Deck 10: Aggregate Supply
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/19
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Aggregate Supply
1
SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY In the short run, prices may rise faster than costs. This chapter discusses why this might happen. Suppose that labor and management agree to adjust wages continuously for any changes in the price level. How would such adjustments affect the slope of the aggregate supply curve?
Slope of short-run aggregate supply curve: wage-price flexibility
In the short run, some factors are fixed and some factors can vary and the costs incurred on fixed factors are constant. Thus, the price level does not change as fast as it could have been if all are variable resources.
However, if prices are subjected to the variation in the wages, then the price level will increase faster than the costs. If actual price level is below the expected level, then the nominal wage rate is more than the expected and vice-versa. This would result in a greater slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve, which means short-run aggregate supply curve will be relatively steeper.
In the short run, the wage rate and price level are sticky downward because fall in nominal wage of workers will reduce the incentive to work.
Hence, if the wage rate adjusts continuously to any change in price, then the aggregate supply curve is relatively steep, and when wage and price level are sticky, then the short-run aggregate supply curve w ill be relatively flat.
In the short run, some factors are fixed and some factors can vary and the costs incurred on fixed factors are constant. Thus, the price level does not change as fast as it could have been if all are variable resources.
However, if prices are subjected to the variation in the wages, then the price level will increase faster than the costs. If actual price level is below the expected level, then the nominal wage rate is more than the expected and vice-versa. This would result in a greater slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve, which means short-run aggregate supply curve will be relatively steeper.
In the short run, the wage rate and price level are sticky downward because fall in nominal wage of workers will reduce the incentive to work.
Hence, if the wage rate adjusts continuously to any change in price, then the aggregate supply curve is relatively steep, and when wage and price level are sticky, then the short-run aggregate supply curve w ill be relatively flat.
2
POTENTIAL OUTPUT Define the economy's potential output. What factors help determine potential output?
Potential output of an economy:
With the given natural resources and level of technology, the sustained maximum level of output produced in the long run is called potential output. At the potential level of output, the actual price level always equals the expected price level.
Factors affecting potential output of an economy:
Factors such as level of technology, stock of capital, availability of natural resources, quantity or quality of labor force, etc. affect the potential output level of an economy.
Level of technology:
Advanced level of technology means high potential level of output because advanced level of technology will enhance the productivity of labor force.
Capital stock:
An economy's potential level of output would be higher, if its stocks of capitals are large. Larger stock of capital means labor to capital ratio is high, which would increase the potential level of output produced.
Stock of natural resources:
An economy's potential output would be higher, if its stock of natural resources is higher and vice-versA.Quantity or quality of labor force:
Economy with higher quantity as well as quality of labor force would have higher level of potential output. Improved quality would lead to an increase in productivity and more quantity of labor would increase the volume of aggregate output produced.
Formal and informal institutions:
Formal and informal institutions also play a vital role in an economy's potential level of output. Economy with better managed property rights, patent rights, and labor contracts is expected to have greater level of potential output.
Government also plays an important role in an economy's potential level of output. Political stability of an economy will encourage domestic as well as foreign investors to invest. Thus, there would be inward flow of capital to the economy, which would increase the potential level of output produced.
With the given natural resources and level of technology, the sustained maximum level of output produced in the long run is called potential output. At the potential level of output, the actual price level always equals the expected price level.
Factors affecting potential output of an economy:
Factors such as level of technology, stock of capital, availability of natural resources, quantity or quality of labor force, etc. affect the potential output level of an economy.
Level of technology:
Advanced level of technology means high potential level of output because advanced level of technology will enhance the productivity of labor force.
Capital stock:
An economy's potential level of output would be higher, if its stocks of capitals are large. Larger stock of capital means labor to capital ratio is high, which would increase the potential level of output produced.
Stock of natural resources:
An economy's potential output would be higher, if its stock of natural resources is higher and vice-versA.Quantity or quality of labor force:
Economy with higher quantity as well as quality of labor force would have higher level of potential output. Improved quality would lead to an increase in productivity and more quantity of labor would increase the volume of aggregate output produced.
Formal and informal institutions:
Formal and informal institutions also play a vital role in an economy's potential level of output. Economy with better managed property rights, patent rights, and labor contracts is expected to have greater level of potential output.
Government also plays an important role in an economy's potential level of output. Political stability of an economy will encourage domestic as well as foreign investors to invest. Thus, there would be inward flow of capital to the economy, which would increase the potential level of output produced.
3
ACTUAL PRICE LEVEL HIGHER THAN EXPECTED Discuss some instances in your life when your actual production for short periods exceeded what you considered your potential, or normal, production. Why does this occur only for brief periods?
Short-run output can be greater than the potential output
In the short run, output produced can exceed the potential level of output.
For example, during the exam time, hours spent on preparing for examination as well as productivity of students increase sharply than the regular study hours. Within a short span of time, students can cover more portion of their syllabus and they also read for more hours. But the same could not be followed regularly as it will decrease their interest.
Similarly, in private companies, the productivity of employees will be higher as the due date of works comes closer. The productivity of workers will be higher than the potential level on the day before the due date of any assignment. Workers even work for longer hours and overtime to contribute productively in the last day of the month to close the target, but the same could not be expected as it would reduce employee's interest on job.
Hence, short-run output produced can exceed the potential level because of the trade-off between less leisure and more work.
In the short run, output produced can exceed the potential level of output.
For example, during the exam time, hours spent on preparing for examination as well as productivity of students increase sharply than the regular study hours. Within a short span of time, students can cover more portion of their syllabus and they also read for more hours. But the same could not be followed regularly as it will decrease their interest.
Similarly, in private companies, the productivity of employees will be higher as the due date of works comes closer. The productivity of workers will be higher than the potential level on the day before the due date of any assignment. Workers even work for longer hours and overtime to contribute productively in the last day of the month to close the target, but the same could not be expected as it would reduce employee's interest on job.
Hence, short-run output produced can exceed the potential level because of the trade-off between less leisure and more work.
4
NOMINAL AND REAL WAGES Complete each of the following sentences:
a. The _______ wage measures the wage rate in dollars of the year in question, while the _______ wage measures it in constant dollars.
b. Wage agreements are based on the _______ price level and negotiated in _______ terms. Real wages are then determined by the _______ price level.
c. The higher the actual price level, the _______ is the real wage for a given nominal wage.
d. If nominal wages are growing at 2 percent per year while the annual inflation rate is 3 percent, then real wages change by _______.
a. The _______ wage measures the wage rate in dollars of the year in question, while the _______ wage measures it in constant dollars.
b. Wage agreements are based on the _______ price level and negotiated in _______ terms. Real wages are then determined by the _______ price level.
c. The higher the actual price level, the _______ is the real wage for a given nominal wage.
d. If nominal wages are growing at 2 percent per year while the annual inflation rate is 3 percent, then real wages change by _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
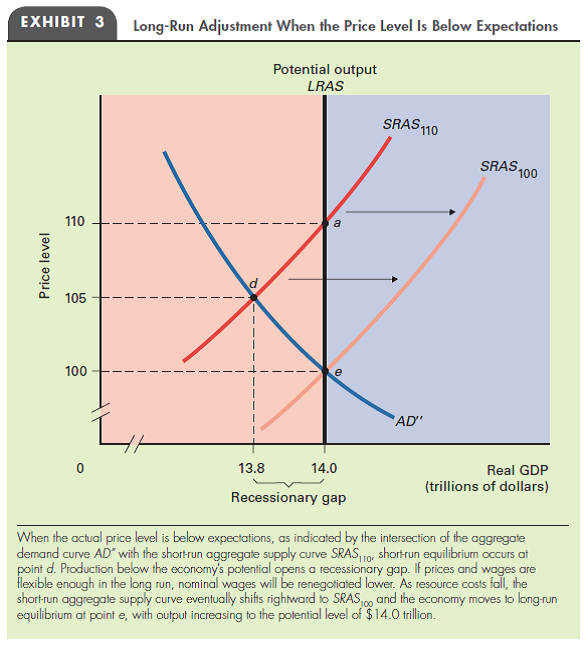
RECESSIONARY GAPS After reviewing Exhibit 3 in this chapter, explain why recessionary gaps occur only in the short run and only when the actual price level is below what was expected.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY In interpreting the short-run aggregate supply curve, what does the adjective short-run mean? Explain the role of labor contracts along the SRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
RECESSIONARY GAP What does a recessionary gap imply about the actual rate of unemployment relative to the natural rate? What does it imply about the actual price level relative to the expected price level? What must happen to real and nominal wages in order to close a recessionary gap?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
EXPANSIONARY GAP How does an economy that is experiencing an expansionary gap adjust in the long run?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Case Study: U.S. Output Gaps and Wage Flexibility
Unemployment is costly to employers, employees, and the economy as a whole. What are some explanations for the coordination failures that prevent workers and employers from reaching agreements?
Unemployment is costly to employers, employees, and the economy as a whole. What are some explanations for the coordination failures that prevent workers and employers from reaching agreements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
LONG-RUN ADJUSTMENT In the long run, why does an actual price level that exceeds the expected price level lead to changes in the nominal wage? Why do these changes cause shifts of the short-run aggregate supply curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
LONG-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at the economy's potential output level. Why is the long-run aggregate supply curve located at this output rather than below or above potential output?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
LONG-RUN AGGREGATE SUPPLY Determine whether each of the following, other things held constant, would lead to an increase, a decrease, or no change in long-run aggregate supply:
a. An improvement in technology
b. A permanent decrease in the size of the capital stock
c. An increase in the actual price level
d. An increase in the expected price level
e. A permanent increase in the size of the labor force
a. An improvement in technology
b. A permanent decrease in the size of the capital stock
c. An increase in the actual price level
d. An increase in the expected price level
e. A permanent increase in the size of the labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
CHANGES IN AGGREGATE SUPPLY What are supply shocks? Distinguish between beneficial and adverse supply shocks. Do such shocks affect the short-run aggregate supply curve, the long-run aggregate supply curve, or both? What is the resulting impact on potential GDP?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
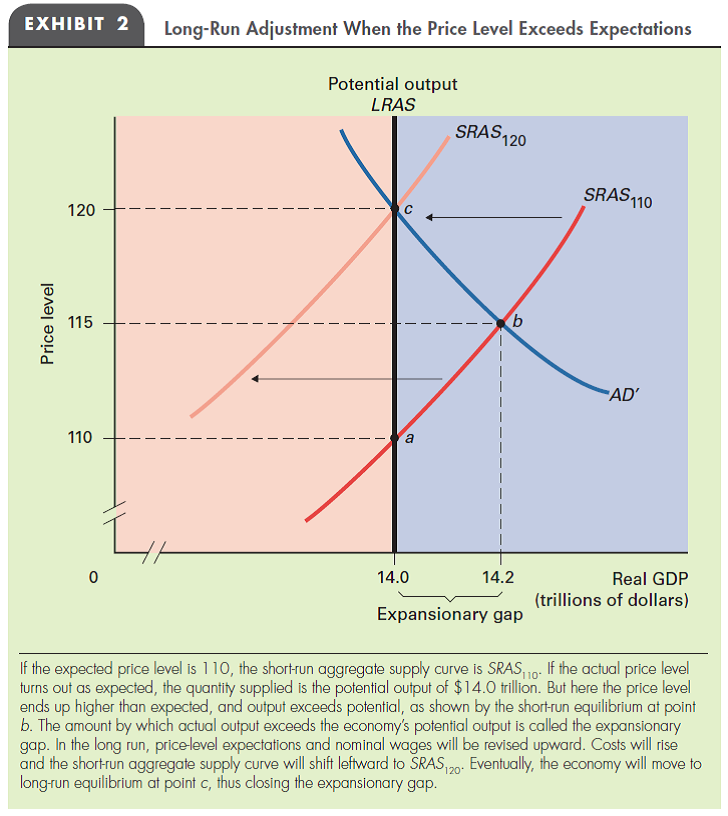
REAL WAGES In Exhibit 2 in this chapter, how does the real wage rate at point c compare with the real wage rate at point a ? How do nominal wage rates compare at those two points? Explain your answers.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
NATURAL RATE OF UNEMPLOYMENT What is the relationship between potential output and the natural rate of unemployment?
a. If the economy currently has a frictional unemployment rate of 2 percent, structural unemployment of 2 percent, seasonal unemployment of 0.5 percent, and cyclical unemployment of 2 percent, what is the natural rate of unemployment? Where is the economy operating relative to its potential GDP?
b. What happens to the natural rate of unemployment and potential GDP if cyclical unemployment rises to 3 percent with other types of unemployment unchanged from part (a)?
c. What happens to the natural rate of unemployment and potential GDP if structural unemployment falls to 1.5 percent with other types of unemployment unchanged from part (a)?
a. If the economy currently has a frictional unemployment rate of 2 percent, structural unemployment of 2 percent, seasonal unemployment of 0.5 percent, and cyclical unemployment of 2 percent, what is the natural rate of unemployment? Where is the economy operating relative to its potential GDP?
b. What happens to the natural rate of unemployment and potential GDP if cyclical unemployment rises to 3 percent with other types of unemployment unchanged from part (a)?
c. What happens to the natural rate of unemployment and potential GDP if structural unemployment falls to 1.5 percent with other types of unemployment unchanged from part (a)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
EXPANSIONARY AND RECESSIONARY GAPS Answer the following questions on the basis of the following graph:
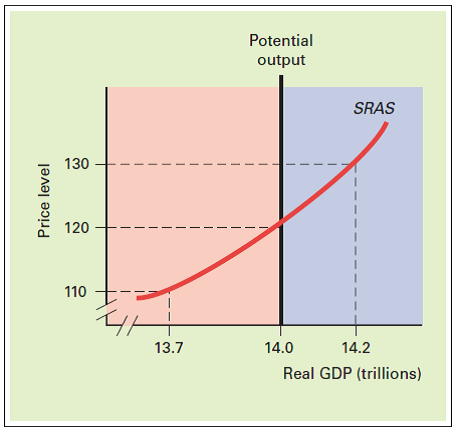 a. If the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
a. If the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
b. The situation described in part (a) results in a(n) _______ gap equal to _______.
c. If the actual price level is lower than the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
d. The situation described in part (c) results in a(n) _______ gap equal to _______.
e. If the actual price level equals the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
f. The situation described in part (e) results in ______ gap equal to _______.
 a. If the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
a. If the actual price level exceeds the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.b. The situation described in part (a) results in a(n) _______ gap equal to _______.
c. If the actual price level is lower than the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
d. The situation described in part (c) results in a(n) _______ gap equal to _______.
e. If the actual price level equals the expected price level reflected in long-term contracts, real GDP equals _______ and the actual price level equals _______ in the short run.
f. The situation described in part (e) results in ______ gap equal to _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
LONG-RUN ADJUSTMENT The ability of the economy to eliminate any imbalances between actual and potential output is sometimes called self-correction. Using an aggregate supply and aggregate demand diagram, show why this self-correction process involves only temporary periods of inflation or deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
CHANGES IN AGGREGATE SUPPLY List three factors that can change the economy's potential output. What is the impact of shifts of the aggregate demand curve on potential output? Illustrate your answers with a diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
SUPPLY SHOCKS Give an example of an adverse supply shock and illustrate graphically. Now do the same for a beneficial supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 19 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



