Deck 28: Appendix
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 28: Appendix
1
A species of antelope contains 20 chromosomes per set. The species is divided by a mountain range into two separate populations, which we will call the eastern and western population. When comparing the karyotypes of these two populations, it was discovered that the members of the eastern population are homozygous for a large inversion within chromosome 14. How would this inversion affect the interbreeding between the two populations Could such an inversion play an important role in speciation
Inversion of a chromosome does not affect the phenotypic traits of organisms. Thus even if chromosome 14 of the eastern population has undergone inversion, still there would be no change in the physiological characters and appearances. Thus, interbreeding among the two populations is very much possible. But an important point to remember here is that though the two populations can interbreed, still the offspring would be less fertile as it would inherit a pair of chromosomes that is largely inverted. This would affect the meiosis of the F1 hybrid during gamete formation and thus the offsprings of the F1 hybrids would not be viable and die. As a result, this very reason could develop a reproductive isolation among the two populations as the offsprings would not be fertile.
Thus in the long run, over generations, when the two populations remain reproductively isolated, they would over the course of time develop distinct traits that are different from each other, leading to the evolution of two different species. Thus inversions, in the long run, play an important role in speciation.
Thus in the long run, over generations, when the two populations remain reproductively isolated, they would over the course of time develop distinct traits that are different from each other, leading to the evolution of two different species. Thus inversions, in the long run, play an important role in speciation.
2
As discussed in this chapter and Chapter 26, genes are sometimes transferred between different species via horizontal gene transfer. Discuss how horizontal gene transfer might give misleading results when constructing a phylogenetic tree. How could you overcome this problem
Horizontal gene transfer is the transfer of genes between two completely unrelated organisms that are at different branches of a phylogenetic tree. This causes confusion as it relates the two organisms with each other and disrupts the branching of tree in the direction of evolution. This is seen to happen more in prokaryotes as compared to eukaryotes. For example if a bacterial gene is transferred to a protozoa, then on assessing the genes and constructing a phylogenetic tree, it would show that the bacteria and protozoa are closely related to one another when it is not the case. Thus horizontal gene transfer gives misleading results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree.This problem can be addressed in two ways:
• The first way is to use the principle of parsimony and choose the simplest way in which least evolutionary changes have occurred.• The second way is to study and consider a larger number of genes and then assume that all the genes have been transferred vertically (from parent to offspring) and not horizontally.
• The first way is to use the principle of parsimony and choose the simplest way in which least evolutionary changes have occurred.• The second way is to study and consider a larger number of genes and then assume that all the genes have been transferred vertically (from parent to offspring) and not horizontally.
3
Horizontal gene transfer is a process in which genetic material from an organism is
A) transferred from cell to cell
B) transferred to its offspring
C) transferred to another organism that is not the offspring of that organism
D) released into the environment.
A) transferred from cell to cell
B) transferred to its offspring
C) transferred to another organism that is not the offspring of that organism
D) released into the environment.
In this question, we discuss horizontal gene transfer.Horizontal gene transfer is a process by which genes are transferred from one species to another. This process can happen between bacterial species or between bacterial and eukaryotic species. In this way, bacteria have transferred useful resistances or powerful virulence factors, such as the transfer of shigatoxin to certain strains of Escherichia coli , creating a violent, hemorrhagic variety of this coliform bacteria.
The exchange from one species to another is the key, thus Option C is correct.
Just between cells is not enough - they must be unrelated, thus we eliminate Option A. Transfer from parent to offspring is simply inheritance, thus we eliminate Option B. Environmental release is not part of horizontal transfer, but can be part of DNA capture, so we eliminate Option D.
The exchange from one species to another is the key, thus Option C is correct.
Just between cells is not enough - they must be unrelated, thus we eliminate Option A. Transfer from parent to offspring is simply inheritance, thus we eliminate Option B. Environmental release is not part of horizontal transfer, but can be part of DNA capture, so we eliminate Option D.
4
Describe three or more genetic mechanisms that may lead to the rapid evolution of a new species. Which of these genetic mechanisms are influenced by natural selection, and which are not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which would you expect to exhibit a faster rate of evolutionary change, the nucleotide sequence of a gene or the amino acid sequence of the encoded polypeptide of the same gene Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Homologous genes found in different species are called
A) orthologs
B) paralogs
C) analogs
D) none of the above.
A) orthologs
B) paralogs
C) analogs
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Discuss the two principles on which evolution is based.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Explain why molecular techniques were needed as a way to provide evidence for the neutral theory of evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When comparing the coding region of protein-encoding genes among closely related species, certain regions of the gene are commonly found to have evolved more rapidly (i.e., have tolerated more changes in sequence) than other regions of the gene. Explain why different regions of a protein-encoding gene evolve at different rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A molecular clock may not be linear because
A) mutation rates may differ among different species
B) differences in population sizes may affect the relative effects of natural selection and genetic drift
C) different species may differ in their generation times
D) all of the above may occur.
A) mutation rates may differ among different species
B) differences in population sizes may affect the relative effects of natural selection and genetic drift
C) different species may differ in their generation times
D) all of the above may occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two populations of snakes are separated by a river. The snakes cross the river only on rare occasions. The snakes in the two populations look very similar to each other, except that the members of the population on the eastern bank of the river have a yellow spot on the top of their head, whereas the members of the western population have an orange spot on the top of their head. Discuss two experimental methods that you might follow to determine whether the two populations are members of the same species or members of different ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Explain the type of speciation (allopatric, parapatric, or sympatric) most likely to occur under each of the following conditions:
a. A pregnant female rat is transported by an ocean liner to a new continent
b. A meadow containing several species of grasses is exposed to a pesticide that promotes nondisjunction
c. In a very large lake containing several species of fish, the water level gradually falls over the course of several years. Eventually, the large lake becomes subdivided into smaller lakes, some of which are connected by narrow streams.
a. A pregnant female rat is transported by an ocean liner to a new continent
b. A meadow containing several species of grasses is exposed to a pesticide that promotes nondisjunction
c. In a very large lake containing several species of fish, the water level gradually falls over the course of several years. Eventually, the large lake becomes subdivided into smaller lakes, some of which are connected by narrow streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Plant seeds contain storage proteins that are encoded by plant genes. When the seed germinates, these proteins are rapidly hydrolyzed (i.e., the covalent bonds between amino acids within the polypeptides are broken), which releases amino acids for the developing seedling. Would you expect the genes that encode plant storage proteins to evolve more slowly or more rapidly than genes that encode enzymes Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When comparing the chromosomes of closely related species,
A) the banding patterns are often similar
B) a few structural alterations may be seen
C) a change in chromosome number may be seen
D) all of the above are common.
A) the banding patterns are often similar
B) a few structural alterations may be seen
C) a change in chromosome number may be seen
D) all of the above are common.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The raw material for evolution is random mutation. Discuss whether or not you view evolution as a random process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Prehistoric specimens often contain minute amounts of ancient DNA. What technique can be used to increase the amount of DNA in an older sample Explain how this technique is performed and how it increases the amount of a specific region of DNA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Take a look at the -globin and -globin sequences in Figure 28.11. Which sequences are more similar, the globin in humans and the globin in horses, or the globin in humans and the globin in humans Based on your answer, would you conclude that the gene duplication that gave rise to the -globin and -globin genes occurred before or after the divergence of humans and horses Explain your reasoning.FIGURE 28.11 A comparison of the - and -globin polypeptides from humans and horses. (a) An alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences obtained by sequencing the exon portions of the corresponding genes. The gaps indicate where additional amino acids are found in the sequence of myoglobin, another member of this gene family. (b) A comparison of amino acid differences between orthologs and paralogs. 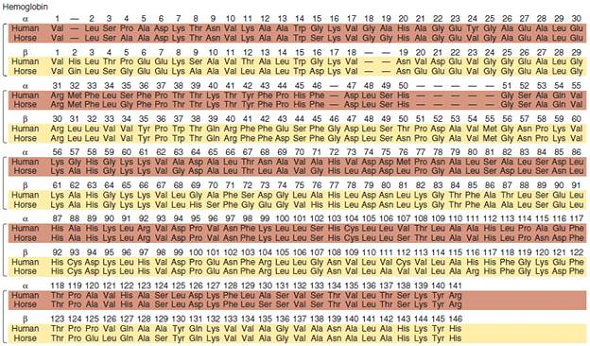
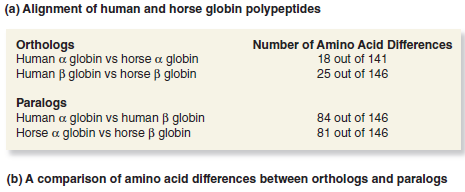



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Evolution, which involves genetic changes in a population of organisms over time, is often described as the unifying theme in biology. Discuss how evolution is unifying at the molecular and cellular levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Alloploids are produced by crosses involving two different species. Explain why alloploids may be reproductively isolated from the two original species from which they were derived. Explain why alloploids are usually sterile, whereas allotetraploids (containing a diploid set from each species) are commonly fertile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Compare and contrast the neutral theory of evolution versus the Darwinian (i.e., selectionist) theory of evolution. Explain why the neutral theory of evolution is sometimes called non-Darwinian evolution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Sympatric speciation by allotetraploidy has been proposed as a common mechanism for speciation. Let's suppose you were interested in the origin of certain grass species in southern California. Experimentally, how would you go about determining if some of the grass species are the result of allotetraploidy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the experiment of Figure 28.13, explain how we know that the kiwis are more closely related to the emu and cassowary than to the moas. Cite particular regions in the sequences that support your answer.FIGURE 28.13 DNA analysis of orthologs reveals phylogenetic relationships among extinct and modern flightless birds.
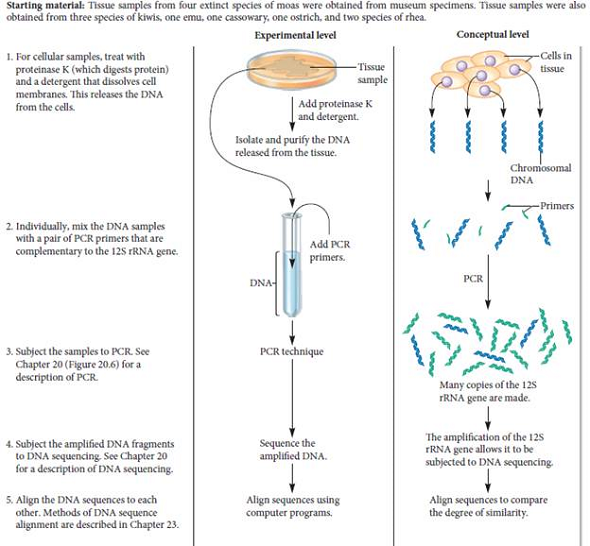


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
For each of the following examples, discuss whether it would be the result of neutral mutations or mutations that have been acted on by natural selection, or both:
a. When comparing sequences of homologous genes, differences in the coding sequence are most common at the wobble base (i.e., the third base in each codon)
b. For a protein-encoding gene, the regions that encode portions of the polypeptide that are vital for structure and function are less likely to display mutations than other regions of the gene
c. When comparing the sequences of homologous genes, introns usually have more sequence differences than exons.
a. When comparing sequences of homologous genes, differences in the coding sequence are most common at the wobble base (i.e., the third base in each codon)
b. For a protein-encoding gene, the regions that encode portions of the polypeptide that are vital for structure and function are less likely to display mutations than other regions of the gene
c. When comparing the sequences of homologous genes, introns usually have more sequence differences than exons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Compare the forms of speciation that are slow with those that occur more rapidly. Make a list of the slow and fast forms. With regard to mechanisms of genetic change, what features do slow and rapid speciation have in common What features are different

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Discuss whether the phenomenon of reproductive isolation applies to bacteria, which reproduce asexually. How would a geneticist divide bacteria into separate species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
As discussed in Chapter 26, genetic variation is prevalent in natural populations. This variation is revealed in the DNA sequencing of genes. According to the neutral theory of evolution, discuss the relative importance of natural selection against detrimental mutations, natural selection in favor of beneficial mutations, and neutral mutations in accounting for the genetic variation we see in natural populations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is a species What types of observations do researchers analyze when trying to identify species

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In Chapter 22, we learned about a technique called fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), during which a labeled piece of DNA is hybridized to a set of chromosomes. Let's suppose that we cloned a piece of DNA from G. pubescens (see Figure 28.4) and used it as a labeled probe for in situ hybridization. What would you expect to happen if we hybridized it to the G. speciosa or G. tetrahit chromosomes Describe your expected results.FIGURE 28.4 A comparison of crosses between three natural species of hemp nettle with different ploidy levels. (a) Galeopsis tetrahit is an allotetraploid that is thought to be derived from Galeopsis pubescens and Galeopsis speciosa. (b) If G. tetrahit is crossed with the other two species, the F 1 hybrid offspring will be monoploid for one chromosome set and diploid for the other. The F 1 offspring are likely to be sterile, because they will produce highly aneuploid gametes. 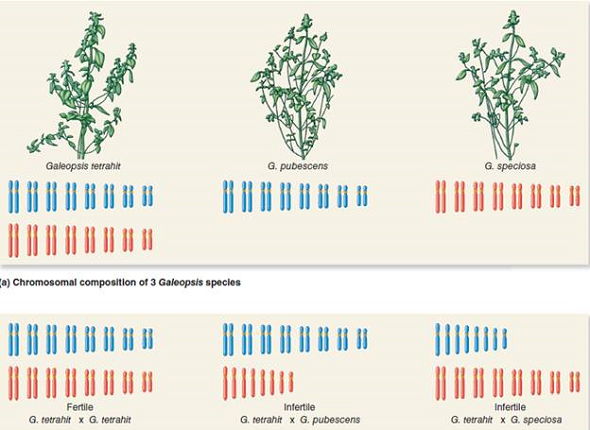


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If you were comparing the karyotypes of species that are closely related evolutionarily, what types of similarities and differences would you expect to find

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Two diploid species of closely related frogs, which we will call species A and species B, were analyzed with regard to genes that encode an enzyme called hexokinase. Species A has two distinct copies of this gene: A1 and A 2. In other words, this diploid species is A1A1 A 2 A 2. The other species has three copies of the hexokinase gene, which we will call B1 , B2, and B3. A diploid individual of species B would be B1B1 B2B2 B3B3. These hexokinase genes from the two species were subjected to DNA sequencing, and the percentage of sequence identity was compared among these genes. The results are shown here.Percentage of DNA Sequence Identity
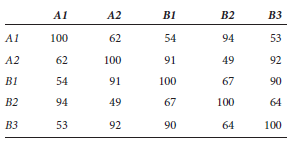
a.
If we assume that hexokinase genes were never lost in the evolution of these frog species, how many distinct hexokinase genes do you think there were in the most recent ancestor that preceded the divergence of these two species Explain your answer. Also explain why species B has three distinct copies of this gene, whereas species A has only two.

a.
If we assume that hexokinase genes were never lost in the evolution of these frog species, how many distinct hexokinase genes do you think there were in the most recent ancestor that preceded the divergence of these two species Explain your answer. Also explain why species B has three distinct copies of this gene, whereas species A has only two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Discuss the major differences among allopatric, parapatric, and sympatric speciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Evolution that results from genotypes with a higher reproductive success is based on
A) genetic variation
B) natural selection
C) genetic drift
D) both a and b.
A) genetic variation
B) natural selection
C) genetic drift
D) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Do you think that Darwin would object to the neutral theory of evolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A team of researchers has obtained a dinosaur bone ( Tyrannosaurus rex ) and has attempted to extract ancient DNA from it. Using primers to the 12S rRNA mitochondrial gene, they have used PCR and obtained a DNA segment that yields a sequence homologous to crocodile DNA. Other scientists are skeptical that this sequence is really from the dinosaur. Instead, they believe that it may be due to contamination from more recent DNA, such as the remains of a reptile that lived much more recently. What criteria might you use to establish the credibility of the dinosaur sequence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Characteristics that are used to establish species include
A) morphological traits
B) reproductive isolation
C) molecular features
D) ecological factors.e. evolutionary relationships.f. all of the above.
A) morphological traits
B) reproductive isolation
C) molecular features
D) ecological factors.e. evolutionary relationships.f. all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What is meant by the term reproductive isolation Give several examples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The following are two DNA sequences from homologous genes:
TTGCATAGGCATACCGTATGATATCGAAAACTAGAAAAATAGGGCGATAGCTA
GTATGTTATCGAAAAGTAGCAAAATAGGGCGATAGCTACCCAGACTACCGGAT
The two sequences, however, do not begin and end at the same location. Try to line them up according to their homologous regions.
TTGCATAGGCATACCGTATGATATCGAAAACTAGAAAAATAGGGCGATAGCTA
GTATGTTATCGAAAAGTAGCAAAATAGGGCGATAGCTACCCAGACTACCGGAT
The two sequences, however, do not begin and end at the same location. Try to line them up according to their homologous regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A pair of birds flies to a deserted island and establishes a colony. Over time, this population evolves into a new species. This is an example of
A) allopatric speciation
B) parapatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) all of the above.
A) allopatric speciation
B) parapatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A researcher sequenced a portion of a bacterial gene and obtained the following sequence, beginning with the start codon, which is underlined:
ATG CCG GAT TAC CCG GTC CCA AAC AAA ATG ATC GGC CGC CGA ATC TAT CCC
The bacterial strain that contained this gene has been maintained in the laboratory and grown serially for many generations.Recently, another person working in the laboratory isolated DNA from the bacterial strain and sequenced the same region. The following results were obtained:
ATG CCG GAT TAT CCG GTC CCA AAT AAA ATG ATC GGC CGC CGA ATC TAC CCC
Explain why these sequencing differences may have occurred.
ATG CCG GAT TAC CCG GTC CCA AAC AAA ATG ATC GGC CGC CGA ATC TAT CCC
The bacterial strain that contained this gene has been maintained in the laboratory and grown serially for many generations.Recently, another person working in the laboratory isolated DNA from the bacterial strain and sequenced the same region. The following results were obtained:
ATG CCG GAT TAT CCG GTC CCA AAT AAA ATG ATC GGC CGC CGA ATC TAC CCC
Explain why these sequencing differences may have occurred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Discuss how the principle of parsimony can be used in a cladistics approach of constructing a phylogenetic tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The formation of polyploids is common in plants and can abruptly produce a new species. This is an example of
A) allopatric speciation
B) parapatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) all of the above.
A) allopatric speciation
B) parapatric speciation
C) sympatric speciation
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Would the following examples of reproductive isolation be considered a prezygotic or postzygotic mechanism
a. Horses and donkeys can interbreed to produce mules, but the mules are infertile
b. Three species of the orchid genus Dendrobium produce flowers 8 days, 9 days, and 11 days after a rainstorm. The flowers remain open for 1 day
c. Two species of fish release sperm and eggs into seawater at the same time, but the sperm of one species do not fertilize the eggs of the other species
d. Two tree frogs, Hyla chrysoscelis (diploid) and H. versicolor (tetraploid), can produce viable offspring, but the offspring are sterile.
a. Horses and donkeys can interbreed to produce mules, but the mules are infertile
b. Three species of the orchid genus Dendrobium produce flowers 8 days, 9 days, and 11 days after a rainstorm. The flowers remain open for 1 day
c. Two species of fish release sperm and eggs into seawater at the same time, but the sperm of one species do not fertilize the eggs of the other species
d. Two tree frogs, Hyla chrysoscelis (diploid) and H. versicolor (tetraploid), can produce viable offspring, but the offspring are sterile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is meant by the term molecular clock How is this concept related to the neutral theory of evolution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Phylogenetic trees are based on
A) natural selection
B) genetic drift
C) homology
D) none of the above.
A) natural selection
B) genetic drift
C) homology
D) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
F 1 hybrids between two species of cotton, Gossypium barbadense and G. hirsutum , are very vigorous plants. However, F 1 crosses produce many seeds that do not germinate and a high percentage of very weak F 2 offspring. Suggest two reasons for these observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A homologous DNA region, which was 20,000 bp in length, was sequenced among four different species. The following number of nucleotide differences were obtained:
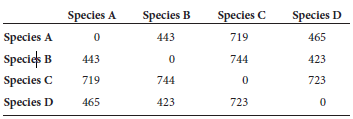
a.
Construct a phylogenetic tree that describes the evolutionary relationships among these four species using the UPGMA method. Your tree should include values that show the percentage of nucleotide substitutions.

a.
Construct a phylogenetic tree that describes the evolutionary relationships among these four species using the UPGMA method. Your tree should include values that show the percentage of nucleotide substitutions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A shared derived character is
A) derived from an ancestral character
B) more recent compared with an ancestral character
C) found in all or most of the members of an ingroup
D) all of the above.
A) derived from an ancestral character
B) more recent compared with an ancestral character
C) found in all or most of the members of an ingroup
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Distinguish between anagenesis and cladogenesis. Which type of speciation is more prevalent Why

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Would the rate of deleterious or beneficial mutations be a good molecular clock Why or why not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An approach that is used to propose a phylogenetic tree is
A) cladistics and the principle of parsimony
B) phenetics
C) maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods
D) all of the above.
A) cladistics and the principle of parsimony
B) phenetics
C) maximum likelihood and Bayesian methods
D) all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



