Deck 16: Adult Nutrition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/11
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Adult Nutrition
1
What are the differences between individual and external or environmental factors that determine nutrition status and health? Give examples for how each type is monitored.
The individual factors that affect nutritional status and health in adults are food intake, nutrient adequacy, physical activity and body weight.
Environmental or external factors that determine the nutritional status and health of adults are community where they live and where they learn, work and play. These factors influence the choice of different types of nutritious foods by the people and also their lifestyle.
Environmental or external factors that determine the nutritional status and health of adults are community where they live and where they learn, work and play. These factors influence the choice of different types of nutritious foods by the people and also their lifestyle.
2
Describe the physiological changes that occur during the adult years. How do those changes relate to the continuum of health? Which changes have implications for development of chronic diseases?
Various physiological changes occur in adulthood stage. They are,
• After twenties individuals will stop growing
• Bone density development takes place up to the age of 30 years in both males and females
• More muscular strength in 25 to 30 years
• Dexterity and flexibility, sensory and perceptual abilities starts to decline
• Changes in vision occurs around the age of 40 years
• Hormonal changes include reduced production of estrogen in females and testosterone in males
The reduced production of estrogen leads to starting of perimenopause and lasts through menopause, the end of reproductive capability in females.
Estrogen also plays important role in both female and male. They are; calcium supply to bones, maintaining healthy blood vessel walls, maintaining blood cholesterol and triglycerides levels and skin's elasticity.
The reduced production of testosterone in males, induce the decline of muscle mass.
• The bone mass will starts to decline after around the age of 40
• Increase in body fat and decrease in muscle mass between the age 20 to 64 leads to increase in body weight and adiposity
Healthy nutrition during adult years reduces or delays the onset of health problems and illness. Nutritional health is observed as continuum or scale represented in six states;
• Resilient and healthy state: in this state the physiological processes works in optimum levels
• Altered substrate availability: there is downfall in nutrient stores and subclinical changes may increase
• Nonspecific signs and symptoms: the metabolic and physiological changes are occurring like accumulation of fat and central adiposity, increased resistance to blood and insulin. These changes may leads to chronic conditions
• Clinical conditions: the alteration in physiological condition may leads to signs and symptoms of illness and these can be diagnosed medically.
• Chronic conditions: complete alteration of metabolism and physiological process are permanent and irreversible which leads to chronic conditions like, kidney failure, cancer, damage to coronary arteries and so on.
• Terminal illness and death (complete shutdown of body systems): it is the final state of continuum in which the physiological and metabolic alterations become advance and leads to complete shutdown of body systems. This causes death.
The physiological changes that lead to development of chronic conditions are Structural damage to coronary arteries, kidney failure, aggressive and metastatic cancer and blindness
• After twenties individuals will stop growing
• Bone density development takes place up to the age of 30 years in both males and females
• More muscular strength in 25 to 30 years
• Dexterity and flexibility, sensory and perceptual abilities starts to decline
• Changes in vision occurs around the age of 40 years
• Hormonal changes include reduced production of estrogen in females and testosterone in males
The reduced production of estrogen leads to starting of perimenopause and lasts through menopause, the end of reproductive capability in females.
Estrogen also plays important role in both female and male. They are; calcium supply to bones, maintaining healthy blood vessel walls, maintaining blood cholesterol and triglycerides levels and skin's elasticity.
The reduced production of testosterone in males, induce the decline of muscle mass.
• The bone mass will starts to decline after around the age of 40
• Increase in body fat and decrease in muscle mass between the age 20 to 64 leads to increase in body weight and adiposity
Healthy nutrition during adult years reduces or delays the onset of health problems and illness. Nutritional health is observed as continuum or scale represented in six states;
• Resilient and healthy state: in this state the physiological processes works in optimum levels
• Altered substrate availability: there is downfall in nutrient stores and subclinical changes may increase
• Nonspecific signs and symptoms: the metabolic and physiological changes are occurring like accumulation of fat and central adiposity, increased resistance to blood and insulin. These changes may leads to chronic conditions
• Clinical conditions: the alteration in physiological condition may leads to signs and symptoms of illness and these can be diagnosed medically.
• Chronic conditions: complete alteration of metabolism and physiological process are permanent and irreversible which leads to chronic conditions like, kidney failure, cancer, damage to coronary arteries and so on.
• Terminal illness and death (complete shutdown of body systems): it is the final state of continuum in which the physiological and metabolic alterations become advance and leads to complete shutdown of body systems. This causes death.
The physiological changes that lead to development of chronic conditions are Structural damage to coronary arteries, kidney failure, aggressive and metastatic cancer and blindness
3
How many calories do you need? Use three methods discussed in the chapter to estimate daily energy requirement. What factors would increase or decrease the number of calories you need to eat in a day?
Calories of energy are needed to people to maintain stable body weight and good health. The energy requirements are fulfilled through dietary intake.
Females: For an adult with sedentary lifestyle requires 1800-1900cal, 2000-2200cal for adults with moderate activity and 2400cal for active adult are required.
Males: For an adult with sedentary lifestyle requires 2400-2600cal, 2600-2800cal for adults with moderate activity and 2800 to 3000cal for active adult are required.
The energy needs of individuals can be calculated by following ways;
• Determination of estimated energy requirements (EER):
EER is an average energy requirement of an adult with good health. It depends up on age, weight, height and physical activity. EER is measured by estimating total energy expenditure of adult by doubly labelled water technique (DLW) in real living condition. Excretion of labelled isotopes in saliva and urine by the adults who are given the dose of tagged water containing isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen is used to estimate the energy usage of individuals for particular period of time.
• Indirect calorimetry for the determination of resting energy expenditure (REE):
REE is closely related to basal metabolic rate (BMR). REE can be measured by conducting indirect calorimetry by measuring the exchange of gases in respiration, for a specific period of time.
• Estimation of REE by Mifflin- St. Jeor formula:
This formula requires age, height (cm) and weight (kg).
For males:
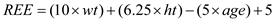 For females:
For females:
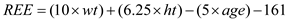 After the calculation of RRE, the value is multiplied by an activity factor for estimating the caloric expenditure by the person. (Activity factor for sedentary 12.5, moderate 1.55 and for active person 1.725)
After the calculation of RRE, the value is multiplied by an activity factor for estimating the caloric expenditure by the person. (Activity factor for sedentary 12.5, moderate 1.55 and for active person 1.725)
• Ballpark calculation :
It is a simple calculation to measure energy requirement for weight management, weight loss or weight gain. To maintain healthy body weight nearly 15 calories per one pound (lb) of body weight are required per day. If individual is taking 13 calories/lb per day, he may subject to weight loss. If the caloric intake value rose to 17 calories/lb per day, overweight will be resulted.
The factors that affect the nutritional intake of adults are biological and genitical, individual and environmental or external factors. The individual factors that affect nutritional status and health in adults are food intake, nutrient adequacy, physical activity and body weight.
Environmental or external factors that determine the nutritional status and health of adults are community where they live and where they learn, work and play. These factors influence the choice of different types of nutritious foods by the people and also their lifestyle.
Females: For an adult with sedentary lifestyle requires 1800-1900cal, 2000-2200cal for adults with moderate activity and 2400cal for active adult are required.
Males: For an adult with sedentary lifestyle requires 2400-2600cal, 2600-2800cal for adults with moderate activity and 2800 to 3000cal for active adult are required.
The energy needs of individuals can be calculated by following ways;
• Determination of estimated energy requirements (EER):
EER is an average energy requirement of an adult with good health. It depends up on age, weight, height and physical activity. EER is measured by estimating total energy expenditure of adult by doubly labelled water technique (DLW) in real living condition. Excretion of labelled isotopes in saliva and urine by the adults who are given the dose of tagged water containing isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen is used to estimate the energy usage of individuals for particular period of time.
• Indirect calorimetry for the determination of resting energy expenditure (REE):
REE is closely related to basal metabolic rate (BMR). REE can be measured by conducting indirect calorimetry by measuring the exchange of gases in respiration, for a specific period of time.
• Estimation of REE by Mifflin- St. Jeor formula:
This formula requires age, height (cm) and weight (kg).
For males:
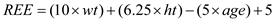 For females:
For females: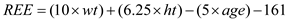 After the calculation of RRE, the value is multiplied by an activity factor for estimating the caloric expenditure by the person. (Activity factor for sedentary 12.5, moderate 1.55 and for active person 1.725)
After the calculation of RRE, the value is multiplied by an activity factor for estimating the caloric expenditure by the person. (Activity factor for sedentary 12.5, moderate 1.55 and for active person 1.725)• Ballpark calculation :
It is a simple calculation to measure energy requirement for weight management, weight loss or weight gain. To maintain healthy body weight nearly 15 calories per one pound (lb) of body weight are required per day. If individual is taking 13 calories/lb per day, he may subject to weight loss. If the caloric intake value rose to 17 calories/lb per day, overweight will be resulted.
The factors that affect the nutritional intake of adults are biological and genitical, individual and environmental or external factors. The individual factors that affect nutritional status and health in adults are food intake, nutrient adequacy, physical activity and body weight.
Environmental or external factors that determine the nutritional status and health of adults are community where they live and where they learn, work and play. These factors influence the choice of different types of nutritious foods by the people and also their lifestyle.
4
If you are a typical male or female as represented in Table 16.5, what nutrient shortfalls and excesses should you be worried about and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
You have been appointed to the Campus Dietary Guidelines Committee. What things do you need to consider when developing dietary guidelines for the campus community?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What do you need to do to meet the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans? What are the benefits if you do? What are the consequences if you don't?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Make a table of different types of strategies for helping adults achieve good nutritional health.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How many calories does Kristen need to maintain her weight?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Is she eating enough to support daily workouts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Describe three health-promoting aspects of Kristen's diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Make three suggestions that could improve Kristen's diet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 11 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



