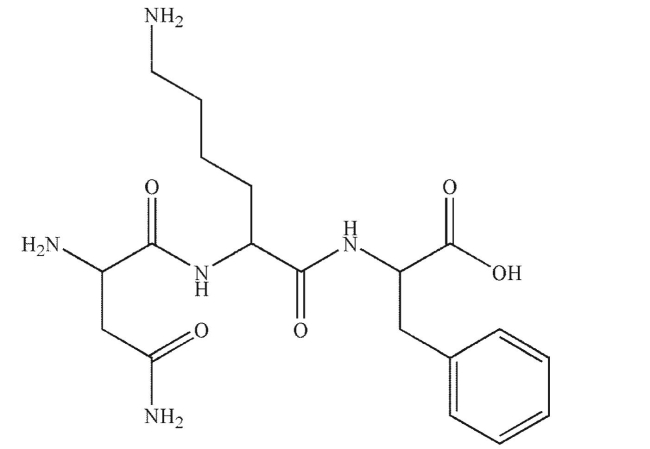


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Provide the missing reagents in this synthesis.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What polypeptide would be produced from an mRNA fragment with the following sequence of
codons?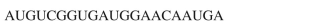
codons?
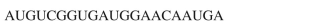

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An octapeptide is subjected to Edman degradation and it is discovered that the amino terminus is
Ser.Treatment of the remaining heptapeptide with BrCN yields a tripeptide
A and a tetrapeptide, B.
The tripeptide A is treated with trypsin, releasing a single residue and a dipeptide.The dipeptide,
on Edman degradation, gives two residues, one of which is not optically active.
The tetrapeptide B is also treated with trypsin, releasing a new tripeptide and a His residue.The
tripeptide from this step is treated with chymotrypsin, resulting in a dipeptide and a single amino
acid.Edman degradation of the dipeptide yields two residues, one of which is Val.
There is no Phe or Trp in the original octapeptide.
Provide a possible sequence of the original octapeptide.
Ser.Treatment of the remaining heptapeptide with BrCN yields a tripeptide
A and a tetrapeptide, B.
The tripeptide A is treated with trypsin, releasing a single residue and a dipeptide.The dipeptide,
on Edman degradation, gives two residues, one of which is not optically active.
The tetrapeptide B is also treated with trypsin, releasing a new tripeptide and a His residue.The
tripeptide from this step is treated with chymotrypsin, resulting in a dipeptide and a single amino
acid.Edman degradation of the dipeptide yields two residues, one of which is Val.
There is no Phe or Trp in the original octapeptide.
Provide a possible sequence of the original octapeptide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 39 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



