Deck 4: Cellular Immunity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Cellular Immunity
1
David (the bubble boy's) SCID was due to defects in genes encoding for
A) the IL-2 receptor alpha
B) the IL-2 receptor gamma
C) the CD4 molecule
D) the CD8 molecule
A) the IL-2 receptor alpha
B) the IL-2 receptor gamma
C) the CD4 molecule
D) the CD8 molecule
Severe combined immunodeficiency, or SCID, is a hereditary disease characterized by an extreme dysfunction of the immune system. Patients suffering from SCID have extremely low B-cell and T-cell counts, and are hence, unlikely to survive for long due to the high likelihood of complications arising from immunodeficiency.
David Vetter, who suffered from a widely publicized case of SCID, was a patient of X-linked SCID. However, there was not a genetic defect in the expression of CD4 (cluster of differntiation) molecules, CD8 molecules, or interleukin-2 alpha chain molecules.
Hence, options a, c and d are incorrect.
The severe combined immunodeficiency disease was the result of a genetic defect in the gene coding for the gamma receptor of the interleukin-2 receptor complex. Since these gamma chain molecules are shared among many other receptors, the loss of its expression has severe consequences.
Hence, the correct answer is option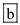 .
.
David Vetter, who suffered from a widely publicized case of SCID, was a patient of X-linked SCID. However, there was not a genetic defect in the expression of CD4 (cluster of differntiation) molecules, CD8 molecules, or interleukin-2 alpha chain molecules.
Hence, options a, c and d are incorrect.
The severe combined immunodeficiency disease was the result of a genetic defect in the gene coding for the gamma receptor of the interleukin-2 receptor complex. Since these gamma chain molecules are shared among many other receptors, the loss of its expression has severe consequences.
Hence, the correct answer is option
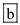 .
. 2
In T-cell tolerance, positive selection is associated with
A) presentation of self-antigens to the T cell
B) production of a large number of B cells
C) deletion of self-reactive T cells
D) MHC restriction of the T cell repertoire
A) presentation of self-antigens to the T cell
B) production of a large number of B cells
C) deletion of self-reactive T cells
D) MHC restriction of the T cell repertoire
T (thymus) cell tolerance is a major aspect of the development of T cell. The development of tolerance refers to the T cells not having an immunogenic reaction to self-proteins and biomolecules within the body.
T cell tolerance has procedures for both negative as well as positive selection of the cells (cells). Presentation of self-antigens to the T cell is an aspect of negative selection, as the T cells that have an immunogenic reaction would be culled. Similarly, T cells (self-reactive) deletion is a selection that is negative, and the production of a large number of B cells (Bursa of Fabricius) is unrelated to T cell tolerance.
Hence, the options a, b and c are incorrect.
The restriction of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) repertoire of T cells is an example of positive selection for the tolerant T cells. This ensures that only those T cells, which are non-reactive for the self-molecules (MHC), would be able to mature and function in the body.
Hence, the correct answer is option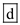 .
.
T cell tolerance has procedures for both negative as well as positive selection of the cells (cells). Presentation of self-antigens to the T cell is an aspect of negative selection, as the T cells that have an immunogenic reaction would be culled. Similarly, T cells (self-reactive) deletion is a selection that is negative, and the production of a large number of B cells (Bursa of Fabricius) is unrelated to T cell tolerance.
Hence, the options a, b and c are incorrect.
The restriction of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) repertoire of T cells is an example of positive selection for the tolerant T cells. This ensures that only those T cells, which are non-reactive for the self-molecules (MHC), would be able to mature and function in the body.
Hence, the correct answer is option
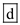 .
. 3
In T-cell tolerance, negative selection involves
A) presentation of self-antigens to a T cell
B) MHC restriction of the T cell
C) deletion of self-reactive antigen-presenting cells
D) elimination of T-independent antigens
A) presentation of self-antigens to a T cell
B) MHC restriction of the T cell
C) deletion of self-reactive antigen-presenting cells
D) elimination of T-independent antigens
The process of how T-cell tolerance is developed is a complex one, and involves aspects of both positive and negative selection. It is important to understand the differences in these procedures, and how they work.
Major histocompatibility complex or MHC restriction of T-cells happens as a result of positive selection of tolerant T-cells. Likewise, deletion of self-reactive antigen-presenting cells and eliminating antigens that are T-cell independent do not factor into the process of negative selection.
Hence, options b, c and d are incorrect.
The procedure of negative selection occurs when T-cells are exposed to self-antigens. T-cells that react to these self-antigens are killed off before they can even mature, hence, ensuring only tolerant T-cells are able to fully mature.
Hence, the correct answer is option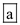 .
.
Major histocompatibility complex or MHC restriction of T-cells happens as a result of positive selection of tolerant T-cells. Likewise, deletion of self-reactive antigen-presenting cells and eliminating antigens that are T-cell independent do not factor into the process of negative selection.
Hence, options b, c and d are incorrect.
The procedure of negative selection occurs when T-cells are exposed to self-antigens. T-cells that react to these self-antigens are killed off before they can even mature, hence, ensuring only tolerant T-cells are able to fully mature.
Hence, the correct answer is option
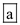 .
. 4
T cells mature in the
A) thymus
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) lymphatics
A) thymus
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) lymphatics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following cytokine receptor subunits possesses no signaling capacity but acts as an affinity modulator? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
IL-2 is made by T cells and can trigger T cells.
a. true
b. false
a. true
b. false

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A T cell that is positive for CD4 and CD8 is
A) a helper and a killer T cell
B) a double negative thymocyte
C) an immature or a tumor cell
D) a T-suppressor cell
A) a helper and a killer T cell
B) a double negative thymocyte
C) an immature or a tumor cell
D) a T-suppressor cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Antigen presentation to T cells is performed by
A) monocytes
B) macrophages
C) B cells
D) any of the above
E) A and B only
A) monocytes
B) macrophages
C) B cells
D) any of the above
E) A and B only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When a cell makes a cytokine that affects a distant cell, the response is called
A) paracrine
B) endocrine
C) autocrine
D) allocrine
A) paracrine
B) endocrine
C) autocrine
D) allocrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
CD8+ cells require interaction with
A) class I molecules
B) class II molecules
C) both class I and class II molecules
D) gamma delta cells
A) class I molecules
B) class II molecules
C) both class I and class II molecules
D) gamma delta cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
IL-6 is made by
A) mast cells
B) B cells
C) T cells
D) macrophages
A) mast cells
B) B cells
C) T cells
D) macrophages

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



