Deck 6: Strategic Rivalry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Strategic Rivalry
1
Unlike a perfectly competitive ?rm, _____.
A) a monopolistically competitive ?rm will have monopoly power in the long run
B) price is equal to marginal cost for a monopolistically competitive ?rm in the long run
C) a monopolistically competitive ?rm is a price taker
D) a monopolistically competitive ?rm produces homogeneous products
A) a monopolistically competitive ?rm will have monopoly power in the long run
B) price is equal to marginal cost for a monopolistically competitive ?rm in the long run
C) a monopolistically competitive ?rm is a price taker
D) a monopolistically competitive ?rm produces homogeneous products
a monopolistically competitive ?rm will have monopoly power in the long run
2
Which of the following could form a barrier to entry in a market?
A) Normal economic pro?ts.
B) Diseconomies of scale.
C) Relatively elastic demand for the good.
D) High sunk costs.
A) Normal economic pro?ts.
B) Diseconomies of scale.
C) Relatively elastic demand for the good.
D) High sunk costs.
High sunk costs.
3
Which of the following is an example of an endogenous cost to a ?rm?
A) The price of labour.
B) The level of advertising expenditure.
C) The cost of production technology.
D) The cost of raw materials.
A) The price of labour.
B) The level of advertising expenditure.
C) The cost of production technology.
D) The cost of raw materials.
The level of advertising expenditure.
4
In a contestable market, _____.
A) potential entrants do not have access to the same technology as incumbent ?rms
B) sunk costs are likely to be zero
C) incumbent ?rms ?nd it di?cult to exit because of high sunk costs
D) there are high barriers to entry
A) potential entrants do not have access to the same technology as incumbent ?rms
B) sunk costs are likely to be zero
C) incumbent ?rms ?nd it di?cult to exit because of high sunk costs
D) there are high barriers to entry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Unlike an oligopolistic market, a monopolistically competitive market has _____.
A) a homogeneous product
B) a differentiated product
C) a large number of ?rms
D) a horizontal demand curve
A) a homogeneous product
B) a differentiated product
C) a large number of ?rms
D) a horizontal demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following industries would be considered an oligopoly?
A) The hairdressing industry that has a large number of small ?rms.
B) The wheat industry that has a homogeneous product and a large number of suppliers.
C) The hotel industry that has a differentiated product and a large number of ?rms.
D) The supermarket industry that has a small number of large ?rms.
A) The hairdressing industry that has a large number of small ?rms.
B) The wheat industry that has a homogeneous product and a large number of suppliers.
C) The hotel industry that has a differentiated product and a large number of ?rms.
D) The supermarket industry that has a small number of large ?rms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Suppose the widget industry experiences signi?cant economies of scale. Which of the following is likely to be true?
A) The economies of scale will provide other ?rms an incentive to enter the industry.
B) Firms in the widget industry will make zero economic pro?ts in the short run.
C) The economies of scale will form a natural barrier to entry in the widget industry.
D) Large economies of scale will provide the ?rms in the market an incentive to co-operate.
A) The economies of scale will provide other ?rms an incentive to enter the industry.
B) Firms in the widget industry will make zero economic pro?ts in the short run.
C) The economies of scale will form a natural barrier to entry in the widget industry.
D) Large economies of scale will provide the ?rms in the market an incentive to co-operate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
_____ refers to an implicit or explicit agreement among ?rms in an industry not to compete with each other.
A) Dominant ?rm hypothesis
B) Collusion
C) Vertical integration
D) Market consolidation
A) Dominant ?rm hypothesis
B) Collusion
C) Vertical integration
D) Market consolidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The N-?rm concentration ratio measures the:
A) total market share attributed to the N largest ?rms in the market.
B) total market share of all the ?rms in the market, where N is the number of ?rms.
C) the number of new entrants in the market, where N is the number of new entrants.
D) the share of total revenues by all the ?rms in an oligopoly.
A) total market share attributed to the N largest ?rms in the market.
B) total market share of all the ?rms in the market, where N is the number of ?rms.
C) the number of new entrants in the market, where N is the number of new entrants.
D) the share of total revenues by all the ?rms in an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following statements is true of monopolistic competition?
A) The goods produced in a monopolistically competitive market have a large number of substitutes.
B) Monopolistically competitive ?rms practice product differentiation.
C) There is only one ?rm in a monopolistically competitive market.
D) Firms are price takers in a monopolistically competitive market.
A) The goods produced in a monopolistically competitive market have a large number of substitutes.
B) Monopolistically competitive ?rms practice product differentiation.
C) There is only one ?rm in a monopolistically competitive market.
D) Firms are price takers in a monopolistically competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following strategies can ?rms undertake to increase the minimum e?cient scale in an industry?
A) Reduce the quantity of raw material used to produce each additional unit.
B) Make large investments in intangible assets such as brand names.
C) Invest in cost-reducing technologies used in production.
D) Reduce the level of sunk costs by reducing the plant size.
A) Reduce the quantity of raw material used to produce each additional unit.
B) Make large investments in intangible assets such as brand names.
C) Invest in cost-reducing technologies used in production.
D) Reduce the level of sunk costs by reducing the plant size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true of the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market?
A) Monopolistically competitive ?rms make supernormal pro?ts in the long run.
B) Monopolistically competitive ?rms are productively e?cient in the long run.
C) Monopolistically competitive ?rms will produce where MC > MR in the long run.
D) Monopolistically competitive ?rms will not produce at the minimum average total cost in
A) Monopolistically competitive ?rms make supernormal pro?ts in the long run.
B) Monopolistically competitive ?rms are productively e?cient in the long run.
C) Monopolistically competitive ?rms will produce where MC > MR in the long run.
D) Monopolistically competitive ?rms will not produce at the minimum average total cost in

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
When a ?rm invests substantially in advertising and product development, it is trying to:
A) make its product similar to the other products in the market.
B) lower the market price.
C) lower its sunk costs.
D) raise entry barriers in the industry.
A) make its product similar to the other products in the market.
B) lower the market price.
C) lower its sunk costs.
D) raise entry barriers in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Firms in a(n) _____ market are price-takers.
A) oligopolistic
B) monopolistic
C) perfectly competitive
D) monopolistically competitive
A) oligopolistic
B) monopolistic
C) perfectly competitive
D) monopolistically competitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) A small number of sellers.
B) Supernormal pro?ts in the long run.
C) Free entry and exit of ?rms.
D) A small number of buyers.
A) A small number of sellers.
B) Supernormal pro?ts in the long run.
C) Free entry and exit of ?rms.
D) A small number of buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements about oligopolistic markets is correct?
A) Firms in an oligopoly face an upward-sloping demand curve for their products.
B) There are a large number of small ?rms in an oligopoly.
C) An oligopolist is a price-setter in the output market.
D) The degree of market power enjoyed by ?rms in an oligopoly is very low.
A) Firms in an oligopoly face an upward-sloping demand curve for their products.
B) There are a large number of small ?rms in an oligopoly.
C) An oligopolist is a price-setter in the output market.
D) The degree of market power enjoyed by ?rms in an oligopoly is very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose the market share of the ?ve largest ?rms in an industry is equal to 31%, 17%, 8%, 5% and 1% respectively. What is the ?ve-?rm concentration ratio for the industry?
A) 62%
B) 93%
C) 31%
D) 5%
A) 62%
B) 93%
C) 31%
D) 5%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In the long run, tangency equilibrium occurs when a monopolistically competitive ?rm's average revenue curve is tangent to:
A) its average cost curve.
B) its marginal revenue curve.
C) its marginal cost curve.
D) its demand curve.
A) its average cost curve.
B) its marginal revenue curve.
C) its marginal cost curve.
D) its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is meant by the strategic interdependence of ?rms?
A) Firms in perfectly competitive markets affect the pricing and output decisions of other ?rms.
B) A monopolistic ?rm decides the price and output level in the market.
C) The actions of one ?rm in a market have pricing and output implications for the rival ?rms.
D) A group of ?rms collude to set the output and price level in the market.
A) Firms in perfectly competitive markets affect the pricing and output decisions of other ?rms.
B) A monopolistic ?rm decides the price and output level in the market.
C) The actions of one ?rm in a market have pricing and output implications for the rival ?rms.
D) A group of ?rms collude to set the output and price level in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a characteristic of an oligopoly market?
A) All the ?rms in an industry make equal pro?ts.
B) The ?rms in the market make zero economic pro?ts.
C) Firms can freely enter and exit the market.
D) The total number of ?rms in the market is small.
A) All the ?rms in an industry make equal pro?ts.
B) The ?rms in the market make zero economic pro?ts.
C) Firms can freely enter and exit the market.
D) The total number of ?rms in the market is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A drawback of the kinked demand curve model is that:
A) it is not applicable to oligopolistic ?rms.
B) it does not explain the process that determines the stable price.
C) it does not include strategic independence between ?rms.
D) it assumes that the marginal revenue curve is vertical, which is not a realistic assumption.
A) it is not applicable to oligopolistic ?rms.
B) it does not explain the process that determines the stable price.
C) it does not include strategic independence between ?rms.
D) it assumes that the marginal revenue curve is vertical, which is not a realistic assumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The following graph shows the marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), demand and average revenue (D = AR) curves for a pro?t-maximizing ?rm. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 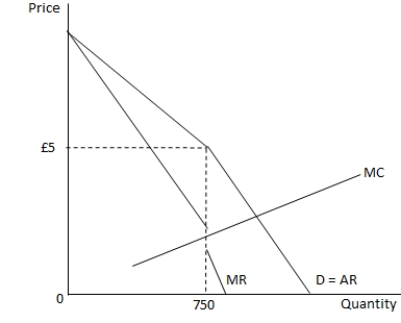 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The ?rm is a price leader in this market.
B) Firms in this market produce highly differentiated products.
C) A small change in the marginal cost will lead to a large change in the equilibrium price.
D) Below the market price, the demand curve is price inelastic.
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A) The ?rm is a price leader in this market.
B) Firms in this market produce highly differentiated products.
C) A small change in the marginal cost will lead to a large change in the equilibrium price.
D) Below the market price, the demand curve is price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that ?ve ?rms in an oligopoly formally sign a contract to establish the price of the product in the market. In other words, they have _____.
A) increased the elasticity of demand for the good
B) increased the variety of the goods available to the consumer
C) formed a cartel
D) increased competition in the market
A) increased the elasticity of demand for the good
B) increased the variety of the goods available to the consumer
C) formed a cartel
D) increased competition in the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose that all the ?rms in an oligopoly face the same horizontal marginal and average cost curves. If all these ?rms agree to co-operate, their joint pro?ts will be maximized by producing at the level where:
A) average revenue equals average cost.
B) marginal revenue equals average revenue.
C) marginal cost equals average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) average revenue equals average cost.
B) marginal revenue equals average revenue.
C) marginal cost equals average variable cost.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that it is relatively easy for new ?rms to enter an industry. Some of the ?rms in this industry want to form a cartel. Which of the following is likely to be true?
A) It would be relatively easy for the ?rms to form a cartel.
B) The market power of the cartel is likely to be low.
C) The industry exhibits substantial economies of scale.
D) The marginal cost of production in this industry is likely to be low.
A) It would be relatively easy for the ?rms to form a cartel.
B) The market power of the cartel is likely to be low.
C) The industry exhibits substantial economies of scale.
D) The marginal cost of production in this industry is likely to be low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
To move from a non-co-operative Nash equilibrium to a co-operative Nash equilibrium, _____.
A) a single-period game must be played
B) a repeated game must be played
C) a threat made by one of the players need not be credible
D) the players should not have any information about their rivals' strategy
A) a single-period game must be played
B) a repeated game must be played
C) a threat made by one of the players need not be credible
D) the players should not have any information about their rivals' strategy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the kinked demand curve model, the kink in the demand curve arises because:
A) the elasticity of the demand curve changes at the equilibrium output.
B) there are no barriers to entry or exit in the industry.
C) the demand for the good is unstable and keeps changing.
D) the products sold by each ?rm in the market are different.
A) the elasticity of the demand curve changes at the equilibrium output.
B) there are no barriers to entry or exit in the industry.
C) the demand for the good is unstable and keeps changing.
D) the products sold by each ?rm in the market are different.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The following table shows the pay-off matrix for West Ltd. and East Ltd. in an oligopolistic market. Each ?rm has two options: co-operate or start a price war. Refer to the table to answer the question. 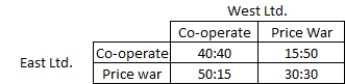 East Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
East Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
A) West Ltd. co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war
B) it co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war
C) both the ?rms co-operate
D) both the ?rms begin a price war
 East Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
East Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.A) West Ltd. co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war
B) it co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war
C) both the ?rms co-operate
D) both the ?rms begin a price war

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Cartels are more likely to fail when _____.
A) the ?rms in the cartel produce identical products
B) the marginal cost of production is high
C) the number of ?rms forming the cartel is high
D) the demand for the good is perfectly inelastic
A) the ?rms in the cartel produce identical products
B) the marginal cost of production is high
C) the number of ?rms forming the cartel is high
D) the demand for the good is perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A ?rm that faces a kinked demand curve will:
A) establish its optimal output at the level where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
B) frequently engage in price wars with its competitors.
C) face a horizontal marginal revenue curve.
D) lose customers if it raises its prices.
A) establish its optimal output at the level where marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue.
B) frequently engage in price wars with its competitors.
C) face a horizontal marginal revenue curve.
D) lose customers if it raises its prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is true of Nash equilibrium?
A) There is no strategic interdependence between ?rms that are in Nash equilibrium.
B) It occurs when each player does what is best for themselves, given their rivals' possible
C) It tends to be more unstable than a market equilibrium.
D) A Nash equilibrium is the same as a tangency equilibrium.
A) There is no strategic interdependence between ?rms that are in Nash equilibrium.
B) It occurs when each player does what is best for themselves, given their rivals' possible
C) It tends to be more unstable than a market equilibrium.
D) A Nash equilibrium is the same as a tangency equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose a cartel operates in the widget industry. It would be weakened if:
A) all the ?rms produced the same type of widget.
B) there were no substitutes for a widget.
C) all the ?rms produced the same quantity of widgets.
D) one of the cartel members sells widgets at a lower price.
A) all the ?rms produced the same type of widget.
B) there were no substitutes for a widget.
C) all the ?rms produced the same quantity of widgets.
D) one of the cartel members sells widgets at a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A cartel is more likely to be successful when:
A) ?rms produce highly differentiated products.
B) there are no barriers to entry or exit of ?rms.
C) there are many ?rms in the industry.
D) demand and costs in the industry are stable.
A) ?rms produce highly differentiated products.
B) there are no barriers to entry or exit of ?rms.
C) there are many ?rms in the industry.
D) demand and costs in the industry are stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A problem often encountered when oligopolists try to cooperate and set output and prices in the market is that:
A) the number of ?rms in the industry is too small to form a successful cartel.
B) most oligopolists produce highly differentiated products.
C) some ?rms might cheat on the agreed-upon market price.
D) market demand and costs are in?exible and do not change.
A) the number of ?rms in the industry is too small to form a successful cartel.
B) most oligopolists produce highly differentiated products.
C) some ?rms might cheat on the agreed-upon market price.
D) market demand and costs are in?exible and do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The following table shows the pay-off matrix for West Ltd. and East Ltd. in an oligopolistic market. Each ?rm has two options: co-operate or start a price war. Refer to the table to answer the question. 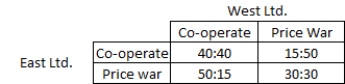 Which of the following is the Nash equilibrium outcome in this oligopoly?
Which of the following is the Nash equilibrium outcome in this oligopoly?
A) East Ltd. co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war.
B) West Ltd. co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war.
C) Both ?rms co-operate.
D) Both ?rms begin a price war.
 Which of the following is the Nash equilibrium outcome in this oligopoly?
Which of the following is the Nash equilibrium outcome in this oligopoly?A) East Ltd. co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war.
B) West Ltd. co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war.
C) Both ?rms co-operate.
D) Both ?rms begin a price war.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following graph shows the marginal revenue (MR), average revenue (AR), marginal cost (MC) and average cost (AC) curves for an oligopoly ?rm. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 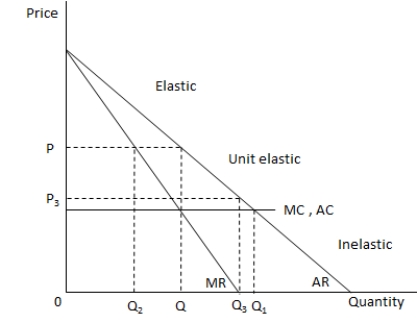
Assume that all the ?rms in the oligopoly market face the same set of cost and revenue curves. If they formed a cartel, they would maximize pro?t at the output level _____.
A) Q
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

Assume that all the ?rms in the oligopoly market face the same set of cost and revenue curves. If they formed a cartel, they would maximize pro?t at the output level _____.
A) Q
B) Q1
C) Q2
D) Q3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Oligopolists collude in order to_____.
A) minimize the social cost of production
B) earn monopoly pro?ts
C) maximize the quantity of output produced
D) increase production costs
A) minimize the social cost of production
B) earn monopoly pro?ts
C) maximize the quantity of output produced
D) increase production costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following graph shows the marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), demand and average revenue (D = AR) curves for a pro?t-maximizing ?rm. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 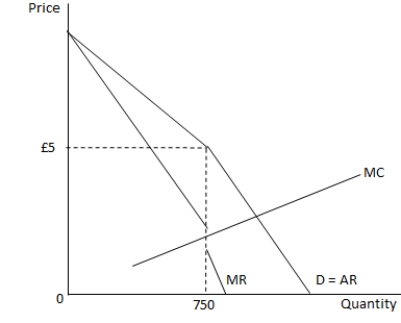 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The demand curve above the market price is relatively inelastic.
B) The demand curve below the market price is relatively elastic.
C) The marginal revenue curve is a vertical line at the pro?t-maximizing level of output.
D) Marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue at the pro?t-maximizing level of output.
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A) The demand curve above the market price is relatively inelastic.
B) The demand curve below the market price is relatively elastic.
C) The marginal revenue curve is a vertical line at the pro?t-maximizing level of output.
D) Marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue at the pro?t-maximizing level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The following table shows the pay-off matrix for West Ltd. and East Ltd. in an oligopolistic market. Each ?rm has two options: co-operate or start a price war. Refer to the table to answer the question. 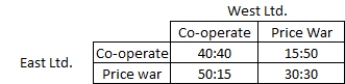 West Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
West Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
A) it co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war
B) East Ltd. co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war
C) both the ?rms co-operate
D) both the ?rms begin a price war
 West Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.
West Ltd. earns its maximum pay-off when _____.A) it co-operates but East Ltd. begins a price war
B) East Ltd. co-operates but West Ltd. begins a price war
C) both the ?rms co-operate
D) both the ?rms begin a price war

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The kinked demand curve pricing model is based on the assumption that:
A) a ?rm's competitors will match both its price increases and price decreases.
B) one ?rm in the industry sets price for all other ?rms.
C) a ?rm's competitors will match a price fall but not a price increase.
D) price in the market is in?exible and unlikely to change.
A) a ?rm's competitors will match both its price increases and price decreases.
B) one ?rm in the industry sets price for all other ?rms.
C) a ?rm's competitors will match a price fall but not a price increase.
D) price in the market is in?exible and unlikely to change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following auction formats offers a solution to the problem of the winner's curse?
A) The English auction
B) The Dutch auction
C) The ?rst-price sealed-bid auction
D) The second-price sealed-bid auction
A) The English auction
B) The Dutch auction
C) The ?rst-price sealed-bid auction
D) The second-price sealed-bid auction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Game theory suggests collusion is more likely to occur in:
A) a single-period game.
B) a zero-sum game.
C) a repeated game.
D) a dictator game.
A) a single-period game.
B) a zero-sum game.
C) a repeated game.
D) a dictator game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The following graph shows the bid value and probability of winning an auction for an oil painting under a ?rst-price sealed bid auction with private values. The bidder is willing to pay a maximum of £2000 for the oil painting. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 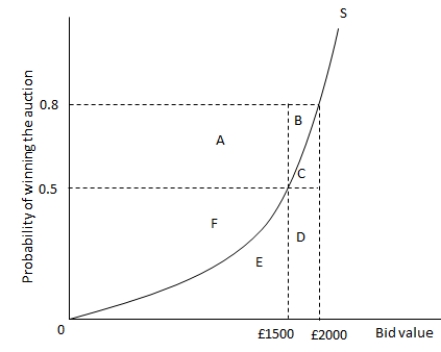 The line S has a positive slope which shows that the _____.
The line S has a positive slope which shows that the _____.
A) probability of winning the auction rises as the bidder increases the bid.
B) the potential gains from winning the auction increases as the bid value increases.
C) the private value of the bidder is in?uenced by the changes in the bid values.
D) the optimal bid is equal to the bidder's maximum willingness to pay.
 The line S has a positive slope which shows that the _____.
The line S has a positive slope which shows that the _____.A) probability of winning the auction rises as the bidder increases the bid.
B) the potential gains from winning the auction increases as the bid value increases.
C) the private value of the bidder is in?uenced by the changes in the bid values.
D) the optimal bid is equal to the bidder's maximum willingness to pay.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is true in a Stackelberg model of duopoly?
A) Both ?rms in the market will take price and output decisions simultaneously.
B) The level of strategic interdependence between ?rms in the market is very low.
C) One ?rm has a ?rst-mover advantage and other ?rms follow this ?rm.
D) Both ?rms will collude and set output in the market.
A) Both ?rms in the market will take price and output decisions simultaneously.
B) The level of strategic interdependence between ?rms in the market is very low.
C) One ?rm has a ?rst-mover advantage and other ?rms follow this ?rm.
D) Both ?rms will collude and set output in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is true of a Cournot model?
A) A ?rm's pro?t-maximizing output does not vary with the decision of its rival.
B) A ?rm will always treat its rival's output as a given.
C) The ?rm will produce where MC > MR.
D) It is a price-based approach to duopoly.
A) A ?rm's pro?t-maximizing output does not vary with the decision of its rival.
B) A ?rm will always treat its rival's output as a given.
C) The ?rm will produce where MC > MR.
D) It is a price-based approach to duopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A reaction function shows that:
A) a ?rm's pro?t-maximizing output varies with its rival's output decision.
B) prices in the market are assumed to be constant.
C) ?rms do not make strategic decisions simultaneously.
D) one ?rm in the market has ?rst-mover advantage.
A) a ?rm's pro?t-maximizing output varies with its rival's output decision.
B) prices in the market are assumed to be constant.
C) ?rms do not make strategic decisions simultaneously.
D) one ?rm in the market has ?rst-mover advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In Nash equilibrium in a Dutch auction with private values, the optimal bid is calculated by _____, where N is the number of bidders.
A) N/(N - 1) × the probability of winning the auction
B) (N - 1)/N × the bidder's maximum willingness to pay
C) N/(N - 1) × the expected value from winning the auction
D) (N - 1)/N × the reserve price in the auction
A) N/(N - 1) × the probability of winning the auction
B) (N - 1)/N × the bidder's maximum willingness to pay
C) N/(N - 1) × the expected value from winning the auction
D) (N - 1)/N × the reserve price in the auction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is true of an English auction?
A) Bids begin low and are increased incrementally until no other bidder is willing to raise the bid.
B) Prices start high and are gradually reduced until a bidder accepts the price and wins the
C) Bidders submit a single bid in writing, without knowing how others have bid, and the highest bid wins.
D) Bidders submit a single bid in writing, without knowing how others have bid, and the
A) Bids begin low and are increased incrementally until no other bidder is willing to raise the bid.
B) Prices start high and are gradually reduced until a bidder accepts the price and wins the
C) Bidders submit a single bid in writing, without knowing how others have bid, and the highest bid wins.
D) Bidders submit a single bid in writing, without knowing how others have bid, and the

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The following graph shows the bid value and probability of winning an auction for an oil painting under a ?rst-price sealed bid auction with private values. The bidder is willing to pay a maximum of £2000 for the oil painting. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 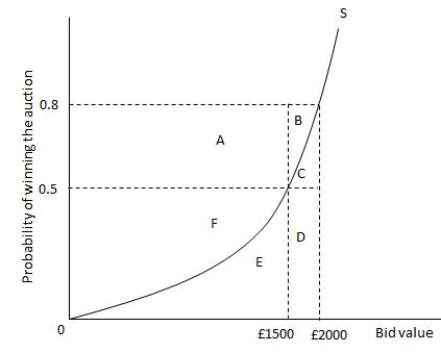 The expected value from winning the auction at the price of £2000 is equal to the area _____.
The expected value from winning the auction at the price of £2000 is equal to the area _____.
A) A + B + C + D + E + F
B) F + E
C) C + D + E
D) A + B + F
 The expected value from winning the auction at the price of £2000 is equal to the area _____.
The expected value from winning the auction at the price of £2000 is equal to the area _____.A) A + B + C + D + E + F
B) F + E
C) C + D + E
D) A + B + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose that a supermarket auctions contracts for manufacturers to provide it with its own-labelled products. Which of the following strategies would prevent co-operation among rival ?rms that bid for the contracts?
A) Running an English auction
B) Reducing the number of ?rms that bid for the contracts
C) Making the auction a repeated game
D) Organizing blind auctions
A) Running an English auction
B) Reducing the number of ?rms that bid for the contracts
C) Making the auction a repeated game
D) Organizing blind auctions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the market for local bus services in the UK, the ?ve-?rm concentration ratio was found to be 69 per cent. Only another ?ve companies had a share of the market which exceeded 1 per cent. Given this information, which of the following statements is most likely to be true?
A) The total number of ?rms serving the market is likely to be very high.
B) It is likely that the ?rms in the market engage in head-to-head competition rather than
C) The quality of the local bus services offered is likely to be high.
D) There are likely to be high sunk costs in the market, which form a natural entry barrier.
A) The total number of ?rms serving the market is likely to be very high.
B) It is likely that the ?rms in the market engage in head-to-head competition rather than
C) The quality of the local bus services offered is likely to be high.
D) There are likely to be high sunk costs in the market, which form a natural entry barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is the Nash equilibrium outcome of an English auction?
A) The highest bidder pays exactly the same price as the second-highest bidder.
B) The highest bidder pays a fraction more than the second-highest bidder.
C) The highest bidder pays the expected value of the second-highest bidder's willingness to pay.
D) The highest bidder pays half the bid of the second-highest bidder.
A) The highest bidder pays exactly the same price as the second-highest bidder.
B) The highest bidder pays a fraction more than the second-highest bidder.
C) The highest bidder pays the expected value of the second-highest bidder's willingness to pay.
D) The highest bidder pays half the bid of the second-highest bidder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following graph shows the bid value and probability of winning an auction for an oil painting under a ?rst-price sealed bid auction with private values. The bidder is willing to pay a maximum of £2000 for the oil painting. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 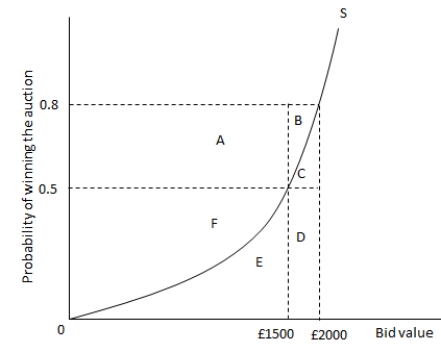 The expected value from winning the auction at £1500 is equal to the area _____.
The expected value from winning the auction at £1500 is equal to the area _____.
A) A + B + C + D + E + F
B) E + F+ D
C) B + C + D
D) C + D + E + F
 The expected value from winning the auction at £1500 is equal to the area _____.
The expected value from winning the auction at £1500 is equal to the area _____.A) A + B + C + D + E + F
B) E + F+ D
C) B + C + D
D) C + D + E + F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In Nash equilibrium, the price received by a seller in a ?rst-price sealed bid auction with private values would be equal to _____.
A) the bidder's maximum willingness to pay
B) the expected value of second-highest willingness to pay
C) the bidder's probability of winning
D) half of the bidder's minimum reserve price
A) the bidder's maximum willingness to pay
B) the expected value of second-highest willingness to pay
C) the bidder's probability of winning
D) half of the bidder's minimum reserve price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In a _____ auction, prices start high and are gradually reduced until a bidder accepts the price and wins the auction.
A) Dutch
B) English
C) ?rst-price sealed-bid
D) second-price sealed bid
A) Dutch
B) English
C) ?rst-price sealed-bid
D) second-price sealed bid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Under a Bertrand model of an oligopoly:
A) ?rms treat the price set by rival ?rms as given.
B) both ?rms collude to ?x the total level of output in the market.
C) both ?rms will choose a price lower than marginal cost.
D) ?rms will produce the level of output produced under a monopoly.
A) ?rms treat the price set by rival ?rms as given.
B) both ?rms collude to ?x the total level of output in the market.
C) both ?rms will choose a price lower than marginal cost.
D) ?rms will produce the level of output produced under a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Sony and Toshiba, are competitors in the high de?nition DVD market. The products that they launched used different recording formats and were incompatible with each other. Given that Blu- ray, Sony's product, is now the dominant format for high de?nition ?lms, which of the following is likely to be true?
A) Sony and Toshiba are likely to have colluded and set prices in the high de?nition DVD market.
B) The race to win market share between Sony and Toshiba is an example of a single-period
C) Sony is likely to have had a ?rst-mover advantage in the market for high de?nition DVDs.
D) Sony and Toshiba must have agreed to split the market for high de?nition DVDs.
A) Sony and Toshiba are likely to have colluded and set prices in the high de?nition DVD market.
B) The race to win market share between Sony and Toshiba is an example of a single-period
C) Sony is likely to have had a ?rst-mover advantage in the market for high de?nition DVDs.
D) Sony and Toshiba must have agreed to split the market for high de?nition DVDs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a _____ auction, the highest bidder pays the price of the second-highest bid.
A) second-bid
B) ?rst-bid
C) ?rst-price sealed-bid
D) second-price sealed bid
A) second-bid
B) ?rst-bid
C) ?rst-price sealed-bid
D) second-price sealed bid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For a threat to be credible it has to be:
A) made jointly by all the incumbent ?rms.
B) made by the incumbent with the smallest market share.
C) an optimal course of action for the ?rm making the threat.
D) made in a single-period game.
A) made jointly by all the incumbent ?rms.
B) made by the incumbent with the smallest market share.
C) an optimal course of action for the ?rm making the threat.
D) made in a single-period game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is a key difference between the Cournot model and the Stackelberg model of an oligopoly?
A) The leader ?rm in the Stackelberg model makes lower pro?ts than it would under the Cournot model.
B) Unlike in the Cournot model, ?rms in the Stackelberg model do not make decisions
C) Firms in the Cournot model have a ?rst-mover advantage unlike ?rms in the Stackelberg model.
D) Unlike in the Stackelberg model, ?rms in the Cournot model treat the prices of rivals as
A) The leader ?rm in the Stackelberg model makes lower pro?ts than it would under the Cournot model.
B) Unlike in the Cournot model, ?rms in the Stackelberg model do not make decisions
C) Firms in the Cournot model have a ?rst-mover advantage unlike ?rms in the Stackelberg model.
D) Unlike in the Stackelberg model, ?rms in the Cournot model treat the prices of rivals as

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Demand below the equilibrium price is inelastic in a kinked demand curve model of an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A Nash equilibrium occurs when each player in a game does what is best for themselves, irrespective of what their opponent may do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
One of the features of a monopolistically competitive market is that the number of sellers in the market is very low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Collusion is likely to fail when there are a large number of firms in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
One of the primary characteristics of oligopolistic industries are barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A cartel faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If all the firms in an oligopoly agree to co-operate, their joint profits will be maximized if they act as one monopolist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
An individual firm in a cartel is likely to earn more profits by cheating on the cartel and reducing prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The soft drinks industry, which is a market with a small number of large players, is likely to be an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An example of a natural barrier to entry in an industry is a very high minimum efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Tangency equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market occurs when the firm's average profit line just touches the firm's average total cost line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A contestable market is one where firms can enter and exit a market freely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A successful brand name owned by an incumbent firm can form barrier to entry in the industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An industry where the minimum efficient scale is large when compared to the overall market is likely to be an oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
An endogenous cost is one which cannot be influenced by a firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly suggests that if one firm increases its price then the other firms will do the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The kinked demand curve model predicts that prices in the market will be relatively stable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Monopolistic competition is the same as perfect competition except for the existence of product differentiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms are not productively efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A dominant strategy is a player's best response when the rival's decision is known.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



