Deck 8: Governing Business
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Governing Business
1
Which of the following is true of the principal-agent problem?
A) It arises when the interests of the agent and the principal differ.
B) It arises when it is relatively easy for the principal to monitor the agent's performance.
C) When there is a principal-agent problem, agency costs are zero.
D) When there is a principal-agent problem, the agent is usually worse off.
A) It arises when the interests of the agent and the principal differ.
B) It arises when it is relatively easy for the principal to monitor the agent's performance.
C) When there is a principal-agent problem, agency costs are zero.
D) When there is a principal-agent problem, the agent is usually worse off.
It arises when the interests of the agent and the principal differ.
2
Which of the following would be an example of moral hazard?
A) An employee is hired to work 10 hours a day, but instead shirks work and leaves early.
B) A taxi driver takes a passenger on a longer-than-usual route hoping to generate a higher
C) A manager informs shareholders that the ?rm's pro?ts may not be as high as expected due to an increase in costs
D) The owner of a ?rm monitors his employees through performance-linked pay and sales
A) An employee is hired to work 10 hours a day, but instead shirks work and leaves early.
B) A taxi driver takes a passenger on a longer-than-usual route hoping to generate a higher
C) A manager informs shareholders that the ?rm's pro?ts may not be as high as expected due to an increase in costs
D) The owner of a ?rm monitors his employees through performance-linked pay and sales
An employee is hired to work 10 hours a day, but instead shirks work and leaves early.
3
Under the piece-rate system, wages are paid _____.
A) according to the output produced
B) as a percentage of the total sales of the ?rm
C) according to the number of hours of labour
D) as a percentage of the pro?ts earned by the ?rm
A) according to the output produced
B) as a percentage of the total sales of the ?rm
C) according to the number of hours of labour
D) as a percentage of the pro?ts earned by the ?rm
according to the output produced
4
For performance contracts to be successful:
A) workers should be able to unduly in?uence the measure.
B) workers must be willing to receive greater reward for greater risk.
C) worker performance is focused on a single objective.
D) there needn't be a strong link between worker effort and the performance measure.
A) workers should be able to unduly in?uence the measure.
B) workers must be willing to receive greater reward for greater risk.
C) worker performance is focused on a single objective.
D) there needn't be a strong link between worker effort and the performance measure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following explains why diversi?cation of a business is in the managers' interest?
A) It protects the shareholders from risk.
B) It is an example of expense preference behaviour.
C) It maximizes the ?rm's pro?ts.
D) It diversi?es a risk that only managers face.
A) It protects the shareholders from risk.
B) It is an example of expense preference behaviour.
C) It maximizes the ?rm's pro?ts.
D) It diversi?es a risk that only managers face.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Managers, and not owners, will seek to maximize growth because:
A) growth maximization is the same as pro?t maximization.
B) measuring the growth of a ?rm can be subjective.
C) a manager's pay is usually linked to the size of the business.
D) growth maximization will allow the ?rm to satis?ce on various targets.
A) growth maximization is the same as pro?t maximization.
B) measuring the growth of a ?rm can be subjective.
C) a manager's pay is usually linked to the size of the business.
D) growth maximization will allow the ?rm to satis?ce on various targets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following correctly describes moral hazard-type behaviour by managers?
A) Managers disclose complete information about their behaviour to the shareholders.
B) Managers offer to increase sales and pro?ts but, once hired, act in their own interests.
C) Managers reduce the monitoring costs through good performance.
D) Managers help in the expansion of the business and increase pro?ts.
A) Managers disclose complete information about their behaviour to the shareholders.
B) Managers offer to increase sales and pro?ts but, once hired, act in their own interests.
C) Managers reduce the monitoring costs through good performance.
D) Managers help in the expansion of the business and increase pro?ts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Moral hazard can be reduced at the workplace by _____.
A) setting and monitoring targets for managers
B) aiming to maximize growth and not sales
C) paying managers higher salaries
D) increasing the number of managers in the ?rm
A) setting and monitoring targets for managers
B) aiming to maximize growth and not sales
C) paying managers higher salaries
D) increasing the number of managers in the ?rm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Pro?ts may decline when sales increase if:
A) there are diseconomies of scale.
B) costs remain constant.
C) there are increasing returns to scale.
D) the variable cost of production falls.
A) there are diseconomies of scale.
B) costs remain constant.
C) there are increasing returns to scale.
D) the variable cost of production falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The senior manager at a ?rm sets a sales target of 20 000 units for the month. Most other ?rms in the market also have similar targets. However, the maximum possible sales in the market was found to be 35 000 units per month. This suggests that:
A) growth maximization is the ?rm's goal.
B) the ?rm does not have principal-agent problems.
C) the senior manager exhibits satis?cing behaviour.
D) salaries at this ?rm are linked to pro?ts.
A) growth maximization is the ?rm's goal.
B) the ?rm does not have principal-agent problems.
C) the senior manager exhibits satis?cing behaviour.
D) salaries at this ?rm are linked to pro?ts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an example of expense preference behaviour by managers in a ?rm?
A) Consumption of perquisites.
B) Goal setting.
C) Satis?cing.
D) Sales maximization.
A) Consumption of perquisites.
B) Goal setting.
C) Satis?cing.
D) Sales maximization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following could explain why bad management teams continue to be employed by a ?rm?
A) The shareholdings in the ?rm are highly dispersed.
B) Ownership and control in the ?rm are not separate.
C) The shareholders' objective is to maximize the ?rm's pro?ts.
D) The objectives of managers and workers in the ?rm are closely aligned with each other.
A) The shareholdings in the ?rm are highly dispersed.
B) Ownership and control in the ?rm are not separate.
C) The shareholders' objective is to maximize the ?rm's pro?ts.
D) The objectives of managers and workers in the ?rm are closely aligned with each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following forms of organization is likely to face problems of ownership and control?
A) A family-run sole proprietorship ?rm.
B) A small not-for-pro?t organization that employs only 10 people.
C) A partnership ?rm where each partner is also a manager.
D) A large corporation where each shareholder owns less than 1% of the total stock.
A) A family-run sole proprietorship ?rm.
B) A small not-for-pro?t organization that employs only 10 people.
C) A partnership ?rm where each partner is also a manager.
D) A large corporation where each shareholder owns less than 1% of the total stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The principal-agent problem arises when:
A) principals and agents have the same objectives.
B) principals have more information than agents.
C) it is di?cult for the principal to monitor the agent.
D) the agents disclose full information regarding their behaviour.
A) principals and agents have the same objectives.
B) principals have more information than agents.
C) it is di?cult for the principal to monitor the agent.
D) the agents disclose full information regarding their behaviour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a solution to the principal-agent problem within a ?rm?
A) Provide the managers with shares in the company.
B) Increase the managers' annual sales target.
C) Increase the ?xed component of an employee's salary.
D) Allow the government to set rules on performance.
A) Provide the managers with shares in the company.
B) Increase the managers' annual sales target.
C) Increase the ?xed component of an employee's salary.
D) Allow the government to set rules on performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
_____ is most likely to be a free rider.
A) A managing director of a ?rm, who also owns a substantial percentage of the ?rm's stocks
B) A manager whose pay is linked to the pro?ts earned by the company
C) An employee who is compensated solely on the basis of his team's aggregate performance
D) A factory worker whose daily work can be easily monitored
A) A managing director of a ?rm, who also owns a substantial percentage of the ?rm's stocks
B) A manager whose pay is linked to the pro?ts earned by the company
C) An employee who is compensated solely on the basis of his team's aggregate performance
D) A factory worker whose daily work can be easily monitored

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Satis?cing behaviour would NOT involve:
A) separation of ownership and control.
B) attaining average levels of performance.
C) setting and achieving the highest target possible.
D) trade-offs between managers and owners.
A) separation of ownership and control.
B) attaining average levels of performance.
C) setting and achieving the highest target possible.
D) trade-offs between managers and owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How might an employer reduce the agency costs associated with an employment contract?
A) Reduce the effort and cost spent in monitoring the employee's work.
B) Reduce the employee's probation period.
C) Link the employee's pay to the level of output.
D) Increase the number of levels in the management hierarchy.
A) Reduce the effort and cost spent in monitoring the employee's work.
B) Reduce the employee's probation period.
C) Link the employee's pay to the level of output.
D) Increase the number of levels in the management hierarchy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to _____, managers use the company's funds to ?nance a prestigious image makeover and lifestyle.
A) the expense preference behaviour theory
B) Maslow's heirarchy of needs
C) Porter's ?ve forces model
D) the human capital and development theory
A) the expense preference behaviour theory
B) Maslow's heirarchy of needs
C) Porter's ?ve forces model
D) the human capital and development theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The costs of _____ are termed agency costs.
A) research and development
B) advertising
C) monitoring performance
D) producing a good
A) research and development
B) advertising
C) monitoring performance
D) producing a good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a good generates a negative externality in the market:
A) society's scarce resources are allocated e?ciently.
B) its marginal social cost is greater than its marginal private cost.
C) the good's price accurately re?ects the cost of the externality.
D) the quantity demanded of the good will be equal to zero.
A) society's scarce resources are allocated e?ciently.
B) its marginal social cost is greater than its marginal private cost.
C) the good's price accurately re?ects the cost of the externality.
D) the quantity demanded of the good will be equal to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following could create a negative externality?
A) A ?rm using pollution-intensive machinery.
B) An individual gaining a university degree.
C) A ?rm increasing the number of training programmes.
D) An individual being vaccinated against a disease.
A) A ?rm using pollution-intensive machinery.
B) An individual gaining a university degree.
C) A ?rm increasing the number of training programmes.
D) An individual being vaccinated against a disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In the following graph, MPC and MSC represent the marginal private cost and marginal social cost of producing a good respectively. QD represents the demand for the good. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 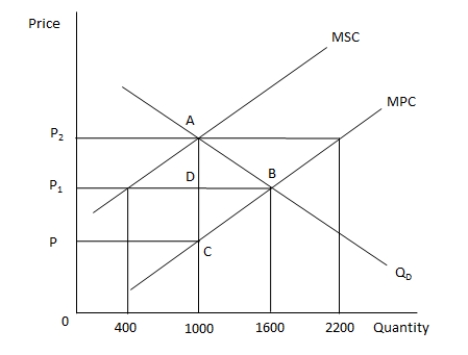 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The MPC of production is greater than the MSC of producing the good.
B) The quantity of the good produced in the market will be higher than the socially optimal
C) For the market to produce the socially optimal level of output, the government should provide a subsidy.
D) There is a positive externality associated with the production and consumption of this
 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?A) The MPC of production is greater than the MSC of producing the good.
B) The quantity of the good produced in the market will be higher than the socially optimal
C) For the market to produce the socially optimal level of output, the government should provide a subsidy.
D) There is a positive externality associated with the production and consumption of this

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Under a performance contract, a dentist would be paid:
A) according to the number of hours spent at the dental clinic.
B) according to the number of days worked in a month.
C) a ?xed amount every month.
D) according to the number of dental treatments provided to patients.
A) according to the number of hours spent at the dental clinic.
B) according to the number of days worked in a month.
C) a ?xed amount every month.
D) according to the number of dental treatments provided to patients.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An externality exists in the production of a good or service when:
A) the marginal cost to society of consuming an extra unit of a good equals the marginal social bene?t.
B) resources are allocated such that no one can be made better off without making someone
C) the marginal social cost differs from the marginal private cost of production.
D) markets are allocatively and productively e?cient.
A) the marginal cost to society of consuming an extra unit of a good equals the marginal social bene?t.
B) resources are allocated such that no one can be made better off without making someone
C) the marginal social cost differs from the marginal private cost of production.
D) markets are allocatively and productively e?cient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If either consumers or producers have incomplete information about the safety of a good, then:
A) the market price would differ from the marginal social cost and marginal social bene?t of the good.
B) the quantity of the good demanded and supplied would be equal to zero.
C) the quantity demanded of the good would exceed the quantity supplied.
D) there would be a persistent surplus of the good on the market since producers will
A) the market price would differ from the marginal social cost and marginal social bene?t of the good.
B) the quantity of the good demanded and supplied would be equal to zero.
C) the quantity demanded of the good would exceed the quantity supplied.
D) there would be a persistent surplus of the good on the market since producers will

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the following graph, MPC and MSC represent the marginal private cost and marginal social cost of producing a good respectively. QD represents the demand for the good. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 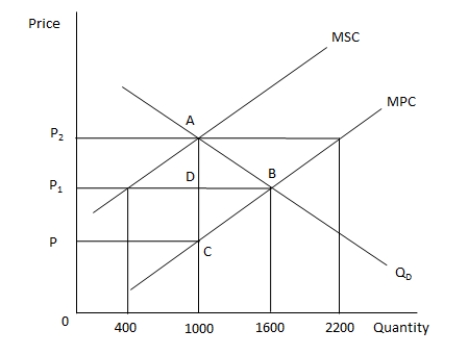 The socially optimum level of output is _____ of the good.
The socially optimum level of output is _____ of the good.
A) 400 units
B) 1000 units
C) 1600 units
D) 2200 units
 The socially optimum level of output is _____ of the good.
The socially optimum level of output is _____ of the good.A) 400 units
B) 1000 units
C) 1600 units
D) 2200 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is likely to generate a positive externality?
A) An industry dumping chemical waste into a local river.
B) An individual planting ?owers in his garden.
C) A teenager playing loud music at home.
D) A tree being hit by lightning.
A) An industry dumping chemical waste into a local river.
B) An individual planting ?owers in his garden.
C) A teenager playing loud music at home.
D) A tree being hit by lightning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is true of Pareto e?ciency?
A) It is consistent with productive and allocative e?ciency.
B) It is an example of a pricing strategy by a price leader.
C) It is achieved when ?rms make the highest possible level of output.
D) It is a measure of accounting e?ciency.
A) It is consistent with productive and allocative e?ciency.
B) It is an example of a pricing strategy by a price leader.
C) It is achieved when ?rms make the highest possible level of output.
D) It is a measure of accounting e?ciency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Market failure is likely in markets that:
A) are perfectly competitive.
B) have complete information.
C) are e?cient in production
D) have negative externalities.
A) are perfectly competitive.
B) have complete information.
C) are e?cient in production
D) have negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the following graph, MPC and MSC represent the marginal private cost and marginal social cost of producing a good respectively. QD represents the demand for the good. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 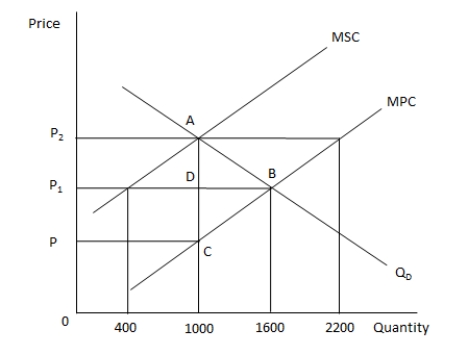 The private ?rm will maximize pro?ts by producing _____ of the good.
The private ?rm will maximize pro?ts by producing _____ of the good.
A) 1000 units
B) 400 units
C) 1600 units
D) 2200 units
 The private ?rm will maximize pro?ts by producing _____ of the good.
The private ?rm will maximize pro?ts by producing _____ of the good.A) 1000 units
B) 400 units
C) 1600 units
D) 2200 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is true of perfect competition?
A) Pareto e?ciency holds in perfect competition.
B) Firms operate at the highest point on their long-run cost curve.
C) The price in the market is higher than the marginal cost.
D) Firms make the highest level of output at the highest possible cost.
A) Pareto e?ciency holds in perfect competition.
B) Firms operate at the highest point on their long-run cost curve.
C) The price in the market is higher than the marginal cost.
D) Firms make the highest level of output at the highest possible cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Pareto e?ciency is achieved when:
A) producers are price-setters in the market.
B) market prices are greater than marginal cost.
C) the marginal cost of a good equals the marginal bene?t from a good.
D) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.
A) producers are price-setters in the market.
B) market prices are greater than marginal cost.
C) the marginal cost of a good equals the marginal bene?t from a good.
D) marginal social costs are greater than marginal private costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When would stock options offered to an employee be ineffective in reducing the principal-agent problem?
A) When the link between worker effort and the share price of the ?rm is clear.
B) When stock options form a large proportion of the worker's pay.
C) When the share price of the ?rm is affected by external factors.
D) When the worker is unable to in?uence the share price of the ?rm.
A) When the link between worker effort and the share price of the ?rm is clear.
B) When stock options form a large proportion of the worker's pay.
C) When the share price of the ?rm is affected by external factors.
D) When the worker is unable to in?uence the share price of the ?rm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When there is an externality in the production of a good:
A) the value that consumers get from consuming the good is equal to the cost of producing the good.
B) some costs are passed on to individuals not involved in production or consumption.
C) the market for the good is likely to be perfectly competitive.
D) resource allocation is likely to be allocatively e?cient.
A) the value that consumers get from consuming the good is equal to the cost of producing the good.
B) some costs are passed on to individuals not involved in production or consumption.
C) the market for the good is likely to be perfectly competitive.
D) resource allocation is likely to be allocatively e?cient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Pareto e?ciency holds in a(n) _____.
A) monopoly
B) oligopoly
C) perfectly competitive market
D) monopolistically competitive market
A) monopoly
B) oligopoly
C) perfectly competitive market
D) monopolistically competitive market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When _____, there is market failure.
A) the costs of production are minimized
B) market price is greater than marginal cost
C) the demand for a good is high
D) the supply of a good is perfectly inelastic
A) the costs of production are minimized
B) market price is greater than marginal cost
C) the demand for a good is high
D) the supply of a good is perfectly inelastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A Pareto e?cient outcome is one where:
A) each individual's welfare depends on the quantity of resources that he owns.
B) each individual receives an equal share of the total resources.
C) an individual cannot be made better off without making another individual worse off.
D) an individual's welfare is maximized at the cost of society's overall welfare.
A) each individual's welfare depends on the quantity of resources that he owns.
B) each individual receives an equal share of the total resources.
C) an individual cannot be made better off without making another individual worse off.
D) an individual's welfare is maximized at the cost of society's overall welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the marginal private cost of a good is greater than its marginal social cost, then the good is said to have _____.
A) a positive externality
B) economies of scale
C) Pareto e?ciency
D) a dead-weight loss
A) a positive externality
B) economies of scale
C) Pareto e?ciency
D) a dead-weight loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is true of the private level of output of goods with negative externalities?
A) The private level of output will be lower than the socially-optimal level.
B) The private ?rm will produce that level of output where marginal social bene?t equals
C) The private ?rm will produce that level of output where marginal social cost equals marginal private bene?t.
D) The private level of output will be higher than the socially-optimal level.
A) The private level of output will be lower than the socially-optimal level.
B) The private ?rm will produce that level of output where marginal social bene?t equals
C) The private ?rm will produce that level of output where marginal social cost equals marginal private bene?t.
D) The private level of output will be higher than the socially-optimal level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the following graph, MPC and MSC represent the marginal private cost and marginal social cost of producing a good respectively. QD represents the demand for the good. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 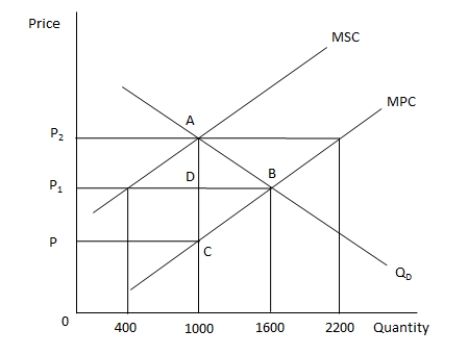 The amount of tax that the government should levy to bring output to the socially optimum level is equal to the distance between the points _____.
The amount of tax that the government should levy to bring output to the socially optimum level is equal to the distance between the points _____.
A) A and B
B) B and D
C) B and C
D) A and C
 The amount of tax that the government should levy to bring output to the socially optimum level is equal to the distance between the points _____.
The amount of tax that the government should levy to bring output to the socially optimum level is equal to the distance between the points _____.A) A and B
B) B and D
C) B and C
D) A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is an example of a menu cost?
A) The cost of printing new price lists.
B) The cost of advertising and brand development.
C) The cost of monitoring the performance of an employee.
D) The cost of producing an additional unit of a good.
A) The cost of printing new price lists.
B) The cost of advertising and brand development.
C) The cost of monitoring the performance of an employee.
D) The cost of producing an additional unit of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is true of a monopoly?
A) A monopoly market is Pareto e?cient.
B) The level of consumer surplus is greater in monopoly compared to perfect competition.
C) The level of producer surplus is higher in monopoly compared to perfect competition.
D) There is no dead-weight loss in a monopoly.
A) A monopoly market is Pareto e?cient.
B) The level of consumer surplus is greater in monopoly compared to perfect competition.
C) The level of producer surplus is higher in monopoly compared to perfect competition.
D) There is no dead-weight loss in a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Under the European system of carbon emissions caps:
A) all industries can pollute an unspeci?ed quantity if they pay a one-time fee.
B) industries with a surplus of permits trade with those that have a shortage.
C) polluting industries have an incentive to invest in pollution-generating technology.
D) the marginal private costs of pollution for polluting ?rms are reduced.
A) all industries can pollute an unspeci?ed quantity if they pay a one-time fee.
B) industries with a surplus of permits trade with those that have a shortage.
C) polluting industries have an incentive to invest in pollution-generating technology.
D) the marginal private costs of pollution for polluting ?rms are reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the following graph, MR and AR represent the marginal revenue and average revenue curves of a monopoly ?rm respectively. MC represents the marginal cost curve of the ?rm. Refer to the ?gure to answer the question. 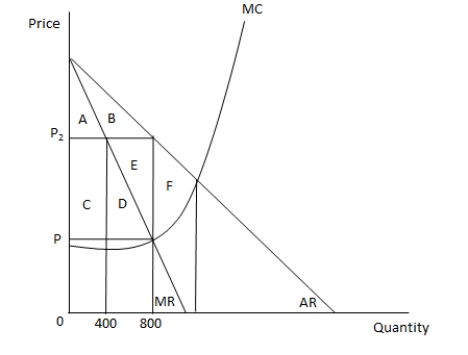 When the price in the market is P2, consumer surplus is equal to the area _____.
When the price in the market is P2, consumer surplus is equal to the area _____.
A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F
 When the price in the market is P2, consumer surplus is equal to the area _____.
When the price in the market is P2, consumer surplus is equal to the area _____.A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is a function of the Competition and Markets Authority in the UK?
A) Promoting cartels.
B) Promoting monopoly.
C) Encouraging large scale mergers to increase competition.
D) Encouraging fair trade and competition.
A) Promoting cartels.
B) Promoting monopoly.
C) Encouraging large scale mergers to increase competition.
D) Encouraging fair trade and competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Price volatility can make budgetary planning for households and ?rms very di?cult.
B) An increase in supply when demand is inelastic will cause an increase in price.
C) The price volatility of consumer products tends to be higher than price volatility in agricultural produce.
D) When supply is elastic an increase in demand drives prices higher than when supply is
A) Price volatility can make budgetary planning for households and ?rms very di?cult.
B) An increase in supply when demand is inelastic will cause an increase in price.
C) The price volatility of consumer products tends to be higher than price volatility in agricultural produce.
D) When supply is elastic an increase in demand drives prices higher than when supply is

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is a drawback of cost-bene?t analysis?
A) Costs and bene?ts that accrue over time cannot be assessed.
B) It may be di?cult to measure costs and bene?ts in monetary terms.
C) The costs of an activity are usually greater than the bene?ts.
D) Cost-bene?t analysis can only be used to assess government interventions.
A) Costs and bene?ts that accrue over time cannot be assessed.
B) It may be di?cult to measure costs and bene?ts in monetary terms.
C) The costs of an activity are usually greater than the bene?ts.
D) Cost-bene?t analysis can only be used to assess government interventions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the following graph, MR and AR represent the marginal revenue and average revenue curves of a monopoly ?rm respectively. MC represents the marginal cost curve of the ?rm. Refer to the ?gure to answer the question. 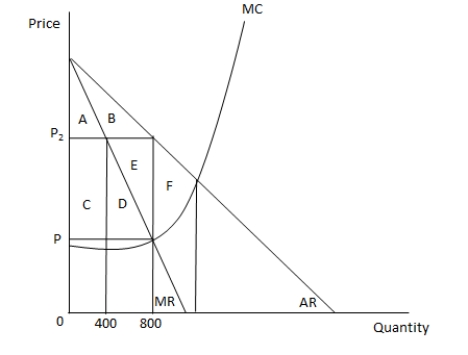 The pro?t-maximizing monopoly ?rm will produce output at the point where:
The pro?t-maximizing monopoly ?rm will produce output at the point where:
A) marginal cost is decreasing.
B) the marginal cost curve intersects the marginal revenue curve.
C) the average revenue curve intersects the marginal cost curve.
D) marginal cost is zero.
 The pro?t-maximizing monopoly ?rm will produce output at the point where:
The pro?t-maximizing monopoly ?rm will produce output at the point where:A) marginal cost is decreasing.
B) the marginal cost curve intersects the marginal revenue curve.
C) the average revenue curve intersects the marginal cost curve.
D) marginal cost is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An increase in the cost of obtaining higher education with no change in the bene?ts received will result in:
A) an increase in the supply of graduates.
B) a decrease in the rate of return to higher education.
C) a relatively lower level of income for college graduates.
D) an increase in the demand for higher education.
A) an increase in the supply of graduates.
B) a decrease in the rate of return to higher education.
C) a relatively lower level of income for college graduates.
D) an increase in the demand for higher education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the following graph, MR and AR represent the marginal revenue and average revenue curves of a monopoly ?rm respectively. MC represents the marginal cost curve of the ?rm. Refer to the graph to answer the question.  When price is P2, the dead-weight loss in the market is equal to the area _____.
When price is P2, the dead-weight loss in the market is equal to the area _____.
A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F
 When price is P2, the dead-weight loss in the market is equal to the area _____.
When price is P2, the dead-weight loss in the market is equal to the area _____.A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the following graph, MR and AR represent the marginal revenue and average revenue curves of a monopoly ?rm respectively. MC represents the marginal cost curve of the ?rm. Refer to the graph to answer the question. 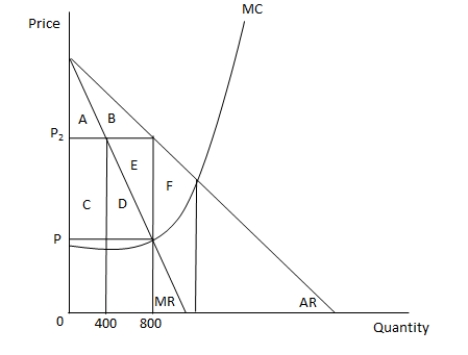 When the price in the market is P2, producer surplus is equal to the area _____.
When the price in the market is P2, producer surplus is equal to the area _____.
A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F
 When the price in the market is P2, producer surplus is equal to the area _____.
When the price in the market is P2, producer surplus is equal to the area _____.A) A + B
B) C + D + E
C) E + F
D) F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is an example of a public good?
A) A street light.
B) An apple.
C) A house.
D) A car.
A) A street light.
B) An apple.
C) A house.
D) A car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When the supply of a good is inelastic, an increase in demand will:
A) increase prices by more than when supply is elastic.
B) not affect quantity supplied.
C) not affect the equilibrium price.
D) increase quantity by more than when supply is elastic.
A) increase prices by more than when supply is elastic.
B) not affect quantity supplied.
C) not affect the equilibrium price.
D) increase quantity by more than when supply is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following measures by the government would increase the level of education in the country?
A) Increase the level of tax on education.
B) Subsidize the rate of interest on education loans.
C) Provide subsidies to ?rms so they can hire more workers.
D) Increase the level of income tax in the economy.
A) Increase the level of tax on education.
B) Subsidize the rate of interest on education loans.
C) Provide subsidies to ?rms so they can hire more workers.
D) Increase the level of income tax in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If a competitive market becomes a monopoly _____.
A) society's welfare increases
B) producer surplus does not change
C) there is a dead-weight loss in the market
D) consumer surplus in the monopoly will increase
A) society's welfare increases
B) producer surplus does not change
C) there is a dead-weight loss in the market
D) consumer surplus in the monopoly will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The environmental Kuznets curve shows:
A) a direct relationship between the emission of carbon dioxide and marginal private costs.
B) a negative relationship between the level of pollution and the demand for a product.
C) a u-shaped relationship between consumer income and the demand for environmentally friendly goods.
D) an n-shaped relationship between production of greenhouse gases and real GDP per
A) a direct relationship between the emission of carbon dioxide and marginal private costs.
B) a negative relationship between the level of pollution and the demand for a product.
C) a u-shaped relationship between consumer income and the demand for environmentally friendly goods.
D) an n-shaped relationship between production of greenhouse gases and real GDP per

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is a feature of a public good?
A) Rivalrous consumption.
B) Excludable consumption.
C) Low levels of consumption.
D) Non-rivalrous and non-excludable consumption.
A) Rivalrous consumption.
B) Excludable consumption.
C) Low levels of consumption.
D) Non-rivalrous and non-excludable consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In a market economy, the ideal solution to the problem of externalities would be to:
A) prohibit all production involving spillover costs.
B) regulate both the amount people may consume and the price they pay for goods whose
C) charge or tax producers of a good the precise marginal cost of the externality generated in production.
D) offer subsidies to the industries causing a negative externality.
A) prohibit all production involving spillover costs.
B) regulate both the amount people may consume and the price they pay for goods whose
C) charge or tax producers of a good the precise marginal cost of the externality generated in production.
D) offer subsidies to the industries causing a negative externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following statements is true?
A) There are likely to be merit and demerit goods in a market where there is complete information.
B) Merit goods provide consumers with more bene?ts than they may expect.
C) Education and health care are examples of demerit goods.
D) Smoking and drinking are examples of merit goods.
A) There are likely to be merit and demerit goods in a market where there is complete information.
B) Merit goods provide consumers with more bene?ts than they may expect.
C) Education and health care are examples of demerit goods.
D) Smoking and drinking are examples of merit goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The stronger the link between worker effort and the performance measure, the stronger the incentive for the worker to work hard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Within a firm, managers are the principals, hired on behalf of the shareholders who are the agents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The separation of ownership from control explains why firms aim to maximize profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The separation of ownership from control exists where the shareholders, who own the company, are a different set of individuals from the managers that control the business on a day-to-day basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The market for public goods is subject to market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
When people are made better off without making others worse off, the total well-being of society improves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Standard deviation is a measure of how much a variable differs from its average value over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A free rider benefits from the actions of others without having to contribute to the costs of these actions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Under the expense preference behaviour theory, managers prefer to maximize the profits of the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a tax is levied on pollution, a polluting firm has an incentive to reduce the level of pollution that it emits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
To increase the number of people installing solar panels, the government should subsidise firms that produce solar panels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Undertaking diversification of the firm's product line is more in the interests of managers than shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Air pollution from a paper mill is an example of an externality in the production of paper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Satisficing behaviour by managers is the attainment of maximum levels of performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A negative externality occurs if production, or consumption, by one group reduces the well-being of third parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Subsidies are provided to goods for which the private level of output is more than the socially optimal level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Managers who are employed to run companies are subject to the principal-agent problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Paying labour with piece rate wages is a strategy that can reduce the agency costs of the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Through the fair fuel stabilizer, the UK government manages volatility in the prices of petrol and diesel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A stock option that is offered to a manager gives him the right to buy a share in the company at the future share price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



