Deck 1: Introduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction
1
The term behavior refers to any activity of an organism that can be o _______ or somehow m _______, whereas the term learning refers to a relatively p _______ change in what an organism does as a result of some type of ex _______.
Any activity performed by an organism which can be observed or measured somehow is called as behavior. This activity can either be internal or external and thus may or may not be visible to any other people.
Learning , on the other hand, refers to a specifically permanent change in the overall behavior of an individual that gets resulted into some kind of experience. Any change in behavior is not necessary to be immediate in nature. In certain circumstances, this change in behavior might not even become evident until a long time passes after the experience. A very good example to accentuate the difference between behavior and learning is by taking the example of reading a book. This is a typical behavior. However, any lasting change in the behavior of the person reading the book will be classic example of learning. Thus, there are two basic processes of learning such as classical learning (also called as Pavlovian or respondent ) and operant conditioning.
A very good example to accentuate the difference between behavior and learning is by taking the example of reading a book. This is a typical behavior. However, any lasting change in the behavior of the person reading the book will be classic example of learning. Thus, there are two basic processes of learning such as classical learning (also called as Pavlovian or respondent ) and operant conditioning.
So, the blank (a) can be filled with , blank (b) can be filled with
, blank (b) can be filled with 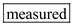 , blank (c) can be filled with
, blank (c) can be filled with  and blank (d) can be filled with
and blank (d) can be filled with  .
.
Learning , on the other hand, refers to a specifically permanent change in the overall behavior of an individual that gets resulted into some kind of experience. Any change in behavior is not necessary to be immediate in nature. In certain circumstances, this change in behavior might not even become evident until a long time passes after the experience.
 A very good example to accentuate the difference between behavior and learning is by taking the example of reading a book. This is a typical behavior. However, any lasting change in the behavior of the person reading the book will be classic example of learning. Thus, there are two basic processes of learning such as classical learning (also called as Pavlovian or respondent ) and operant conditioning.
A very good example to accentuate the difference between behavior and learning is by taking the example of reading a book. This is a typical behavior. However, any lasting change in the behavior of the person reading the book will be classic example of learning. Thus, there are two basic processes of learning such as classical learning (also called as Pavlovian or respondent ) and operant conditioning. So, the blank (a) can be filled with
 , blank (b) can be filled with
, blank (b) can be filled with 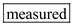 , blank (c) can be filled with
, blank (c) can be filled with  and blank (d) can be filled with
and blank (d) can be filled with  .
. 2
The nativist position, as exemplified by the Greek philosopher _______, emphasizes the role of (learning/heredity) _______.
Aristotle, a Greek philosopher, lived back in between 384 to 322 B.C. His teacher Plato believed that everything an individual knows is innate or inborn. Thus, all of the knowledge of that individual resides in his/her soul.
For him, learning was a phenomenon of inner reflection that would help uncover the knowledge which exists within a human. However, Aristotle did not agree with Plato's ideology, and he went on to argue that knowledge of an individual is not innate. Rather, he stated that knowledge is something that is acquired over a time through experiences.
This disagreement between Aristotle's and Plato's ideologies serves as a classic example of a debate between the ideas of nativism and empiricism. These concepts are basically the nature and nurture perspectives respectively. The concept of Nativist (nature) takes into assumption that an individual's abilities as well as tendencies are mostly innate. Hence, Plato's ideology is an example of nativist.
On the other hand, the empiricist or the nurture perspective takes into assumption that an individual's abilities as well as tendencies are mostly acquired or learned through experience. Therefore, Aristotle's ideology is an example of empiricist.
So, the first blank can be filled with and the second blank can be filled with
and the second blank can be filled with  .
.
For him, learning was a phenomenon of inner reflection that would help uncover the knowledge which exists within a human. However, Aristotle did not agree with Plato's ideology, and he went on to argue that knowledge of an individual is not innate. Rather, he stated that knowledge is something that is acquired over a time through experiences.
This disagreement between Aristotle's and Plato's ideologies serves as a classic example of a debate between the ideas of nativism and empiricism. These concepts are basically the nature and nurture perspectives respectively. The concept of Nativist (nature) takes into assumption that an individual's abilities as well as tendencies are mostly innate. Hence, Plato's ideology is an example of nativist.
On the other hand, the empiricist or the nurture perspective takes into assumption that an individual's abilities as well as tendencies are mostly acquired or learned through experience. Therefore, Aristotle's ideology is an example of empiricist.
So, the first blank can be filled with
 and the second blank can be filled with
and the second blank can be filled with  .
. 3
Descartes' dualistic model proposed that human behavior has two aspects: an inv_______ aspect that functions like a machine and a v_______ aspect governed by f_______ w _______. By contrast, the behavior of animals was believed to be entirely _______.
Descartes was known to oppose this notion. He went on to propose a dualistic model for the nature of humans. He claimed that the human body functions just like a machine does and produces reflexive or involuntary behaviors as a response to external stimuli like sneezing, which is caused due to dust. His model also proposed that there is another aspect of the humans, their mind, having free will and producing behaviors, which are regarded as voluntary like choosing the food for dinner.
This model proposed by Descartes was called mind-body dualism. Basically, it proposes that there are behaviors of humans, which are like reflexes, getting switched on by any sort of external stimuli, whereas there are certain other behaviors also, which are rather freely chosen and under the control of the human mind. Descartes had another belief that only the humans possess this self-directing type of mind and the nonhuman behavior is reflexive in nature.
Hence, the first blank can be filled with . The second blank can be filled with
. The second blank can be filled with  . The third blank can be filled with
. The third blank can be filled with 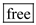 . The fourth blank can be filled with
. The fourth blank can be filled with 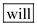 and the fifth blank can be filled with
and the fifth blank can be filled with 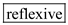 .
.
This model proposed by Descartes was called mind-body dualism. Basically, it proposes that there are behaviors of humans, which are like reflexes, getting switched on by any sort of external stimuli, whereas there are certain other behaviors also, which are rather freely chosen and under the control of the human mind. Descartes had another belief that only the humans possess this self-directing type of mind and the nonhuman behavior is reflexive in nature.
Hence, the first blank can be filled with
 . The second blank can be filled with
. The second blank can be filled with  . The third blank can be filled with
. The third blank can be filled with 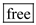 . The fourth blank can be filled with
. The fourth blank can be filled with 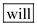 and the fifth blank can be filled with
and the fifth blank can be filled with 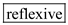 .
. 4
The (functionalist/structuralist) _______ approach proposed that the goal of psychology should be to identify the basic elements of the mind. The primary research method used for accomplishing this was the method of i _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An ev _______ ad _______ is a trait that has evolved through n _______ s _______ _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Watson noted that a major problem with the method _______ of was that the results obtained were often unreliable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Watson's brand of behaviorism is often referred to as _______ behaviorism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Hull believed that it might be useful to incorporate internal events into one's theorizing so long as they can be op _______ by defining them in such a way that they can be measured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Tolman's approach is known as _______ behaviorism because it utilizes mentalistic concepts, such as "expectations," to explain behavior. This approach is also sometimes called p _______ behaviorism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Bandura's _______ _______ theory emphasizes the importance of o _______ learning and c _______ variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Skinner's _______ behaviorism emphasizes both internal and external behaviors as resulting from e _______ influences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Skinner is most similar to (Hull/Watson/Tolman) _______ in arguing that behavior is best viewed from a m _______ perspective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Skinner's philosophy of behaviorism (meaning the set of basic assumptions for how best to conduct a science of behavior) is called _______ behaviorism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Name and briefly describe the two fundamental forms of learning emphasized in this textbook.
Name and briefly describe the two fundamental forms of learning emphasized in this textbook.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In _______ conditioning, behaviors that the average person typically regards as (voluntary/involuntary) come to be elicited in new situations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The empiricist position, as exemplified by the Greek philosopher _______, emphasizes the role of (learning/heredity) _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The British _______, such as John _______, maintained that knowledge was largely a function of ex and that the mind of a newborn infant is a (in Latin) t r (which means).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In contrast to the above, those who adopted the (functionalist/structuralist) _______ approach to psychology emphasized the adaptive processes of the mind and were thus very interested in the study of learning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The three main components to the theory of natural selection are:
a.
b.
c.
a.
b.
c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A basic problem with relying on someone's report about his or her thoughts and feelings is that we are making a(n) _______ that the report is accurate. This term is defined in the footnote as a supposition or guess based on logical d rather than direct o _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
According to this type of behaviorism, psychologists should study only those behaviors that can be _______ _______

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In Hull's approach, the internal events he included were hypothetical ph _______ processes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A _______ _______ is an internal representation of one's surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The concept of _______ _______ proposes that three variables: e _______, b _______, and p _______ variables, all interact with each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Skinner views thoughts and feelings as pr _______ behaviors that themselves need to be explained. These can also be called _______ behaviors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For Skinner, an S-R interpretation can best be applied to behavior that is r _______ and can be _______ conditioned. It cannot be applied to behavior that is under the control of its c _______ and has a more fl_______quality about it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The science that grew out of that philosophy is called the e _______ a of behavior or, more briefly, _______ _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe the nativist versus empiricist approaches to knowledge. How would a nativist versus an empiricist explain how Picasso became such a great artist?
Describe the nativist versus empiricist approaches to knowledge. How would a nativist versus an empiricist explain how Picasso became such a great artist?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In _______ conditioning, a behavior produces some type of consequence that strengthens or weakens its occurrence. Such behaviors are typically those that are generally regarded as "g _______ -directed" and which the average person often perceives as being "v _______ " in nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Nativist is to (nature/nurture) as empiricist is to (nature/nurture) _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
They also believed that the mind is composed of a finite set of basic _______ that are then combined through the principles of _______ to form our conscious experiences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The functionalist approach was strongly influenced by Darwin's theory of _______. As such, these psychologists viewed animal research as (relevant/ irrelevant) _______ to the study of human behavior in that humans were assumed to have evolved in a (similar/dissimilar) _______ way to other animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
To say that a trait is h _______ means that it has a genetic basis and can be inherited by offspring.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The notion that the proper subject matter of psychology should be the study of consciousness was so strong that even those who studied _______ behavior felt compelled to make inferences about possible mental processes in their subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Watson believed that all reference to events _______ should be eliminated from the study of behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Such internal events are called i _______ variables in that they are presumed to m _______ between the environment and behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The experiment by Tolman and Honzik (1930) has traditionally been regarded as a demonstration of _______ learning, in which learning appears to take place in the absence of any reward. The experiment has also been regarded as a demonstration of the distinction between learning and _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Bandura's work has influenced the development of a type of therapy known as _______-_______ therapy, in which an attempt is made to change behavior by altering both environmental and c _______ factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In teaching children to label their thoughts and feelings, parents first have to make an inf _______ about what the child is feeling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Tolmanian rat runs through the maze because it e _______ that doing so will result in food; the Skinnerian rat runs through the maze because, in its p _______ exp _______, doing so resulted in food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The technology that has grown out of that science is known as _______ _______ _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Name and briefly describe the four laws of association.
Name and briefly describe the four laws of association.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Feeling anxious as you enter a dentist's office is an example of a behavior that has most likely been learned through _______ conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The law of _______ states that we associate events that are opposite to each other, whereas the law of _______ states that we associate events that occur in close proximity to each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The functionalists were similar to the structuralists in that they still emphasized the study of c _______ experience and in doing so often used the method of i _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The real driving force behind evolution is not survival of the fittest, but rather the r _______ advantage held by those individuals who possess adaptive traits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Watson argued that psychology needed to become a n _______ science (like biology, chemistry, and physics) based solely on the study of directly ob _______ events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Watson proposed a(n) _______-_______ theory of learning which hypothesizes that learning involves the formation of a direct connection between a st _______ and a r _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hull's theory was a pure _______-_______ theory in that it assumed that the process of learning involves the creation of connections between specific s _______ and specific r _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Tolman believed that introspectively observed thoughts and feelings are (useless/ useful) _______ in the analysis of behavior. As well, almost all of Tolman's research was conducted using as _______ subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In determining the relationship of thoughts and feelings to behavior, it is sometimes difficult to know if the internal event pr _______, f _______, or occurs pa _______ to the behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Although he emphasized the role of the environment, Skinner also believed that behavior was fundamentally the result of the interaction of g _______ and the environment. He was in fact quite interested in evidence indicating g _______ limitations on _______ conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Outline Descartes' dualistic model of human behavior. In his view, what is a basic distinction between the behavior of humans and the behavior of other animals?
Outline Descartes' dualistic model of human behavior. In his view, what is a basic distinction between the behavior of humans and the behavior of other animals?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Speaking with a loud voice in a noisy environment so that others will be able to hear you is an example of a behavior that has most likely been learned through _______ conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
According to the law of _______, we easily associate events that resemble each other. According to the law of _______, the more often two events occur together, the stronger the association.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
William James was a (functionalist/structuralist) _______, and Edward Titchener was a _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
It is simplistic to assume that one can draw a clear distinction between n _______ and n _______ because the way we learn is itself an i _______ trait.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
According to the law of p _______, the (simple/complex) _______ explanation is generally the preferable explanation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In his 1913 article on behaviorism, Watson emphasized the role of both h _______ and e _______ in the development of human behavior. In his later theorizing, however, he downplayed the role of _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The modern-day study of cognitive processes in nonhuman animals is known as a _______ c _______ or com _______ c _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Yet another issue with respect to using internal events to explain behavior is that we (can/cannot) _______ directly change such events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Skinner believed that the processes of ev _______ and op _______ conditioning were quite similar in that both involved the selection of what was beneficial from what was not beneficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
How did the British empiricists view the acquisition of knowledge and the composition of the conscious mind?
How did the British empiricists view the acquisition of knowledge and the composition of the conscious mind?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the notational system to be used in this text, the term "A: B" means that event A (produces/is followed by) _______ event B, and the term "X ã Y" means that event X (produces/is followed by) _______ event Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Animals that have fur, four legs, a tail, and can bark are quickly perceived as belonging to the same species. This is an example of the law of _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
One version of the above law, known as M _______ C _______, holds that it is preferable to interpret animal behavior in terms of lower, more primitive processes, such as reflex or habit, than higher, more mentalistic processes, such as reasoning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In his later theorizing, Watson proposed that humans inherit (many/a few) basic reflexes, along with three basic emotions: _______, _______, and _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Saying that you are feeling "happy" to explain why you are always smiling and laughing is, from Skinner's perspective, an example of using feelings as a ps _______ explanation for your behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
On a practical level, Skinner was (enthused/cautious) about _______ genetic explanations for behavior because he believed that such explanations tend to be (optimistic/pessimistic) _______ about the possibility of change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe the structuralist approach to psychology. Name and define the basic method by which the structuralists gathered data.
Describe the structuralist approach to psychology. Name and define the basic method by which the structuralists gathered data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The fact that the words full and empty are easily associated with each other is an example of the law of _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Altering the environment so as to control our own behavior is referred to as c _______ control. However, in Skinner's view, even this type of behavior is ultimately the result of some type of e _______ influence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe the functionalist approach to psychology. Where did functionalists stand on the issue of animal experimentation, and what was their reasoning behind this?
Describe the functionalist approach to psychology. Where did functionalists stand on the issue of animal experimentation, and what was their reasoning behind this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The more often one practices a particular move in wrestling, the more likely one is to perform that move in a real match. This is an example of the law of _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe Darwin's principle of natural selection. What are the three main components of the principle of natural selection?
Describe Darwin's principle of natural selection. What are the three main components of the principle of natural selection?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
After once encountering a snake in her garage, Lisa is now quite nervous each time she is in the garage. This is an example of Aristotle's law of _______. This is also an example of (classical/operant) _______ conditioning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Define the law of parsimony and Morgan's Canon.
Define the law of parsimony and Morgan's Canon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe Watson's methodological behaviorism. How did Watson's position on the nature-nurture debate change over time?
Describe Watson's methodological behaviorism. How did Watson's position on the nature-nurture debate change over time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe Hull's neobehaviorism. How does Tolman's cognitive behaviorism differ from it?
Describe Hull's neobehaviorism. How does Tolman's cognitive behaviorism differ from it?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Because many students tend to ignore long lists of broad study questions (or learning objectives) that attempt to cover all the material in a chapter, the end-of-chapter study questions in this text focus on the most basic information. To determine if you have a grasp of this information, see if you can write out a clear answer to each of these questions. Be aware, however, that obtaining an excellent mark in this course will require more than just a simple reiteration of this basic material.
Describe Bandura's social learning theory. Outline or diagram his concept of reciprocal determinism.
Describe Bandura's social learning theory. Outline or diagram his concept of reciprocal determinism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



